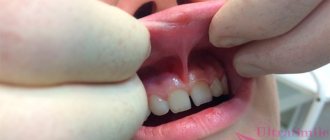
Frenules in the oral cavity
When parents talk about the frenulum in the child’s mouth, most often they mean the frenulum of the baby’s tongue, which is quite natural. Problems arise more often precisely because of this oral frenulum: from improper attachment to the breast in the first days of life to speech impairment in the future.
Even dentists give the leading role and importance to this particular frenulum, but this does not mean that the remaining frenulums are unimportant and cannot provoke any pathology.
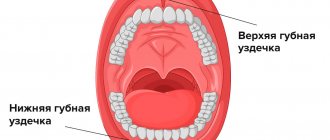
There are three frenulums in the child's mouth. A frenulum in the oral cavity is nothing more than a small strand of mucous membrane. But, despite this, the frenulum in the oral cavity is of great importance in the life of a child; the child’s nutrition, correct pronunciation of sounds, the condition of the mucous membranes, not to mention the child’s bite and facial aesthetics depend on their condition.
Dentists distinguish between the frenulum of the upper and lower lips and the frenulum of the tongue. Each of them has its own location and performs a number of functions. The frenulum of the lower lip connects the body of the lower jaw and the lower lip; normally, the frenulum is woven into the gum of the lower jaw below the level of the central incisors.
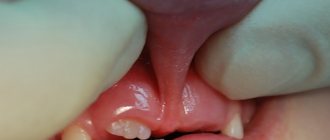
The frenulum of the upper jaw is located according to the same principle as the frenulum on the lower lip. This mucous cord also raises many questions and complaints from parents, since it is primarily associated with the formation of an aesthetic defect in the oral cavity - a gap between the teeth. And the last frenulum in the baby’s mouth is the lingual frenulum, which is woven into the tongue and sublingual space.
What operations are used?
Types of labial frenuloplasty:
- Frenulotomy;
- Frenulectomy;
- Frenuloplasty using the Limberg method;
- Fixation with sutures using the Dieffenbach method;
- Correction using laser.
The main type of treatment is surgical. First, the patient is given anesthesia. For children, before the injection, it is recommended to use gels with local anesthetics to numb the injection site. Thus, pain during basic anesthesia is reduced. After a couple of minutes, several injections are made into the frenulum area.
Next, a wedge-shaped incision is made and the attachment is excised. A deep incision is made on the side of the frenulum down to the bone, without touching the gum near the incisors. The resulting area is grabbed with tweezers and cut off. It is best to do this in the area of the papilla, since the level of aesthetics will be higher with this method.
At the end of the manipulation, the edges of the wound are connected to each other and sutures are applied. The patient is prescribed rinsing with antiseptic solutions and the use of healing drugs (for example, solcoseryl). You must return for examination and removal of sutures after 7-10 days.
If desired, the invasiveness of the operation can be reduced using a laser. Anesthesia is carried out using the same technique. The laser is set to pulse mode, power 1 W. Movements during tissue excision should be short and intermittent. Be sure to stretch the fabrics to achieve the best effect.
After the operation, there is no need to apply stitches, since the wound is slightly smaller in size. Instead, a special protective film is applied, which contains keratoplasty.
Recommendations after surgery include: using a toothbrush with soft bristles, rinsing with antiseptic solutions. You can also prescribe antiseptic tablets “Lizobakt” and apply “Solcoseryl” paste to the wound surface.
Contraindications to surgery
It is recommended to postpone lip frenuloplasty in the following cases:
- Diseases of the circulatory system;
- Oncological diseases;
- Stage of infection activity;
- Chronic pathologies that may affect the duration of recovery after surgery on the labial frenulum;
- Diseases of the oral mucosa.
Lip frenuloplasty is not a complicated operation and is easily tolerated even by the smallest children. Quick recovery eliminates any discomfort. After just a couple of days, the child recovers completely. And after 2 weeks, it becomes possible to correct the changes caused by the incorrectly growing frenulum.
