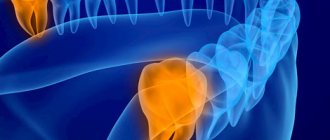
The problem occurs several weeks before the eruption of a baby or permanent tooth. The appearance of a cyst is indicated by a bluish-purple spot (hematoma). This is due to difficulty in tooth eruption.
An eruption cyst is a type of soft tissue benign tumor that appears when a tooth has already begun to erupt through the gum. Scientists and doctors have not agreed on why it occurs. The most likely causes: infection, trauma, improper development of teeth, which causes a lack of space for the “newbie”. In addition, it may be a consequence of caries and improper care.
Eruption cysts occur during the growth of baby teeth or, more often, at 6–9 years of age, when permanent teeth emerge. The fact is that, due to its anatomical structure and location, the chewing group of teeth is the most difficult to erupt.
If you notice a large formation in your baby’s mouth, in the place where a tooth should appear, consult a doctor. Do not resort to self-medication under any circumstances. Infusions, rinses and even strong antibiotics most likely will not help, but ruining a child’s health in this way will cause serious harm.
If you contact a specialist, treatment can follow one of two scenarios. In the most favorable option, the doctor will advise giving the child toys, special teethers, crackers - everything that the baby can chew. This will help break through the mucous membrane.
In difficult situations, surgery may be necessary. Then the surgeon will cut the gum under local anesthesia. This will make teething easier.
It is forbidden to try to cut or tear the mucous membrane on your own; you can cause a serious infection or injure your baby.
Causes of Teething Cysts in Children
During teething, a hematoma is formed; it occurs due to the fact that the tooth cannot break through the mucous membrane and thereby injures the gums and ruptures blood vessels. The longer the formation is in the oral cavity, the larger its size; in addition, the amount of swelling will depend on the group affiliation of the tooth.
The main causes of the tumor:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- periodontitis;
- improper tooth treatment or lack thereof;
- eruption injuries.
The baby’s body tries to limit the source of infection, which is why a dense protective capsule is formed, which eventually develops into a cyst. The occurrence of such formations is quite common. An infection caused by carelessness, an unsuccessful attempt to chew hard food, a fall that led to a tooth injury - all this can serve as a starting point for gum inflammation and further development of a cyst.
Another fairly common mistake parents make, which can lead to the appearance of a tumor during teething, is negligence in caring for baby teeth.
It is generally believed that you should take serious care of your dental health after changing them. Since there is no point in treating non-permanent baby teeth - they will soon fall out. In fact, not taking things seriously leads to many problems. Any gum diseases and oral infections should be eliminated in a timely manner, regardless of how many teeth the baby has and whether they are permanent or not.
Why gums may turn blue
Experts identify a large number of factors that can affect the condition of the gums.
Reasons for discoloration of gums in a child:
- Eruption of baby or molar teeth. Due to strong mechanical pressure on the soft tissue vessels, a blue hematoma appears.
- Bruise or cut. Due to mechanical trauma to the gums, a blood clot accumulates at the site of the bruise, causing the gums to turn blue.
In an adult, soft tissues may change color for the following reasons:
- Improper functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Kidney diseases;
- Problems with the thyroid gland;
- Inflammatory diseases of teeth and gums: gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, herpetic and candidal stomatitis, which are accompanied by increased accumulation of bacterial plaque on the enamel.
- Carious formations localized in the cervical area of the tooth.
- Errors in orthopedic treatment. An incorrectly made crown or denture reduces blood flow along the gingival margin, which causes the periodontium to turn blue. In this case, the color change occurs due to a violation of the blood supply to the soft tissues.
- Surgical interventions. After tooth extraction, the soft tissue in the area of the formed hole may turn blue.
- Burns (regular thermal or chemical burns). A chemical burn can occur due to contact with the mucous membrane of an aggressive substance that is used in the treatment of root canals.
Complications with cyst growth
Tooth trauma, advanced caries, nasopharyngeal or periodontal disease, dental malformations - one or more of these factors can lead to the development of a cyst. The danger is that the cyst grows unnoticed. It usually does not hurt and at the initial stage does not cause discomfort or reaction of the lymph nodes. With further development, suppuration and various unpleasant sensations may appear. But even if there is no pus, the cyst is very dangerous. Therefore, do not delay treatment.
A cyst can lead to intoxication of the body due to the fact that waste products of harmful microorganisms enter the blood. The consequence of this can be headaches, high fever and, in the worst case, sepsis.
