Symptoms and clinical picture of a short frenulum of the tongue in a child
Signs of a short frenulum may not be noticed by inexperienced parents or those who do not know about this pathology; usually the problem is identified by nurses and doctors in the maternity hospital. The characteristic manifestations of ankyloglossia are as follows:
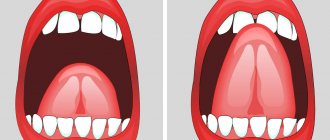
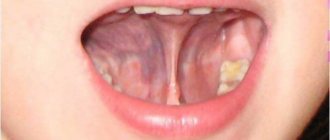
- when trying to stick out the tongue, it takes an arched position;
- when the tongue is raised, the frenulum is tensioned, as a result of which the body of the organ takes on the appearance of a heart;
- the tongue is fixed at the bottom of the oral cavity and cannot fully “come out” out.
Since the symptoms of a short frenulum of the tongue in a child are not obvious, you should pay attention to the following nuances.
In the first year of life, problems arise when breastfeeding. The child cannot properly grasp the nipple with his lips, squeezes it excessively with his gums, or bites it. This leads to malnutrition, hence anxiety and frequent crying.
Later, irregular teething may occur, with displacement or initial malocclusion.
At the time of speech development, difficulties are also noted; the child has difficulty pronouncing hissing and upper articulation sounds, and may burr.
At a later age, frequent and very painful tears of the shortened ligament are added to the described troubles.
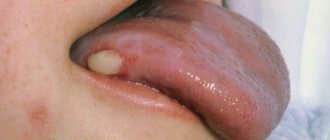
Short frenulum of the tongue
Short frenulum of the tongue - causes, treatment. The condition, known as a tongue tie, severely limits the tongue's mobility during articulation and chewing. In such cases, certain treatment is required.
The membrane connecting the floor of the mouth and the tongue is called the frenulum. This piece of muscle tissue (a kind of fastening) limits the movement of the tongue and prevents it from dangling uncontrollably.
Problems with a short hyoid frenulum are usually resolved in early childhood; the pathology is visually determined immediately after the birth of the child or in the early stages of its development. Like any anomaly, a short frenulum of the tongue can cause a whole range of problems in the process of growing up, therefore, immediately after diagnosis, the disease must be treated.
Causes of the anomaly
Formed during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, a short frenulum of the tongue can be caused by many factors associated with the condition and behavior of the mother during pregnancy.
The reasons may be of the following nature:
- Chronic diseases;
- Abdominal injuries;
- Bad ecology;
- Hereditary factor;
- Intrauterine infections;
- Infectious diseases of the mother in the first and last periods of pregnancy;
- Late motherhood (40 years and older).
Diagnostics
A short hyoid frenulum can be easily diagnosed visually. Depending on the degree of pathology (complete or partial), the child’s tongue is tightly fixed on the lower jaw or has very limited freedom of movement. Simply put, the baby cannot fully stick out his tongue.
As a result of the defective process of sucking mother's milk (the child is not able to wrap his lips around the nipple well), the baby is underweight. At a later age, a lisp and other speech (diction) defects can lead to problems with the child’s socialization, interfere with his communication with peers and cause depression.
Having found out the causes of the disease (pathology), treatment can begin.
Treatment of ankyloglossia
An operation to correct pathology of the frenulum of the tongue is called frenuloplasty. This is the most common type of treatment in modern conditions, effective and reliable.
There are several methods for performing frenuloplasty (according to Glikman or Vinogradova, Y-shaped and Z-shaped), but they all agree on one thing - excision of the frenulum, relocation of the place of its fixation and suturing. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia, and after surgery, special exercises and classes with a speech therapist are required to develop speech skills.
Recently, a laser technique has begun to be used to correct a short frenulum of the tongue. After treating the tissue with a special gel, a focused laser beam is directed at the frenulum, which practically dissolves it. The entire operation takes a few minutes and is well tolerated by young children.