Why are short bridles dangerous?
Short frenulum in the mouth can cause many unpleasant consequences. The first of them: the baby cannot attach to the breast correctly, so during feeding it expends a lot of effort, but at the same time receives a smaller volume of milk, and it is simply not enough to satiate. This is sometimes the reason for poor weight gain, but quite often mothers and doctors mistakenly look for the cause in a mythical lack of milk, or some disease, although, first of all, it is necessary to look into the oral cavity and assess the condition of the frenulum.
It is very important for parents to know and remember about this problem, because according to statistics, every 14th child has short frenulum in the oral cavity. If you notice this feature in time, then in the future you can avoid many problems and unpleasant consequences - disturbances in nutrition, speech, bite and, accordingly, facial aesthetics.
For the first time, doctors may notice a short frenulum in the baby’s mouth during the first examination, immediately after birth, and if the fact is confirmed, correction is carried out on the spot. This rule applies to a short frenulum of the tongue, but if the frenulum does not interfere with full natural feeding, the frenulum will not be trimmed in the maternity hospital. Symptoms of a short frenulum may appear later - the child may have difficulty pronouncing some sounds, in which case “treatment” will be carried out later, and, as a rule, in tandem with a speech therapist.
Upper lip frenulum
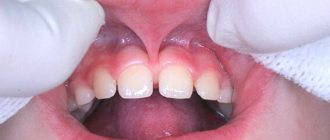
Even with a simple smile you can see the frenulum of the upper lip, but few people pay attention to it. During a routine examination, the doctor assesses its length; in order to assess the size of the frenulum at home, parents just need to move the baby’s upper lip, and it will become noticeable where exactly the frenulum is woven. In the event that the frenulum is woven between the two front incisors 5–8 mm higher, this is a normal option. If the frenulum is woven below this level, these are obvious symptoms of a shortened frenulum, but the final word always remains with the doctor.
A short frenulum on the upper lip can provoke a violation of the aesthetics of a smile when a gap is formed between the central incisors - a trema, a diastema. It is worth remembering that tremors can be physiological; this period is observed during the period of primary occlusion, when the child’s jaws are preparing for the change of primary teeth to permanent ones. In addition, trems can be pathological, which are formed as a result of some pathology. Treatment of this problem is most often carried out in tandem by a surgeon and an orthodontist.
A short frenulum in a child’s mouth can cause malocclusion, which is formed due to the constant tension of the mucous membrane on the upper jaw and bone tissue. As a result, the front incisors move forward. In addition, such pressure on the mucous membrane provokes inflammation of the mucous membrane - gingivitis. There is a loss of gums, as a result of which the necks of the teeth are exposed and the child develops hypersensitivity of the teeth, and all the conditions are created for the formation of cervical caries.
How does the correction happen?
Treatment of the problem is exclusively surgical, but with one big “BUT”. The frenulum on the upper lip can be corrected only after the eruption of the permanent central incisors, not earlier!!! In some cases, the doctor will recommend adjusting the oral frenulum at the time of the eruption of the permanent lateral incisors - in order to close the gaps between the teeth, such a correction can eliminate orthodontic treatment.
The reason for this ban is very simple. The fact is that during the growth of the jaws, the frenulum on the upper lip can self-correct. That is why there is no point in correcting the frenulum at an earlier age. The correction itself is carried out in a surgical room, under local anesthesia. There are no nerve endings in the mucous cord itself, and therefore the operation is painless; pain relief is necessary when suturing. The operation lasts no more than half an hour and ends with stitches. Thanks to the use of a laser, there is no need for stitches. But there is a certain condition that must be observed after excision of the frenulum: the little one must immediately be attached to the chest.
Retention cyst on the lip: treatment
A lump on the inside of the lip is treated in the same way as a lump under the tongue.
