Palate cancer is a malignant neoplasm that forms from the mucous membrane of the hard and soft palate. This is a fairly rare disease. It is more common between the ages of 40 and 60 years. Men get sick 4 times more often than women.
Diagnosis of cancer of the soft and hard palate at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern research methods. The oncology clinic is equipped with modern equipment from leading American and European manufacturers, which allows you to quickly establish an accurate diagnosis. To treat malignant tumors of the palate, surgical interventions, chemotherapy drugs and innovative methods of radiation therapy are used.
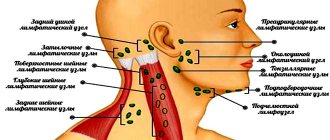
The most malignant tumor of the palate occurs due to metastases of cancer of the nasopharynx and nose. The neoplasm affects the periosteum of the hard palate, lower and upper jaws, muscles and tissue of the oral cavity, and tongue. Atypical cells spread to the submandibular, mental and cervical lymph nodes.
Classification of palate cancer
Based on location, cancerous tumors are divided into 2 types of malignant tumors of the palate. In case of cancer of the hard palate, the malignant neoplasm is located at the border of the nasopharynx and the oral cavity, affects the bone structures and spreads to all layers of the oral mucosa. In the case of cancer of the soft palate, the tumor is localized in the mucous layer and muscles of the vault of the oral cavity.
Based on the histological structure of the tumor, there are 3 types of malignant neoplasms of the palate:
- Cylinder;
- Adenocarcinoma;
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
Cylindroma (adenocystic carcinoma) is formed from glandular tissue. It is characterized by rapid, uncontrolled growth of pathologically altered cells and quickly metastasizes. Adenocarcinoma develops from the epithelium of the oral cavity. The tumor can be localized in all parts of the hard and soft palate. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of oral malignancy. The tumor affects the mucous membrane.
Causes and risk factors for palate cancer
Malignant tumors of the oral cavity occur under the influence of the following provoking factors:
- Irritating effects of aggressive substances contained in cigarettes, alcohol, smoking mixtures;
- Constant consumption of too hot dishes, which burn the mucous layer and change the structure of cells;
- Chronic injury to the palate due to poorly installed dentures.
A tumor in the palate develops against the background of precancerous conditions of the oral cavity - leukoplakia, papillomatosis. They often degenerate into a cancerous tumor under the influence of provoking factors.
Risk factors for the development of malignant neoplasms of the palate include hereditary predisposition, periodic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, vitamin A deficiency, which occurs with poor nutrition or in smokers due to a disruption in the process of its absorption in the body. Palate cancer can be a secondary disease - metastases of malignant neoplasms of the neck and head.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
If swelling occurs, you should ensure a sufficient supply of fresh air, comfortable humidity and temperature in the room, and avoid taking food and drinks that are too cold, too hot, or irritating the mucous membrane of the throat. For swelling of infectious and inflammatory origin, you can gargle with herbal decoctions and use local remedies. In case of allergic reactions, it is necessary to use antiallergic drugs.
An increase in body temperature and signs of intoxication are reasons to contact a therapist or otolaryngologist. Self-administration of antibiotic therapy is prohibited due to the ineffectiveness of this type of treatment without taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, the possible development of side effects and adverse consequences.
Conservative therapy
The treatment regimen may include drug and non-drug methods. For diseases with swelling of the throat, the following are used:
- Local preparations
. Sprays, lozenges, lozenges, and other local dosage forms with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects are effective symptomatic remedies for viral and bacterial infections and help reduce swelling and discomfort in the throat. - Antiallergic medications
. To quickly eliminate throat swelling and other allergy symptoms, antihistamines and mast cell membrane stabilizers are used. - Antibiotics
. Antibiotic therapy is indicated only for bacterial diseases and is ineffective for viral infections. First, broad-spectrum agents are prescribed, then the treatment regimen is adjusted taking into account the antibiotic sensitivity of the pathogens, as determined by the results of smear culture. - Physiotherapy
. For throat diseases, inhalations, ultraviolet irradiation, UHF, laser therapy, ultraphonophoresis, medicinal electrophoresis, and other methods are prescribed. - Intubation.
Necessary for the development of severe swelling of the throat, the threat of asphyxia.
The first signs and symptoms of palate cancer
During the first weeks and months, malignant neoplasms may occur without subjective sensations. In some cases, patients, when touching the palate area with their tongue, notice a small compaction that is surrounded by a cushion. If the patient consults a doctor at this stage of the pathological process, treatment is most effective.
As the cancer progresses, the size of the tumor increases. The tumor invades new areas of the palate and grows deeper. Patients present the following complaints:
- Pain in the oral cavity, which radiates to the ear, temporal region of the head;
- Discomfort while eating, as the process of chewing and swallowing becomes difficult;
- Bad breath;
- Unpleasant taste;
- The change in speech articulation is disrupted due to the fact that the mobility of the tongue changes, and the tumor interferes with the normal movement of air.
- Poor appetite;
- Noticeable weight loss;
- Rapid, unreasonable fatigue.
When examining the oral cavity, plaques, compactions, and ulcers of various shapes and sizes can be seen on the roof of the mouth. In advanced cases of palate cancer, the ulcers bleed and the septum between the nose and throat may collapse. For this reason, pieces of food get into the nose while eating, and speech becomes completely slurred. At the last stage, the cancer tumor destroys all tissue adjacent to the palate.
