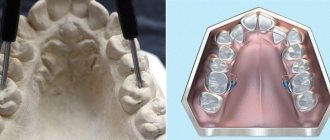
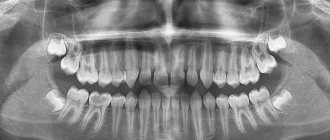
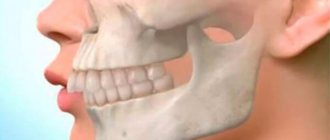
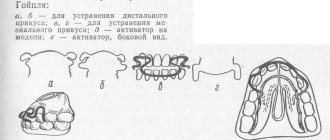
Dental abnormalities are divided into malocclusion, configuration and location of specific teeth and rows.
A special pathology that can lead to severe complications:
- reducing the distance between the jaw arches and disrupting their configurations;
- narrowing of the dentition.
The configuration of a normal dentition is an ellipse (upper teeth) or a parabola (lower teeth). The remaining configurations are an anomaly. In mathematical terms, when the row decreases, the transverse diameter of the jaw arch decreases.
Features of a narrow jaw
When one of the parts of the bite is underdeveloped, the formation of micrognathia (narrow jaw) is observed.
The upper or lower jaw is subject to deformation. Externally, the pathology is easy to see; facial features are disproportionate (look at the photo). If the area above is distorted, then the chin recedes, and the bottom is pushed forward. Uneven incisors, prognathia, and the absence of one or more elements of the dentition are characteristic features of micrognathia. The formation of the disease occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- severe illnesses during pregnancy,
- abnormal intrauterine development of the child,
- congenital pathologies of the fetus (dentition defects),
- genetic predisposition,
- facial injury,
- untimely loss of primary incisors,
- constant mouth breathing
- prolonged and incorrect bottle sucking, artificial feeding during infancy.
When is jaw expansion indicated?
In some cases, jaw expansion is the only option for correcting malocclusion. Depending on the functionality of orthodontic structures, this technique is used for adults and children. Its reproduction is indicated in the presence of certain pathologies:
- crossbite - disproportionality of width in the lateral segments (discrepancy from the general line of the dentition in a specific area),
- mesial occlusion (with a change of grade 3 according to Angle),
- compression of the borders and apical base of the jaw arch,
- micrognathia (vestigial upper or lower part),
- protrusion of incisors,
- significant narrowing of the dentition.
Teeth size for prosthetics
It is especially important to preserve and, if necessary, restore the natural size of teeth during prosthetics, so as not to disrupt the bite and the full functioning of the dental system. The size of the crown is selected by the dental technician, focusing on neighboring or teeth of the same name, monitoring the correct closure of the rows and adjusting the prosthesis during installation.
Determining the size of artificial teeth with complete edentia is carried out by measuring the distance between the corners of the mouth using a special ruler - it corresponds to the width of the six front teeth. And the segment from the edge of the gum to the smile line is equal to the height of the crown. For example, during implantation it is necessary to correctly calculate not only the parameters of the orthopedic design, but also the size of the dental implant. It should be equal in length to the real root, but the choice of titanium rod parameters depends largely on the volume of the jaw bone tissue.
Diagnosis of the disease
To establish a final diagnosis and select an adequate treatment method, the doctor must carry out the following procedures:
| Diagnostic manipulation | Clinical picture |
| History taking |
|
| Visual inspection |
|
| Taking impressions |
|
| Studying jaw models |
|
| X-ray examination |
|
How are tooth sizes determined?
To determine the size of a person’s permanent teeth, the calculation tables of Wetzel and V.L. Ustimenko with average standards and permissible deviations are used. However, an experienced dentist is able to independently identify the anomaly during a visual examination or by applying the formula for the ratio of the height and width of the natural crown. During diagnosis, the specialist takes into account the patient’s face shape and height. For example, with a wide jaw, the size of teeth exceeding the norm is not a pathology.
To determine the size of the root canal, there are also tables that indicate the average distance from its apex to the cutting edge or cusp of the tooth surface. The longest is the root of the canines - about 26 millimeters, the root canal of the incisors is 21 - 23 millimeters, and the size of the roots of the chewing zone and premolar teeth ranges from 19 to 22 millimeters.
Operating principle and advantages of the hardware technique
To open the palatal suture, the Derichsweiler apparatus is used. It is a device that is fixed on the upper jaw and consists of support rings and corrective arches. A special screw is located in the area of the palatal arch. When rotating, it exerts constant pressure, due to which the palatal suture opens.
The optimal time for installation of the Derichsweiler apparatus is early mixed dentition. For adults, this technique helps less. This is due to ossification of the palatal suture.
The advantages of the hardware method for correcting jaw narrowing are:
- soft impact,
- no discomfort,
- surgical restoration of the upper jaw,
- absence of periodontal and soft palatine tissue injuries.
