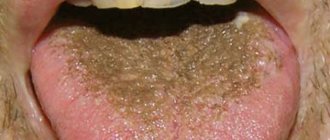
- Uncontrolled use of potent drugs and antibiotics;
- Weakened immunity;
- Presence of AIDS, HIV;
- Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- Damage to internal organs and systems;
- Poor nutrition;
- Alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction;
- Infectious diseases;
- Dehydration of the body;
- Avitaminosis;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms and their manifestation
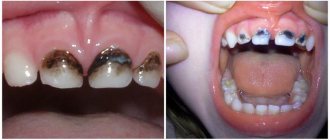
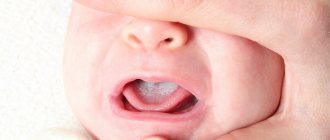
Oral diseases can be diagnosed independently at home. It is only necessary to notice changes that have characteristic signs of a pathological process:
- The appearance of itching, burning or pain;
- Swelling;
- Formation of ulcers and pustules;
- Bleeding gums;
- Damage to tooth enamel;
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- Weakness and sickness.
Classification
Oral cancer is divided into three types:
- papillary. The nodule in the mucous membrane increases in size and hangs into the oral cavity. The neoplasm progresses slowly;
- infiltrative. The seal on the pinkish mucosa is distinguished by a whitish color, clear contours and shape, and thinning of the membrane around it. On palpation from the side of the cheek, a dense infiltrate is felt. The tumor tends to grow rapidly. The patient complains of unbearable pain;
- ulcerative The most common form of the disease. Ulcers on the mucous membrane do not heal, they grow, and the border around them turns red. The outline is torn and its edges are bleeding.
Tumor metastases appear quickly. Malignant cells grow into the mental, submandibular, and deep jugular lymph nodes. This process is influenced by the thickness and depth of the tumor. Thus, when the tumor deepens by 4-5 mm, metastases occur in 98% of cases. At the T1 stage of oncology, metastasis is detected in half of the cases, and when the T4 stage is reached, distant spread of cancer cells is observed in 85% of cases.
The most common diseases of teeth and gums
- Caries.
This is a common problem that affects almost every person at different ages. At the first stage of development, spots appear on the enamel, and as a result of development, hard tissues are destroyed;
- Gingivitis.
An inflammatory process that causes swelling and tenderness of the soft tissues. If treatment is not treated in a timely manner, the problem worsens and becomes chronic;
- Periodontitis.
A popular problem in which the initial stage is asymptomatic. Pain and discomfort appears after damage to bone and soft tissue;
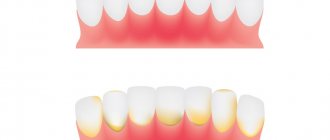
- Periodontal disease
is expressed in periodontal damage, which can lead to tooth loss. Therefore, it is important to start treatment in a timely manner.
Oral anatomy
The oral cavity is the beginning of the digestive apparatus. The oral cavity is divided into two sections by the alveolar processes of the jaws and teeth: the vestibule of the mouth and the oral cavity itself.
The vestibule of the mouth is the space located between the lips and cheeks on the outside and the teeth and gums on the inside. The vestibule of the mouth opens outward through the oral opening. The transverse oral fissure is limited by the lips, which are muscle folds, the outer surface of which is covered with skin, and the inner surface is lined with mucous membrane.
The oral cavity is located on the inner side of the alveolar processes, limited above by the hard palate and the anterior portion of the soft palate; the bottom is formed by the diaphragm of the mouth and is occupied by the tongue.
The oral cavity is lined by the oral mucosa, covered with stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium. It contains a large number of glands. The area of the mucous membrane attached around the neck of the teeth on the periosteum of the alveolar processes of the jaws is called the gum. The oral cavity communicates with the pharynx through the isthmus of the pharynx.
The cheeks are covered on the outside with skin, and on the inside with the oral mucosa, which contains the ducts of the buccal glands and is formed by the buccal muscle. Subcutaneous tissue is especially developed in the central part of the cheek. Between the masseter and buccal muscles is the fatty body of the cheek.
The upper wall of the mouth (palate) is divided into two parts. The hard palate is located in the anterior part of the oral cavity, formed by the palatine processes of the maxillary bones and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones. The palatine bones are covered with a mucous membrane, along the midline of which there is a suture of the palate, and on the sides there are several transverse palatine folds.
The hard palate passes into the soft palate, formed mainly by muscles and aponeurosis of tendon bundles. In the posterior part of the soft palate there is a small conical protrusion, called the uvula, which is part of the so-called velum palatine. Along the edges, the soft palate passes into the anterior palatoglossal arch and the posterior palatopharyngeal arch. Between the arches on each side, in the recesses lie the palatine tonsils. The lower palate and arches are formed mainly by muscles that help swallowing.
