Benign growths that appear on the body as a result of exposure to the human papillomavirus (HPV) are called warts. They are neoplasms in the epidermis. Basically, warts on the skin are divided into types according to the type of HPV that caused the appearance on the skin. There are more than 200 genotypes of the virus. It affects not only humans; warts are also found in mammals and some species of birds. Very often, the virus is transmitted to humans from an infected animal. The most common HPV viruses include genotypes 2, 27, 57, 4 and 1. Below we will look at how to diagnose and remove warts, as well as avoid their appearance.
general information
A common wart is a growth on the skin that has a rough surface and protrudes to a certain height above the surface of the epidermis. The color of warts is lighter or darker than the surrounding tissues; on large formations, internal vessels can be seen. The main cause of warts is infection with the human papillomavirus. HPV enters the body through damaged or water-soaked skin. Sometimes infection is possible even if there is no damage to the body. The difficulty of identifying the cause of infection is due to the fact that some warts in adults appear on the body only six months after infection.
HPV mainly affects children and young people. Patients who have a history of chronic skin diseases are susceptible to the problem:
- Psoriasis;
- Dermatitis;
- Eczema, etc.
Patients who have a weakened immune system are also at risk. We are mainly talking about people infected with HIV or those who have undergone organ transplantation. If a patient has problems with immunity, treatment difficulties may arise in the future. In this case, a viral wart most often recurs after removal.
Warts can be found on the skin anywhere on the body. Moreover, most often they are localized in the area of the fingers, elbows, knees, and hands.
Senile (age-related keratomas, seborrheic keratoses) warts
Senile warts are one of the most common skin lesions that appear in old age as a general sign of skin aging. Despite their name, they are not caused by the human papillomavirus.
Seborrheic keratoses are extremely common. According to statistics, more than 90% of the population over the age of 60 have one or more of them. They are equally common in both men and women. It is not uncommon for the disease to affect people aged 30-40 years, as well as young people under 20 years of age.
Keratomas and keratoses can appear on any part of the body, including the scalp, face and genitals. The exception is the palms, soles of the feet and mucous membranes. It is rare for a person to develop only one growth. Over time, age-related keratomas become more and more numerous. Many people inherit a tendency to develop a very large number of these tumors. Some of them may have hundreds of wart-like growths scattered throughout their body.
In the early stages, aging warts appear as slightly raised light brown spots or papules. They can remain very flat and resemble freckles in appearance, or they can gradually thicken and develop a rough, warty surface, like a tumor on the skin. In most cases, they darken slowly and may eventually turn black.
These color changes are harmless. Many senile warts remain pinkish in color. Typical of these are small keratin plugs that can be seen on the surface of the wart.
Keratoses are usually round or oval in shape. Some seborrheic warts are irregular in shape. Their size can vary from one to several centimeters in diameter.
The cause of age-related keratomas is unknown. They are generally considered to be degenerative in nature and appear in large numbers as the skin ages. It is assumed that ultraviolet radiation increases the likelihood of their development.
There are five traditional forms of age-related warts:
- Spotted, or popularly “death freckles” . They form in numerous clusters on the hands and face. Such growths are round with an uneven contour and a smooth or slightly rough surface. It has several color options: light brown, brown-brown or pinkish-yellow;
- Papular or nodular . Larger growths tend to grow. Their typical color is gray or yellow. The surface of the wart is covered with horny layers;
- Classic keratoma . It is a collection of plaques tightly connected to each other. It is characterized by a jagged outline and a copper or pinkish color. As it grows, the middle part of the wart sinks;
- Cutaneous horn. It is a modification of keratoma. It is expressed as a cluster of dense keratinized dark brown plaques up to 1.5 cm.
Adverse reactions to certain medications and many chemotherapy drugs can contribute to the formation of irritated seborrheic keratoses—inflamed, red, crusty lesions. This leads to the development of eczematous dermatitis around the growth. Dermatitis can also cause new seborrheic keratoses to appear.
Age-related keratomas are always benign. This means that they do not spread and do not degenerate into a malignant form. The main problem is a cosmetic defect, especially if they develop on the face.
