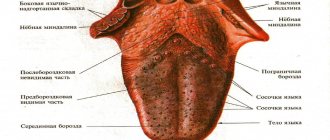
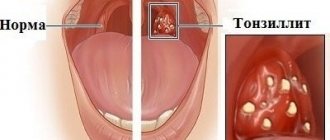
The condition of the oral mucosa is one of the indicators of human health. It is involved in most pathological processes occurring in the body and reacts even to minor changes in the microbial composition of the oral cavity. Therefore, many people have experienced red dots on their gums and palate at least once in their lives. This is a natural reaction to mechanical and temperature stimuli. Redness may be caused by:
- consumption of hot and spicy foods and drinks;
- damage to soft tissues with a hard brush, toothpick, bones and pieces of hard food;
- Using the wrong toothpaste or mouthwash;
- wearing prostheses, braces, retention caps.
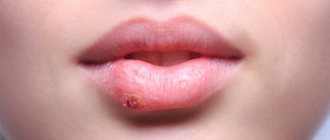
However, red spots can also indicate various diseases. Let's look at the most common cases.
Causes of herpangina
Herpangina can be caused by about 70 serotypes of enteroviruses. Most often these are Coxsackie B, Coxsackie A17 viruses and enterovirus 711.
Since the only carrier of enteroviruses is humans, you can become infected through contact with a sick person or with a virus carrier who has no symptoms of the disease1. According to the literature, the number of virus carriers can be up to 46% of people2.
The virus is released into the external environment with feces and droplets of saliva. It is also contained in bubbles that appear in the patient’s throat. Enterovirus infections most often affect children, although the disease also occurs in adults5.
The patient or virus carrier excretes viruses from the upper respiratory tract within 3 weeks after infection, and with feces - up to 8 weeks. In the first two weeks, herpetic sore throat is most contagious1.
You can become infected in the following ways:
- through dirty hands, objects and food if they are exposed to the virus;
- drinking contaminated water from a reservoir;
- upon contact with a patient or virus carrier.
The herpangina virus is also transmitted transplacentally - from mother to fetus3.
Up to contents
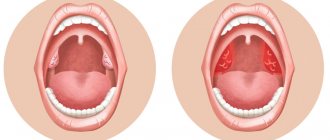
Symptoms of herpetic sore throat
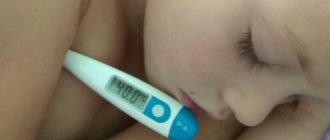
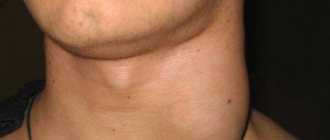
The disease begins acutely. From the moment of infection to the first symptoms, it takes from 2 to 14 days3. The temperature rises to 38-39°C. The patient feels weakness, headache, chills, less often nausea, possible vomiting and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, 1,2,3.
Herpangina goes through several stages2:
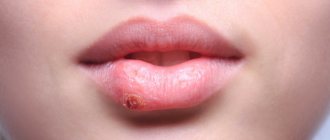
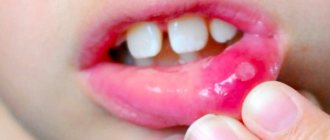
- The day before the rash appears in the throat, the patient feels a mild pain. On examination, you may notice redness of the palatine arches and the back wall of the pharynx.
- Then, rashes appear on the mucous membrane of the soft palate, palatine arches, tonsils and uvula - small papules (nodules) up to 5 mm in diameter with a red rim.
- The nodules turn into vesicles, which open after 1-2 days.
- In their place, painful erosions with a gray-white coating form.
Up to contents
Herpetic sore throat in children
Children usually become infected at school or kindergartens2,3. Due to pain and fever, they are restless, tearful, and often refuse to eat and drink because food irritates erosions on the mucous membrane and causes discomfort. But due to refusal to drink water or juices, children often develop dehydration. At the same time, the child’s tongue becomes dry, and the elasticity of the skin decreases1. Convulsions may occur due to high temperature1.
Blistering rashes in children can appear not only on the mucous membrane of the throat, but also on the hands and feet, and even on the buttocks and forearms. This manifestation of enterovirus infection is called viral pemphigus of the oral cavity and extremities or mouth-hand-foot syndrome. The disease is contagious in 100% of cases, is often mild, and can affect nails3.
