Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
More than 300 varieties of microorganisms live in the oral cavity (streptococci, lactobacilli, fungi of the genus Candida, staphylococci, etc.), which make up its microflora, or microbiota. Constant humidity, optimal temperature and pH values, the presence of food residues - all this creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of various types of microbes.
The composition of the oral microbiota is individual for each person, so the concept of “normal microflora” is also individual. Many opportunistic microorganisms that make up the normal microflora of the oral cavity play an important role in the etiology and pathogenesis of caries, diseases of the mucous membrane and periodontal tissue. The microbiota of the oral cavity is involved in the primary processes of food digestion and absorption of nutrients, in the synthesis of vitamins, and in maintaining the proper functioning of the immune system.
The qualitative and quantitative composition of microflora usually changes little throughout a person’s life, but under certain factors this is possible. In this case, they speak of an imbalance of microflora, that is, dysbacteriosis, when the proportion of normal microflora decreases, and the growth of pathogenic microorganisms increases.
The ailment itself, designated by the term “dysbacteriosis,” is not a disease and is not included in the official international classifications of diseases. It should be considered as a set of symptoms indicating the presence of pathological processes in various body systems. Occurs in adults and children. Let's talk about oral dysbiosis: how it manifests itself, why it is dangerous, how to treat it.
Stages of development of dysbiosis in the oral cavity
Some researchers identify several stages in the formation of oral dysbiosis:
- Stage 1 - dysbiotic shift (compensated dysbiosis). Characterized by an increase in the number of one type or several types of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. At this stage there are no manifestations;
- Stage 2 - subcompensated dysbacteriosis. There are fewer lactobacilli, and barely noticeable manifestations appear;
- Stage 3. The lactobacilli needed by the body are replaced by pathogenic microorganisms;
- Stage 4. Yeast-like fungi begin to actively multiply in an unnatural niche for them.
At stages 3 and 4 (decompensated dysbacteriosis), inflammatory elements, ulcers, and excessive keratinization of the oral epithelium may occur.
All this can lead to the development of stomatitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease. An infection of the nasopharynx may occur.
Symptoms of oral dysbiosis
Symptoms designated by the term “oral dysbiosis” occur in many different diseases and syndromes, so the disease is difficult to diagnose. Let's name the signs of an imbalance in the oral microflora:
- bad breath (halitosis);
- metallic taste, burning sensation in the mouth;
- the development of candidiasis, or thrush - a white coating on the tongue and mucous membranes of the cheeks;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes and gums;
- swelling, redness and soreness of the tongue;
- The appearance of so-called jams in the corners of the mouth is characteristic.
The pathology of normal microflora in the mouth is fraught with the danger of endogenous infections.
The listed manifestations are due to the following changes:
- colonization resistance (local immunity) of the mucous membrane is disrupted - yeast-like fungi easily adhere to the surface of the epithelium, where there are optimal conditions for reproduction;
- the bacterial antagonism of normal microflora changes significantly - normally, antagonistic microbes do not allow pathogenic fungi to actively multiply, but with dysbiosis, the former are destroyed, which provokes rapid proliferation of Candida fungi;
- In patients, a significant shift in local protective factors is detected - the weakened defense does not cope with its function, so the volume of pathogenic microflora increases unhindered.
Types of Oral Probiotics
Biologists call the most common types of probiotics:
- Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium (Lactobacillus and bifidobacteria), obtained mainly from dairy products. However, it is important to normalize the population of these bacteria, but not to “overdo it” with them, since their excessive quantity provokes the formation of caries.
- Bacterial strains Bacillus subtilis, L. salivarius WB21, L. casei Shirota, L. brevis, L. reuteri, L. acidophilus may be useful in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
- Candidiasis, the most common cause of oral dysbiosis, can be treated with L. rhamnosus strains (GG and LC705) as well as Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii JS. This type of oral probiotic can be obtained from cheese or other fortified dairy products.
- To treat halitosis (bad breath), probiotics E. coli Nisle 1917 and S. salivarius K12 can be used.
Reasons for the formation of oral dysbiosis
The reasons that lead to disturbances in microbiocenosis in the mouth are, for the most part, the same as for dysbacteriosis in other areas of the gastrointestinal tract. These include:
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- use of antibacterial and antiseptic agents for mouth rinsing. Long-term use of bactericidal rinses, antimicrobial toothpastes, and local antiseptics like chlorhexidine leads to the destruction of not only harmful, but also beneficial bacteria in the oral cavity. At the same time, the resistance of pathogenic flora to antibiotics increases;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases, intoxication and weakening of the macroorganism against their background;
- hypovitaminosis - lack of vitamins.
Often the cause of dysbiosis in the mouth is incorrect or insufficient oral hygiene. A factor that provokes a violation of the microflora of the oral cavity is smoking.
Reasons for the development of oral dysbiosis
As a rule, oral dysbiosis develops due to the proliferation of yeast-like fungi Candida albicans. These fungi have an adhesive ability to the epithelial cells of the oral mucosa, and the presence of carious cavities in teeth creates conditions for their long-term existence.
With prolonged antibiotic therapy or immunodeficiency, the obligate microflora that suppresses the development of fungi dies due to which candidiasis develops. Proteases, neuraminidases and other enzymes synthesized by fungi play an important role in pathogenesis.