In addition, complications are caused by local problems - phlegmon, abscesses, osteomyelitis. These complications are inflammatory in nature and often occur when the cyst suppurates. The spread of pus can lead to destruction of the jaw bones, damage to the internal organs of the digestive system, liver, and heart.
It is impossible to avoid the appearance of a cyst, but if you properly care for baby and permanent teeth and treat infections in a timely manner, you can reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. In addition, periodic visits to the dentist will allow you to notice the problem at an early stage, when treatment will be as simple and easy as possible for the body.
Symptoms
In addition to visual changes in soft tissue, the following symptoms may occur:
- pain when eating and brushing teeth;
- itching;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- the appearance of bleeding;
- abundant plaque on the teeth and the appearance of mineralized deposits.
Symptoms depend on the cause of the pathology and on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Eliminating cyanosis of soft tissues is the first step in treatment and in making the patient feel better.
When to seek help from a specialist
- The blue color of the gums does not subside for more than four to five days;
- Blue discoloration is accompanied by swelling and bleeding;
- Acute pain appears that is not relieved by painkillers;
- Body temperature can rise to 38 - 39 degrees;
- Loss of strength, general weakness.
Ignoring the disease is fraught with the development of serious complications, including the formation of an intraoral cyst.
Cyst treatment
A dental cyst is treated either with therapeutic methods or with surgical intervention. The first ones are used in simple cases.
Surgery involves two types of operations - cystotomy and cystectomy. In both cases, local anesthesia is used. With cystomy, only the anterior wall of the cyst is removed. This is a less traumatic option, as it allows you to preserve the rudiments of permanent teeth during surgery on milk teeth.
Cystectomy is performed if the size of the cyst does not exceed 1.5 cm. This operation is more difficult, but postoperative recovery is much faster.
No matter how small and insignificant the swelling may seem to you, contact your dentist. This will avoid complications. And the problem will be resolved more easily and in a short time. Remember that no rinses, infusions or other folk remedies can guarantee recovery.
Main reasons
Why can one or more teeth turn blue? There may be several reasons for this; sometimes there is nothing dangerous to health in this process, and sometimes this is a reason to urgently seek advice from a dentist. A change in shade is possible due to poor quality nutrition or adherence to a strict diet. This can also happen if you eat a lot of fresh berries, such as blueberries, blueberries or blackberries.
Newly installed fillings may differ in color from natural tissues. A pulpless, that is, dead tooth can also change its color. This is explained by the fact that when the pulp is removed, nutrients stop flowing to the tissues.
If a seemingly healthy tooth begins to turn blue, this may indicate that there are problems with the root system. This is usually preceded by serious dental diseases. In addition, the cause of blue enamel may lie in the patient’s body; this phenomenon may be caused by the presence of chronic diseases or problems with the digestive system. Another common reason is the use of low-quality water with high levels of iron.
How to avoid complications
To avoid missing a cyst in the early stages, check with your dentist at least once every six months, especially if your child has chronic pulpitis or periodontitis. The occurrence of cysts is most likely between the ages of 6 and 12 years, especially during the formation of the first molars in the lower jaw.
Teach your child proper and regular oral hygiene. This will reduce the likelihood of inflammation and caries in both milk and permanent teeth. For this, use high-quality children's toothpaste for a specific age. Asepta has developed Baby, Kids and Teens pastes that take into account the dental needs of children of different ages. For the little ones, specialized Asepta wet wipes designed in the form of finger pads are suitable - wipe the gums after each feeding.
It is necessary to treat infections and caries in a timely manner so that they do not lead to the formation of a cyst in the future.
A lump above a tooth on a child’s gum: causes
What parents call a “bump” may have different names, different causes, and require different approaches to treatment.
Periodontitis
After hypothermia or acute respiratory viral infection with decreased immunity, purulent processes on the roots of damaged teeth worsen. Then the child develops a painful lump with a white center on the inflamed gum and a very bad breath. This is a small abscess that signals the need to see a dentist.
Purulent fistula
A child often has a red lump on the gum, up to 1 cm in size - soft and practically painless. This is what a purulent fistula looks like - a passage into the bone from the source of inflammation at the root of the tooth to the gum. Pus periodically flows through this channel. Due to the presence of drainage, such a fistula does not cause discomfort to the baby in the form of pain.
The fate of a tooth can only be decided by a dentist, taking into account the condition of the hard dental tissues, the size of the pathological focus and its effect on the permanent follicle (bud). A purulent lump on a child’s gum disappears after comprehensive treatment of the tooth; in severe cases, it has to be removed.