The muscle that lifts the velum palatine of the soft palate and narrows the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube begins on the lower surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone and attaches to the middle section of the aponeurosis of the palate, intertwining with bundles of the muscle of the same name on the other side.
The palatoglossus muscle narrows the pharynx, bringing the anterior arches closer to the root of the tongue. Its beginning is located on the lateral edge of the tongue root, and its attachment point is on the aponeurosis of the soft palate.
The triangle of the velopharyngeal muscle brings the velopharyngeal arches closer together, pulling the lower part of the pharynx and larynx upward. The muscle begins on the back wall of the lower part of the pharynx and attaches to the aponeurosis of the soft palate.
The tongue is a mobile muscular organ located in the oral cavity and facilitates the processes of chewing food, swallowing, sucking and speech production. The tongue is divided into the body of the tongue, the apex of the tongue, the root of the tongue and the dorsum of the tongue.
From above, from the sides and partially from below, the tongue is covered with a mucous membrane, which fuses with its muscle fibers, contains glands, lymphoid formations and nerve endings - receptors. On the back and body of the tongue, the mucous membrane is rough due to the large number of papillae of the tongue, which are divided into four groups:
- Filiform papillae are located throughout the body of the tongue and represent a conical body with racemose appendages at the apexes.
- Fungiform papillae are located on the back of the tongue closer to its edges and have the shape of pineal growths.
- Leaf-shaped papillae are concentrated in the lateral sections of the tongue and represent 5-8 folds separated by grooves. They are unequal in size and are most pronounced in the posterior parts of the tongue.
- Cylindrical papillae, surrounded by a ridge of mucous membrane, the largest, but weakly protruding above the surface, are located on the border between the root and body of the tongue.
The muscles of the tongue are represented by skeletal muscles and the actual muscles of the tongue. Skeletal muscles connect the root of the tongue to the bones of the skull. The actual muscles of the tongue have points of origin and attachment points in the thickness of the tongue, located in three mutually perpendicular directions: the lower longitudinal muscle shortens the tongue; the superior longitudinal muscle flexes the tongue, shortening it, and raises the tip of the tongue; the vertical muscle of the tongue makes it flat; The transverse muscle of the tongue reduces its diameter and makes it transversely convex upward.
When the mouth is closed, the tongue with its upper surface comes into contact with the palate. The mucous membrane, passing to the lower surface of the tip of the tongue, forms the so-called frenulum along the midline. On either side of it, at the bottom of the mouth, on the sublingual fold, the ducts of the submandibular gland and sublingual gland open, which secrete saliva and are therefore called salivary glands.
The submandibular gland is an alveolar-tubular protein-mucosal gland located in the lower part of the neck in the submandibular fossa, below the mylohyoid muscle.
The sublingual gland is an alveolar-tubular protein-mucosal gland located under the mucous membrane of the mouth on the mylohyoid muscle under the tongue.
The excretory duct of the third, the parotid salivary gland, opens in the vestibule of the mouth on the mucous membrane of the cheek, at the level of the upper second molar.
Teeth, depending on their structure and functions, are divided into large molars, small molars, canines and incisors. All of them are strengthened in the sockets of the alveolar processes of the lower and upper jaws.
Each tooth consists of a part that protrudes above the gum - the crown of the tooth, a part covered by the gum - the neck of the tooth and an internal part - the root of the tooth. Moreover, some teeth have two or more roots.
The bulk of the tooth is dentin, which is covered with enamel in the crown area, and with cement in the neck and root area.
The root of the tooth is surrounded by a root membrane - the periodontium, which, with the help of tooth ligaments, attaches it to the dental alveolus. Inside the crown of the tooth there is a tooth cavity, which continues into a narrow canal of the tooth root. Vessels and nerves pass through a small hole in the apex of the tooth root into the tooth cavity containing the pulp, or pulp.
According to data from dental reference books
A full range of dental services in Istra for adults and children: from consultation to complex operations within one clinic “Doctor Nebolit”
Consultation and appointments daily from 9:00 to 19:00
- +7 (49831) 4-42-12
- Contacts
Diagnostics
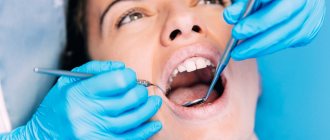
At the initial consultation, the doctor examines the oral cavity, examines ulcers, erosions, damage to the mucous membrane, and then takes a smear for examination. To confirm the inflammatory process, the patient is sent for a general and biochemical blood test.
The diagnosis is confirmed by the results of the examination:
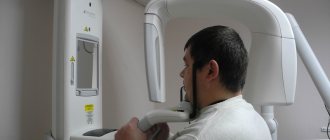
- MRI and ultrasound of soft tissues of the neck. The images reveal the localization of the pathology, the depth of germination and the structure of the tumor, compaction from blood and lymph, decomposition of the cortical layer of the bone;
- if metastases are suspected, a fine needle aspiration biopsy of the lymph nodes under the chin, under the jaw and in the upper third of the neck is performed;
- positron emission tomography. Shows the depth of the tumor, as well as early metastases;
- osteoscintigraphy. Skeletal bones are examined to look for displaced cancer cells;
- CT scan of facial bones with contrast. The images show the tumor growing into the neck vessels, jaw or base of the skull.
