Despite the fact that the mucous membrane is quite resistant to various types of disorders, there are times when blisters, plaque, cracks or ulcers appear on it. Any manifestations indicate some kind of abnormality, some may be completely harmless and go away on their own, others cause significant discomfort, making it difficult to speak and eat. They indicate the presence of quite serious problems. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose the disease after studying the test results.
In addition, if there are disturbances in the digestive system or if an infection penetrates, the color of the mucous membrane may change. For example, in patients with diabetes mellitus, dry mouth may develop and red spots may appear, this is due to a disruption in the functioning of the salivary glands.
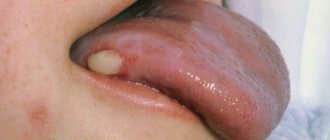
Very often, the development of a ball under the tongue indicates the presence of a ranula - this is a painless vesicle containing fluid. It is easily destroyed, but nevertheless quickly forms again. During an exacerbation of the chronic stage, ranula has the appearance of an inflamed dense nodule, and the period of relapse can range from one week to several months, followed by a stage of remission.
Causes
The presence of a ranula under the tongue indicates a formed cyst; this pathology is common, and various factors can cause its development. This indicates a disruption in the release of salivary fluid.
When the outlet narrows, secretion is produced, but cannot be excreted in full, this leads to the development of an inflammatory reaction, and in more advanced stages, saliva may not be released at all.
A narrowing of the opening can occur due to a plug (stone), caused by injury, or due to thickening of the salivary fluid or a change in its composition. A characteristic feature of the disease is that in the absence of necessary therapy, the cyst tends to gradually grow, causing increasing discomfort to the patient; in addition, the risk of complications increases.
What could be a growth on the gum?
The following factors can lead to decreased saliva production:
- Pathologies of the mucous membrane of an inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature (oral candidiasis, stomatitis, herpes virus, glossitis and others). These are called primary infections.
- Autoimmune disorders of the mucous membrane - pemphigus, which manifests itself as small blisters, the disease is caused by pathological microflora. In the absence of timely treatment, it often ends in death of the patient.
- A developed tumor that compresses the gland.
- Injury to the mucous membrane - can be caused under various circumstances: a toothbrush, fork or other sharp object, fish bone, teeth, braces and others. This also includes thermal and chemical burns.
- Syphilis is a secondary infection, the appearance of a bubble as a concomitant symptom of the main pathology.
- Serious mechanical trauma - dislocations, fractures of the jaw, which lead to a violation of the integrity of the skin; an infection penetrates through them, causing an inflammatory reaction.
- Lipoma is a benign tumor that is most often localized on the sublingual or posterior zone of the tongue. In appearance they are round or flat. This neoplasm is characterized by an asymptomatic course in the first stages of development and slow growth. As the bladder grows, more and more discomfort occurs because the swelling interferes with speaking and eating. Treatment is carried out surgically.
- Papilloma can form in any area, including the sublingual. The vesicle is lighter in appearance and often painful. The causative agent is the human papillomavirus. It is provoked by a sharp decrease in immunity, which can be caused by drinking alcohol, excessive smoking, psycho-emotional stress and other factors.
- Boil - easily differentiated from other pathologies, since a red lump quickly forms, in the center of which purulent exudate develops. A characteristic feature is severe pain, which subsides after the abscess breaks through. Opening the pathology on your own often leads to infection and blood poisoning.
A number of minor factors are also highlighted:
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products. Exposure to nicotine leads to thinning of the mucous membrane, making it more vulnerable.
- Unhealthy eating.
- The presence of scars on the frenulum of the tongue after surgical interventions.
- Long-term infectious processes at the level of the whole organism.
- Insufficient oral and hand hygiene
- Lack of vitamins in the body.
- Thyroid diseases .
All such factors lead to blockage and narrowing of the passages of the salivary glands; if a cyst is observed, then it is removed surgically.
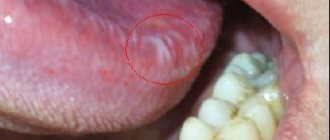
Causes of papilloma on the frenulum of the tongue
Papillomas on the frenulum of the tongue always occur due to exposure to certain strains of HPV. They are mainly caused by types 2, 13 and 16. The virus enters the body through wounds on the skin and mucous membranes. This becomes possible as a result of using the things of its owner - clothes, toys, dishes, bath accessories. You can also become infected through unprotected sexual contact with untested partners.
