When deep caries reaches the dental nerve, pulpitis begins - during pregnancy it is much more severe than in ordinary patients. And if the expectant mother postpones a visit to the doctor and suffers pain, this can affect the baby’s health.
Untreated pulp inflammation becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations, and there is a high risk of serious purulent complications. Sluggish pulpitis in pregnant women contributes to the penetration of infection into the blood, which means that the developing fetus may also suffer. Therefore, at the first signs of illness, you should see a dentist, for example, come to the VAODENT clinic.
Pulpitis in pregnant women
A pregnant woman's teeth are especially susceptible to the negative effects of pathogenic bacteria. This contributes to the more frequent development of caries and pulpitis. There are several reasons why a pregnant woman's teeth are more susceptible to disease:
- The development of pulpitis is promoted by saliva, the composition of which is influenced by changes in hormonal levels.
- Contact with enamel of vomit during toxicosis. They have a low level of acidity, which leads to thinning of tooth enamel.
- Supplying gums with plenty of blood. The gums become loose and susceptible to the negative influence of bacteria. As a result of inflammation, caries appears, developing into pulpitis.
- A large amount of calcium is required for normal fetal development. The lack of this element in the body of the expectant mother leads to tooth decay.
If pain occurs, you should consult a specialist. The method of treating the disease is determined by the dentist. Delaying treatment can lead to complications and the development of other diseases.
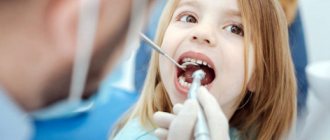
Dental treatment during pregnancy
Often, the period of waiting for a baby is associated with the appearance of various health problems, in particular with teeth. This phenomenon is observed in women even if there were no such problems before. Pregnancy is a difficult period during which doctors have to decide how safe treatment for various diseases of the teeth and oral cavity will be for the fetus. This article addresses issues that will interest many expectant mothers.
- The effect of pregnancy on dental health
- Factors that affect dental health
- Possible consequences for dental diseases
- The most favorable timing for treatment
- Dental treatment for pregnant women: Filling
- Removal
- Anesthesia and X-ray
- Prosthetics
- Whitening
The effect of pregnancy on dental health
Changes for the worse in most cases are associated with hormonal imbalance. Under the influence of an increased amount of progesterone, blood supply to all organs, including the gums, increases. As a result, the tissues become softer and looser, which greatly facilitates the access of pathogens to them. The result of this is stomatitis, gingivitis and caries.
Untreated pathologies contribute to the development of more serious diseases:
- periodontitis;
- pulpitis;
- tissue suppuration;
- necrosis;
- abscesses;
- cyst formation;
- sepsis;
- osteomyelitis of bone tissue.
If the crown is destroyed, the shape and structure of the tooth changes, its mobility increases and the bite changes, which disrupts the digestive function.
During pregnancy, the acid-base balance of saliva always changes. This happens due to:
- hypersolivation or increased salivation;
- toxicosis;
- eating a significant amount of simple carbohydrates that are broken down directly by saliva.
The pH shift leads to thinning (demineralization) of tooth enamel and accelerated spread of the carious process. A change in the composition of the secretion of the salivary glands and its acidity, combined with reduced immunity, also leads to accelerated formation of plaque, which can transform into tartar.
Factors that affect dental health
Despite the fact that all pregnant women experience the above changes in their bodies, not everyone experiences problems with their teeth. This happens because there are a number of aggravating factors that contribute to the appearance of various pathologies of the teeth and oral cavity. Among them:
- Heredity. Bad teeth at a young age in an expectant mother indirectly indicate the presence of similar problems in her parents.
- Unfair implementation of hygiene measures. In addition to daily procedures for cleaning the oral cavity, a woman is required to regularly visit the dentist during gestation. This is done in order to identify early signs of oral diseases, as well as timely elimination of problems.
- Poor nutrition. Dental diseases are caused by eating foods low in vitamins, minerals and other beneficial elements.
- Chronic stress. In such situations, cortisol levels increase. Under the influence of this hormone, local and general immunity, which is already weakened in a pregnant woman, decreases. As a result, pathogenic microorganisms are activated, ultimately causing diseases of the teeth and oral cavity.
- Bad habits. In addition to the well-known smoking and drinking alcohol, which have a harmful effect on the acidity and composition of saliva, and also impair the absorption of beneficial substances, these include the habit of gnawing hard candies and nuts, and opening lids with your teeth.