There is only one treatment option - surgery, which involves removing the entire cyst (there are no other treatment options). The surgery is very simple and usually does not take more than 15 minutes of the dental surgeon's time. It is performed under local anesthesia with lidocaine solution, and you will not feel any pain at all. It looks like this: a small incision is made on the surface of the mucous membrane next to the cyst, through which the entire cyst is removed, along with its contents. After this, 2-4 sutures are placed on the edges of the mucous membrane, which will need to be removed after about 7 days.
Removal of a retention cyst: video of the operation
During the operation, it is very important not to damage the cyst membrane, because if the walls of the cyst collapse, it is immediately lost in the tissues, and it is almost impossible to remove it entirely after this. If you leave a small fragment of the cyst shell in the tissues, the retention cyst on the lip will appear again.
Frenum of the lower lip
Dentists say that not all babies have a frenulum on the lower lip; it may be completely absent or forked. To study the length of the frenulum, the same technique is used as for studying the frenulum of the upper lip. Normally, the frenulum should be thin and attached in the middle of the body of the jaw. An important condition is that the frenulum of the lower lip must coincide with the center line between the incisors. If these conditions are not met, the bridle is short.
A short oral frenulum interferes with breastfeeding, as the baby cannot properly latch onto the mother's nipple. Fortunately, this situation is quite rare; the most typical manifestation of a short frenulum in the oral cavity is the presence of inflammatory gum diseases in the area of the lower incisors and malocclusion according to the same principle as in the upper jaw.
There are no age restrictions when excision of the mandibular frenulum; usually the mandibular frenulum is diagnosed and corrected at approximately the same time. The principle of the operation is similar to correction on the upper jaw.
Tongue frenulum
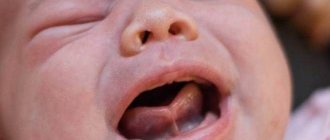
The most complex and insidious frenulum in a child's mouth. It is this frenulum that is able to regulate the movement of the tongue in the oral cavity. Normally, the frenulum is woven approximately in the middle of the tongue, and its length is approximately 8 mm. If the frenulum is attached almost to the tip of the tongue, this is a direct indication for correction.
After birth, the doctor must examine the baby’s oral cavity, which makes it possible to diagnose the pathology. If the frenulum is short, this can lead to difficulties in feeding, and correction is carried out in the maternity ward.
In some cases, the doctor may not notice a short frenulum, but when feeding, the child may experience symptoms that indirectly indicate pathology.
When feeding, the baby makes “smacking” sounds, often drops the breast and tries to rest - the feeding schedule changes, and the number of feedings increases. Babies may be capricious at the breast or even refuse, as a result the child does not gain weight well. Mothers often complain that babies bite their breasts because they cannot get their tongue between the gums and the mother’s nipple.
A short frenulum in the oral cavity can be diagnosed throughout life. In order to make sure once and for all that everything is in order in the child’s mouth, it is necessary to carry out a series of tests. Parents can also do this, although the doctor will most correctly conduct the tests.
The child should be asked to open his mouth and reach his tongue to the roof of his mouth. If the baby performs this operation without any difficulties, there is nothing to fear. But, if the child experiences unpleasant or painful sensations, or the baby is not able to reach the sky, this is an indication for a quick visit to the dentist. Parents should remember that such a test is informative only for children two to three years old.
Only a dentist or speech therapist can confirm shortening of the frenulum of the tongue in children of school and preschool age. Usually, an examination is prompted by a speech disorder in a child, when the child cannot pronounce a certain set of sounds - “r”, “sh”, “sch”, “zh”, “ch”, etc.
How does the correction happen?
There are features of correction depending on the age of the child. In the case of frenulum correction in newborns, which occurs in the maternity ward and with the obligatory presence of the mother, the frenulum is cut using special scissors or a laser, the latter is preferred. There are no nerve fibers in the frenulum itself, but there are many blood vessels. When using a laser, all blood capillaries are closed - there is no bleeding, and there is no need for stitches. A prerequisite is the presence of the mother during the procedure, since immediately after excision of the frenulum, the baby must be attached to the breast. It is at this time that the frenulum returns to normal and possible bleeding stops.
