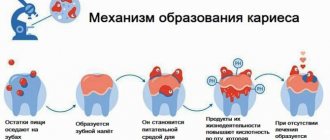
Most children have their first teeth at 6-8 months. And when we see that a newborn baby has these “pearls” in his mouth, we are sincerely surprised. Indeed, the so-called natal teeth in newborns occur 1 time per 2-3 thousand crumbs. By the way, this phenomenon occurs much more often in girls than in boys.
Natal teeth are teeth that a baby develops in utero and are already present at birth. As a rule, parents observe two lower front teeth in the child’s mouth at birth. Neonatal teeth appear in a child in the first month of life.
Historians claim that Napoleon Bonaparte, Louis XIV, Julius Caesar, Charlemagne and other great people were born with natal teeth.
Are natural teeth dangerous?
In 95% of cases no. Natal and neonatal incisors are ordinary baby teeth that a child develops in the womb. The main feature of such teeth is that they usually fall out at 3-4 years.
However, natural teeth bring a lot of inconvenience to mother and child. Firstly, during feeding, the mother constantly experiences pain, because the baby unknowingly injures her nipples with his teeth. Secondly, the incisors damage the baby’s gums, frenulum and tongue. The baby develops cracks and ulcers in his mouth, the baby suffers, becomes capricious, and often cries. But, most importantly, if there are ulcers in the mouth, the child can easily get an infection on his own.
In approximately 5% of cases, natal teeth are additional. These supernumerary incisors form in the fetus on top of the baby tooth buds. This means that they will fall out very soon, leaving room for the incisors.
What types of teeth do children have at birth?
The teeth found in the oral cavity of a newborn child may be complete or spare. Regardless of the variety, such teeth are characterized by inferior structure, softness, weakness and rapid wear.
Depending on the variety, “early” teeth also have certain characteristics:
- The eruption of complete teeth
occurs during the baby’s intrauterine development. Their main drawback is represented by the weakness of the structure. These bone structures deteriorate and wear down very quickly and most often fall out before the child reaches the age of four, causing a lot of inconvenience to caring parents and the child. The main inconveniences are associated with the inability to ensure normal breastfeeding of the child, because the woman will constantly face injury to her nipples. Sharp teeth in a child’s mouth can also be the cause of regular disruption of the integrity of soft tissues, accompanied by the formation of ulcers and wounds. - Spare teeth
are represented by an additional row of milk teeth, the formation and eruption of which also occurs during intrauterine development. Most often, spare teeth fall out soon after the baby is born, but they can also remain for a long period. In this case, they most often resort to removing these teeth so that a full-fledged dentition can be formed. Spare teeth also cause a lot of inconvenience, limiting normal feeding and causing many wounds and ulcers in the baby’s mouth.
Why do natural teeth appear?
Most dentists associate the appearance of natal teeth with the processes that occurred during pregnancy:
- unbalanced nutrition when carrying a baby;
- superficial presence of rudiments in the fetus;
- infectious diseases of a pregnant woman with high fever;
- excess calcium and vitamin D;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- long-term exposure to toxins;
- a woman taking illicit drugs in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- congenital pathologies of the fetus;
- unfavorable environment.
Natal teeth are diagnosed immediately at the birth of the child during an examination in the maternity hospital.
It has also been recorded that children are born with natal teeth suffering from the following pathologies:
- Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome. Genetic pathology of the fetus, which is characterized by growth retardation, disproportionate dwarfism and abnormal growth of all types of bone tissue.
- Hallerman-Streiff syndrome. Many anomalies that appear due to disturbances in the visceral mesoderm of the embryo. Dysmorphia of the maxillofacial part of the skeleton.
- Sotos syndrome. A congenital, sporadic disease in which the child grows very quickly. The pathology is also characterized by accelerated development of teeth.
- Craniofacial type of synostosis. Premature closure of cranial sutures, deformation and limitation of the volume of the skull.
- Multiple steatcystoma. A benign neoplasm characterized by multiple cystic nodules on the skin.
- Cleft in the sky. The palatal parts do not fuse, a congenital disease.
- Congenital pachyonychia. A genetic disease that affects the nail plates.
- Robin's syndrome. A disease characterized by underdevelopment of the mandibular bone, palatal clefts and recessed tongue.
Problems with enamel
Another congenital problem can be called a violation of the formation of enamel of permanent teeth. It can be:
- enamel hypoplasia;
- yellow-brown spots appearing on the enamel;
- complete or partial absence of enamel.
“All these are pathologies that appear on permanent teeth due to the effect on their buds of various strong medications that the expectant mother could use. In addition, accumulated chemical elements or, for example, X-ray radiation received during hazardous work, or when entering an irradiation zone, or when abusing prohibited substances, may have such an impact,” explains the dentist.
