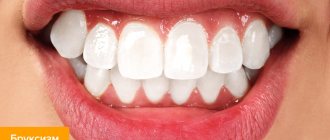
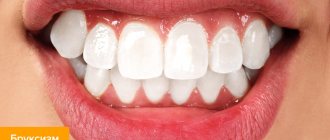
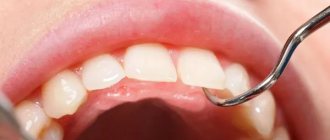
Bruxism is an involuntary chewing activity that manifests itself during the day and at night and is expressed in teeth grinding and jaw clenching. The prevalence of this pathology among the world population, according to various sources, ranges from 5 to 20%, with half of the cases recorded in childhood.
What is considered pathology? Normally, the teeth of the upper and lower jaws touch for 25-30 minutes during the day - this is the time of chewing food. With bruxism, teeth can be in contact for 40 minutes every hour. The chewing muscles work unconsciously, so it is difficult for a person to control his condition. The result of bruxism in children and most adults is accelerated tooth wear. This is a serious dental problem that requires proper treatment.
Causes of Bruxism
The pathology may be based on a complex of causes that mutually reinforce each other. Teeth grinding often occurs due to stress (disappears after the patient’s psychological state has stabilized) or develops as a symptom of a serious systemic disease.
The main causes of bruxism:
- Impact of psychological factors. Bruxism is observed in patients with chronic stress, fatigue, and depression. People with unstable mental health may chatter and grind their teeth at night with varying intensity. The reason is that psychological stress causes pathological activity in the brain and nervous system, causing muscles to involuntarily contract. At the same time, pathological work of the masticatory muscles is also observed in people with a positive psycho-emotional state.
- Neurological disorders. It is assumed that bruxism can occur with various pathologies of the central nervous system, which cause tonic muscle tension. Sleep disorders such as apnea, snoring, and somnambulism are often accompanied by unnatural jaw movements. Bruxism affects patients with epilepsy, enuresis and other disorders.
- Anatomical features of the maxillofacial system. The development of bruxism is facilitated by an incorrect bite, the absence of some teeth or, conversely, supernumerary units, poorly installed implants. Disorders of the temporomandibular joint can also cause abnormal contraction of the masticatory muscles.
- General and systemic diseases. Night and daytime bruxism is often associated with traumatic brain injury, rhinitis, adenoids, helminthic infestation, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Parkinson's disease, etc. In childhood, grinding can occur during teething. Involuntary clenching of the jaws is also observed in people under severe drug and alcohol intoxication, while taking antidepressants and sleeping pills.
Content
- What caused the development of the disease?
- Signs of Bruxism
- Recognition of pathology
- Treatment of bruxism
- The most effective methods of treatment
- Kappa in the treatment of bruxism
- How can the patient help himself?
- Children and bruxism - factors in the onset of the disease and its treatment
- What danger does the disease pose?
What caused the development of the disease?
Factors in the appearance of this unpleasant phenomenon can be various disorders in the structure of the jaw, joint deviations, problems in the field of dentistry and emotional and psychological reasons. Some claim that teeth grinding at night indicates the presence of worms in a person. Of course, such an assumption may turn out to be correct, because if a parasite lives in the body, then people suffer from a lack of B vitamins, which ensure emotional stability.
Psychologists think that neurosis, being under constant stress or depression can lead to the appearance of bruxism, since these conditions contribute to increased tension in the facial and jaw muscles and intense clenching of the teeth. During the daytime, the pathology is controlled by the body, but at night, during sleep, it manifests itself in the form of teeth grinding. If a person is in frequent stressful situations, then bruxism is characterized by periodic reminders of oneself. As for neuroses, the disease manifests itself much more painfully. To get rid of pathology, it is necessary to normalize a person’s nervous state.
In adults, complexes that are laid down at a subconscious level can also become the causes of this disease. Or, if a person is unable to resolve any issue or influence anything in real life, in a dream all his anger and tension, not released, will manifest itself in the form of grinding his teeth.
Bruxism can torment a person who suffers from sleepwalking or apnea, as well as nightmares. Often, teeth grinding becomes a sign of many diseases of the nervous system.
Important: in adults, various dental problems such as malocclusion or poorly installed braces also affect the development of bruxism. Treatment in such a case is prescribed by a dentist.