Painless and quick, laser frenuloplasty does not cause complications and does not require sutures. The healing process is also quick and painless.
A short tongue frenulum is not a problem
After the use of lasers became widespread in medicine, tongue tie began to be treated with a new painless method. Elimination of anomalies of the hyoid frenulum has ceased to be problematic due to the versatility of the new technique and the absence of complications in the postoperative period.
Waiting for a baby and his birth is a great happiness for parents. And at the same time there is a great responsibility, including for the health of the child. Parents, naturally, are very upset when their baby is diagnosed with any disease. Sometimes in young children a pathology is found that is called a short frenulum of the tongue. It is easy to diagnose visually. But don’t worry, aesthetic dentistry can easily solve this problem. And, to dot all the i's, we will answer questions about the treatment of this disease.
Basic treatment methods and contraindications
Ideally, dissection of the frenulum should be performed in the first days of the child’s life, but there are 2 options for the development of events.
In infancy, the incision is made by a surgeon using scissors, which at this stage of life is absolutely painless, since there are still no nerve endings in this area. After this, the baby is applied to the breast in order to calm and prevent the development of bleeding.
How to treat a short frenulum of the tongue in older children? Also, the operation will only be more painful, since the membrane thickens over the years. Typically, frenuloplasty is performed - transfer of the site of fusion of the frenulum, followed by suturing.
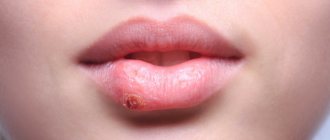
Short frenulum of the upper lip
Normally, the frenulum of the upper lip should look like a thin triangular fold of the mucous membrane. In practice, we are faced with various types of incorrectly developed frenulums of the upper lip: shortened, massive, wide and located in the interdental space (between the two central upper incisors).
All these anatomical disorders lead to unsatisfactory aesthetics and the following negative consequences:
- limitation of upper lip activity;
- violation of diction;
- development of dental anomalies;
- looseness and soreness of the gums in the area of the central upper incisors;
- exposure of the necks of the central upper incisors;
- the formation of a diastema - a gap between the central incisors of the upper jaw.
Treatment
We correct tongue and lip frenulum using surgical intervention. Severe anomalies of the frenulum of the tongue (situations when the baby does not latch on well) are eliminated in infancy: from birth to 7 days. In such cases, a painless procedure is performed to correct the frenulum of the tongue, which does not require anesthesia or sutures.
Surgery on the frenulum of the upper lip is performed for orthodontic and aesthetic reasons and is advisable only after the permanent lateral (side) incisors of the upper jaw have erupted, i.e., after the child is 7-8 years old.
In our Dentistry Center, all plastic corrections are carried out using high-quality anesthesia, which allows the child not to experience any discomfort. Depending on the structural features of the soft tissues, frenuloplasty surgery is carried out by dissecting, excising and moving the area of attachment of the frenulum. The procedures are performed using minimally invasive instruments, which allows for bloodless operations. After the operation, the pediatric surgeon applies a thin, neat suture using self-absorbing materials. The recovery period takes place under the supervision of specialists and usually takes only a few days.
Short lip frenulum and frenuloplasty
Essential anatomical formations in dentistry and periodontology are: vestibule of the oral cavity, free gum, mobile gum, attached gum, transitional fold, frenulum of the upper and lower lips.
Vestibule of the oral cavity
- this is the space between the teeth and/or edentulous alveolar ridge, on the one hand, and the lips and cheeks, on the other hand.