Also, such changes, warns Ilya Antonov, are possible due to chronic diseases of the mother - such as diseases of the endocrine system, toxoplasmosis, rubella.
If your back is hunched, check your bite. How a dentist can correct your posture Read more
Classification
Natal and neonatal teeth were classified by Veronica Habling. The basis for the maturity of incisors is the quality of dental tissue, as well as the degree of its development.
Today there are four categories of natal elements:
- 1st category. The crown is shaped like a shell. The teeth have no roots, the incisors are barely fixed by the gums.
- 2nd category. Characterized by dense crowns and a very weak root structure. Often the roots of the teeth are completely absent, the tooth is weakly fixed in the alveolus.
- Category 3. The incisal edge of the tooth breaks through the gum slightly. The main part of the tooth is located inside the jaw bone.
- Category 4. The teeth can be easily felt, but are hidden by swollen tissues and are invisible to the eye.
Bite
Abnormal bite often causes:
- increased load on individual teeth, which contributes to their rapid destruction or damage to the ligamentous apparatus;
- crowding of teeth, leading to gum inflammation and dental caries.
- The hereditary factor is detected in no more than 50% of cases of abnormal structure of the dental system. The remaining 50% is due to the following circumstances:
- artificial feeding;
- formation of bad habits at an early age (sucking pacifiers, fingers, lips, holding pencils or pens in the mouth);
- the habit of sleeping in one position, especially with your hand under your cheek;
- incorrect posture;
- lack of calcium and other trace elements in the body.
In preventing the development of pathological occlusion, the role of parents is great, who should pay attention to the early identification and elimination of provoking factors.
Diagnostics
As we have already said, diagnosis of natal teeth is carried out at the birth of the child. The doctor conducts a full clinical examination of the baby’s condition, evaluates the characteristics of the teeth and determines the cause of their appearance.
During the initial visual examination, the pediatrician assesses:
- mobility of incisors and their hardness;
- dental anatomy - matching the shape, color and size of the teeth;
- presence of root (if possible). If a tooth is mobile, most likely its root system is not developed or underdeveloped. It will most likely fall out on its own within a few weeks.
The doctor also conducts a mandatory examination of soft tissues:
- Examines the surface of the tongue and gum tissue. The pediatrician identifies the presence of granulomatous lesions and inflammation caused by irritation from the cutting edge of the tooth. If there is a risk of infection, the doctor advises not to save the incisors.
- Performs a general examination of the patient to exclude infections and other diseases. If necessary, the doctor prescribes a series of tests for the patient, recommends undergoing diagnostic examinations and obtaining consultations with specialists.
Composition of saliva
When parents complain about bad teeth, they often do not realize that the cause may be the composition of saliva, which determines heredity. It may vary in the ratio of mineral and organic components. And this has a direct impact on dental health.
With a reduced content of oligosaccharides in saliva, the population of microorganisms increases, which settle on the surface of the enamel, creating a predisposition to caries. To avoid this disease, you need to brush your teeth at least twice a day and use special mouthwashes.
An increase in the concentration of class A immunoglobulins (IgA) in saliva, which have an antibacterial effect, protects the enamel from cariogenic bacteria.
The specialists of the Shifa clinic will help you choose toothpaste and other hygiene products to create the right environment in the oral cavity. Dentists will also give recommendations on diets that reduce the negative effects of saliva.
Indications for removal of natal teeth
Unusual early incisors should be removed if the doctor notices:
- The edges of the teeth are too sharp;
- Significant mobility of teeth (absence and underdevelopment of roots);
- Weakened incisor structure;
- Thin, discolored tooth enamel;
- Irregular shape of “pearls”.
If natal teeth have at least one of the problems listed above, they can injure the soft tissues of the oral cavity and mucous membranes. Moreover, teeth with weak roots can fall out at any time and fall into the respiratory tract, which is dangerous for the baby’s life.
Sign
There is more than one sign about “toothy” babies. If a child is born with one or more teeth, the belief promises a comfortable, happy life and good health. Children who are born with teeth will be strong in life, able to stand up for themselves and fight back. Another sign, on the contrary, promises health problems. If a child was born with teeth, then there will be little strength in the future, since they have gone into the early teeth.
- Interesting read: why does a child grind his teeth in his sleep?
To believe in omens or not, to each his own. And clean air, healthy nutrition, vitamins and parental love will help your baby grow up healthy.
Preservation of teeth
Most often, natal teeth do not have any negative consequences for the child. The baby was just born special. If the parents and the doctor decide to preserve the incisors, it is worthwhile to be attentive to his oral cavity from the very first day of the child’s life.
