Why do stains appear on teeth: the main reasons
The initial form of caries can be provoked by various factors, but most often this happens due to the formation of an acid-base imbalance in the oral cavity. A large number of harmful microorganisms constantly live in the mouth, which actively participate in the process of food decomposition. Food particles tend to remain between the teeth and on their surface, which leads to the destruction of tooth enamel.
Other reasons leading to the destruction of the structure of the enamel layer on the teeth include:
- incomplete or poor oral hygiene. After some time, failure to comply with hygiene rules leads to the appearance of white plaque on the teeth, which acts as an excellent environment for the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria. As a result, microorganisms produce harmful acids, which negatively affects the condition of tooth enamel. This process can be prevented by regular oral hygiene procedures. If, nevertheless, destruction of the enamel is observed, then treatment of caries at the spot stage will help prevent complications;
- hereditary predisposition. Even at the moment of conception and during intrauterine development, the structure and strength of tooth enamel is laid in the baby. When the mother’s body during this period lacks fluoride, calcium, vital vitamins and minerals, the risks that the child’s teeth will be excessively fragile and prone to the formation of carious processes are maximum;
- poor nutrition. Tooth enamel will be hard and durable if the daily diet contains foods high in calcium, fluorine and phosphorus (fish, cheese, cottage cheese, nuts, milk). But foods containing a large amount of carbohydrates (sweets, baked goods) must be kept to a minimum. This will protect the enamel from premature destruction;
- changes in the composition of saliva and its increased viscosity. Along with the fact that saliva is involved in the process of softening the food consumed, it also cleanses the surface of the teeth from food debris. When, due to changes in the structure of saliva, its acidity increases, a constant destructive effect on the teeth is formed. This process leads to the development of carious pathologies.
Often the initial form of caries appears in the area of the neck of the tooth, which is difficult to clean with a toothbrush. Regular examination of the condition of the teeth by a dentist and, if necessary, professional cleaning will help prevent the development of carious processes.
Possible reasons
As a rule, red gums indicate the development of gingivitis. This is a common disease characterized by inflammation of the gum tissue. It develops as a result of non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene. Due to irregular brushing of teeth, soft plaque accumulates on them, which is an ideal environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. If it is not removed in time, it turns into tartar, which injures the mucous membrane.
Red gums are not always a symptom of a serious illness. It can also be associated with eating hard foods and scalding drinks, using too hard a brush, wearing dentures, braces, mouthguards, plates and other structures. A dentist will help determine the exact cause and eliminate the problem.
Stages of caries spots
Dentists distinguish several stages of damage to one or more teeth by caries. Each stage is characterized by certain features, differences and symptoms.
Caries in the white spot stage
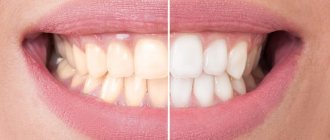
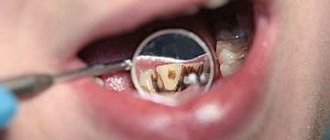
During the initial stage of caries, a person does not experience any discomfort and does not feel pain. The pathogenic process can be identified only by the white spots formed on the surface of the teeth. Although at first glance the tooth seems absolutely healthy, when stains appear in it, the process of destruction of structural tissues already occurs.
The spots that appear on the enamel in the initial stage have a whitish tint and are small in size, so upon visual inspection they are practically invisible. Only a professional specialist is able to identify the onset of pathogenic destruction of tooth enamel and promptly treat caries in the stain stage.
If you ignore treatment, then over time the light spot fades, tooth enamel loses its natural shine, becomes fragile and loose, and the carious process progresses more and more.
Important! If you identify the development of the initial form of caries, which manifests itself as microscopic specks, then you can avoid serious dental treatment. Therefore, every person should visit the dentist at least 2 times a year for a preventive examination of the oral cavity and, in particular, the condition of the teeth.
Black spot on teeth
If you ignore the appearance of white spots, then caries gradually passes into the next stage of a dark spot. This form is more serious and dangerous in comparison with the previous one.
Demineralized tissues grow very quickly, the white spots become darker and more visible. The white shade turns into brown or brown due to pathogenic bacteria entering the porous structure of the enamel.
Pathogenic microorganisms increasingly destroy the tooth surface and the disease moves into the next stage - superficial caries, the treatment of which is longer and more complex.
Symptoms of inflammation
During the normal healing process, the pain after tooth extraction lasts 1-2 days, after which it gradually subsides, the wound becomes covered with a blood clot and heals over time. With inflammation, the pain can come in waves, not subside or even intensify. The nature of the pain is pulsating, can radiate to the ear, and manifests itself after eating. Does not respond to painkillers.
When examining yourself, pay attention to the following signs:
- the gums at the extraction site are red;
- the socket is dry, a blood clot does not form or is quickly destroyed;
- there is a gray or yellow coating;
- bleeding from the socket;
- increased body temperature;
- unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
If at least one of the listed signs is present, you should consult a doctor. There is a suspicion of alveolitis.