Periostitis
A lump with pus on a child’s gum sometimes appears near a damaged or previously treated tooth. If the soft tissues around are swollen, hyperemic and painful, then we can conclude that inflammation of the periosteum has developed - periostitis, which is commonly called “flux”. In children, this condition is accompanied by fever and deterioration of well-being. This is a dangerous disease that can develop into osteomyelitis or phlegmon. The help of a dental surgeon is required.
Cyst
Much less often, when a child has a lump on his gum, a cyst is diagnosed - a purulent sac at the top of the root, prone to aggressive growth. With significant magnification, the cyst looks like a very dense rounded bulge on the gum of a normal color. Next to it there is a decayed tooth - the culprit for the formation of the cyst.
This tumor is removed by a dental surgeon. The cyst is not prone to spontaneous resorption.
Hematoma
During teething, a child sometimes develops a blue lump on his gum. This is a bruise - a hematoma that occurs as a result of damage to a blood vessel by an erupting tooth.
To prevent purulent inflammation from developing, the surgeon dissects the gum above the site of blood accumulation under anesthesia.
Localized gingivitis
Trauma to the soft tissue of the gums (sharp bone, sharp object) can lead to infection and inflammation of the wound with the formation of swelling. Complex conservative treatment helps stop the pathological process.
Benign neoplasm
A tumor of the gum or bone is usually discovered by chance, because for a long time the lump on the child’s gum does not hurt or cause concern. Its density varies. Requires surgical removal.
Exostosis
Occasionally, a child near a tooth, usually on the lower jaw on the inside, has a lump on the gum, which is a small bone growth. It does not require any treatment, because... is a feature of the anatomical structure and does not cause any discomfort.
Treatment options
The choice of one or another treatment method is made by the attending dentist based on the diagnosis and visual examination of the small patient.
Treatment of a bruise from an injury on the gum
If you are sure that the bruise on the child’s gum is the result of an injury, you can try to provide the child with first aid, which consists of using the following methods:
- applying cold compresses to the injured half of the jaw,
- rinsing the mouth with decoctions of chamomile, calendula and sage.
If the bruise does not resolve for a long time (more than 5 days), and the main symptom is accompanied by severe pain and a rise in temperature, then most likely an inflammatory process has begun deep in the gums. In this case, medical assistance is necessary , which may consist of both the use of medications and surgical intervention.
Treatment of a cyst on the gum of a child
Treatment of the cyst is prescribed by the dentist after examining the child. There are two ways to do this:
- if the cyst formed during teething . In this case, experts recommend using special teething toys that help break the tissue and speed up the process of tooth extraction. If this technique does not help, and temperature is added to the main symptoms, it is possible to use a technique for dissecting the upper layer of the mucosa,
- if the cyst is large and accompanied by pain . In this case, the surface of the “blue bump” is usually dissected and the bloody or purulent contents are removed. After which the wound is treated and washed. In some cases, complete healing may require several visits to the dentist.
Medicines are usually not prescribed for blue gums. The only exceptions are those cases when the hematoma is accompanied by the formation of an abscess and an increase in body temperature.
Treatment of gingivitis
In this case, experts recommend resorting to plaque removal and prescribing anti-inflammatory rinses. In some cases, antibiotics are used as a rinse solution.
Painkillers
If the blueness is accompanied by severe pain, the child can be given painkillers. The most popular are “Ibuklin”, “Ibufen”, “Nurofen” and many others. In addition, you can use analgesics in the form of suppositories, for example “Viferon” - suppositories that, in addition to pain relief, have an antiviral effect. In addition, you can use special dental gels:
- "Holisal"
- "Kamistad"
- "Baby Doctor"
Memo for parents. Actions for trauma to temporary and permanent teeth in children
• In summer, the physical activity of children and adolescents is especially high - jumping, running, cycling, skateboarding and roller skating, playing outdoors and visiting rope parks sometimes lead to falls and injury to temporary and permanent teeth.
• Unfortunately, many parents do not immediately seek dental treatment for children due to injury, but only after the development of inflammatory complications or in order to eliminate aesthetic problems. Often, some injuries to the children's dental system are completely ignored by adults.
• There is a misconception that an injured temporary tooth will still be replaced by a permanent one, so it is not necessary to show the child to a pediatric dentist. Meanwhile, if a temporary tooth is injured, not only its root can be damaged, but also the germ of the permanent tooth. This subsequently leads to the development of complications such as underdevelopment of permanent tooth enamel (enamel hypoplasia), disruption of its formation, and even death of the permanent tooth germ. In the latter case, the absence of a tooth in the dentition can lead to malocclusion and the need for orthodontic treatment.