If its depth, that is, roughly speaking, the distance (height) from the deepest place - the transitional fold to the necks of the teeth, free gums or the top of the toothless alveolar ridge, is less than 6 -7 mm, then it, the vestibule, is considered small. In this case, movements and tensions of the surrounding muscles can, breaking the barrier of the attached gum (this is the immobile rigid gum between the transitional fold and the free gum), pull the gum away from the necks of the teeth and dental implants and, over time, lead to recession (exposure of the necks of the teeth) of the gums, gingivitis, marginal periodontitis. The result of this process will be loosening and loss of teeth or implants. This anatomical feature, for preventive or therapeutic purposes, requires surgical correction - deepening the vestibule of the oral cavity
.
Figure 1. Diagram of the oral cavity organs in a sagittal section along the central incisors: 1 – upper lip pulled forward, 2 – low attached frenulum of the upper lip, 3 – upper transitional fold, 4 – upper jaw, 5 – lower lip, 6 – lower vestibule, 7 – lower jaw, 8 – tongue.
Frenum of the upper or lower lip
- This is a two-layer fold of the mucous membrane, triangular in profile, in shape along the midline of the vestibule of the oral cavity of the upper and lower jaw. Its point of attachment on the attached gum is approximately 5 mm from the gingival margin. On the other hand, the frenulum smoothly goes into the lip. An anatomical feature such as a short (or strong) frenulum of the lip stands out. In this case, the gingival point of attachment of the frenulum is very close to the interdental space (papilla). Movements of the lip muscles, as in the case of the small vestibule of the oral cavity, cause tension in the gingival margin between the central incisors (the gums may turn pale when the frenulum is pulled). The presence of a short frenulum, in addition, may be associated with a condition such as the appearance of spaces (three and diastemas) between the teeth.
Figure 2. The vestibule of the oral cavity and the short frenulum of the upper lip, front view: 1 – upper lip, 2 – attached gum, 3 – lower point of attachment of the frenulum, 4 – body of the frenulum, 5 – frenulum merges with the lip.
Surgical correction of the condition of a short frenulum is frenuloplasty
, excision of the frenulum, or, which is the same, frenotomy and frenectomy. During this manipulation, a V-shaped incision is made along the contour of the attachment of the frenulum to the gingival margin and to the attached gum, the cut-off tissue is pulled towards the lip and sutured. Thus, a vertical suture of 3–4 ties is formed from the lip to the transitional fold and a small open V-shaped wound surface between the transitional fold and the gingival margin. It heals by secondary intention.
Figure 3. Tissues of the vestibule of the oral cavity after frenuloplasty: 1 - open V-shaped wound surface between the transitional fold and the gingival edge, 2 - vertical suture from the lip to the transitional fold.
To be continued…
Lower lip frenulum problems
The frenulum of the lower lip is located from the middle of the alveolar process to the lower lip. With anatomical defects, it can be thickened, shortened and attached to the base of the lower incisors. In addition, our pediatric dentists often observe a complete absence of the lower lip frenulum. In other cases, on the contrary, it manifests itself in a double or triple form.
Pathologies of the development of the frenulum of the lower lip cause various disorders:
- development of malocclusion;
- lesions of the lower central incisors;
- formation of gaps between the lower front teeth;
- bleeding gums.
Rehabilitation
After correcting the frenulum of the lips and tongue, you must follow all the doctor’s instructions. It should be noted that each case is individual and requires a separate approach. Depending on the situation, during the rehabilitation period you may need:
- myogymnastics: exercises with which the main muscles of the oral cavity are developed;
- classes with a speech therapist;
- orthodontic treatment using functional removable appliances;
- elimination of diastema (gap between the front incisors) using a removable orthodontic design with a loop.
Children's surgeons in Kuntsevo quickly and efficiently perform plastic surgery on the frenulum of the tongue, upper and lower lips. In addition to surgeons, orthodontists and speech therapists are involved in the treatment process, which allows not only to correct the position of soft tissues, but also to cope with its consequences: correct the bite, work with diction. This interdisciplinary approach is very important during the formation of the bite (at 7-8 years of age). After the recovery period, our patients begin to quickly catch up: improve their speech skills, smile correctly and enjoy chewing.