In the case of correction of the tongue frenulum in older children, both surgical and speech therapy treatment can be used. Everything will depend on its length and the age of the child, and on the consequences that this pathology provoked. Parents must clearly remember that the final verdict rests with the dentist, and not with the speech therapist, who can sometimes give false hopes for stretching the oral frenulum using various exercises.
It is the dentist who can assess the damage and clearly predict whether speech therapy treatment is suitable in each specific case. Quite often, dentists advise using complex treatment: surgical dissection of the oral frenulum and the use of speech therapy exercises - this combination gives excellent results.
Abnormalities of attachment of the frenulum of the lips and tongue
One of the preventive measures aimed at the timely prevention of dental diseases is the correction of the frenulum of the lips and tongue. When examining children, a pediatric dentist often reveals abnormalities in the attachment of the frenulum, which must be promptly corrected. The frenulum of the lips and tongue is an important component of the normal development of the dental system. They are folds of the mucosa, which are normally located along the midline and provide additional attachment of the lips and tongue to the jaw bones. A lot can depend on them: correct speech and bite, the ability to chew normally, the aesthetics of the face and smile, as well as the timely development of both jaws.
Tongue frenulum
The frenulum of the tongue starts from the middle of the tongue and goes down almost to the base of the gums. If the end of the frenulum is close to the tip of the tongue, then they speak of a “short” frenulum. At the same time, such a frenulum limits the movement of the tongue. The child cannot fully suckle at the mother's breast, which leads to lack of nutrition and, as a consequence, a significant lag in the baby's growth and development. At the age of 0 to 6 months, the incision is made by pediatricians and dentists without any anesthesia, the operation does not require sutures, and the wound heals within a few days thanks to breast milk.
Often, a shortened frenulum in children aged 5-9 years causes incorrect pronunciation of certain sounds, usually palatal ones: “r”, “d”, “l”. It is difficult for a child to touch the tip of his tongue to the upper incisors and simply stick out his tongue. And the speech therapist refers the child to a plastic surgeon. At the moment, there are several options for performing the operation. The most common is dissection of the frenulum lengthwise under local or general anesthesia, followed by suturing. An alternative to traditional surgery may be laser excision of the frenulum. This manipulation does not require sutures, due to the fact that the wound is covered with fibrin plaque and does not bleed. This is a very important circumstance, since large lingual veins are located nearby.
Lip frenulum
Most often, orthodontists, periodontists and speech therapists refer for plastic surgery of the upper lip frenulum. The fact is that the frenulum of the upper lip is often woven into the interdental papilla, between the central incisors, and sometimes into the incisive papilla, leading to an increase in the gap between the front teeth - the formation of a diastema. In addition, the shortened frenulum, when moving the upper lip, pulls along the mucous membrane of the alveolar process of the upper or lower jaw - as a result of this, the gums expose the necks of the incisors, causing their hypersensitivity, exposure of the roots, and periodontal disease in older people. And in children, during the period of formation of a permanent bite, a shortened frenulum of the upper lip can lead to the advancement of the front teeth forward, especially if there is not enough space in the dentition. Subsequently, such malocclusions are corrected orthodontically. Another complication of a short labial frenulum is a speech impediment. The child pronounces some sounds “u” and “o” poorly.
The surgery is performed under local anesthesia. The main point is to cut the frenulum lengthwise and apply sutures. The stitches are removed after 5-7 days. Modern methods of dental surgery make it possible to perform frenuloplasty without pain and blood. The frenuloplasty operation is performed using a laser device. Laser frenuloplasty lasts only a few minutes, does not require sutures, and never leads to the development of postoperative complications such as inflammation or swelling. In addition, laser plastic surgery does not cause severe pain in the child, and therefore is performed without serious anesthesia (applying a small amount of anesthetic gel to the frenulum is sufficient).
Doctor Ivanov K.A.
St. Petersburg State Budgetary Healthcare Institution "Dental Clinic No. 6".