There are rare cases of skin cancer called melanoma that develops in a seborrheic wart. It is unknown whether this is just a coincidence or represents a true change in the cells in a seborrheic wart. A large number of age-related keratomas may be a sign of cancer of internal organs.
Typically, seborrheic keratoses are treated for cosmetic reasons or because they become itchy and irritating. If the growths, especially large and warty ones, are injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something), they may bleed or become inflamed.
Diagnosis of the disease is usually made through a clinical examination. This type of wart is difficult to distinguish from skin cancer without histological examination. Therefore, very dark lesions that have changed in some way or that are growing rapidly require a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and rule out the possibility of cancer. Darker lesions should also be checked by a doctor to make sure they are not melanoma.
Types of warts
There are several types of formations. Basically, the division into types of warts is associated with the external aspect, the cause of occurrence and other factors. The following types of warts are distinguished:
- Ordinary (vulgar)
. This type of formation is characterized by an age limitation - predominantly the problem caused by HPV develops in childhood. Warts on the hands, fingers and toes are a common location for the problem. What a wart looks like - a colorless lump the size of a pin's head. Sometimes larger formations are possible. A viral wart rarely manifests itself as a single rash; most often you can find a whole scattering of neoplasms in the affected area. An interesting fact is that if the largest wart in the affected area is correctly removed surgically, the rest will disappear on their own over time. - Flat
. These types of warts mostly appear between the ages of 10 and 25. They are small papules that practically do not stand out above the skin. The surface of the wart is colorless, in some cases the skin in the affected areas acquires a yellowish tint. Viral warts most often appear on the back of the hand, hands, neck and face. - Plantar
. Most often, people with this problem have the question of how to get rid of warts. This is due to the fact that the rashes cause discomfort and pain, especially while walking. They mainly occur on the feet in places that experience excessive friction when walking. The main problem of such a neoplasm is difficulty in self-identification due to its appearance, which is very similar to ordinary plantar calluses. - Seborrheic
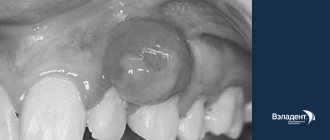
. The types of warts in this category are diagnosed in elderly patients. A distinctive feature of education is long-term formation, sometimes it takes several years. Appears as a dark brown small spot on the body, which gradually increases in size, eventually reaching a diameter of 5-6 centimeters. Warts are characterized by the presence of a greasy surface with crusts. Over time, the formation thickens, becomes covered with cracks and darkens significantly. Senile warts occur on closed areas of the body. - Condylomas
. It has a specific place of occurrence - in the area of the perineum and genitals. Warts can also be found in the armpits, under the breasts in women, and in the area of the nasolabial triangle in children. They got their name due to their pointed and lobed structure. Such warts are characterized by multiple distribution in the affected area - the rash is never isolated. The color of the new growth is colorless or pale pink. In some cases, warts begin to rub against clothing or other objects, eventually become damaged, become purple in color, and begin to bleed.
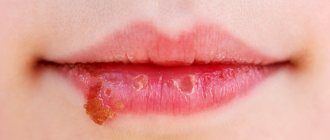
What is the danger of warts on the lip?
Warts on the lip are, first of all, a pronounced cosmetic defect. They are located on a noticeable area of the face and can cause certain psychological discomfort in a person. However, in addition to this, they also pose a certain threat to the patient’s health.
Many people who first encountered this pathology are interested in what to do with warts on the lip. The answer is clear: treat under the supervision of a doctor. These are viral formations, which means that a person is an active carrier of HPV and poses a potential threat to others.
In addition, some warts can be caused by oncogenic strains of papillomavirus. This means that sooner or later the growths can degenerate and become malignant tumors, which require much more serious treatment than simple benign tumors.
There are many factors that can cause malignancy of warts on the lip. First of all, this is injury to growths. In the case of lips, this happens quite easily, since the integrity of thin and delicate skin and neoplasms here can be damaged by teeth, food, hands, and clothing.
Even if an injury to a wart does not lead to its degeneration, it can cause severe bleeding, inflammation, and the addition of an additional infection followed by suppuration.