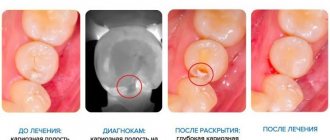
Caries in the spot stage: diagnostic measures
The most reliable and effective diagnostic procedure for the initial form of caries is to check the integrity of tooth enamel using special organic dyes. Dentists use:
- carmine;
- tropeolin;
- methylene red;
- methylene blue.
The latter is more often used in dental practice. First, the specialist removes accumulated plaque from the tooth surface. Use cotton swabs to isolate the tooth from saliva and then apply the coloring solution. After a few minutes, the solution is thoroughly washed off and the condition of the enamel is analyzed. If it is stained, this indicates the presence of caries.
There are other ways to diagnose caries in the spot stage:
- drying of enamel. The surface of the tooth is treated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, then the enamel is thoroughly dried with a stream of warm air. After drying, areas with white spots will immediately become noticeable;
- radiography. The area affected by caries appears as a small spot on an x-ray. The method is used mainly for contract caries;
- examination with a stomatoscope. First, all accumulated plaque is removed from the surface of the teeth, then the dentition is illuminated with the device. Under ultraviolet radiation, it is not only easy to distinguish damaged tissue from healthy tissue, but it is also possible to determine the boundaries of pathology.
In order to treat caries in the spot stage, it is very important to undergo a timely diagnosis, accurately recognize the presence of pathology and exclude similar diseases that resemble caries.
Treatment methods for caries in the spot stage
Since the main cause of stains is demineralization of the enamel, treatment of caries at an early stage is carried out using a conservative method without the need to drill the tooth.
Professional treatment of initial caries
After diagnosing caries in the stain stage, it is very important to carry out adequate treatment and prevent complete tooth destruction. At an appointment with a specialist, treatment of caries in the spot stage can be carried out in different ways:
- remineralization;
- Borovsky-Leus method;
- gel applications;
- fluoridation.
The essence of the treatment is to saturate the damaged areas with calcium and fluoride using special professional preparations.
In general, the treatment process in the dentist’s office is carried out in the following order:
- professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and stones;
- washing and drying;
- application of specialized preparations depending on the chosen method;
- consultations on further dental care;
- monitoring the further condition of the teeth;
- preventive actions.
After treatment for “white caries,” you should contact your dentist no later than 2-3 months. The specialist will evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and the quality of the patient’s oral hygiene.
Treating white spots at home
Not only in the dental clinic is treatment of caries in the spot stage carried out; a course of therapy is also possible at home. Just first you need to consult a dentist and, if necessary, have your teeth professionally cleaned.
For home treatment you can use:
- remineralizing gel, for example, ROCS Medical Mineral. The composition is enriched with magnesium, calcium and other microelements that penetrate tooth enamel, remove stains and restore its natural shine;
- special toothpastes with a healing effect. ROCS Medical and Elmex cope well with such problems;
- fluoride gel remineralizes white spots and prevents the destruction of the enamel coating of teeth.
Along with professional remedies at home, you can also use traditional medicine recipes:
- Finely chop the pumpkin tail. Pour boiling water and leave for an hour. Rinse your mouth with the solution several times a day;
- Chew a piece of dried calamus daily for 5-7 minutes. The number of days depends on the size of the spot.
Both in the case of medications and folk remedies, treatment of caries in the spot stage is aimed at enriching the enamel with useful elements and minerals.
Types and differential diagnosis
Like most diseases, periodontitis can occur in acute or chronic form. Sluggish periodontal inflammation is divided into three types:
Granulating
Depending on the type of infection that affects the tooth tissue, and on the specific immune response of the body, various kinds of altered tissues are formed in the periodontal cavity. With chronic periodontitis of this type, granulating tissue appears. It looks like a loose red formation near the top of the tooth root, which quickly grows and thereby destroys the bone tissue of the jaw. Of all three types of chronic inflammation, granulating periodontitis is considered the most active and pronounced. Its characteristic manifestation is the formation of fistulas, which can keep the tooth in a latent form of the disease for a long time. Connective tissue can not only affect the plate of the alveolar process (jaw), but also spread even to the skin. Therefore, advanced cases of periodontitis are much more difficult to treat and can affect large areas of tissue, including adjacent teeth. An X-ray image allows differentiation of granulating periodontitis from other types of periodontal disease. It clearly shows darkening in the area of the apex of the tooth root with circular outlines of tissue or in the form of flames. At the same time, the image does not show sharp boundaries, as in some other classifications of periodontitis. These dark spots indicate that the bone tissue has dissolved as a result of inflammation and has been replaced by connective tissue.
Fibrous
This form of the disease is quite rare and is accompanied by an asymptomatic chronic course. As a result of sluggish periodontitis, connective fibrous tissue forms around the tooth root. It is denser and is visible on an x-ray as a periodontal tooth gap, more widened than usual. The result of the appearance of fibrous tissue can be:
- suffering from acute periodontitis, which was successfully treated;
- poor-quality filling of tooth root canals;
- lack of treatment for granulating periodontal inflammation.
