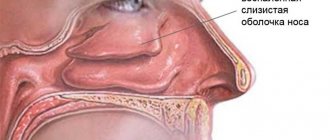
Causes of floss getting stuck
Before you figure out how to get dental floss stuck between your teeth, you need to understand why it gets stuck in the first place. Indeed, according to their structure, floss is thin silky threads that consist of many fibers that mechanically remove plaque. Manufacturers make flosses in such a way that they glide well and do not cause injuries. For example, regular flosses are very thin; they can penetrate even the narrowest interdental spaces. Waxed flosses are slightly thicker, but they are impregnated with wax, which improves glide. So what causes dental floss to get stuck between teeth? Let's consider all possible risk factors further.
Incorrect use
Dental floss must be used carefully, slowly moving it into the interdental space (especially if the teeth are very close to each other). There is no need to make sudden “sawing” movements. So, firstly, the enamel and gums are injured, and secondly, the clamped thread will simply break and get stuck.
Poor quality floss
There is a possibility that if a person “runs into” a low-quality product or a fake, even if floss is used correctly, he will find that the dental floss has broken or split. And its fibers or pieces got stuck between the teeth.
Dental disease
It happens that the floss is of high quality, and a person uses it correctly, but the floss still gets stuck between the teeth. This can happen, for example, if there are cracks and microscopic chips on the side (contact) surfaces of the crowns. And also for caries in the same area. Another reason is the growth of tartar in the interdental space, on which the thread clings and breaks. As a result, she gets stuck.
When should you not use dental floss?
Floss is considered one of the simplest and safest hygiene tools; it is simple and inexpensive to use, just a few minutes of free time is enough. However, even this device has contraindications. It cannot be used in the following cases:
- if your gums are bleeding, you can aggravate the situation and introduce an infection into the soft tissues;
- with periodontal disease - floss can damage weakened gums, provoke bleeding and even inflammation, plus there is a risk of infection on neighboring dental units;
- in the presence of caries - the disease weakens the teeth, makes them brittle and brittle; if floss is used carelessly, fragments may break off from the affected tooth, therefore, before purchasing floss, it is highly advisable to treat the entire oral cavity;
- for any inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity during the period of exacerbation;
- You cannot floss crown and bridge prostheses - there are special threads for such structures.
If you know how to properly brush your teeth with dental floss and use it along with toothpaste and brush, you can achieve excellent results: a charming smile and fresh breath will delight you every day.
What are the consequences
You need to understand that harmful microbes are present in the “narrow” interdental space. Food plaque also accumulates here, in which pathogens “love” to settle. And a floss stuck between the teeth, as well as unsuccessful attempts to pull it out, can lead to the following complications:
- gum injury: bleeding, redness,
- gingivitis, periodontitis, gumboil (periostitis): the transfer of microbes from the thread into the soft tissue provokes superficial inflammation of the gums. Then it invades deeper areas and can “spread” to the gums next to adjacent teeth, to the jaw bone,
- trauma to tooth enamel: a microscopic groove is formed on the lateral surface of the crown, which subsequently deepens. Then microbes penetrate the enamel, causing the development of caries.
Steps to flossing your teeth
- Wash your hands to prevent bacteria from entering your mouth.
- Tear off a thread with a length of 20 to 45 cm. If you are just starting to use floss, you can measure the length using a ruler.
- Fasten the thread to the middle or index fingers of both hands in turn. There should be a section about 5 cm long between the fingers. One hand fixes the floss, the other secures its remaining part.
- Stretch the floss and carefully insert it into the space between the teeth. Cleaning should begin with forward and backward movements.
- Move the floss from top to bottom, pressing it against the side surface of the tooth. All movements must be neat and smooth.
Remember, each tooth should be flossed with an unused piece of floss to avoid transferring bacteria and plaque. Be careful! When using the floss, do not tug or pull it with force, as this may cut the delicate gums.
What to do if the floss gets stuck
How to remove dental floss if it is stuck between teeth? Here you can first try to get it yourself. The following methods are often used for this:
- active rinsing of the mouth with water,
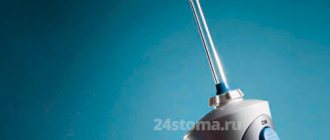
- washing the interdental space with an irrigator or a stream of water from a syringe (without a needle),
- you can try to remove the problematic piece with a new thread (sometimes it is better to use a thinner floss),
- if it’s not a lint that’s stuck, but the whole floss seems to be “jammed,” then you need to carefully cut it off on one side and pull it out,
- You can use clean tweezers.
“Somehow my dental floss got stuck. It just tore and that’s it, both halves remained in my hands. But I feel like something is getting in the way. I tried to pull it out with another thread, and that one also broke. In general, there was no way they could get it from there. The next morning I started to feel pressure on my teeth and had to go to the dentist. They got her there in one fell swoop.”
Lisa_0101, review from the woman.ru forum
What you shouldn't do on your own
Sometimes you can hear or read that stuck dental floss is removed using a fishing line. There is no need to do this, because the fishing line is solid (and floss consists of several twisted threads) and is very strong - that is, it can seriously injure the tissues of the oral cavity. Also, do not use a needle, toothpick, fork tine or knife - one careless movement and injury is guaranteed, or the thread will get stuck even more.