Existing chronic diseases also have a negative impact on the condition of teeth. These include diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, gastritis, enteritis), endocrine system (thyroid problems, diabetes), and musculoskeletal system (osteoporosis, arthrosis, arthritis). All of them create favorable conditions for disturbances in calcium metabolism in the body. As a result, it is much less absorbed, which entails demineralization of bone tissue and enamel.
Possible consequences for dental diseases
If a pregnant woman has problems, the question invariably arises: to treat her teeth now or is it better to wait until childbirth? Experts advise not to delay, because dental diseases are a source of chronic infection, which can cause:
- gestosis;
- infection of amniotic fluid and membranes of the membranes;
- spontaneous abortion and miscarriage in the first trimester;
- late premature birth.
Pathogenic microorganisms from the outbreak in the mouth spread through the bloodstream throughout the body of the expectant mother and easily penetrate to the fetus, resulting in its infection. The child is born at low birth weight with reduced immunity; he may have diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system, as well as the skin.
The most favorable timing for treatment
The best option is to treat chronic foci of infection before conception. Unfortunately, most often women neglect examination at the planning stage or the pregnancy turns out to be unexpected. During the entire period, every expectant mother is required to visit the dentist three times for preventive purposes:
- after the first visit to the gynecologist;
- at 30–32 weeks;
- before childbirth.
When diagnosing problems with teeth and/or gums, you will have to visit the dentist much more often. When prescribing treatment and preventive procedures, the gestational age is taken into account, since each period has its own characteristics:
- First trimester. Its duration is 14 weeks. During this period, the placental barrier has not yet been formed, but at the same time all the systems and internal organs of the child are formed. The vulnerability of the embryo to stress, which may well include a visit to the dentist, and medications is very high. Therefore, dental treatment during pregnancy of this period is carried out only in cases where the benefit prevails and only after agreeing on the tactics with the gynecologist.
- Second trimester. Lasts from 14 to 26 weeks. At this time, psycho-emotional stability is observed, the placental barrier is fully formed and is able to fully perform a protective function, and the child’s organ formation has completed. This stage is considered the most favorable for carrying out various manipulations.
- Third trimester. It is undesirable to treat teeth in the last weeks of pregnancy due to the acute reaction of the uterus to external irritants and the high risk of developing acute vascular insufficiency due to compression of the inferior vena cava and aorta when in a horizontal position. In case of acute pain, tooth extraction or treatment is carried out immediately, regardless of the stage of pregnancy.
Dental treatment for pregnant women
The choice of treatment tactics depends on what manipulations experts allow and which they advise to postpone until the postpartum period due to a possible high risk to the fetus. For acute pain, it is permissible to use such traditional medicine recipes as:
- rinsing with decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, calendula, St. John's wort, mint), a solution of sea salt and soda;
- applying propolis or a cotton swab moistened with oil extracts of cloves, fir, sea buckthorn to the most painful point;
- applying an application of chopped onions with the addition of garlic and salt.
It is imperative to consider whether there are any unwanted reactions to any of the products. All these remedies are used only to relieve acute pain at home, but do not replace a visit to the dentist. At the first opportunity, you should visit a doctor to eliminate the cause of toothache.
- Sealing
The presence of caries of any degree is an indication for a filling, regardless of gestational age. A small hole during pregnancy can transform into a large cavity that can destroy a tooth, or become a trigger for the development of pulpitis or osteomyelitis. Superficial and medium caries are treated without anesthesia; for deep caries, a drug with an anesthetic effect is used. All types of filling materials can be used. If it is necessary to remove the nerve, arsenic-free paste is used.
- Removal
Tooth extraction is always very stressful, so if possible it is better to postpone it until the postpartum period. If this procedure cannot be avoided in any way, then it is best to carry it out in the second semester. The tooth is removed after radiography and under local anesthesia. The main indications for manipulation are severe pulpitis, a severely damaged crown, a tumor or a cyst on the apex of the tooth. It is very important that after extraction a woman follows the dentist’s recommendations for preventing complications.
- Anesthesia and X-ray
Fears about the use of x-rays and anesthesia are completely unfounded. Modern digital equipment and medications with an analgesic effect do not pose a particular danger to the fetus. In addition to the fact that the X-rays are directed strictly at the tooth being examined, the radiation dose is minimal. Anesthetics used during pregnancy do not cause narrowing of the vascular walls and practically do not penetrate to the baby through the placenta.
- Prosthetics
The installation of prostheses during pregnancy has no special contraindications, since the manipulations performed do not pose any harm to the baby. In order to align the bite and dentition, it is possible to install special supporting mouthguards. The only thing that is not recommended is installing implants. Too much energy is spent on tooth implantation, which will not be enough for the normal development of the fetus. In addition, during implantation, drugs prohibited during pregnancy are prescribed, the effect of which is aimed at suppressing the immune system.
