Who's at risk
First of all, these are people who have the following unfavorable factors:
- Weakened immunity.
Defects in immune defense are the main factor predisposing to the occurrence of mycoses (fungal infections)1,2,4. The increase in their incidence in all countries of the world is due, first of all, to various types of conditions accompanied by weakened immunity1,[3]. It is not for nothing that “thrush” is called “the disease of the sick”1. Among its reasons:
- severe general diseases, for example, infectious2,3;
- cancer accompanied by sudden weight loss, lack of vitamins and microelements, requiring radiation and chemotherapy2,3;
- congenital and acquired forms of immunodeficiency, including AIDS2,3;
- endocrine disorders, for example, diabetes mellitus2,3.
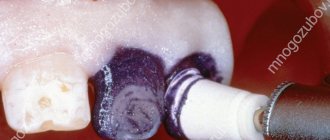
- Dental diseases.
- Inflammatory , such as caries and its complications, gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease and others2. The huge number of bacteria present during inflammation weakens the immune system and contributes to the proliferation of fungal microflora2. A diseased tooth with a carious cavity “infested” with microbes or a periodontal pocket filled with pus may well provoke the development of “thrush”3,[4].
- Non-inflammatory , which change the structure of the oral mucosa, for example, folded tongue and leukoplakia4. It is easier for fungi to attach to a damaged surface than to a healthy one.
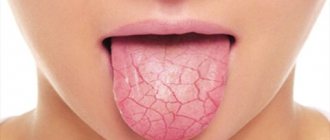
- Constant dry mouth.
- Insufficient saliva (xerostomia), associated with a variety of problems, contributes to the development of oral mycosis4. Saliva contains many enzymes and antibodies that protect the mucous membrane from the action of microbes4. If there is little saliva, it dries out, its protection is weakened, which creates favorable conditions for the development of other infections.
- Defects in oral hygiene.
- Insufficient care . Problems more often arise in those who rarely brush their teeth and ignore the care of their tongue, interdental spaces and dentures4.
- Injuries . Sometimes the cause of an “outbreak” of oral mycosis is a too hard toothbrush or rough manipulation of dental floss and toothpicks. Injured gums are easy prey for fungi2.3,4.
- Incorrect use of removable dentures.
- Poorly customized removable dentures can rub the gums3,4, making them accessible to germs.
- No night break in using prostheses4. The gum located under the prosthesis is poorly enriched with blood, it lacks oxygen, it is not washed with saliva - this predisposes to the development of infection4.
- Improper care of dentures. Artificial teeth need care just as much as your own. Deprived of attention, they become covered with a thin film of various microbes, which then “attack” the gums.
- Age.
- Most often, doctors find “ thrush” in the mouth of infants and the elderly4. The reason for this is the imperfections of the immune system, which create favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora1,4,[5]. In addition, in childhood, dietary habits affect, and in old age – constant dry mouth and lack of teeth, forcing you to wear dentures1,5.
- Medicines
- Antibiotics. They kill not only pathogenic microbes, but also beneficial ones, thereby disturbing the balance of microflora and creating conditions for mycoses to flourish1,2.
- Drugs that inhibit cell proliferation (cytostatics). They interfere with the renewal of surface mucosal cells and disrupt local and general defense mechanisms against infections1,2.
- Immunosuppressive medications, which are prescribed when immune responses need to be suppressed, such as during transplantation1,2.
- Inhaled corticosteroids, which are used in the treatment of bronchial asthma and, due to their side effects, increase the susceptibility of the mucous membrane to infections2,[6].
- Unbalanced diet
- Lack of iron, vitamins C and B12, and folic acid1 in the diet, which leads to decreased immunity.
- Excess carbohydrates1,2. Excessive consumption of sweets, flour products, sweet fruits, starchy vegetables and other foods containing large amounts of simple carbohydrates contributes to the appearance of thrush in adults and children1,2.
Up to contents
Drug-induced stomatitis
Occurs when there is an allergy to a drug. Often, allergies can occur to antibacterial, antimicrobial drugs, vaccines, iodine. The mucous membrane is red, swollen, the lips and tongue also often swell, blisters appear, which burst, leaving erosion. The gums are inflamed and bleed when touched. General manifestations are possible, such as urticaria, nausea, vomiting. In severe cases, anaphylactic shock occurs (an emergency condition manifested by decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, fainting, suffocation), Quincke's edema (an atypical reaction of the body, manifested by rapid and severe swelling)
Both conditions are extremely dangerous and require immediate action and calling an ambulance!