Also, warts on the lips can grow, interfere with eating, speaking, and cause speech defects. When exposed to frosty air, painful cracks and crusts appear on these formations.
There is also a risk of self-infection. This happens especially often in children, when when the patient frequently touches the wart, he spreads the virus throughout the body. For this reason, pathological growths may appear in other areas.
Causes of warts
A question that worries even those who have not encountered this: why do warts appear? The main method of infection is contact. If you come into contact with a person who already has HPV in their body, there is a high probability that it will be transmitted to you, especially if there are associated factors. The main method of transmission is through handshakes. You can also become infected through common household items, such as bed linen, towels, slippers, etc. There is a high risk of catching the virus in public places - in swimming pools, baths, gyms, etc.
The risk of contracting warts increases under the influence of various unfavorable factors
:
- There are small injured areas on the arms and legs. People who do physical labor at work are at risk. It is extremely difficult for such employees to keep their hands from injury while performing work tasks. Cracks, scratches, and cuts appear on the hands, through which HPV can easily penetrate.
- Decreased protective immune functions of the body. You can determine the problem yourself. Just keep track of how often you get colds throughout the year. An indicator of 4 times or more should cause concern.
- Violent sweating in the hands and feet.
These factors make it easier for the papilloma virus to enter the patient’s body and cause the appearance of warts. The infection is characterized by a long incubation period - the first rash in some cases appears only 1.5 months after infection.
Symptoms
The types of warts also affect the symptoms experienced by an infected patient. Moreover, all types of formations are characterized by a list of identical symptoms:
- The appearance of single or multiple neoplasms. Warts can appear not only on the skin. A rash on the mucous membranes is also possible.
- When pressing on the surface of the formation, painful sensations occur.
- The nail plate becomes deformed, and the periungual fold grows in the affected area.
- Deformation of the feet in case of massive lesions, severe pain.
Diagnosis: which doctor to contact
The examination is prescribed by a dermatovenerologist after a visual examination in a number of cases:
- the presence of papillomas on the skin or mucous membranes (or their presence in a sexual partner);
- pregnancy planning;
- infertility or unsuccessful pregnancies in the past.
The very fact of detecting a virus is not decisive - it is much more important to identify its type and degree of oncogenicity.
The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- colposcopic examination - examination using a special microscope of the cervix and vagina;
- cytological examination - taking a smear, has low accuracy; if the result is poor, additional analysis is carried out;
- histological examination of a biopsy specimen - sampling of a small fragment of tissue for analysis;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - the material for the study is a smear, urine or blood, the accuracy is close to 100%.
PCR is most often used in specialized clinics. The accuracy of the result depends on compliance with the research technique. Such analysis is best done in laboratories with strict compliance with standards.
Types of warts and specific symptoms:
- Molluscum contagiosum
. Localization - on the body or in the genital area. There are depressed areas on the surface. If you press on the wart, a mushy substance may begin to ooze. - Nevi
. May be a congenital problem, raised significantly above the surface of the skin. Characterized by a dark brown color, as well as the presence of hair. - Basalioma
. It has a crust on the surface; if it is removed intentionally or accidentally, bleeding begins.
Diagnostics
The differential diagnosis is based on the clinical picture of the specific type of neoplasm, as well as on the study of the anamnesis. The size of the papule, the rate at which it increases in size, the number of formations and other factors are taken into account.
To make a final diagnosis, the patient may be referred for histological examination.
If the appearance of warts is planned to be excluded using destructive methods, it is first important to be tested for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis.
How to get rid of papillomas?
There are only two main methods of treating papillomas
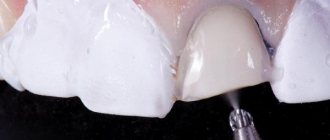
- The simplest and most effective method of treatment is the removal of papillomas using various methods ( laser, radio wave surgery, electrocoagulation
, etc.). In most cases, a one-time complete removal of papillomas from the entire body is sufficient. I will tell you in more detail about how papillomas are removed using radio wave surgery in our clinic below. - Removing papillomas at home
has recently become a very popular method . Most often, this happens with the help of two types of drugs - acid solutions with names like “Super Celandine” and a mixture of dimethyl ether and propane (the popular drug “Cryopharma”). I can’t say anything about the effectiveness of these two methods, because... I have never removed papillomas this way.
