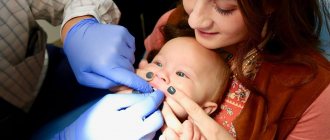
Short frenulum of the tongue - parents encounter this problem around the time their baby turns 3-4 years old. He has been trying to speak for a long time, knows a lot of words, knows how to construct complex phrases, but does not pronounce some words accurately.
Grandmothers assure that in another year the child will “speak out”; mothers work with their children using special methods for early development, but the problem is not solved. If your child is still babbling at 4 years old, it is time to visit the pediatric dentist.
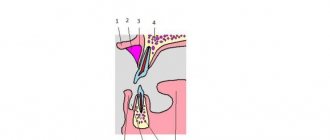
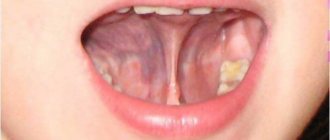
The frenulum of the tongue externally resembles a thin membrane, consisting mainly of connective tissue, the function of which is to attach the tongue to the bottom of the oral cavity.
In other words, a short frenulum of the tongue in a child is some kind of defect in the oral cavity that interferes with the joint movement of the tongue.
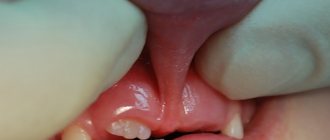
In some cases, the frenulum does not look thin at all, which significantly aggravates the situation. Almost half of all parents face this problem. And although a short frenulum can be noticed by a specialist even in newborns, parents learn about it when the baby begins to talk.
Pathology of the frenulum of the tongue can be congenital and hereditary. It should be understood that these concepts are completely different. If a congenital pathology is already present at birth, then a hereditary pathology is most often already present in one of the family members.
The concepts of complete and partial short frenulum of the tongue in a child are also distinguished. The level of discomfort of the child and the type of treatment chosen (surgical intervention or corrective exercises) depend on the type of pathology.
With a full frenulum, the child's tongue is practically immobilized, which makes it much more difficult to pronounce most speech sounds. With this type of pathology, muscle cords form. In the case of partial pathology of the frenulum of the tongue, the role of muscle cords is performed by connective tissue.
Why is a short frenulum dangerous?
A short frenulum is a congenital pathology in which the development and functionality of the ligamentous connection between the tongue and the lower jaw is disrupted. At the same time, the mobility of the tongue in the oral cavity is limited so much that it causes speech problems in the child.
Problems with the frenulum of the tongue in a child can occur in two ways. Young children who are breastfed or bottle-fed and have this pathology may have problems with sucking. This occurs due to the fact that the frenulum of the tongue is so short that it simply does not allow the tongue to function adequately.
With a short frenulum of the tongue, the baby cannot be fully breastfed, due to the fact that it is difficult for him to suck out a sufficient amount of breast milk. Therefore, in this case, immediately after the birth of the baby, he has real difficulties with feeding.
The second option for realizing the problem associated with a pathological frenulum of the tongue is speech defects and they arise much later. Partial immobility of the tongue leads to the fact that the child is not able to pronounce certain sounds correctly; his speech remains similar to babbling, “lisping.”
Recovery of the body after surgery
After surgery, the patient will need to undergo a period of rehabilitation. When asked how long it takes for a torn frenulum on the head to heal after surgery, it is difficult to give a definite answer. This depends not only on the individual characteristics of the body, but also on the chosen method of eliminating the problem. Moreover, the rehabilitation period is the same in all cases. A man needs:
- abstain from sexual intercourse for a period of 2 weeks to 2 months;
- deny yourself self-satisfaction;
- minimize physical activity;
- pay great attention to personal hygiene (after surgery, it is recommended to treat the surface after each trip to the toilet);
- regularly visit a specialist who monitors the wound healing process.
Reasons for the development of tongue frenulum pathology in a child
The formation of an anomaly associated with a short hyoid membrane begins before the birth of the child. This is preceded by negative factors, which include:
- genetic predisposition;
- infection of the fetus during pregnancy;
- viral and infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy;
- mechanical injuries to the expectant mother’s abdomen;
- the age of the expectant mother is over 35 years;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- the influence of other factors of unknown etiology.