The disadvantages of the apparatus for opening the palatal suture include difficulties with oral hygiene and the impossibility of self-correction. To change the position of the screw, you must visit your dentist regularly.
An alternative to installing the Derichsweiler apparatus is the fixation of palatal expanders and special expansion plates. They are designed to expand the dentition of the upper jaw and allow you to eliminate even serious malocclusions.
Expansion devices
Dentists use several types of devices to expand the jaw. The devices are absolutely safe and have a gentle effect on the jaw. During their use, the parameters of the dental arch increase - it expands and the teeth move to the correct location.
Special designs are made to solve pathological problems of the upper and lower jaw, namely narrowed dentition (displacement relative to the center of the palatal part). Almost always the defect can be corrected without surgery, but there are exceptions. Anomalies formed in a certain way cannot be corrected by hardware.
Designs for jaw expansion are presented in several types, their operating principle is similar - they apply light pressure on the lateral sections, as a result of which a slow displacement of the dental units occurs and the destruction of bone tissue.
Orthodontic plate
This dental design is designed to correct a mixed bite, which is accompanied by an abnormal decrease in the size of the jaw bones. It is advisable to use a plate apparatus for expanding the upper jaw from an early age.
Orthodontic plates
Dentists recommend this treatment for children aged 5-10 years. A significant advantage of the technique is the parallel possibility of correcting the location of individual groups of teeth. The production of the device is individual and is carried out in a dental laboratory.
The plate for jaw expansion consists of hard plastic, which completely follows the relief of the oral mucosa. In the central part of the structure there is a special activator screw; its gradual unwinding causes an increase in the upper jaw.
The main advantages of this technology include: comprehensive treatment of dental abnormalities, simplicity and safety of the procedure. The key disadvantage is the long period of therapy.
Palatal expander
This device is usually used as a preparatory method for the main stage of treatment. This expansion of the upper jaw in adults is indicated when there is a significant narrowing of the dentition.
The device has a cruciform configuration, in the central part of which there is a sliding lobe.
Palatal expander
Stretching of the jaw bones in children occurs very quickly, within three weeks. But for adult patients, treatment is delayed for 1-1.5 years.
This jaw expansion system provides stable and measured pressure on the lateral areas of the alveolar process of the upper jaw. The device has the advantages of quickly achieving results, painless movement of the dentition and the possibility of autonomous activation of the device.
The device is tightened once every two days. At the same time, experts note some disadvantages of such an orthodontic device: chronic trauma to the mucous membrane, the need to activate the device by 1 mm and the need to use additional means of cleaning the oral cavity.
Functions of the palatal expander
Another orthodontic device that is successfully used to correct pathologies is the palatal expander. The name speaks for itself: it is used to expand the upper jaw, while other structures are used for the lower jaw. Most often it has a cruciform shape, each end of which is fixed to the molars. The main sliding part is located in the center of the device.
It takes literally three weeks for the jaw to expand in children; in adults, this process can take a longer period. After this, it is recommended to wear the device for some more time so that the resulting gap is filled with new bone tissue. But even taking this into account, the palatal expander allows you to quickly adjust the length of the dentition.
Quite often you can hear the erroneous name of an expander - palatal clasp. Despite some similarity in names, these are completely different devices. The clasp is used to strengthen the position of the molars when correcting the bite. That is, it is an additional part of a non-removable orthodontic structure. For example, it can be used with braces.
The palatal clasp can be called differently - an arch, which in the classic version has the shape of a rocker. Special rings are put on the molars, onto which the supporting arch is fixed. This device is suitable for both children and adults. That is, unlike the expander, the palatal clasp performs a different function (fixing the position of the teeth during bite correction) and has nothing to do with jaw expansion.
Derichsweiler device
The Derichsweiler device is considered the most effective of all the devices described above. Expansion of the upper jaw occurs as painlessly, effectively and in a short time as possible. It is used only during the period of infant temporary occlusion. The main characteristics and features of the device are shown in the table:
| Description | It consists of support rings, connecting corrective arcs and an activator screw, which supplies a given pressure force. |
| Age limit | From birth to 7 years. |
| pros |
|
| Minuses |
|
| Price | Calculated based on the cost of materials. |
Design and principle of operation
The Derichsweiler apparatus consists of elements :
- plate made of plastic or metal;
- metal screw;
- hooks, wire arches.
This design is located at the top of the palate, cast arches are attached to the side teeth, exerting pressure on them . The plate inside is equipped with a screw and metal fittings - hooks, which are fixed on the supporting molars.
Having securely fastened the device, the doctor looks at the effect it has on the teeth.
In addition to jaw expansion, there is also the movement of certain teeth that need correction.
During the treatment process, the design undergoes changes - a metal screw is tightened, which increases the area of the plate and increases the pressure.
