20.11.2019
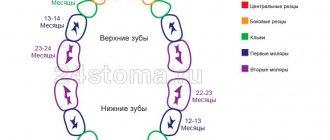
The eruption of baby teeth in a child is a gradual process, and it takes approximately 2-3 years until all 20 baby teeth erupt. Initially, when the first baby teeth erupt, children, as a rule, experience difficulties of various kinds. So, at the age of 3-9 months, children may increase salivation, they begin to bite and gnaw at everything, and they may experience shooting pain in the ears.
In this case, parents may assume that the child is actively teething. In addition, during this period children become extremely irritable and whiny. If you experience shooting pains in the ear, it is important to make sure that they are not associated with an infectious ear disease, since many of the symptoms of teething and ear infections are similar. While teething is a natural process and there are many ways to help your baby get through this difficult time, ear infections (ear infections) require special medical evaluation and treatment.
Why does toothache radiate to the ear?
The cause of illness does not always lie in viruses, as a result of the flu. The culprit may be a growing unit or the removal of a masticatory organ. Discomfort on the left side is associated with advanced caries or periodontal disease when the same side is affected. Through the canals of the teeth, bacteria quickly penetrate into the ENT organs. The provoking factors by which oral diseases provoke ear tingling or lumbago are varied.
- Pathologies of the extreme molars of the upper jaw affect the hearing aid, since their roots are located nearby.
- Inflamed soft tissues and nerves of abnormal units have an adverse effect on the ears. Ripple, which intensifies when pressing on the diseased crown, indicates problems in the oral cavity.
- Pathological eights, which have a powerful branched root system, can negatively affect the hearing aid. For example, wisdom tooth decay can cause tingling in the ear. When third molars grow abnormally, soft tissues and facial muscles become inflamed.
- Complications to the hearing organs are caused by injuries to the crowns, roots or soft tissues of the oral cavity. In such a situation, swelling occurs.
- Removal of molars when the surgical socket swells and festers.
- The ear canals suffer from cysts of the masticatory organs.
- Inflammation of the nerve fibers of the tooth.
- Malocclusion.
- When the anatomical integrity of the crowns or roots on the right side is damaged, there will be a tingling sensation in the ear on the same side. Mechanical impact aimed at the soft tissues of the oral cavity or the root of the unit provokes swelling and pulsating pain in neighboring organs, on half of the face.
Of course, the inflammatory process can be localized in the middle ear. With otitis media, discomfort can be traced in the jaw.
Child fiddling with ears
24.11.2020
At times, as a result of long-term observation, new parents notice increased attention from the baby to the ear . The child picks at his ears , so much so that he can involuntarily scratch the skin with his nails, trying to remove the cap he is wearing. The best scenario in this case is that a lint is discovered by the parents, which accidentally came from a cotton swab and creates anxiety for the newborn. However, in most cases, the occurrence of such a phenomenon is based on quite serious violations.
Causes of the phenomenon
In order to allay parents' concerns, it is indispensable to master some theoretical aspects regarding the reasons why a child touches his ears . At a minimum, such knowledge will allow them to achieve calm in the absence of compelling reasons for groundless panic, and at maximum, it will guarantee the ability to independently eliminate the underlying factors that caused the formation of such an unpleasant phenomenon. By following instructions for overcoming discomfort, parents will be able to neutralize the sensation of itching, which can affect the quality of children's sleep.
Among the main reasons why a child picks his ears are:
- the presence of fungus in the area of the external auditory canal;
- the presence of an allergic reaction to a certain external or internal irritant (as a result, the child touches the ears , and may also focus on the eyes and nose ; there is a possibility of a runny nose for no apparent reason);
- the appearance of purulent phenomena followed by discharge from the ear canal (in the presence of otitis media );
- desire to explore one’s own body and body parts;
- manifestation of a natural desire to go to sleep or get the necessary food;
- the presence of skin diseases;
- lack of sufficient level of personal hygiene;
- the likelihood of teething (especially important for 6-8 months of age);
- the result of bites of various insects.
In the case of continuous mechanical impact from the child on the ear , increased attention should be paid to determine the reason for the appearance of such interest. The ability to identify an irritating factor and its subsequent elimination guarantees the disappearance of the child’s anxiety. Despite the existence of home options for resolving this situation, one should not forget about the importance of obtaining qualified advice from the attending physician regarding the child’s health condition and recommendations regarding the necessary treatment and prophylactic complex.
Treatment methods
Among the existing options for treating discomfort in a child are:
- systematically carry out hygienic procedures of the ear canal (it is necessary to pay attention to the absence of villi after the procedure);
- neutralize possible contacts with allergenic factors (plants at the time of flowering, dust, animals);
- create a well-functioning daily routine (due to the occurrence of skin diseases as a result of disruptions in the children's nervous system );
- take a vitamin course for a nursing mother;
- eliminate possible acts of prescribing medications for infants (to do this, you need to visit your doctor );
- periodically bathe the child in a bath with the addition of anti-inflammatory herbs (chamomile, string, oak bark).