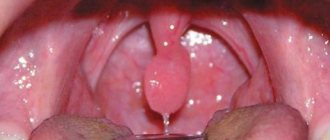
Causes of swelling of the soft palate and uvula
The cause of swelling of the soft palate and uvula is associated with a violation of the integrity of the venous plexus located in the uvula, in particular due to the rupture of a vessel in the uvula and infection of the resulting hematoma by opportunistic microflora of the oral cavity (uvula apoplexy).
This could be the result:
- Injury to the uvula by food, as well as during sudden sneezing or coughing, prolonged laughter
- under the influence of cold or other reasons, under the influence of which a hematoma may occur
- injury or compression by a foreign body or instrument
- venereal diseases (primary syphilis - characterized by the appearance of chancre on the tonsils, soft palate and palatine arches; gonorrheal stomatitis - affects the soft palate, palatine suture, lateral surfaces of the palatine vault, dorsum of the tongue)
- A characteristic symptom of diphtheria is vitreous swelling of the soft palate and especially the uvula.
- drinking alcohol the day before and associated dehydration (dehydration) of the mucous membranes
- smoking tobacco in excess of the usual dose, smoking marijuana, spice
- snoring (the tongue can be injured by vibrating in the air stream)
- hereditary angioedema is a very rare, inherited disease
- taking certain medications, for example, so-called ACE inhibitors (captopril, lisinopril, enalopril, etc.)
Often the cause of swelling of the soft palate is the consequences of pharyngitis, tonsillitis and tonsillitis. Therefore, for reliable recovery it is necessary to eliminate the cause of its occurrence, that is, its treatment must be comprehensive.
Diagnosis of cancer of the soft and hard palate
The resulting cancerous tumor of the palate is difficult to determine independently in the early stages. If the pathological process has affected large areas of the soft or hard palate, a preliminary diagnosis can be made after a visual examination of the oral cavity.
To confirm the diagnosis, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform the following diagnostic procedures:
- X-ray – finds pathological changes in bone tissues adjacent to the oral cavity;
- Biopsy – taking a piece of tissue for histological examination (analysis is necessary to identify altered tumor cells and its type);
- Blood tests - signs of anemia;
- Radioisotope examination - allows you to examine the structure of the neoplasm.
Ultrasound examination is carried out to detect cancer metastases in distant organs. Patients of the Yusupov Hospital can undergo complex diagnostic procedures in partner clinics and receive advice from leading dental oncologists in Moscow.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are carried out by an otolaryngologist. If appropriate indications are identified, the patient is referred for consultation to an allergist, oncologist, or gastroenterologist. The diagnostic plan includes the following activities:
- Questioning, general examination
. The doctor clarifies the time and circumstances of the onset of the symptom, finds out other complaints, and establishes the dynamics of the disease. During the physical examination, the specialist examines the throat, paying attention to specific signs: fever, rash, enlarged lymph nodes, swelling of other areas of the body. - Express diagnostics
. Performed during a consultation, it allows you to reduce the time for laboratory diagnostics and identify common infections. A streptate test and a flu test can be performed. For allergies, allergy tests are performed. - Endoscopic studies
. Depending on the existing symptoms, the otolaryngologist performs pharyngoscopy, direct or indirect laryngoscopy, and endoscopy of the larynx. In case of infectious pathologies and neoplasms, material is collected for subsequent laboratory tests. - Lab tests
. Along with a general blood test, which confirms the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, most often in case of swelling of the throat mucosa, a microbiological examination of a smear is performed to determine the microflora and its sensitivity to antibiotics. If tumor processes are suspected, biopsies are studied during histological or cytological examination.
In some cases, radiography of the nasopharynx, larynx or trachea, and X-ray examination of the lungs are indicated. For GERD, esophagoscopy and gastroscopy are performed. Appropriate tests are performed to identify specific infections.
Taking a swab from the throat mucosa
Treatment of palate cancer
The choice of treatment method for cancer of the hard and soft palate depends on the histological type and stage of the malignant tumor, the extent of the pathological process to nearby tissues. The main method of treating the disease is irradiation of a malignant neoplasm of the palate with X-rays. Radiation therapy can stop the development of cancer cells. If it is started at an early stage, complete destruction of the malignant neoplasm is possible. Radiation is performed before and after surgery.
Surgery for palate cancer involves removing the tumor and the soft tissue and bones located next to it. After surgery, a defect remains on the face, to eliminate which plastic surgery is performed. In advanced cases of cancer, surgery and radiation therapy sessions are performed.
For palate cancer, treatment is carried out with cytostatic drugs. They are administered as droppers or prescribed for oral administration. Chemotherapy for cancer of the soft and hard palate is effective in combination with radiation and surgery. The action of chemotherapeutic drugs is aimed at preventing and eliminating metastatic foci.
Timely diagnosis and selection of a well-designed treatment regimen allow doctors at the oncology clinic to achieve an almost complete cure for 80% of patients. If you experience unpleasant sensations in the oral cavity, contact oncologists and make an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Treatment methods
In most cases, the inflammatory process can be stopped by conservative treatment. Therapy may include:
- rinsing the mouth with herbal infusions and antiseptic solutions,
- treating affected areas with ointments and gels,
- taking painkillers and antipyretics, antibiotics, drugs that stimulate tissue regeneration, vitamin and mineral complexes.
If the inflammation was caused by poor-quality prosthetics, a new prosthesis may need to be installed.