What does thrush look like in the mouth - its symptoms in adults
After Candida attaches to the mucous membrane, they multiply and “grow” deep into it2, causing inflammation, swelling and redness. There is a feeling of a “scalded mouth” and discomfort when eating and swallowing. There may be a change in taste and the appearance of a metallic, sour, salty or bitter taste1.
The proliferation of the fungus leads to the appearance of small white spots on the gums, tongue, inner surface of the cheeks and palate, reminiscent of curdled milk or grains of semolina porridge. Increasing in size, the “grains” turn into plaques, which, in turn, merge to form solid white films.
If plaques and films are removed with a spatula or a cotton swab (this does not require additional effort), then a bright red inflamed, eroded mucous membrane is revealed underneath them.
Oral mycosis can spread to the red border of the lips , causing redness, dryness and peeling. Seizures appear in the corners of the mouth: the skin becomes inflamed, covered with grayish-white scales and cracks5.
If candidiasis is not treated at this stage, the fungi “spread” to the tongue and pharyngeal tonsils.
When the tongue is damaged, glossitis develops - the tongue swells, its papillae are smoothed out, a characteristic white coating appears on its back and lateral surfaces1 - and when the pharyngeal tonsils are damaged, a sore throat occurs.
A sore throat caused by fungal microflora is very different from normal. With obvious inflammation of the tonsils and the presence of white films and plugs on them, there is no temperature or pain when swallowing, and the submandibular lymph nodes remain of normal size1.
Candidiasis can spread further - affecting the respiratory tract, causing pneumonia and blood poisoning, so it is important to stop the process at the very beginning.
Up to contents
Acute herpetic stomatitis
It occurs most often, and mainly affects children from 10 months to 3 years.3 The appearance of rashes is preceded by inflammation of the lymph nodes.
With a mild form
In acute herpetic stomatitis, the temperature rises to 37-37.5°C, the general condition is satisfactory, slight swelling and redness may occur on the gums, then up to six blisters appear, which burst with the formation of painful aphthae surrounded by a red rim.
Afta is a round-shaped erosion. Aphthae may merge together. The rash appears once, and after 1-2 days the erosion gradually heals.
Moderate form
Acute herpetic stomatitis is characterized by deterioration of the child’s well-being, weakness, and headache. The child is capricious, has no appetite, the lymph nodes are enlarged and painful, the temperature rises to 38-39°C, the symptoms resemble ARVI. The oral mucosa is swollen, reddened, rashes appear (bubbles, then erosions) of 10-15 pieces, and often there are rashes on the face. Salivation increases, and gingivitis appears (inflammation of the gums, accompanied by bleeding). The rash may appear several times, i.e. after the old ones heal, new ones appear. Healing of erosions takes up to 4-5 days. Bleeding gums and swollen lymph nodes persist for some time after the erosions have healed.
Severe form
It begins as an acute respiratory viral infection, there is pain in the muscles, joints, tachycardia and bradycardia (increased and slow heartbeat), and nosebleeds may even be observed. In this form, the temperature is high up to 40°C, gingivitis is pronounced, the mucous membrane is bright red, swollen, the child’s lips are dry, the mucous membrane of the eyes is swollen, reddened. The rashes constantly appear again, their number can reach 100. Rashes often appear around the mouth, on the eyelids, on the mucous membranes of the eyes, between the fingers, on the earlobes. Simple gingivitis turns into ulcerative (a more severe form of gum inflammation, with the formation of ulcers), salivation increases, and bad breath appears. Recovery is long and hospitalization is often required.
Features of “thrush” in the mouth in children of the first year of life
Mycoses in children, and very young ones at that, are not that uncommon. According to statistics, the first illness of a newborn in 33% of cases is associated with Candida fungi5. Moreover, they mainly affect the skin and tissues of the oral cavity5.
Why does thrush appear in the mouth of a child under one year old?
Mycotic stomatitis, or fungal inflammation of the oral mucosa, is the most common form of mycosis in children under one year of age1.5. How do mushrooms get into a baby’s mouth and why do they take root there? There are many reasons for this.
- Infection during childbirth.
During childbirth, the fetus comes into contact with the microflora of the woman’s vagina. If the mother suffered from vaginal candidiasis before giving birth and did not undergo the necessary course of treatment, the baby has every chance of inheriting a large amount of the causative agent of this disease1.5, which is a big burden for the immature immune system. According to statistics, on the first day of life, Candida fungi are found in the oral stool of 25-40% of newborns5.
- Unsanitary conditions.