Possible complications and repeated visits to the doctor
Having discovered such a delicate problem, a man should immediately contact a specialist. Otherwise, the negative consequences of a torn frenulum on the head will not keep you waiting. They may appear as:
- abundant growth of connective tissue at the site of injury (formation of scars);
- decreasing the length of the foreskin with each subsequent tear;
- deterioration of the emotional background and well-being, provoked by the experience of severe pain;
- the appearance of phobias and fears of sex;
- decreased libido;
- deterioration of erection;
- inability to perform full sexual intercourse.
If you notice the possibility of microtrauma to the genital organ, then it is worth organizing a trip to the hospital to prevent complications from occurring. At the same time, resorting to traditional medicine methods or trying to increase the length of the frenulum on your own is not recommended. In this case, negative consequences are fraught with infection of the genitourinary system with infectious diseases, damage to the arteries, and heavy blood loss.
How to recognize pathology in a child
A neonatologist, pediatrician, or the mother herself can recognize a pathological frenulum of the tongue in a newborn. If during the first and subsequent breastfeedings the baby experiences difficulties and cannot grasp the nipple correctly, then there is a reason to consult a doctor.
The second common sign of a pathological frenulum of the tongue in children is the occurrence of a speech defect when they begin to speak in phrases, namely at 3-4 years. Most often, with this anomaly, children do not pronounce several letters: “zh”, “sh”, “sch”, “ch”, “z”, “l” and “r”. Moreover, the sound “l” is easily pronounced if it is followed by a soft vowel, for example, “i”, “yu”, “e”, “e”, “ya”, in other cases it is simply “swallowed”. If there is incorrect pronunciation of sounds, then an examination by a speech therapist is necessary.
The most common symptoms of a tongue tie in a child are the following:
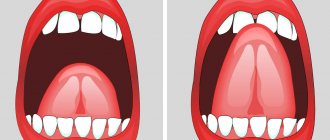
- the child is not able to reach the front teeth of the upper jaw or palate with the tip of his tongue;
- the child may have difficulty moving the tip of the tongue from one side to the other;
- the front teeth of the lower jaw may have a gap between each other;
- when the tongue is pulled forward, its tip remains flat, square or heart-shaped (that is, the front edge of the tongue seems to bifurcate);
- feeding problems in newborns.
It is important to understand that if the problem of the tongue frenulum exists, then sooner or later it will have to be solved. The sooner measures are taken, the easier and more painlessly the baby will endure them.
In what cases is it necessary to trim the bridle?
The operation of cutting the frenulum of the tongue is called frenulotomy . It is classified as simple and requires only local anesthesia.
Heavy bleeding during frenulotomy is very rare; after a couple of hours the child will be able to return to the usual rhythm of life.
If a short frenulum interferes with the newborn baby's ability to receive nutrition, it must be trimmed. The decision about surgery is made by a pediatric neonatologist.
For infants, as a rule, the operation is performed without anesthesia, since only the sublingual film of connective tissue is dissected, which has practically no blood vessels or nerve endings.
For children aged 3-5 years, surgery to cut the frenulum is performed under local anesthesia. The dentist decides whether surgery is necessary, and the speech therapist prescribes the referral.
Before the operation, the child needs to donate blood for a detailed analysis, which will display numerous indicators, including the number of platelets and the rate of blood clotting.
Surgical intervention is performed provided that the pathology is moderate or severe with limited tongue mobility. After surgery, speech therapy sessions are necessary.
There are a number of indications for frenulotomy, and limited tongue mobility is not the only one. The formation of malocclusion in a child, displacement and disturbances in the formation of the dentition, low effectiveness of speech therapy and articulation gymnastics, as well as the need to install dental implants or orthodontic structures for the child.
Pathology of the tongue frenulum does not always require surgical intervention. If the child does not experience any discomfort during breastfeeding, and his pronunciation of sounds is satisfactory, then it is likely that a speech therapist will help solve the problem. In this case, the child attends special classes, performs speech therapy exercises, articulation gymnastics, etc.
Treatment methods
Problems associated with a short frenulum of the tongue can be solved with medicinal and non-medicinal methods.
Medicinal methods involve surgical intervention of varying degrees.
If the sublingual membrane requires dissection, but it is quite thin and elastic, then the doctor dissects it right at the appointment. In this case, anesthesia is not provided, since the procedure is classified as mild.