If the disease has entered the stage of remission (quiescence), and the patient does not complain about the causative tooth, then fibrous periodontitis cannot be treated. However, in cases of exacerbation, therapy in the form of refilling the root canals of the tooth is possible.
Granulomatous
If granulating periodontitis does not have clear outlines on an x-ray, then granulomatous periodontitis is characterized by the presence of a capsule with purulent contents. It occurs at the apex of the tooth root and gradually grows, affecting the bone tissue.
There are three degrees of development of periodontal abscess:
- Granuloma. The size of the capsule with this diagnosis reaches 0.5 cm in diameter.
- Cystogranuloma. It is diagnosed when the dense membrane reaches 1 cm.
- Cyst. More than one centimeter in diameter suggests the cystic development of periodontitis.
An increase in granuloma indicates that the inflammatory process does not find a way out and continues to dissolve the bone tissue near the tooth. In this case, a whole chain of pathological processes occurs in the human body. Sometimes particularly advanced cases showed a cyst of up to 4-5 cm in the tissue, which significantly impaired the integrity of the lower jaw, increasing the risk of its fracture.
On the other hand, the accumulation of serous fluid in the tooth area regularly causes additional intoxication to the entire body, which can be accompanied by periods of weakness, fatigue, low-grade fever and other symptoms of periodontitis.
Among all forms of chronic
Granulomatous periodontitis is considered to be the most sluggish. The fibrous tissue of the capsule serves as a protective barrier that prevents pathogenic bacteria from entering the blood. Therefore, the liquid in the capsule can remain in the tooth tissue for years without showing itself. Depending on their location, granulomas can be located either immediately under the root apex or in the tissues of the lateral cavity.
Preventive measures for “white caries”
The main component of dental health and prevention of caries development is compliance with the rules of prevention:
regular and proper oral hygiene. It is necessary to brush your teeth not only with a brush, but also after each meal you should use dental floss. After removing pieces of food with a thread, it is advisable to chew chewing gum for 5 minutes;
- Maintain a nutritious diet and try to avoid frequent snacks between meals. A common cause of caries is frequent consumption of sweets, flour, candies, chips, fast foods, and carbonated drinks. For dental health, the diet should contain fish, vegetables, fruits, kefir, nuts, cottage cheese, milk and other products with a high content of fluorine, phosphorus and calcium;
- periodically carry out professional teeth cleaning and treat the enamel with fluoride-containing preparations.
If you follow these basic rules, you can keep your teeth strong and healthy. But in order to avoid complications and prevent the pathology from becoming severe, you need to regularly visit the dentist and, if necessary, carry out proper and effective treatment of caries in the spot stage.
Acute periodontitis
The acute form of this disease is characterized by similar symptoms as in the chronic course of the disease, only in a more pronounced form. Sharp pain in a tooth can begin spontaneously, often at night. In this case, the slightest touch to the causative tooth leads to a “lumbago” effect. The periodontal tissues swell significantly, which causes the tooth to rise, as if to grow. This fact further injures the diseased tissue, since the enlarged tooth, when chewing, receives more pressure from the closing tooth from the other jaw.
The active phase of the disease is divided into two types:
- serous periodontitis;
- purulent periodontitis.
The first two to three days pass through a serous period, when fluid with a large number of leukocytes accumulates at the site of infection. After this time, the serous tissue becomes purulent and all the symptoms of periodontitis intensify. A so-called throbbing pain in the tooth appears, which practically does not subside. If a person has not yet consulted a dentist, then before the visit, acute pain can be eased by taking painkillers. It is simply impossible to delay going to the doctor at this stage, since the symptoms will not allow the person to eat, sleep, or live normally. The accumulation of purulent contents at the root of the tooth corrodes hard tissues, which leads to the organ’s staggering. The areas of the gums, cheeks and lips are also painful and have swelling of varying degrees. Acute purulent periodontitis is a rather dangerous disease, since in the absence of effective antibacterial treatment it can acquire various stages of complications.
- Periodontal stage. Pus accumulates in the area of the periodontal gap, causing the feeling of an overgrown tooth. This is the initial stage of dental tissue abscess, which must be stopped immediately.
- Endosseous stage. The infection, along with pus, enters the bone tissue. The process of damage to the alveolar plate begins.
- Subperiosteal stage. The amount of pus under the root of the tooth increases, and it accumulates under the periosteum. This formation is called flux. In parallel with the increase in flux, the swelling of the cheek intensifies. Acute and aching periods of pain worsen.
- Submucosal stage. It is characterized by a breakthrough of the periosteum and the release of exudate into the soft tissue. Opening the fistula relieves acute symptoms of pain in the tooth, transforming periodontitis into a chronic form. However, as soon as the outflow is disrupted, periodontitis immediately reactivates.