Infection is possible due to violation of the rules of care for the newborn and defects in the hygiene of the nursing mother herself1,5. The infection is transmitted through dirty nipples and hands during feeding, through toys, nipples, dishes and linen.
- Imperfect immunity1, 5.
In a baby under one year old, the immune system is only “gaining experience”, because in the womb it did not come into contact with the infection and therefore “did not learn” to fight it.
- Prematurity and illness.
Candida can only harm a weakened body. The best conditions for their development are created if the birth occurs before term, the fetus is premature and/or has developmental defects or congenital diseases5.
- Nutritional features.
The threat is posed by regurgitation, the habit of putting the baby to bed with a bottle of milk and feeding with sweet artificial formulas. If milk remains in the mouth, which also contains a large amount of sugar, it becomes an ideal breeding ground for mushrooms.
- Features of salivation.
Due to physiological characteristics, the salivary glands of infants produce little saliva1 - they simply do not need it, since food is already liquid. At the same time, saliva has antifungal activity, and when there is little of it, the likelihood of oral thrush in a newborn increases1,5.
What does oral candidiasis look like in children?
The symptoms are the same as in adults: first, white “grains” appear on the mucous membrane, then “clumps” resembling curdled milk, and white films1. The difference is that the process is almost always accompanied by severe tissue swelling and the formation of numerous painful ulcers on the oral mucosa and tongue1,5. Therefore, due to oral thrush, infants often refuse to eat5.
In children, a fungal infection can affect not only the tonsils (tonsillitis), but also the pharynx (pharyngitis) and larynx (laryngitis). If the larynx is affected, the baby's voice becomes hoarse and low, and there is a risk of swelling of the airways and breathing problems1, 5.
Up to contents
Acute pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis (thrush)
Acute pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis (thrush) occurs:
- Light shape
- Medium-heavy forms
- Severe form
The main symptom of the disease is a white or yellow coating.
With a mild form
The plaque is located in islands, most often on the tongue and cheeks. Children are restless, sleep poorly, and suck the breast sluggishly. Older children may complain of a burning sensation. The plaque is easily removed; underneath there is a bright red mucous membrane. The disease lasts no longer than 7 days.5
Moderate form
The plaque is located on the cheeks, tongue, hard palate, and mucous membranes of the lips. Under the plaque, erosions form, which sometimes bleed. The plaque is more difficult to remove. Lymph nodes are sometimes enlarged and painful. The duration of the disease is 10-15 days, there are relapses.
Moderate form
The plaque is dirty gray, almost cannot be removed, and is located on the tongue, cheeks, soft palate, tonsils, pharynx, and mucous membranes of the lips. Cheilitis appears in the corners of the mouth - inflammation of the lips. The oral mucosa is dry and inflamed. The child’s health is impaired, the child refuses to eat, and the temperature rises. Lesions in the genital area, neck folds, and between the fingers are also common. The disease is long-term, with frequent relapses.
Diagnosis of oral mycosis
Most often the diagnosis is obvious. However, in difficult situations, for example, in the presence of complications or individual intolerance to certain drugs, to confirm it, microscopic and cultural analysis of scrapings from the surface of the mucous membrane is used to determine the sensitivity of the microflora to antifungal drugs. Moreover, the mere presence of Candida threads in scrapings from the oral cavity is not always enough to make a diagnosis - fungi can be present in the mouth, but not cause any diseases. In such a situation, quantitative assessment is important, that is, counting the pathogen cells, and increasing their number when re-analyzed after 2-3 days.
Up to contents
General information
Candidiasis in children is a common disease among children. Normally, small amounts of fungi are part of the opportunistic microflora and are constantly present in the body. If the child’s immunity is strong, microorganisms are safe for health. In weakened children, the fungus begins to multiply uncontrollably, affecting the mucous membranes, skin, and genitals. If candidiasis is left untreated, serious health problems can follow. The main task of parents in the fight against the disease is to establish good nutrition and strengthen the child’s immunity.
How and with what to treat thrush in the mouth
Since candidiasis often develops as a secondary disease1, treatment of oral thrush requires an individual approach. What do we have to do?
1. Eliminate the factors that contributed to the appearance of oral mycosis
To do this you need:
- cure diseased teeth and gums, relieve exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- replace old “outdated” removable dentures with new ones, follow the rules for using and processing dentures;
- every time after using inhalers with steroid drugs (for bronchial asthma), rinse the mouth and gargle with water6;
- take antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor;
- use toothbrushes with soft bristles, toothpastes, and mouthwashes with an anti-inflammatory effect1;
- follow the rules of caring for a newborn and feeding hygiene (if the disease manifests itself in an infant);
- use formulas that do not contain sugar for artificial feeding of a newborn.