If there are no visible results after carrying out the measures described above, it is strongly recommended to visit a specialist in order to receive recommendations regarding the implementation of treatment and preventive measures.
Published in Otorhinolaryngology Premium Clinic
Finding the cause – who to contact?
Pathologies of the molars often lead to pain in the ears and jaw, and the pain radiates to the temple. To avoid serious complications, you should consult a general practitioner in time. If necessary, he will refer the patient to a dentist, neurologist, ENT specialist, or endocrinologist. If your visit to the doctor is delayed, you can take a pain reliever. But this measure is temporary. When eights grow, some patients even have trouble hearing. This situation is especially typical with the growth of third molars in the upper jaw. For diagnosis, visiography is done. Based on its results, the patient is referred to a dentist or otolaryngologist.
Pain in the area of the auditory organs causes pulpitis. In this case, the dentist must eliminate the inflammatory process that occurs in the nerve fibers. You cannot self-medicate so as not to aggravate the situation and lose one unit. For successful therapy, the root cause of the pathology must be removed. Before going to the dental office, you can rinse your mouth with a solution of chlorhexidine, infusions of sage, oak bark, and chamomile. Warming compresses should not be used to prevent flux from forming and spreading the infection.
Measures taken during teething and treatment of otitis media
Teething in children is a natural process that causes discomfort to the child, but is amenable to measures that do not require serious drug treatment. You can, for example, lightly massage your child's gums to soothe irritation. You can lubricate your gums with clove oil or vanilla extract. Teething rings or chilled foods are used that can be given to the child to chew on. It is important that the object that enters the child’s mouth is very clean so as not to cause infection. If these measures don't help, you can give your child a pain reliever.
If the child has a very high temperature and there are other symptoms of otitis media, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician or pediatric ENT doctor. Mild forms of otitis can be managed without medication, while serious forms will require antibiotic therapy (although pediatricians are generally not inclined to prescribe antibiotics for children under 6 months). Applying warm compresses to the sore ear may also help. Since the precursors of otitis media are usually the flu, runny nose or allergies, make sure that all measures are taken to prevent the development of these diseases.
Category Children Published by Mister stomatolog
Preventive measures
Units with a hollow, even in the absence of discomfort, are a source of infection. Caries can cause ENT problems. Therefore, do not put off visiting the dentist if your tooth hurts and radiates into your ear. To prevent pathology:
- You need to visit the dentist regularly. This minimizes the risks of developing oral diseases. The dentist will identify the problem at its inception and correct it in a timely manner.
- You should carefully care for the oral cavity, clean the chewing organs twice a day, use floss, irrigator, and rinses.
- Timely treatment of viral and infectious diseases is necessary. Untreated flu often causes otitis media.
- It is necessary to prevent inflammation of the nerves by strengthening the body's defenses.
- You should eat a balanced diet and lead a healthy lifestyle.
The lack of preventive measures and treatment of diseases leads to serious complications.
Teething and otitis media in babies
Parents should be able to clearly distinguish between the symptoms characteristic of teething and otitis media. While older children can tell what's bothering them, toddlers are not yet able to do so, so parents must be extremely careful as the symptoms are similar in the two cases of ear pain, and the causes (and therefore treatment) ) are different.
Inflammation of the middle ear (otitis) is a common disease in very young children. A child suffering from otitis may be very irritable and may refuse to eat. Meanwhile, the same thing often happens when his first teeth are cut.
What is the connection between the process of teething and shooting pains in the ear? Although such ear pain is typical for infectious diseases of the ear, the occurrence of pain during teething is due to the proximity of the ear and jaw muscles. Pain that occurs in the gum can radiate to the ear or cheek. Therefore, children may rub their cheek or ear, but in fact the cause of the pain is in the gum, at the site of tooth eruption. The child experiences discomfort in places other than where it really hurts.
However, although teething can mimic ear inflammation, there are some factors that can help differentiate ear infections from teething. For example, when teething, the child’s body temperature may increase only slightly, and high temperature is not typical for this process. When a baby is teething, he will not be capricious all the time, but only when the tooth is actively cutting. With an ear infection (otitis media), the child may cry inconsolably for a long time.
More often, middle ear inflammation occurs in children who have recently had a runny nose. Otitis occurs, as a rule, with the onset of cold weather (in the hot season, otitis is rare). In addition, characteristic signs of otitis media include fluid accumulation or swelling in the ear. You should consult a pediatrician or ENT doctor if you feel that your child has become less responsive to sounds.