Up to contents
How to treat red dots on the sky
Therapeutic prescriptions must be made by a doctor, because it is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. If your throat hurts badly against the background of red rashes, this does not always mean the development of a sore throat. For example, scarlet fever, cancer, tonsillitis and other pathologies will also “show” such symptoms. First, the specialist finds out the true cause of the phenomenon in question and only after that makes prescriptions:
- antibacterial drugs, if the cause of red dots is the settlement of pathogenic bacteria in the oral mucosa;
- antiviral – when a herpes virus is identified as the causative agent of the disease;
- antifungal if fungi are found in the mouth during examination.
As part of complex treatment, local antiseptics are also used, which help eliminate acute inflammation and discomfort. The red throat becomes paler, and it hurts much less, which leads to the restoration of general condition and appetite. These products include solutions “Miramistin”, “Chlorhexidine”. Metrogil Denta, Kamistad (gel) and Solcoseryl will also be effective.
No folk remedies will help, and independent choice of medications will not give results. They, of course, will make the symptoms less pronounced, but without eliminating the main cause of the appearance of red dots on the sky, it will not be possible to solve the problem.
Course of herpetic sore throat
The diagnosis of herpetic sore throat can be made by an otolaryngologist, therapist or pediatrician after examining the patient and clarifying his complaints. To monitor changes characteristic of a viral infection, the doctor may prescribe a general blood test, and to confirm enteroviral sore throat, a specialist may prescribe a pharyngeal smear and a blood test for specific antibodies. The pathogen can also be detected in stool or inflammatory fluid that is released from vesicles1,4.
Manifestations of herpetic sore throat can go away on their own in less than 10 days. But in any case, at the first symptoms of the disease, you should definitely consult a doctor. You cannot self-medicate2,3.
In some cases, herpetic sore throat can cause complications from the nervous system. In this case, 1 appears:
- severe spasm of the neck muscles, due to which the child cannot bend his head;
- weakness of the muscles of the limbs;
- disturbance of consciousness.
A severe complication of herpetic sore throat is damage to the soft membranes of the brain, brain and spinal cord1,3.
Newborns are at highest risk of developing complications, so they need careful treatment and care3. It is important to maintain hydration and give your child enough fluids1.
Up to contents
Treatment of herpetic sore throat
Patients with complications require hospitalization in an infectious diseases hospital and treatment under the supervision of specialized specialists - a neurologist and a cardiologist. If the doctor has recommended treatment at home, it is necessary to closely monitor the patient's condition2.
The sick person should be isolated and stay in a clean, well-ventilated area so as not to infect other family members. Quarantine must be observed until symptoms subside1.
For herpangina you should 1,3,4:
- Wash your hands as often as possible, including after feeding and changing a sick child’s diaper.
- Disinfect surfaces and objects with which the patient has been in contact.
- Drink enough fluids to avoid dehydration. At the same time, pay attention to the temperature of the drink: hot, warm drinks irritate the mucous membranes and cause additional discomfort. You can drink cool drinks.
- Consume food in liquid or mushy form. Spicy, salty, sour foods, including fresh fruits even in the form of puree, are not suitable for a patient with herpetic sore throat.
- Rinse your mouth with a saline solution after every meal to maintain oral hygiene and prevent bacterial infections from erosions.
- Use a soft toothbrush to reduce trauma to the mucous membrane.
Currently, there is no proven antiviral drug to treat herpangina by acting on its causative agent. Sometimes a doctor may prescribe medications that support local immunity of the pharyngeal mucosa1. Antibiotics are not prescribed for herpangina6.
The goal of treatment for herpangina is to relieve the symptoms of the disease4.
If the body temperature is above 38.5°C, physical methods such as cold compresses and ice packs may be used. Your doctor may also recommend anti-inflammatory and antipyretic medications1. Local treatment includes agents with anti-inflammatory, analgesic, enveloping and antiseptic effects1.