2.Keep a diet
Meals include:
- limiting the daily intake of simple carbohydrates: sweets, flour products, potatoes, rice, legumes, boiled beets and carrots, sweet fruits and dried fruits;
- supplementing the diet with fresh vegetables with a lot of fiber, which contribute to the formation of normal microflora in the intestines and the formation of immunity9;
- consumption of sour berries and lactic acid products, which, due to their acid content, hinder the spread of fungi1;
- taking vitamins1 necessary for the normal functioning of the immune system;
- eating enough easily digestible meat and eggs for the normal functioning of the immune system.
3. Carry out local treatment
For oral thrush in both adults and children, treatment may include topical use of drugs with antifungal activity. Moreover, if the fungus affects only the oral cavity, local therapy may be sufficient5 to cope with the problem.
To treat the oral mucosa, today it is recommended5 to use hexetidine preparations, for example, HEXORAL® solution and HEXORAL® aerosol .
HEXORAL® with hexethidine:
- is active against biofilms[7] that are resistant to other drugs, and is harmful to fungi of the genus Candida, which cause oral candidiasis;
- has a high safety profile;
- can be used not only in adults, but also in children from 3 years old8;
- eliminates discomfort and relieves pain7;
- lasts for a long time, up to 12 hours[8];
- Available in the form of a solution and an aerosol, for comfortable use in any situation (for fungal laryngitis in children, it is especially convenient to use the aerosol form of the drug)2.
Important: doctors prescribe general antifungal drugs only if local treatment is ineffective and multiple relapses of candidiasis occur against the background of severe immunodeficiency and/or severe concomitant diseases. In these cases, HEXORAL® can be an addition to the main therapy1, 2, 5.
When treating oral thrush in newborns, there is often no need to use systemic antifungal agents1, 2, 5.
Up to contents
Prevention of candidiasis
To avoid thrush, follow the disease prevention measures:
- Mothers in labor are advised to sanitize the birth canal before giving birth. To do this, the woman takes a smear, based on the results of which the doctor determines the need for treatment. If candidiasis is diagnosed, vaginal suppositories with antiseptics are prescribed. This measure will prevent the baby from becoming infected with fungi.
- Follow the rules of hygiene in the maternity hospital.
- Breastfeed your baby only unless there are medical indications for bottle feeding. In the latter case, you need to choose the right mixture together with your pediatrician.
- Limit the consumption of sweets and sugar in children over one year of age. Try to keep your diet varied, healthy and nutritious.
- If the baby is weakened, strengthen the immune system with hardening procedures, proper nutrition, physical exercise, etc.
Candidiasis is an unpleasant but treatable disease. Timely consultation with a pediatrician, the correct course of therapy and compliance with preventive measures will allow you to forget about thrush for a long time. SM-Doctor specialists are always ready to help your child in the fight against candidiasis.
How to prevent the disease
So, what will help avoid an “outbreak” of fungal infection?
- Careful oral care.
- Solving dental problems and treating common diseases.
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, hygiene of infant feeding and care1.
- Mandatory treatment of the disease during pregnancy and after childbirth1.
- Prophylactic use of antifungal agents, for example, during treatment with antibiotics and immunosuppressive drugs (radiation or chemotherapy)1.
Important: frequent outbreaks and severe cases of candidiasis are a reason to consult a doctor and undergo a full examination. Taking into account the fact that mycoses develop against a background of reduced immunity, they can act as a marker of serious diseases2. According to the World Health Organization, recurrent candidiasis should be a reason for testing for HIV.
Up to contents
Can Fluconazole be used during breastfeeding and pregnancy?
The use of the drug during pregnancy should be avoided, with the exception of severe or life-threatening systemic fungal infections, when the expected benefit of therapy for the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus.
Women of childbearing age should also use reliable methods of contraception during treatment with Fluconazole and for at least a week after taking the last dose. Since there is information about cases of spontaneous abortion and the appearance of congenital pathologies in children whose mothers received Fluconazole at a dose of 150 mg once or repeatedly in the first trimester of pregnancy.
When pregnant women take increased doses for a long time in the first trimester, the number of defects in infants also increases: curvature of the femurs, impaired formation of the cranial vault, brachycephaly, impaired development of the facial part of the skull, cleft palate, thinning and elongation of the ribs, arthrogryposis and congenital heart defects.
Fluconazole passes into breast milk, so use during breastfeeding is prohibited.