The screw allows you to apply a gradually increasing load on the teeth, thereby fixing their displacement.
In addition to the problem of a narrow jaw, another, accompanying problem is solved - gaps between the teeth. As a result of pressure on the molars, incisors and premolars, these gaps are eliminated using springs and screws.
Installation sequence
The accuracy of installation of the mechanism is important for the patient, because he will feel a foreign body in the oral cavity for at least another 3 months.
Treatment takes place in several stages:
- After checking the screw mechanism and adjusting the plate on the plaster jaw, the device is installed on the patient . The patient is given a day to master the device. At this time, he learns to use it and gets used to it.
- Then the patient, if nothing bothers him, has crowns and rings attached to his molars using special dental cement.
- 24 hours after fastening, the doctor begins the treatment process: the screw is unscrewed .
- Every day the screw is activated half a turn, the doctor and the patient monitor the condition of the device in the oral cavity and general well-being.
If the pain after turning the screw disappears within a minute, then you can continue treatment.
It is important not to overtighten the screw - this can lead to complications. If you add a little pressure, you may experience pain in the temples and bridge of the nose. In this case, the doctor returns the screw a little back.
After just a week, you can see the first result of the device - a diastema appears between the front teeth - a gap that grows and then goes away. There is a gradual alignment of the teeth.
Upon completion of treatment:
- the side teeth fall into place,
- the sky slightly increases its area,
- the lower part of the face visually becomes larger,
- the lower jaw falls into place,
- teeth align their position.
At what stage of bite correction is the Derichsweiler apparatus used, look at the video:
When the process of tightening the screw is completed, it is covered with a plastic plate for the patient’s convenience and to minimize discomfort.
Cost of the device
The device is manufactured individually in each case, so its cost may vary. It depends on the following factors:
- region;
- materials from which plates, crowns and rings are made;
- cost of doctor's services.
Typically, the price of the Derichsweiler apparatus is 8,500 rubles. During treatment you will also have to pay for medical consultations, installation and configuration of the structure.
The Derichsweiler device is the most effective way to correct a narrow upper jaw. Often its installation is the only way to solve the problem. The device gives quick results and is suitable for those who want to correct uneven teeth in a short time.
Mandibular distraction systems
In cases where there is pathology of the lower jaw, a fundamentally different type of device is used - distractors. These devices provide a process of gradual expansion of the lower jaw with the replacement formation of new tissue. Particularly good results can be achieved when treating a child. In adulthood, a central dissection of the lower jaw with an ultrasonic scalpel is required. In this case, the dental roots and, if possible, the mucous membranes are not affected.
These devices can have different designs depending on the problem to be solved. Many of them can be used even to treat a very young child. This is very good, since such pathologies in most cases are congenital, and it is easier to correct them immediately by correcting the child’s jaw.
Indications for installation of the Bidermann apparatus
Crossbite, that is, a discrepancy between the shape and size of the lower and upper jaws in the transverse direction, is a difficult case in the practice of any orthodontist.
This developmental defect is most often caused genetically, and leads to various pathological consequences - chewing disorders, speech defects, pain in the TMJ, mouth breathing, cheek biting.
The incidence of crossbite development is about 3% in adults, and from 0.4 to 1.9% in adolescents and children.
One of the reasons for the anomaly is a narrowed upper jaw, leading to a transverse displacement of the lower and upper chewing teeth relative to each other.
The defect can have different forms - buccal, midsagittal, combined buccal, lingual.
An important characteristic feature that influences the approach to treatment is its symmetry or asymmetry relative to the sagittal (passing from front to back through the center of the human axis) plane.
When treating various forms of crossbite, orthodontic appliances with different characteristics are used.
The use of the Bidermann apparatus is indicated in the following cases:
- cross symmetrical bite, characterized by a narrowed upper row of teeth;
- lack of space in the upper jaw, which cannot be eliminated by tooth extraction;
- breathing problems due to the small volume of the nasal cavity;
- some other cases of congenital facial defects.
The Biederman appliance cannot be used in cases of asymmetrical crossbite (in this case, unilateral expansion is required) and weak periodontium.
Main characteristics
The Biederman apparatus owes its name to Dr. William Biederman, who developed and improved the specially designed Hyrax screw (HygienicRapidExpansionScrew).
This world-famous dentist - the author of many works on dental ankylosis and orthognathic surgery - died in 1981. However, his invention is still widely used in RPE devices designed for rapid expansion.
There are many orthodontic devices available that contain a Biederman screw. In addition, devices that expand the upper jaw have thrust parts that transmit force from the screw to the chewing teeth and bone.
In different modifications, this persistent part is implemented in different ways - in the form of a set of orthodontic rings, clasps, retainers, trays made of cobalt-chromium and titanium alloys and polymers.
The force created by the Biederman screw on the dentition reaches 100 N. Thanks to its compactness, elegant shapes and smooth surfaces, the design provides patients with a minimum of discomfort.