• Dear parents! Experienced pediatric dentists at the Jasmine Clinic have prepared for you a memo on the sequence of actions in case of trauma to the dental system in children and adolescents.
• Immediately after the injury occurs, it is necessary to reassure the child and not show your confusion and excitement. Set your child up in a positive way, convincing him that you know how to act correctly in such a situation.
• Try to get an appointment with a pediatric dentist as soon as possible. Call your loved ones or friends who will urgently begin searching for a qualified pediatric dentist, followed by making an appointment as soon as possible.
In such a clinical situation, the doctor will try to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible and begin measures to save the injured tooth. If the damage is serious, you need to inquire about the availability of not only a therapist, but also a surgeon in the clinic, since tooth extraction and/or suturing of soft tissue may be required.
• Ask the child whether his general condition has changed after the injury - whether there has been any memory impairment (does he remember what preceded the fall or hit an object and what happened after that), whether dizziness, flickering of “spots” before the eyes occurred, nausea, vomiting, headache. Chipping and dislocation of teeth can be accompanied by a concussion, therefore, if there is a change in the general condition, a mandatory examination by a neurologist is necessary, along with actions to save the injured or dislocated tooth.
• Examine the child's oral cavity to understand what happened to the teeth during an impact or fall. After all, even minor injuries such as chipped enamel or a bruised tooth do not go away without consequences. It is very important to see your dentist on time! Pay attention to the preservation of the soft tissues of the lips adjacent to the injured tooth, bleeding of the dentogingival groove of the injured tooth, and its displacement outside the dentition. The cause of tooth injury is usually a blow to it. And, nevertheless, injuries are different: tooth bruise, tooth dislocation (complete or incomplete), tooth fracture (at the level of enamel, dentin, dental pulp or longitudinal tooth fractures), tooth root fracture, tooth germ injury and combined injuries. The simplest of the above types of injuries can be identified immediately by a number of symptoms. If it is a tooth bruise: the child may experience pain, especially in the first hours after the injury, which intensifies when biting. If this is a dislocation of a tooth, then significant pain, which intensifies when biting, is combined with its mobility. Diagnoses of “tooth fracture”, “tooth root fracture”, “tooth germ injury” can only be made by a dentist after an X-ray examination.
• If a tooth or part of it is missing, try to find it as quickly as possible, enlisting the help of others.
• If you find a tooth or its fragment, get to the nearest pharmacy as quickly as possible, buy a test container, saline solution and miramistin. You can use milk instead of saline solution.
• Place the tooth or its fragment in a container with saline solution or milk.
• Treat the child's oral cavity with miramistin.
• If a child, in addition to a dental injury, has suffered a bruise with damage to soft tissues (hematoma, bitten wound of the lips), buy a briquette with frozen meat or minced meat at the nearest grocery store, wrap it in a napkin and apply it every 2-3 minutes with the same breaks to the skin in projections of damage. Under the influence of low temperature, the vessels will contract, bleeding, swelling and pain will decrease.
• If a tooth is dislocated (complete or incomplete), it is important to consult a dentist as soon as possible - within 1 hour! This will give you a good chance of saving your child’s tooth. There are cases when informed parents bring in their hands a child’s tooth that has fallen out due to an injury. If the condition of the bone tissue at the root of the tooth allows, then an experienced dentist, after X-ray examinations and special preparation of the oral cavity, will be able to put the tooth back into the socket and splint it, that is, strengthen it to the neighboring teeth. A successful manipulation, with full compliance with all the recommendations of the dentist, allows you to save the injured tooth for a long period.
• If you consult a doctor within the next 2 hours after injury, the tooth also has a chance of being saved. With each subsequent hour, these chances decrease significantly. When contacting 6 hours after injury, the likelihood of saving the tooth after its reposition is very low. A permanent tooth that has been completely dislocated from its socket can and must be returned to its place as quickly as possible, but not on your own! This should be done by a doctor.
• Primary teeth cannot be repositioned. If, as a result of a fall in 2-3 year old children, the front temporary tooth has penetrated deep and disappeared under the gum, after 2-3 weeks it may come out on its own. But an urgent consultation and examination by a dentist, as well as systematic monitoring of a child’s injured tooth, are strictly necessary!