More complex types of dissection of the frenulum of the tongue include frenulotomy, which is indicated for children with thicker frenulums. Frenulotomy is performed under local anesthesia with tissue dissection and subsequent suturing.
Complications of this operation may include stomatitis, prolonged bleeding from the wound, infection in the wound, etc. After frenulotomy, the child should receive pureed food for some time, as chewing may be painful.
Non-drug treatment methods include special types of massage, exercises to correct the frenulum of the tongue, and individual sessions with a speech therapist.
Non-drug methods are recommended when the condition of the child’s tongue frenulum is not critical and allows refusal of surgery. The decision on this is made by a speech therapist, pediatrician and dentist. Classes with a speech therapist include various exercises, articulation gymnastics, tongue twisters and poems.
Since a short frenulum of the tongue causes some speech defects, classes with a speech therapist are necessary both in the postoperative period and as a correction.
A massage aimed at stretching the frenulum of the tongue includes a list of special exercises. It is important that the classes are systematic so that they give a positive result.
Massage instead of cutting the frenulum is recommended for children in two cases: if the condition of the frenulum is not so critical and the problem can be solved with non-drug treatment methods; if the frenulum is cut when the child is older (over 5 years old) and the surgery will not solve problems with speech impediment.
What to do if you have such symptoms?
For many men, the relevant question is when the frenulum on the head is torn - what to do? There is no need to panic initially. All actions must be extremely careful and safe. If bleeding and bruising are present, you need to treat the damaged surface with peroxide or other antiseptic preparations on hand (with the exception of iodine solution) to minimize the risk of infection. First, you need to pinch and press the frenulum against the penis with your fingers to stop the bleeding. The manipulation must be done carefully, since strong squeezing and pressing is fraught with negative consequences. You can keep your penis in this position for no more than 10 minutes. Next, you need to apply a bandage at the site of the tear, but do not wrap the penis completely. This can cause stagnation of blood in the vessels. After this, you can perform hygiene procedures, but we must not forget about the obligatory trip to the hospital.
In case of swelling, a compress of gauze soaked in cool boiled water will help relieve symptoms.
Local inflammations that provoke irritation of the dermis can be removed using a gauze bandage and water hygiene procedures.
But in any case, comprehensive treatment prescribed by a specialist will be required.
Exercises for correcting the frenulum of the tongue and in the postoperative period
Postoperative frenulum stretching and correction exercises are aimed at developing new muscle movements of the tip of the tongue inside and outside the mouth. Regular practice will increase the range of movement of the tongue.
Articulation exercises by themselves will not improve speech and will not be able to correct the defect, so it is very important to carry them out in conjunction with individual speech therapy sessions.
The most common and universal exercises for stretching and correcting the frenulum of the tongue are given here in the article. Following them, you can study at home with your child on your own:
- Stretch your tongue forward, then stretch the tip up to your nose, then down to your chin. Relax, repeat the exercise several times (at first, up to five repetitions are enough, gradually the number of repetitions must be increased, bringing them to twenty).
- The exercise is performed by analogy with the previous one, moving the tongue left and right. The number of repetitions is also gradually increased to twenty.
- Open your mouth wide. Use the tip of your tongue to touch the upper incisors and try to press on the teeth with all your might, not allowing your mouth to close. During each execution, mentally count to ten. The number of repetitions is the same as the previous ones.
- The exercise is performed in front of a mirror. The mouth is wide open. When performing the exercise, it is important to monitor the movements of the tongue. Pronounce the syllables “dar-dar-dar”, “nar-nar-nar”, “tar-tar-tar”, etc.
- Sticking your tongue forward as much as possible, alternately “lick” your upper and lower lips.
- Closing your mouth, move your tongue from right to left and back, forcefully pressing the inside of your cheeks with the tip of your tongue.
To achieve good results, exercises should be performed daily, in several approaches, for 15-20 minutes . The articulation of specific sounds can be gradually corrected.
Important! You can begin to perform exercises for the frenulum of the tongue only after the wound has completely healed.
Speech therapy classes should include exercises to improve the functioning of the speech apparatus and oral kinesthesia, without which it is difficult to claim significant improvements in the development of a child’s speech. Many young patients, after cutting the frenulum, begin to speak more quietly and more quickly, trying to “drown out” speech problems.