- Whitening
Among all manipulations related to teeth, professional cleaning of tooth enamel from plaque and tartar using chemical pastes and other means is completely prohibited. In extreme cases, the mechanical method is allowed, as well as the use of ultrasonic or laser equipment. It is best to postpone bleaching and cleaning until a more favorable period.
Prevention: how to prevent dental problems
In addition to preventive examinations by dentists, a woman herself needs to follow a number of rules to help preserve her teeth:
1. Hygiene measures:
- 2-time daily brushing of teeth with a soft toothbrush and a paste based on herbal ingredients;
- use of dental floss (floss);
- the use of rinses and chewing gums with xylitol;
2. Proper nutrition, including foods rich in:
- calcium;
- phosphorus;
- vitamin D;
3. Taking vitamin complexes designed for pregnant women.
Taking care of your teeth and following the dentist’s instructions is incomparably easier than treating them later, experiencing stress and worrying about the baby’s health!
The need for treatment of pulpitis
Some women do not know whether they should have dental treatment during pregnancy, or whether the procedure should be postponed until postpartum. Pulpitis must be treated when it appears. Several reasons requiring immediate treatment of the disease:
- Pulpitis is inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. Untimely treatment leads to the absorption of bacteria into the blood of the expectant mother. This can lead to fetal developmental disorders.
- Presence of acute throbbing pain. Promotes the production of large amounts of hormones. This negatively affects the development of the child. Severe toothache can lead to uterine contractions and premature birth.
- Infection in the gastrointestinal tract. Infections that enter the gastrointestinal tract from the tooth can lead to late toxicosis.
Taking into account the above factors, a pregnant woman should immediately consult a dentist if symptoms of pulpitis appear.
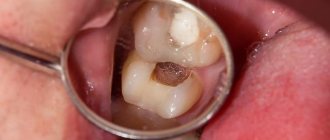
Caries
Dental caries is not a harmless hole in the tooth. This is a silent enemy of health, causing considerable damage with human connivance. During pregnancy, the disease is quite treatable even in the later stages, degenerating into pulpitis. Here it is permissible to use anesthesia, any fillings of your choice - chemical or light-hardening. Ultraviolet light does not harm the patient. The only exception is that arsenic-based drugs cannot be used to kill the nerve. However, modern medicines have practically replaced the mentioned method.
How long does it take to treat pulpitis?
Treatment of pulp inflammation has features depending on the stage of pregnancy. The expectant mother needs to inform the dentist about her situation and the stage of pregnancy. The specialist will select medications that will not harm the baby’s health for a certain period of time.
First trimester (from the moment of conception to the 12th week inclusive)
Treatment of pulpitis in pregnant women in the first trimester is not recommended. During this period, the fetus experiences increased sensitivity to toxins. The use of even the safest anesthesia can provoke developmental disorders.
The need for treatment is determined by the dentist. Treatment of chronic pulpitis is postponed to a later date. In the first trimester, the disease is treated during exacerbation.
Second trimester (from week 13 to week 28 inclusive)
At this time, the likelihood of harm to the fetus during dental treatment is reduced. The second trimester is the most favorable period for the treatment of pulpitis during pregnancy. The doctor performs the treatment under local anesthesia. Drugs are used that have a minimal amount of vasoconstrictor substances and do not penetrate the placenta. Such medications do not harm the baby.
Third trimester (from 29 weeks until birth)
The presence of acute toothache in a pregnant woman in the later stages can lead to premature birth. In the third trimester, treatment of pulpitis is necessary. Before visiting the dentist, you should consult with a gynecologist accompanying your pregnancy.
First aid for acute toothache. How to relieve pain at home?
- For completely unbearable toothache, you can take painkillers. The safest medications during pregnancy are those containing paracetamol.
- Clean the carious cavity, rinse your mouth with a warm solution, which contains: 1/2 teaspoon of baking soda, 1/2 teaspoon of salt and a few drops of iodine.
- You can use dental drops (Denta or others) by applying a swab soaked in them to the gum.
- Attacks of pain are reduced by rinsing the mouth with herbs: a decoction of calendula, chamomile, valerian, St. John's wort, plantain.
- A very ancient and effective remedy is applying garlic to a sore tooth. You can also apply crushed garlic to the pulsating vein on the wrist (to the left hand for tooth pain on the right side and to the right hand if the tooth hurts on the left side).
- Never apply warm compresses to a sore spot.