The virus, which can cause papilloma on the frenulum of the tongue, infects approximately 70% of the world's population, but it does not appear in everyone. After penetration into the body, several months or years may pass until this point. This period is influenced by the state of the immune system: the weaker it is, the faster the symptoms appear.
Here are the reasons why a papilloma may appear on the frenulum of the tongue:
- Bad habits . People who abuse alcoholic beverages and smoke a lot are most at risk of infection. Tobacco smoke and alcohol have a destructive effect on the immune system, negatively affect cell health and weaken the body's protective functions.
- Visiting doctors . The danger of infection with a virus and the occurrence of papilloma on the frenulum of the tongue occurs when doctors use non-sterile instruments during an examination. Such problems may arise if seen by irresponsible ENT specialists, dentists, gynecologists, endoscopists, or proctologists. This is due to the fact that these accessories may contain traces of blood or lymph, in which the concentration of HPV is very high.
- Hormonal disorders . This applies mainly to women, especially those who are over 40 years old. At this age, menopause usually begins, which negatively affects the body's protective functions. A deficiency or excess of testosterone, progesterone and other hormones of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and ovaries can lead to the appearance of papilloma on the frenulum of the tongue.
- Gastrointestinal diseases . First of all, those who have been suffering from colitis, gastritis, stomach and intestinal ulcers for a long time should be wary of the appearance of papillomas on the frenulum of the tongue. The problem arises due to a violation of the absorption of nutrients, as a result of which vitamin deficiency develops and immunity deteriorates.
- Treatment with various drugs . First of all, the threat of papilloma appearing on the frenulum under the tongue is created by hormonal therapy. Various antibacterial medications, which are often used to treat colitis, gastritis, stomach and intestinal ulcers, tonsillitis and many other diseases, also have a negative impact on health.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules . This applies to people who ignore brushing their teeth, do not use antibacterial mouthwash, and have the bad habit of biting their lips and nails.
Separately, it is worth noting the negative impact of poor nutrition on the immune system. Papilloma on the frenulum of the tongue can appear due to insufficient consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables, which is why vitamin deficiency often develops. Stress, an inactive lifestyle, and poor environmental living conditions also have a negative impact on the immune system.
Note! The occurrence of papilloma on the frenulum of the tongue in children is often associated with their infection during childbirth, at the time of exit from the mother’s uterus.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a neoplasm directly depend on the cause of its occurrence. With any injury, one bubble most often forms, and it may not differ in color from the mucous membrane, sometimes with redness, and an accumulation of blood may be observed - this is a hematoma, it occurs with more severe injuries.
Typically, such blisters do not cause problems with treatment and go away on their own. But with severe injuries with an extensive hematoma, the risk of the development of pathogens with subsequent inflammation increases, since this is a very favorable environment for them.
If the neoplasm has formed as a result of an acute lack of vitamins, then when the diet is normalized and a complex of vitamins is taken, the mucous membrane is restored and the ball disappears. There is no pain syndrome in this case.
For what reasons does a lump appear on the roof of the mouth?
With the development of ranula, a dense capsule is observed, which gradually increases and leads to complications in nutrition and speech function. Diagnosis and surgery are carried out by a specialist.
Pemphigus is characterized by easy peeling under mechanical stress and palpation. When you press on the lump itself, it enlarges, and erosion is observed around the perimeter.
Stomatitis manifests itself in the form of ulcers and redness, while patients complain of pain that intensifies while eating.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with a medical history, which is based on an examination of the patient, taking into account his complaints. The presence of concomitant diseases that could cause the formed pathology is determined; it is also necessary to make sure. That there were no complications.
During the examination, the general condition of the patient, the integrity of the skin and the presence of pathological elements are determined, regional lymph nodes are checked for enlargement and pain, and the degree of opening of the oral cavity is determined. The condition of the mucous membrane itself is noted. It is also necessary to determine the presence of liquid inside the bubble.