Signs of Bruxism
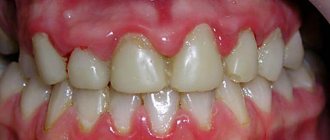
The very first and main sign of the disease is very strong grinding of teeth during sleep. This phenomenon lasts from a few seconds to a couple of minutes and occurs repeatedly. The attack comes unexpectedly. The pathology is often accompanied by great tension, restlessness, eating and sleeping disorders, and irritability. Among other things, the disease can cause headaches, pain in the joints and muscles of the face, increased sensitivity of the teeth and the appearance of cracks in them.
Recognition of pathology
First of all, you should consult a dentist with such a problem. Based on the patient's complaints and dental examination, a diagnosis of Bruxism will be made. The factors that contributed to the onset of the disease and its treatment are related to each other. In some cases, it is necessary to conduct a polysomnographic study, during which the contraction of the masticatory muscles of a person in a state of sleep will be recorded in order to exclude epilepsy from the list of causes of teeth grinding.
There is an increase in symptoms with strenuous activity and stress. Very often, children are susceptible to this disease, but there are also a large number of adults - both men and women - who suffer from bruxism.
Treatment of bruxism
With such a pathology, it is quite difficult to establish the causes that influenced the onset of the disease, so completely eliminating the symptoms of bruxism is also problematic, but still feasible. The most important task in treating teeth grinding is to relax the masticatory muscles. Children can often get rid of this disease on their own, but adults should take this problem seriously. If the disease is detected in the first stages, then its treatment will be as successful as possible.
A patient suffering from bruxism should stop clenching and grinding their teeth during emotional stress and begin to fully control their chewing movements. Psychotherapy has a very positive effect on the treatment of pathology; with its help, you can learn to overcome everyday difficulties, causing minimal harm to the nervous system. To put your emotional state in order, you can take walks before bed, read and listen to music that promotes relaxation.
Important: it is also recommended to drink sedative tinctures, which can be purchased at the pharmacy. And magnesium, calcium and B vitamins will help reduce muscle spasm activity during sleep.
The most effective methods of treatment
Methods of increased effectiveness include the use of special drops that prevent the abrasion of tooth enamel and are selected personally for each patient. You can also use a special plastic splint - an overlay on the teeth, which does not allow them to become thinner. Such devices help reduce muscle activity during sleep.
For bruxism, it is also very effective to use mandibular thrusters. Such devices consist of two linings with springs on the teeth. In most cases, retractors are used to eliminate snoring, but they can also cope well with such pathology. Thanks to the device, the tongue and jaw are extended, facilitating easier breathing. Botox is often used in treatment.
Kappa in the treatment of bruxism
Compared to daytime symptoms of the disease, nighttime symptoms cannot be controlled. Therefore, it is very effective to seek help from night guards. The device is placed on the teeth and provides them with effective protection against abrasion. The mouthguard is made according to the exact dimensions of the patient. During an attack, the device takes on all the stress, thereby preserving the enamel and not causing harm to orthopedic structures.
Also, the mouthguard will prevent the teeth from moving and becoming loose. Naturally, the device will not be able to save the patient from the disease, but it perfectly protects the teeth from all kinds of injuries. The use of a mouthguard is part of the treatment element. A custom-made product will never fall out in your sleep.
It is very easy to care for such a device. In the morning it must be rinsed with water and the outer part cleaned with a brush. You can store the mouthguard in a special case or in a glass of water.
Important: periodically the mouthguard should be shown to your dentist to assess its condition and, if necessary, order the manufacture of a new orthopedic device.
How can the patient help himself?
For many people, being diagnosed with bruxism is a complete surprise. After all, not all of us know what kind of disease this is and how it can be cured.
A warm or, on the contrary, ice compress will help relieve severe tension in the jaw muscles. A massage of the shoulders, neck and face or gymnastics with a relaxing effect helps greatly. When doing a massage, you should pay special attention to those places where extreme pain is felt, radiating to the face or head.
You also need to learn how to fully relax before going to bed and remove yourself from possible stressful situations as soon as possible. It is recommended to drink soothing herbal drinks and relax in a warm bath. Before going to bed, you can chew something hard or, say, gum, so that your muscles get a little tired and calm down. You should not eat foods that contain a lot of carbohydrates and caffeine. Spend a lot of time outdoors and play sports.