Early teeth, much more than baby teeth, require careful care and attention. The child should be regularly shown to the dentist to have the oral cavity cleaned of bacteria.
An ideal care product and method for massaging fragile children's gums and, accordingly, natal teeth are Asepta Baby wet wipes, intended for children from 0 to 3 years old. Finger wipes prevent the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity, reduce discomfort during the eruption of subsequent baby teeth and perfectly clean all surfaces of the oral cavity.
So, now you know how to take care of a baby who was born with teeth. Don’t forget that there is a popular saying: if a child is born with incisors, a happy, rich life awaits him. The baby will grow up brave and strong, and will always be able to stand up for himself!
Should I worry?
There are currently no strict limits on teething. There are teething charts and they reflect the situation that occurs most often. According to this schedule, the lower incisors appear first at the age of approximately 4-5 months; in some cases, the timing of their eruption can extend to 10-12 months.
However, teeth can appear much earlier. If you notice early teeth in your baby, you should not panic; most likely, this feature does not mean anything terrible, but this is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. Only a doctor can give an accurate diagnosis and instructions for further actions.
You may also be interested in
CHILDHOOD
Finger wipes from 0 to 3 years ASEPTA BABY
For gentle oral hygiene of babies and massage of gums during the eruption of the first teeth
More about the product
CHILDHOOD
Children's gel toothpaste from 0 to 3 years ASEPTA BABY
Designed for gentle care of baby's gums and baby teeth
More about the product
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Dr. Komarovsky is also studying the question of whether a child can be born with teeth, who notes that deviations of 6 months in the established time frame, both upward and downward, are considered an acceptable norm.
However, the specialist insists on a mandatory visit to the dentist if teething is very late and there is an uncharacteristic localization of developing baby teeth. The doctor also considers the appearance of teeth before birth to be situations that require additional study.
Important! All of the above deviations may be associated with dangerous pathological processes in the baby’s developing body, and therefore should not be left without due attention. Only a specialist will be able to exclude dangerous deviations and prescribe timely and effective treatment, if necessary.
Now you know for sure whether children are born with teeth and what this may be connected with, but if such an anomaly is identified, you should not worry, because most often it is a minor deviation from the norm that can be easily corrected.
Waiting for the tooth fairy
The most popular tradition in the modern world is the tale of the tooth fairy. This tradition began in Iceland, but gradually it spread to America, and then it was adopted by almost the whole world. This transition occurred thanks to the cartoons that children watch.
According to tradition, when a baby loses a baby tooth, he should put it under the pillow, and when the child falls asleep, a little fairy with wings flies to him. With a wave of her magic wand, she takes out a tooth from under the pillow, and in its place puts a coin or sweets. This is the fairy tale that modern children believe.
If a tooth was removed at a dental clinic, then parents can confidently ask the dentist to give the tooth back so as not to upset the child, and also put it under the pillow at night.
Parents who do not believe in omens requiring burning, burying or any other actions with baby teeth can, after “magically” replacing the tooth with sweets or money, wrap the tooth in a napkin and dispose of it in the usual way. Whatever decision is made, it is important to preserve the child’s faith in magic and the importance of the events taking place.
Teeth “as a keepsake” - is it worth keeping?
The first baby teeth are of great importance for mothers, not only when they erupt, but also when they fall out. Many mothers keep things that are memorable to them from their baby (tags from the maternity hospital, a footprint and handprint, a cut lock of hair, etc.). When milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones, mothers do not always decide to throw away the teeth, so they store them along with other things the child has that are dear to them.
But is it possible and worth saving baby teeth? There are many beliefs about where a child's teeth should be placed. Some are inclined to dispose of them, while others, on the contrary, attach great importance to this moment and the tooth itself. Disposal does not have any bad consequences, just like storing the tooth. If you leave a baby tooth at home, over time it may simply crumble or dry out.
The storage of baby teeth can be approached from the other side - scientifically. British scientists have proven that stem cells can be extracted from the pulp of a baby tooth, which are increasingly used in the fight against serious diseases and in cosmetology. Scientists were also able to prove that dental pulp stem cells are “stronger” than those obtained from the umbilical cord connecting mother and child. But the properties of a tooth can only be preserved if it is stored correctly. To do this, you can contact the stem cell center.
Dental hypoplasia - symptoms and treatment
Hypoplasia is a malformation of the hard tissues of one or an entire group of teeth [13]. It can be congenital or acquired. It develops when the rudiments of milk or permanent teeth are formed. It is not a carious lesion.