Good to know! As for chewing gum, it can help push out a piece of floss or “stick” it to yourself. But provided that it is not stuck very deeply. However, it may happen that the chewing gum pulled out the floss between some teeth, and pushed the same piece deeply between others - so it got stuck again.
When do you need dental help?
Even a small piece of dental floss can cause quite dangerous and painful pathologies [1] that require timely treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to remove this piece. If you can’t get it at home, you need to see a dentist as soon as possible. A professional will be able to remove it quickly and without problems, especially if he has a special microscope at his disposal.
Read on the topic: a microscope for teeth - an expensive whim of a dentist or a guarantee of quality treatment?
The doctor will also find the reason why the floss is stuck. If the cause is caries or tartar buildup, then appropriate treatment or professional oral hygiene will be carried out.
Errors in dentistry: they made loose contact between the teeth, as a result, food began to get stuck.
Errors in dentistry: they made loose contact between the teeth, as a result, food began to get stuck.
Medicine is a complex science associated with great responsibility.
After all, we are talking about the most important thing: human health. Dentistry is a branch of medicine that deals not only with teeth, but with the entire head/neck area where vital organs are located. Even with the highest qualifications and extensive experience of a doctor, medical errors are not excluded among dentists. This is due to the uniqueness of each person and their clinical situation. In our opinion, the most important thing is to know how to solve problems that arise during the treatment process, and most importantly, to prevent them. Below we will discuss the most common mistake. Patients encounter it after installing a filling - food gets stuck due to the creation of loose contact between the teeth. Connection of all elements of the dental system.
Normally, all teeth are closely intertwined as a single system with each other by a ligamentous apparatus, which is dense connective tissue, parts of which are woven into the bone, gum, and root cement.
In the mouth, the crowns of the teeth tightly touch in the widest part - the equator: in the chewing teeth, pointwise, in the front teeth, tangentially. Since the tooth is an “oval”, the resulting gap below the equator is filled with a triangular interdental papilla, which is part of the gum. Due to the close contact between healthy teeth, the chewing load is evenly distributed throughout the entire dentition. It is also a guarantee of protecting the gums and bones from food bolus ingress and traumatizing them when chewing food. What happens when there is a loss of contact between teeth?
As a result of caries or tooth trauma, when there is a crown defect in the interdental space, this contact is disrupted.
This further leads to an increase in the affected area due to the chronic accumulation of plaque and cariogenic flora there. In addition to it, microorganisms that cause gum disease - gingivitis and periodontitis - like to live in such a secluded place. Well, the most unpleasant complication is dysfunction of the jaw joint and malocclusion. When the anatomical closure of teeth laid down by nature is disrupted, this affects not only the remaining teeth, but also the joint. The patient may be bothered by pain, clicking, limited mouth opening. There are 3 main complaints of the patient when the contact point between the teeth is poorly restored: 1. Pain and bleeding of the gums 2. Bad breath 3. Sticking of food debris and disintegration of dental floss when brushing teeth. What technological errors can lead to this?
1. Insufficient polishing of the seal on the contact.
Due to the roughness and pores, plaque sticks well, and if it is also poorly removed during home cleaning, chronic inflammation occurs. 2. The overhanging edge of the filling on the gum is a long-term mechanical injury, which can lead to inflammation of the gum and its descent (recession) with exposure of the root and, as a result, the occurrence of increased sensitivity and unsatisfactory aesthetics due to the “lengthening” of the tooth. 3. Contact is not restored at all - a gap appears between the teeth, complications as in the previous paragraphs. 4. Restoration of flat tooth walls, without a pronounced equator. 5. Insufficient adherence of the filling to the tooth tissue can lead to relapse of caries at the filling/tooth interface. 6. Exceeding the indications for the filling. When a tooth is destroyed by more than 1/2, it is worth restoring it using inlays or onlays made of composite or ceramic in a laboratory. This will allow you to create a perfectly fitting structure that restores the anatomical shape on a model of your teeth, and subsequently fix it in the oral cavity. What picture does a doctor most often see before treating contact caries or a defect in a contact filling?
The tooth is often severely damaged, and if previously treated, the filling is defective or with secondary caries, the interdental papilla is inflamed, and bleeding is pronounced.
If this condition exists for a long time, the position of the teeth may change. If there is a formed gingival periodontal pocket, it is necessary to remove the traumatic factor and carry out anti-inflammatory periodontal treatment before the final restoration. During this period, the doctor restores the tooth with a temporary filling or crown. What steps need to be taken to avoid this complication?
1. Compliance with dental treatment protocols, which certainly includes isolation using a rubber dam system. During the treatment process, saliva, blood, and water entering the formed cavity greatly disrupt the action of the components of the filling material. 2. Knowledge of the anatomy of each tooth, coupled with the correct selection of matrix systems to restore the contact point. 3. High-quality final processing of the restoration: grinding and polishing using pastes, brushes, rubber cups, etc. 4. Use of tooth restoration options “according to indications.” Where it is necessary to do this with an orthopedic construction, do not place a filling. We hope that the article has become the answer to your questions; we will be happy to advise you at a personal meeting at the Familyist Arkhangelsk dentistry if you have any questions.