Children and bruxism - factors in the onset of the disease and its treatment
In stressful situations or tension in the nervous system, children can also suffer from bruxism. Parents begin to worry about how this pathology should be treated and is it necessary at all? If the cause of bruxism is problems with the nervous system, then only a neurologist can help. The disease may disappear on its own as you grow older. A dentist can help correct malocclusion and pathological tooth structure.
If nervous overexcitation is a factor in the development of the disease, then you should definitely think about organizing the child’s daily routine. Children need energetic walks outside. The baby should also start eating solid foods, which will help reduce the high activity of the masticatory muscles. Before going to bed, you should not play lively games, but give preference to taking a warm bath and massage.
Parents may be frightened by severe attacks, the duration of which is quite long. After such phenomena, the baby may complain of pain in the head and teeth. There are also other consequences of the disease in children. The factors influencing the development of bruxism and its treatment will be determined and prescribed by the doctor.
What danger does the disease pose?
Teeth grinding causes thinning of the enamel, and even tooth loss, headaches, soreness in the neck and chewing muscles. Many people with bruxism tend to thicken the jaw bones, which becomes visually very noticeable. People with pathology experience severe psychological discomfort, and this seriously affects their quality of life. Children and young people can get rid of bruxism on their own - the disease will go away on its own, without any consequences. Treatment in such cases is not prescribed, but it is recommended to consult a dentist for ways to prevent damage to the teeth.
Clinical manifestations of bruxism
During the day, a person himself may notice atypical jaw movements. With night bruxism, everything is more complicated. Most often, close people and relatives pay attention to the first manifestations: chattering of teeth, grinding. The sounds may be so loud that they wake the patient. Each episode lasts a few seconds, but can be repeated many times throughout the night. During an attack, you may notice a change in the frequency and rhythm of breathing and heartbeat. A person's blood pressure changes.
If the patient lives alone, bruxism may be indicated by such manifestations as toothache and headache in the morning, discomfort in the jaw area, and facial myalgia. Due to the atypical functioning of the nervous system, a person does not get enough sleep.
If you notice the first signs of teeth grinding or chattering during sleep, consult a doctor. The sooner the cause of the disease is determined, the easier it will be to cope with its consequences.
We know how to deal with bruxism
Helping children with bruxism
Whether the cause is physical or psychological, children can control bruxism by relaxing before bed—for example, taking a warm bath or shower, listening to soothing music for a few minutes, or reading a book. For infants who are teething, you can offer them a pacifier. She will calm the baby and give a light massage to the gums.
If you are teething or have an ear infection, ask your doctor to prescribe the correct dose of ibuprofen to relieve discomfort.
If teeth grinding is caused by stress, ask about what is upsetting your baby and find solutions.
In rare cases, when stressful situations cannot be resolved within the family circle and sleep problems arise, the help of a psychologist is required. He will help you find the cause of stress and prescribe the right course of treatment.
Possible complications
With prolonged bruxism, the following pathologies may develop:
- disease and dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
- restriction of jaw movement;
- constant pain in the temples, shoulders, neck;
- hypertrophy of the masticatory muscles, which visually changes facial features;
- gingivitis;
- persistent sleep disturbances;
- oral fibroids;
- cervical arthrosis;
- damage to mucous membranes under dentures;
- scalloped tongue;
- lichen planus.
Diagnosis of bruxism
Diagnosis and treatment of bruxism begins with consulting a doctor. At the first consultation, the doctor collects an anamnesis: finds out the duration and severity of symptoms, the presence of indirect signs of jaw clenching in sleep and complications of the pathology. It is important to take into account the social environment and psychological state of the patient. Based on the set of symptoms, the doctor determines the possible causes of teeth grinding and prescribes an examination.
The following procedures may be required:
- Dental examination. The doctor will determine the degree of destruction of the teeth and draw up a treatment plan. If bruxism develops against the background of malocclusion or other anatomical pathology, an orthopantomogram is prescribed.
- X-ray of the temporomandibular joint. The photographs show the condition of the tissues, signs of arthrosis, and various cartilage defects.
- Computed tomography of the temporomandibular joint. A more informative study that provides information about the condition of hard and soft tissues and blood vessels.
- Electromyography. The procedure helps to analyze the functioning of the masticatory muscles. Based on the results of electromyography, the doctor determines the symmetry of chewing, the maximum force of jaw compression and other important parameters.