Hypoplasia is accompanied by a heterogeneous color of the enamel, its thinning and changes in relief - depressions of various shapes and sizes (from dots to grooves and pits). When teeth erupt, they immediately differ: there are white, yellow or brown spots on their surface.
Otherwise, such dental damage is called hereditary hypoplasia, aplasia, dysplasia or brown enamel dystrophy, and the affected teeth are grooved or plaster [1].
Statistics
Hypoplasia is the most common non-carious lesion of hard tooth tissues - enamel and dentin. It occurs in 50% of children with chronic metabolic disorders that arise before or after birth [10].
As a dental examination of the Russian population in 1999 showed, the prevalence of non-carious lesions among children 12 years old is 43.5%. At the same time, systemic enamel hypoplasia accounts for 36.7% [1].
The most common form of the disease is systemic hypoplasia - damage to all teeth in the permanent or primary dentition. It accounts for 90.6% of all types of hypoplasia [1]. More often, the defect affects the cutting edges or cusps of the teeth. In three out of five cases it develops in children under 9 months of age.
In foreign literature, hypoplasia of molars and incisors (lateral and anterior teeth) is called Molar Incisor Hipomineralisation (MIH) [1]. This form of the disease is common throughout the world [18]. The increase in its incidence of MIH can be explained by stress, deterioration of the general condition of the body, and the negative influence of the environment and food [17].
Causes and risk factors
The development of hypoplasia is associated with metabolic disorders at the time of formation of tooth buds. This is facilitated by external and internal negative factors that affect the body of the expectant mother or her already born child.
Intrauterine factors include:
- Rh conflict (incompatibility of the negative Rh factor of the mother and the positive Rh factor of the child);
- toxicosis and other disorders in the body of a pregnant woman;
- rubella, toxoplasmosis during pregnancy;
- taking tetracycline by a pregnant woman (or a child) [5].
Internal factors associated with child diseases:
- Down syndrome, cerebral palsy and other lesions of the central nervous system (they are both the cause of hypoplasia and associated pathologies) [4];
- rickets or infectious diseases in a child (measles, scarlet fever);
- hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- changes in mineral and protein metabolism in dyspepsia (digestive disorders) and diseases of the endocrine glands (usually the thyroid gland) [3];
- penetration of infection from the inflammatory focus of a baby tooth into the germ of a permanent tooth.
External factors:
- prematurity, low birth weight of the newborn [16];
- artificial feeding of a child;
- local impact on the tooth germ, for example, birth trauma;
- trauma to the jaws and rudiment at the time of tooth formation.
If pathological factors affect the fetus, hypoplasia of baby teeth develops. If this happens in early childhood, the rudiments of permanent teeth are already affected.
At what age does a permanent bite form?
Permanent elements of the dental series begin to appear even before the temporary ones fall out. The first teeth to appear (at about 6 years old) are the “sixes” (first molars). At 8, the incisors erupt, at 9–10, the canines and premolars, then the second premolars and molars. Well, wisdom teeth (aka “eights”) – after 20 years, and not for everyone. The principle of paired appearance of teeth is preserved during the formation of a permanent dentition. In this case, the molars on the lower jaw grow first, then on the upper jaw. Next, the elements of the lower dentition are replaced, then the upper ones. The surest sign of the early appearance of a permanent tooth is the loss of a temporary one.
Doctors' recommendations for painful teething
Dentists recommend paying more attention to the baby during this period and carefully maintaining hygiene, because the child strives to “test everything by heart.” You should also give him rubber teething rings chilled in the refrigerator, silicone toys, or special “teethers” with soft bristles. If the child does not have allergies, then you can give him a decoction of chamomile, valerian or sage. The dose should be checked with your pediatrician.
The dental network offers dental preventive services, including consultations on teething for children. Our specialists are highly qualified and improve their skills in leading Russian and foreign clinics. The pediatric dentist will conduct visual and hardware diagnostics and give recommendations on further actions. We have a system of family and cumulative discounts.
“Smile” branches are located in Moscow within walking distance from metro stations:
- Art. Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Art. Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Don't leave your children's dental problems to chance. Our doctors will provide effective, qualified assistance to you and your children. We are waiting for you every day without breaks and weekends.
What are baby teeth and how do they erupt?
Temporary teeth are colloquially called baby teeth because they begin to appear when the baby is still breastfed. The rudiments of dental elements are formed during intrauterine development (6–8 weeks of pregnancy). Eruption is the process of teeth emerging onto the gum surface. Mechanism: the tooth root develops, over time it begins to rest against the hard bone tissue of the bottom of the alveoli, pushing the crown part of the tooth onto the surface of the gum. In total, 20 elements appear in the primary occlusion, 10 on each jaw.