For the symptomatic treatment of herpetic sore throat, the doctor may prescribe the drugs HEXORAL®7,8,9,10,11. It is convenient to use HEXORAL® spray to irrigate the pharyngeal mucosa. The active substance of the spray is hexethidine. It acts against the main bacteria found in the oral cavity and pharyngeal mucosa8. The drug is also active against some viruses and fungi of the genus Candida8. Thanks to the local anesthetic effect of hexethidine, HEXORAL ® spray helps reduce pain8. HEXORAL®7 solution is suitable for rinsing. The use of HEXORAL ® spray and solution is allowed in children over 3 years of age7,8.
If herpangina causes severe pain and discomfort, adolescents over 12 years of age and adults can benefit from HEXORAL ® TABS EXTRA lozenges, which contain the anesthetic lidocaine10. For children over 4 years of age, HEXORAL ® TABS lozenges may be suitable. The anesthetic benzocaine in their composition helps reduce pain in the throat and mouth9.
All medications for herpetic sore throat should be used only after consultation with a doctor. In case of severe erosions, HEXORAL ® solution and spray are contraindicated7,8, and lozenges can only be prescribed by a specialist after examining the pharynx9,10.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Possible complications
In the absence of appropriate treatment for a red rash that has formed on the palate, changes in the cellular structure and epithelial tissue are likely.
This can cause the red rash to increase in size and trigger the development of the following diseases :
- Pyogenic granuloma. It is characterized by thickening of blood vessels with disruption of their blood flow. The dots in the sky will change their usual reddish hue to blue. They will interfere with conversation and eating. In the future, they can cause malignancy and can cause death.
- Petechiae of the palate. The last stage of hardening of reddish spots on the sky, when the baby was not helped. It is characteristic of pathology that new ones can form near previous formations. In many situations, such adverse effects are provoked by a rash associated with herpes virus or mononucleosis.
- Kaposi's sarcoma. A red rash of viral origin that is not eliminated in a timely manner can transform into flat growths of bright red color. This pathology, characteristic of children with weak immunity or infected with HIV, is a complex disease with an extremely high mortality rate.
Pyogenic granuloma
Petechiae of the palate
Kaposi's sarcoma
It is possible to eliminate such complications with timely treatment of emerging diseases.
Video about clinical observation of Kaposi's sarcoma:
Sources
- Corsino CB, Ali R, Linklater DR. Herpangina. 2022 Jun 23. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan–. PMID: 29939569. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507792/
- Ter-Baghdasaryan L.V., Ratnikova L.I., Stenko E.A. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of enterovirus infection // Infectious diseases: news, opinions, training. 2022. T. 9, No. 1. P. 88-93. doi: 10.33029/2305-3496-2020-9-1-88-93 https://infect-dis-journal.ru/ru/jarticles_infection/672.html?SSr=2601343bdb01ffffffff27c__07e4040b011a36-9772
- Alacheva Z. A., Rybalka O. B., Kulichenko T. V. Should everyone escape from Coxsackie?! Or fear has big eyes. Issues of modern pediatrics. 2017; 16 (4): 286–290. doi: 10.15690/vsp.v16i4.1774) https://vsp.spr-journal.ru/jour/article/viewFile/1787/713
- Herpangina Brenda L. Tesini. University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry // MSD Handbook - 2019 https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/professional/infectious-diseases/enteroviruses/herpangina
- Kozlovskaya O.V., Katanakhova L.L., Kamka N.N., Evseeva A.N. Epidemiological, clinical and diagnostic features of enterovirus infection in children and adults. Bulletin of Surgu State University. Medicine. 2018;(2):56-60. https://surgumed.elpub.ru/jour/article/view/140/141
- Kuo KC, Yeh YC, Huang YH, Chen IL, Lee CH. Understanding physician antibiotic prescribing behavior for children with enterovirus infection. PLoS One. 2022 Sep 7;13(9):e0202316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202316. PMID: 30192893; PMCID: PMC6128467. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30192893/
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® SOLUTION:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® AEROSOL:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA:
Up to contents
Classification of HRAS (chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis)
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | According to the degree of damage to the mucous membrane: | a comment: | 1) Superficial (catarrhal, fibrinous) 2) Deep (ulcerative, necrotic) |
| classification: | According to the clinical course: | a comment: | 1) acute 2) chronic |
All types of stomatitis occur in children, but the most common are: herpetic, candidal and traumatic stomatitis.