IMPORTANT!!!!
Please do not diagnose yourself with papilloma based on research on the Internet. Before using the above drugs, you should always see an oncologist and make sure that what you are going to remove at home is really a papilloma. If the diagnosis is made incorrectly and any of these liquids are applied to the pigmented nevus, the consequences can be extremely sad.
Treatment methods for warts
Treatment of warts does not guarantee 100% results. Even a healed wart may reappear in the future. Removal of warts only in 70% of cases does not result in relapse after a while. The behavior of warts is unpredictable. Treatment of warts may often not bring any results, and in some cases the problem resolves on its own without any intervention at all.
Treatment of warts has two goals - destruction of the viral tumor, improving the quality of life for the patient. Indications for starting treatment are the clinical manifestation of the problem. The most common method is based on the destruction of education. However, there is no guarantee that after complete healing of the tissue in the affected area, the problem will not reappear. Most often, relapses are typical for neoplasms of a large area - from two centimeters. Warts on the fingers and in the area of the periungual plate are also considered problematic.
Warts are treated using several methods. The choice of a specific method for treating warts directly depends on the type of lesion, its prevalence, location and other factors. All interventions are carried out without mandatory hospitalization of patients.
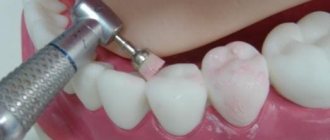
Treatment of warts with physical destructive methods
- Electrocoagulation
. The affected area is numbed, then an electric current is applied to the wart using a needle tip. The method allows you to remove the wart layer by layer. - Cryodestruction
. Freezing the surface of the tumor using liquid nitrogen. The duration of exposure is from 1 to 5 minutes. A repeat procedure is required a week after the first. - Laser exposure
. Depending on the size of the wart, laser contact on the area lasts from a few seconds to 2-3 minutes. The crust formed on the surface is cut with scissors, then the bottom of the wart is re-exposed using a laser. The disadvantage of this method is that a wound surface is formed, which the patient needs to treat independently. The affected area should not be re-injured, and it is also important to avoid getting wet. The scab that appears on the surface is removed by the patient. - Radiosurgery
. The affected area is exposed to electromagnetic waves. As a result of this effect, the surface of the wart is dissected without mechanical force. The intervention is carried out with local anesthesia of the affected area. Most often, a 2% lidocaine solution is administered.
Treatment of warts with chemical methods
- Zinc solution. Before removing the wart, the doctor treats the surface with alcohol to disinfect and facilitate penetration of the composition. The solution is applied using a spatula or capillary, it all depends on the size of the wart. The duration of application is until the neoplasm changes its color. The procedure is repeated after 1-2 weeks. For ordinary warts, 1-2 procedures are most often sufficient; if we are talking about plantar warts, applying the solution may require three times. The wart tissue undergoes mummification under the influence of the composition, in order to increase the effectiveness of the effect; dead areas are removed before new application. During the periods between procedures, the patient is not recommended to wet the area. The surface is also subjected to antiseptic treatment using alcohol-free compounds.
- Composition based on nitric, acetic, oxalic, lactic acid and sodium nitrate trihydrate. In this method, the surface of the wart is also pre-degreased. It is important to apply the composition exclusively to the affected areas, without touching healthy tissue. The product turns tumors on the skin yellow and on mucous membranes white. The patient is required to return for an examination 3-5 days after treatment. The method is not suitable for warts that exceed 5 centimeters in diameter.
How to remove warts in childhood? Treatment is possible only with the help of destructive methods in order to avoid possible toxic effects on a fragile organism.
It is important to remember that it is easier to prevent the appearance of warts than to subsequently treat them in a clinic. There are several rules of prevention:
- Maintain personal hygiene, wash hands after visiting public places, use only personal items.
- If damage appears on the skin of the hands or feet, they must be treated with iodine or brilliant green until they heal. It is also advisable to limit contact with HPV carriers.
- Normalization of nutrition. The body must receive all the elements necessary for the normal development of the body. It is also important to remove stress from your daily life as much as possible.