Important! The listed methods are temporary - they will only slightly reduce toothache, but will not cure pulpitis! So don't put off visiting the dentist!
Stages of treatment
Treatment of pulpitis is carried out in one or several visits to the doctor. Treatment is carried out in several stages:
- Diagnostics. The doctor conducts a survey and examination of the pregnant woman’s oral cavity.
- Introduction of anesthesia. The drugs used are safe for the fetus.
- Removal of the part of the tooth affected by caries.
- Pulp removal. A pulp extractor is used - a rod with spikes that engage the tissue.
- Cleaning of channels and their mechanical treatment.
- Installation of a seal. The root canals and crown part of the tooth are filled.
- Checking the filling of the canals using radiography.
In some cases, treatment is carried out in 2–3 visits to the doctor. For the period between appointments, the doctor installs a temporary filling. It protects the tooth cavity from food and pathogenic bacteria.
Gingivitis, stomatitis
Expectant mothers sometimes experience gingivitis due to hormonal instability in the body. In this case, the gingival edge of the mucous membrane adjacent to the tooth enamel increases in size. There may be plaque on the gums, causing bad breath. This condition is not considered acceptable and the woman requires the help of a doctor. The fact is that gingivitis can progress, and the disease will end in a severe form of periodontitis. And this is already fraught with loss of teeth and bone damage.
You should not rely on alternative medicine recipes and practice self-medication. The doctor will study the picture of the disease and prescribe adequate therapy: prescribe sanitation of the gums with a disinfectant, perform professional hardware cleaning of the oral cavity, and recommend rinsing. This is where homemade recipes come in handy - only they will be prescribed by a competent specialist who is aware of the pros and cons of the prescribed herbal decoction or other remedy.
Stomatitis is caused by bacteria that constantly live in the oral cavity, but against the background of a weakened immune system, they begin to multiply too actively. Pathogens provoke ulceration of the mucous membrane in the mouth of a pregnant woman, causing pain and discomfort. With a timely diagnosis, stomatitis can be cured without complications.
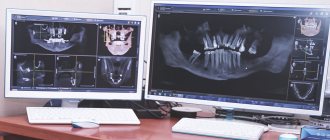
Use of radiography
Treatment of pulpitis involves the use of x-rays. They are necessary for the dentist for diagnostics, high-quality cleaning of root canals from inflamed pulp and control over the quality of the work performed.
The dentist must take into account the individual characteristics of each patient’s teeth. To determine the depth, location and curvature of the root canals, the specialist needs to send the expectant mother for an x-ray. This will allow him to get a more detailed picture and correctly treat pulpitis.
Radiography during dental treatment does not harm the health of the fetus. The rays pass through the tissue in the tooth area. A specialized apron that does not transmit x-ray radiation is put on a pregnant woman's stomach. This makes the procedure safe for the baby.
Treatment of pulpitis during pregnancy is necessary. The presence of the disease can negatively affect the fetus. A timely visit to the dentist will help avoid complications and the development of other diseases.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- The role of hygiene products in the treatment of periodontal diseases (S.B. Ulitovsky Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Dentist StAR Prof., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Department of Preventive Dentistry of Pavlov Pavlov State Medical University, St. Petersburg) S.B. Ulitovsky - Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Dentist of StAR, Prof., Doctor of Medical Sciences; E.S. Alekseeva - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences; A.A. Vasyanina - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences; V.A. Grigoriev - Associate Professor, Ph.D.
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
Tartars
Plaque that has hardened and settled on the teeth in the form of stones can be removed at any time, as soon as the woman is ready for the procedure. Professional teeth cleaning is performed with an ultrasonic scaler and an air flow device. There is no need for anesthesia, and ultrasound does not harm the fetus in any way. Stones cause damage to oral health and become a platform for the accumulation and reproduction of pathogenic microflora. By cleaning the enamel and periodontal grooves, a woman gets rid of many causes of dental disease.
Removal and prosthetics of teeth
It is sometimes necessary to remove teeth at any time in life if it is discovered that the tooth is not viable and has become a source of infection spreading throughout the body. If possible, it is better to wait with the upper teeth so as not to provoke an accidental perforation of the maxillary sinus, especially if the procedure is performed without prior x-rays. But the lower teeth are removed without consequences. The main thing is to follow the doctor’s instructions after surgery and not to subject the injury site to excessive cooling or overheating.
Prosthetics also does not cause obstacles, especially if the pregnant woman is in excellent health. It is even possible to install a braces system if you really want to. But there is a nuance here: installing braces requires the ideal condition of the teeth. If serious preliminary treatment is required, the doctor will probably ask you to wait until the time of birth.