Biederman apparatus:
- allows you to expand the entire dentition;
- vary the rate of expansion;
- make body movements of the teeth, and not tilt them;
- can be activated by patients themselves;
- used in conjunction with other orthodontic devices.
Operating principle
The device uses the principle of expanding the upper jaw with a rupture of the median palatal suture. The force is transmitted as widely as possible to the entire dentition, not only to the teeth, but also to the bone.
This is necessary so that the bone expands due to the expansion of the palatal suture, and not the inclination of the teeth with the alveolar processes. In the enlarging suture, new bone tissue is formed, preventing reverse narrowing.
The device works as follows. When the screw rotates, the thrust parts move apart, creating a constant load through clasps, orthodontic rings and mouthguards on the molars, fangs, and, accordingly, on the osseous frame.
The mode of activation (rotation) of the screw is determined by the doctor , but the patients themselves or their parents can rotate the screw. This is done daily, 1-2 times a day, using a key inserted into the hole in the screw head.
Classification
The types of row configuration deformations are different. The following types of violations have been recorded:
- Narrowing of the row along the entire length of the arc.
- Characterized by an elongated front part of the teeth. As the incisors become densely spaced, their undulation occurs.
- Clenched jaw.
- Saddle-shaped reduction. Chewing teeth can shift because there is not enough space in the jaw. The arc acquires a V-shaped position. There is a close connection. Then they move forward.
- The arc takes on a trapezoidal shape. Closely spaced teeth create a straight line. But they are not inclined to meet you. Due to insufficient space, they often rotate around an axis, forming 4 corners of a trapezoid.
- Uneven narrowing. The problem affects individual teeth, namely those that are cramped in a given place. The rest develop normally.
Wearing period of devices
The length of time you wear the device depends on several factors:
- his type
- patient's age,
- features of the condition of the dentofacial apparatus,
- degree of severity of abnormalities in the structure of the jaw.
The average duration of hardware therapy is from 1 to 6 months. After its completion, a retention course is carried out to consolidate the achieved result. Its duration is determined individually. The total treatment period can be up to 11-12 months.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is indicated when hardware treatment does not produce positive results. The method allows you to qualitatively expand the narrow dental arch and enlarge it using a specially installed device. In the future, the patient will periodically activate it.
The approximate duration of treatment is 1 month, it is adjusted depending on the severity and age of the patient. After complete tightening of the tissues, hardware treatment is prescribed for subsequent correction of the dentition and formation of the correct position of the incisors. Taking into account the course of rehabilitation procedures, the total treatment time is 11-12 months.
Sequence
The procedure for surgical expansion of the dental arch takes place in several stages :
- Setting up anesthesia. As a rule, the operation is performed only under general anesthesia, as it involves deep trauma to the tissues of the oral cavity.
- Using an ultrasonic scalpel, an incision is made into the mucous membrane and periosteum. Depending on the type of anomaly, an incision can be made on one or both sides of the jaw.
- The soft tissue flaps are peeled away, exposing the cortical plate of the jaw. Then, by perforation, certain segments are dissected.
- An expanding apparatus is installed in the area of dissection.
- The mucosal flap is returned to its place and sutured.
The correction procedure begins only 3 days after the operation.
The primary activation is carried out by a doctor, and then the patient carries out it independently at home. Activation is completely painless and does not cause any difficulties.
Surgery. Forecast
The doctor assesses the need for correction of macrognathia and micrognathia based on detailed diagnostic data, medical indications, and the wishes of the patient himself, taking into account his state of health and emotional state.
The solution to most problems associated with unexpressed disorders can consist of conservative treatment , the use of various orthodontic systems. In case of pronounced skeletal disorders, in cases where there are also concomitant significant functional and aesthetic disorders, it is advisable to resort to combined orthodontic-surgical treatment , which will be aimed comprehensively at simultaneously eliminating both aesthetic and functional disorders. During complex treatment, including orthodontic preparation and subsequent orthognathic surgery, extensive joint work is carried out between the orthodontist and the surgeon, aimed at correcting the bite, changing the shape and position of the bone structures of the face.
Orthognathic surgery requires high-quality orthodontic preparation (on which the correct closure of the dentition after surgery and the final predicted result of the entire combined treatment depend) and detailed planning. Orthognathic surgery is performed under anesthesia through intraoral access. The surgeon moves the jaws, changes their shape if necessary, gives the jaws the correct position and secures them with special fixing elements. Upon completion of the rehabilitation period and the end of the orthodontic treatment stage, the final result no longer requires any additional correction and remains stable throughout life.
Thus, once having corrected the functional and aesthetic disorders of the maxillofacial area and restored the harmony of facial features at the level of not only the dentition, but also the jaw bones, a person forever forgets about the problems that previously bothered him.