- Polysomnography. A comprehensive examination, which is prescribed according to indications. The patient spends the night in the clinic. During sleep, sensors are attached to the human body to record an electrocardiogram, electromyogram, electroencephalogram, and electrocoagulogram. The devices also record the patient’s breathing, movements of the limbs, chest wall, and snoring. Video recording is carried out to better understand human behavior during sleep. The results of polysomnography help in identifying undiagnosed epilepsy.
- General clinical blood and urine tests. The data is necessary to assess the patient's overall health.
- Blood chemistry. The electrolyte composition is important, which affects muscle function.
- Blood and stool tests for helminthic infestations. It is recommended to conduct the widest possible range of research.
What causes bruxism?
The following predisposing factors are known:
- sleep disorders - parasomnias and obstructive sleep apnea, sleepwalking, sleep talking, and nocturnal enuresis
- anxiety and other mental and neurological disorders (Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Moreover, the mother’s condition is also very important - there are scientific works where they found a connection between bruxism and maternal depression
- some medications, in teenagers - caffeine, smoking and alcohol
- enlarged adenoids and tonsils, which also lead to mouth breathing during sleep, snoring and sleep apnea. In children who had to have their adenoids and tonsils cut (surgery “adenotonsillotomy”), 3 months after the operation, not only a significant improvement in nasal breathing was described, but also a decrease in bruxism.
- family predisposition
- reflux disease
Treatment of bruxism
Therapy must be comprehensive and systemic. Depending on the results of the examination, a dentist, psychiatrist, neurologist, otolaryngologist, and therapist are involved in the treatment of patients with bruxism. The work of the patient himself is of great importance, especially during daytime manifestations of the disease.
- Conservative therapy. The complex of drugs is selected taking into account the test results. The patient may need vitamins, magnesium and calcium supplements, sedatives to improve sleep, muscle relaxants, antibiotics for severe inflammation, and medications to restore joint tissue.
- Dental treatment. It is necessary to remove caries, relieve inflammation of the gums, and correct dentures, if any. For patients with malocclusion, orthodontic and/or surgical treatment is indicated.
- Physiotherapy. Good results are shown by laser treatment, ultrasound, magnetic therapy courses, and electrical neurostimulation.
- Myogymnastics. The doctor will select a set of exercises to relieve muscle spasms. Special gymnastics will relax the muscles, make them more elastic, and eliminate pain.
- Wearing a cap. In difficult cases, the patient is recommended to wear special dental splints at night. Mouth guards will not affect the quality of your sleep, but will protect your teeth from abrasion.
Treatment must be individualized. It is important to understand the causes of bruxism in each specific case.
Disease prevention
To prevent tooth wear, it is necessary to regularly sanitize the oral cavity at the dentist and visit other doctors as part of a routine examination. It is recommended to walk more, relax, and avoid stress and nervous shock - common causes of pathology.
Patients at risk and to prevent relapses of bruxism need to carefully monitor the condition of the tongue, jaws, and oral cavity:
- Control of tongue position. In the correct position, the tongue should touch the hard palate with its middle, and the tip touches the incisors without pressure. This is the optimal position in which the masticatory muscles relax and normal nasal breathing is maintained. To better control your movements, you can periodically rotate your tongue in different planes.
- Swallowing control. When we swallow food or liquid, the teeth close as much as possible, and the tongue makes a wave-like movement. Disruption of this process leads to dysfunction of the masticatory muscles. When swallowing, you need to control your body position. The head and neck should be straight, without bending. The molars are not in contact. Immediately after swallowing, the tongue returns to its anatomically correct position.
There are many proprietary methods and sets of myogymnastics exercises. The doctor will select those that are right for you. There is no need to be ashamed of the problem. Bruxism is a polyetiological disease that can and should be treated. Take care of your health! Contact your doctor promptly for help.
What to do if your child grinds his teeth?
- The first step is to make an appointment with a dentist and pediatric neurologist. The first will give practical recommendations on how to prevent enamel wear, the second will determine why the child has teeth grinding.
- Monitor the psychological microclimate in the family. The child should be honest about his worries and be sure that he will receive help from his parents.
- Adjust your daily routine. An hour before going to bed, the child should be occupied with a calm activity to avoid overstimulation of the nervous system.
- Balance the children's menu. The daily diet should include solid vegetables and fruits - the load on the masticatory muscles during wakefulness will lead to their relaxation during sleep.
- Teach self-control. In the form of a joint game, practice every day following the simple rule: “Lips are closed, teeth are apart.” This way, the baby will not form the bad habit of clenching his teeth during the day, even at the moment of strong excitement.