During palpation, cysts are determined by their softness, the presence of fluid can be determined, and sometimes an unpleasant pain symptom occurs.
After this, it is possible to prescribe additional diagnostic methods:
- Contrast sialography is a method of x-ray examination of the salivary glands based on the absorption of x-ray radiation or an iodine-containing substance that is administered for contrast. It is considered one of the more informative ways to make a diagnosis for pathologies of the salivary glands.
- A scraping is done to determine the pathogen that provoked the development of the disease.
- Biopsy of the contents of the substance.
If a bubble appears under the tongue or some minor inflammation, you should immediately contact a medical facility, since such a sign may present itself as a serious illness.
Treatment
Only a doctor can provide adequate treatment after carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures. Therapy is prescribed based on the causes of occurrence:
- Stomatitis - a course of physiotherapy and treatment of the tumor with antiseptic agents is prescribed. Often, the doctor recommends rinsing the mouth with Rotokan, treating with Stomatidin and sea buckthorn oil. Also suitable for the procedure are decoctions of medicinal herbs such as calendula, chamomile, and oak bark.
- Infection - when this cause is identified, therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease:
- Herpes - Acyclovir is prescribed.
- Candidiasis - antifungal medications (Clotrimazole, Flucanazole, Flucostat).
- Glossitis - anti-inflammatory and antibiotic medications.
- Syphilis - antibiotics based on Penicillin, Tetracycline.
- Vitamin deficiency – requires nutritional adjustments and taking a complex of vitamins.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland - hormone replacement treatment and iodine-containing drugs are prescribed.
- Cyst-like disorders - surgical removal is prescribed. Local anesthesia is performed, after which cystosialadenectomy is performed - cutting off the cyst. The operation is performed by an experienced surgeon, since there is a high risk of injuring the nerve, which will lead to serious consequences for the patient. After removal, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Methods for treating papillomas on the frenulum of the tongue
To treat papilloma on the frenulum of the tongue, you will need to use both oral medications and external agents. They can be used both in combination and separately; in the first case, the effect will be obtained faster and it should be brighter. On average, therapy lasts from 1 to 3 weeks, depending on the body’s capabilities.
Medicines for papilloma on the frenulum of the tongue
In the photo there are preparations for papillomas on the frenulum of the tongue
In order to eliminate papilloma on the frenulum under the tongue, you need to use immunostimulants, among which Viferon stands out. It costs about 300 rubles. (140 UAH), and use it in the form of an ointment. It is applied in a thin layer directly to the affected area and allowed to absorb. The permissible frequency of treatments is 2 times a day with a break of 12 hours, therapy lasts up to 10 days. Pharmacies offer the analogue Kipferon instead, but it is only available in the form of suppositories.
As immunomodulators for oral administration for papilloma on the frenulum under the tongue, we can especially note the tincture of Echinacea purpurea in alcohol and Lymphomyosot, the price of which is about 500 rubles. (220 UAH). They need to be taken 20-40 drops 1-2 times a day for 10-20 days. It is also worth paying attention to the tablets “Immunal” and “Imudon”.
For papilloma on the frenulum under the tongue, rinsing the mouth with Miramistin is useful. It is a powerful antiseptic and suppresses the activity of HPV, facilitating the process of combating the formation itself. To do this, it is recommended to use it 2-3 times a day, and the composition should not be swallowed. The cost of the solution is 200 rubles. (80 UAH).
You can also lubricate the papilloma on the frenulum under the tongue with silver nitrate, which dries out the growth well and effectively fights the virus itself. To do this, it is enough to carry out this treatment 2-3 times a day, but it is best to entrust this to a specialist to avoid burns. Instead, you can use eucalyptus oil, lubricating the growth with it three times a day using an ear stick. The duration of treatment can be 2-3 weeks. The cost of the product is 70 rubles. (30 UAH).
To eliminate papilloma on the frenulum under the tongue, vitamin deficiency, which is often detected in HPV carriers, the drugs “Perfectil”, “Vitrum”, “Alphabet”, “Supradin” are prescribed, which can successfully replace each other. On average, their price is 500 rubles. (200 UAH), and you need to take all this for about a month, but no longer. Then you need to take a break for at least 3 months.