Treatment
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the stage and extent of the tumor. When the tumor grows rapidly, treatment methods are combined.
Operation
The doctor determines the principle of surgical intervention after determining the stage of the tumor and its spread. If cancer cells have penetrated the periosteum and surrounding tissues, a wedge-shaped, planar or sagittal resection of the jaw is performed. If the examination reveals the growth of cancer cells directly into the bone or the defect is noticed during surgery, segmental resection of the lower jaw is performed. The doctor assesses the lesion on site and determines the thickness of the excised layer.
The next stage of the operation is partial or complete excision of the cervical lymph nodes to prevent metastases if the thickness of the tumor is more than 4 mm or the location of the tumor in the floor of the mouth or on the tongue. If the tumor is located in the midline, then the cervical lymph nodes are excised on both sides. The operation ends with the immediate replacement of damaged tissue.
After removal, the tumor is sent for histological examination. Its size, thickness, depth, edges are assessed. Further treatment is affected by cell growth beyond the boundaries of the capsule of the removed lymph node, and the spread of cancer cells to neighboring organs.
Radiation therapy
Radiation after surgery is prescribed when diagnosing T3, T4, N2, T3 stages of the disease no later than six weeks after tumor removal. The need for radiation therapy increases with perineural invasion of the lymphatic vessels. The total focal dose for all sessions is 60 g, and the single focal dose for one session is 2 g. When metastases are detected on the neck, the SOD increases to 66 g, and if there is no risk of metastasis, the SOD decreases to 50 g.
As the main treatment, radiation therapy is used in a total focal dose of 60-70 g. The procedure is performed five days a week and is combined with chemotherapy. Every three weeks, 100 mg of cisplatin is administered.
Chemotherapy
Anticancer drugs are prescribed before surgery or along with radiation therapy to reduce the size of the tumor. Sometimes therapy is prescribed simultaneously with surgery.
Treatment involves the use of a 5-fluoroacyl regimen together with cisplatin or other agents - carboplatin, methotrexate, bleomycin. They cause a number of side effects, for example, vomiting or nausea, hair loss, decreased appetite, and increased bleeding. Symptoms disappear after treatment, but permanent hearing loss is sometimes observed after taking cisplatin.
The prognosis of oral cancer depends on the stage at which the disease is detected. If treatment is started at stage zero, the disease will stop. It is worth noting that smoking provokes relapse or degeneration of the tumor, so repeated surgery or radiation may be required. Surgery at the first stage increases survival rate to 80-85%, and the combination of radiation therapy with surgery at the second stage by 60-80%. Already at subsequent stages of cancer development, the survival rate is no more than 50%, and all three treatment methods are used simultaneously.
Dispensary observation
Since the tumor can recur and metastasize, after completing the course of treatment the patient is registered with the oncology clinic. The first year you should visit a doctor every month, the second year a preventive examination is carried out every 4-6 months, and then once a year or in case of any ailments. The examination involves an examination - ultrasound and contrast MRI of the soft tissues of the neck, PET, osteoscintigraphy. Consultation with an otolaryngologist, dentist and oncologist is required. The doctor may shorten the period of medical examination if there is a high risk of relapse.
List of references on the topic:
- Gantsev Sh.H. Oncology – M, 2012 – P.204-205.
- Golovin D.I. Errors and difficulties in diagnosing tumors, D.: Medicine. Leningr. department, 2015 305 pp.
- Selected lectures on clinical oncology/Ed. IN AND. Chissova, S.L. Daryalova. – M., 2010
- Matyakin E.G., Alferov V.S. Chemotherapy of head and neck tumors // Mat. 2nd Ros. oncol. conf. “Current trends in the development of drug therapy for tumors” December 8–10, 2016 – M., 256 p.
- Tumors of the head and neck: hands/ A.I. Paches. - 5th ed., add. And revised - M.: Practical Medicine, 2013. -478 p.
- Shine A.A. Oncology. M – 2014 365 pp.
- Encyclopedia of Clinical Oncology/Ed. M.I. Davydova. – M., 2014 –P.140-179.
- Bityutsky P.G., Kitsmanyuk Z.D., Trofimov E.I. Diagnosis and treatment of cancer of the oral mucosa // Medical consultations. - 2014. - No. 1. - P. 23-27.
- Byakhov M. Yu. Options for combined and complex treatment of locally advanced cancer of the oral mucosa and oropharynx: Dis. Dr. med. Sci. - M., 2013.