• A high-quality diagnosis before dental treatment in case of injury to the dentoalveolar system is the first thing a dentist does. The standard set of studies is a targeted (using a radiovisiograph) or panoramic (orthopantomograph) image, 3D diagnostics depending on the nature and severity of the injury, as well as electroodontodiagnostics (EDD) to check the viability of the dental pulp. To exclude a fracture of the root of an injured tooth and to identify the integrity of the adjacent bone tissue, targeted radiovisiographic images are necessary, and for sufficient information in case of chipped teeth, not one image is needed, but several, taken in different projections. Splintered fractures of the crowns of the anterior teeth can be accompanied by the penetration of small fragments into the soft tissues - the adjacent areas of the lips. To exclude this complication, an X-ray examination of soft tissues - lips - is also performed.
• For 2 weeks after treatment, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet (purees, soups, cereals) with the exception of hard foods.
• To prevent inflammatory complications, high-quality systematic oral hygiene using a soft toothbrush, as well as toothpaste and herbal rinse is important.
• A patient with dental trauma should be under dynamic observation and examined by a dentist after 2 weeks, 1, 3,6.9 and 12 months, and then 3 times a year.
• As a rule, children with malocclusion are susceptible to injury because protruding teeth are damaged when they are hit or fall. Early detection and timely treatment of malocclusion pathology is the prevention of traumatic dental injuries in children.
Dear parents! The pediatric dentists at the Jasmine Clinic are always ready to respond to a call for help and choose the best restorative treatment option for your child if an injury suddenly occurs. Let our little patients receive only pleasant emotions and a charge of vivacity, being in constant motion, surrounded by our common care and attention!
Causes of blue gums in adults
The reasons may be different, the most common include:
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- thyroid diseases;
- kidney pathologies;
- stomatitis;
- inflammatory periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease;
- caries and its complications;
- improper orthodontic treatment;
- incorrectly selected or incorrectly manufactured orthopedic design.
- a consequence of surgical intervention (blue discoloration of the periodontium can occur after tooth extraction);
- chemical (exposure to the mucous membrane of an aggressive substance used in the treatment of root canals) or thermal burn (exposure to high temperatures on the gums).
Teething symptoms
The main signs of dental development:
- swollen gums;
- restless sleep;
- increased salivation;
- poor appetite;
- elevated temperature;
- general weakness.
You will notice that the child will try different objects on the tooth, pulling everything into his mouth to scratch his gums. This means teeth will appear soon.
Baby with teether
It is important to pay attention to unusual symptoms such as cough, nasal congestion or stomach upset. Such problems may be a specific reaction of the child to teething or a sign of more serious problems; it is better to immediately consult a pediatrician.
The appearance of a hematoma
- The formation may be white in the shape of a ball, have a red tint or darken.
- Usually the bruise is located at the site of the new tooth. Size up to 2 cm.
- A hematoma appears before the tooth erupts and resolves within 3 weeks.
Pay attention if:
- dark spots appear throughout the child’s mucous membranes;
- there is inflammation, suppuration or infection in the affected areas;
- itching and bleeding gums;
- general painful condition of the child.
In this case, immediately go to a specialist to avoid disastrous consequences. Do not use traditional methods and remedies. They are ineffective and will cause more problems.
"Shark Teeth"
During the process of root resorption, baby teeth become loose and, pushed out by growing permanent teeth, fall out. But sometimes the mechanism of this process fails. The permanent tooth has time to grow before the milk tooth that precedes it falls out.
Sometimes a whole row of such permanent teeth grows parallel to a row of milk teeth, which, for some unknown reason, do not fall out. Such teeth are usually called “shark” teeth, by analogy with the dentition of sharks, in which the teeth grow in three rows.
Studies have confirmed that “shark teeth” do not cause problems in the long term. When a baby tooth falls out, the “shark tooth” begins to shift and takes its normal place.
Treatment of blue teeth
If during diagnostics it is determined that the cause of blueness of all teeth is the use of special products, the dentist or hygienist may prescribe a professional cleaning of the oral cavity. Quite often the patient requires enamel polishing; this allows for the best results.
If after such manipulations the blue discoloration does not disappear, you can try other methods.
First of all, the doctor should send the person for an X-ray examination of the jaw, this will make it possible to make a correct diagnosis, as a result of which the treatment will be as effective as possible. It may also be necessary to remove previously installed fillings and caries-infected hard tissues. If necessary, treatment of the annals and root system of the tooth will be prescribed.
There are several methods to restore the original whiteness of your teeth. One of the most common options is the installation of a composite filling, that is, direct artistic restoration of a row. A more expensive procedure is the production of an artificial crown or special onlays - veneers (indirect restoration).