Yeast fungi attach to the epithelial cells of the oral mucosa, and sucrose, glucose, maltose and other carbohydrates further increase adhesion activity. The strength of attachment (adhesiveness) of the fungus determines its ability to spread. For example, C. albicans attaches to epithelial cells 1.5 times faster than other species, and the more antibiotics a person takes, the stronger the adhesion.
The yeast-like fungus destroys tooth enamel and “settles” in carious cavities and further contributes to the development of fungal stomatitis and tonsillitis. Lactic acid produced by lactobacilli prevents the proliferation of yeast-like fungi, so microorganisms cannot multiply uncontrollably.
However, they are given this opportunity if a person takes antibiotics (especially broad-spectrum antibiotics) or suffers from immunodeficiency conditions. Candidiasis can cause local lesions of the oral cavity or provoke multiple lesions of internal organs (generalized candidiasis).
The development of oral dysbiosis can be caused by:
- intestinal infections;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- a diet limiting the consumption of animal protein;
- lack of vitamins;
- allergic diseases;
- use of medications (hormonal contraceptives, steroids, antiviral drugs);
- smoking and drinking alcohol.
To confirm the diagnosis, bacteriological tests are performed:
Dysbacteriosis in pregnant women
- bacterial culture of saliva or scrapings from the gums. The analysis makes it possible to determine the degree of contamination of the oral cavity with pathogenic microorganisms;
- urease test. Reveals the ratio of urease and lysozyme (if the indicator is more than one, then this indicates the development of dysbacteriosis);
- Gram staining. The quantitative ratio of gram-positive and gram-negative microbes is checked;
- determining the amount of bacteria in exhaled air and comparing the indicator with a smear taken from the oral cavity.
Influence of the state of the oral microflora on other organs and systems
The connection between the general condition of the body and dental health is known. Thus, those patients who have oral diseases are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases. Clinical studies confirm the presence of oral bacterial microflora in the blood and atherosclerotic plaques. Periodontopathogenic microflora is the main source of local and systemic chronic inflammatory process. Acts as a risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease.
In addition, scientists have discovered a connection between bacteria living in the mouth and the occurrence of migraines.
Another dangerous consequence of disruption of the oral microflora is the aggravation of intestinal and esophageal cancer. One study found that bacteria living in the mouth can trigger the development of colon cancer.
Diagnosis and treatment of oral dysbiosis
Oral cavity dysbiosis syndrome in the initial stages of development is detected during laboratory tests. To diagnose oral dysbiosis, microbiological examination of a smear from the oral mucosa or saliva is used. When diagnosing, the number of opportunistic microorganisms in the test material is determined.
Important: it is necessary to accurately establish the root cause of the disease, which a comprehensive examination of the body will help with, and treat the primary disease.
For pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract that affect the condition of the oral cavity, they are first treated.
If the balance of the oral microflora is disturbed, treatment is mainly used in the form of sanitation and taking medications to normalize the microflora in the mouth. However, all drugs that are used to treat oral dysbiosis are considered drugs with unproven effectiveness. The following is used as therapy for this condition:
- eubiotics - needed to increase the number of beneficial bacteria in the mouth;
- immunomodulators - increase local immunity and prevent the growth of pathogenic microorganisms;
- antimicrobial and antifungal agents.
Oral probiotics (oral probiotics)
Probiotics are live microorganisms that promote the growth of friendly microbiota. Most often, such substances are used to improve intestinal microflora, but not many people know that there are probiotics for the oral cavity.
It is important to understand that probiotics for the oral cavity are represented by one group of substances, and probiotics for the intestines are a completely different one. Scientific research regarding these drugs is very controversial, so dentists recommend using them only as an addition to the prescribed treatment for dysbiosis.
Prevention of dysbiosis in the mouth
Prevention of oral dysbiosis includes the following measures:
- use of antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor in the recommended course;
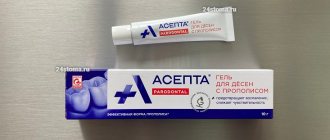
- use of alcohol-free and antiseptic rinses for daily oral hygiene, for example, ASEPTA Parodontal Fresh with plant extracts and microelements;
- smoking cessation: it is advisable to eliminate smoking altogether;
- strengthening local immunity: timely sanitation of the oral cavity, maintaining oral hygiene. You also need to strengthen your general immunity.
The main advice for normalizing the microflora of the oral cavity: do not feed the bad microbiota and do not destroy the good one.
Let's summarize: we have given a definition of oral dysbiosis, which is understood as a violation of the ratio between normal and pathogenic microflora in the direction of increasing the latter. They indicated that this condition is not an independent disease, but only a complex of symptoms. The stages of formation of oral dysbiosis, symptoms and causes of disturbances in the microflora of the oral cavity were named. Also from this article you learned how to treat oral dysbiosis and how to prevent its occurrence.
Treatment
Depending on the stage of the disease and its causative agent, therapy is prescribed, which may include:
- sanitation of the oral cavity. Plaque and tartar must be removed from the teeth, and carious cavities must also be filled, since they act as a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria;
- taking antiseptics or antimycotics to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms;
- taking immunostimulants. These drugs help increase local and systemic immunity;
- consumption of vitamins. Vitamins A, E, C help restore the oral mucosa. In addition, with pathology, the absorption of nutrients is impaired, and vitamin complexes help to avoid a lack of vitamins and minerals.
The causative agents of disease are most often fungi of the genus Candida, Escherichia coli, Proteus, and enterococci.
Depending on the causative agent of the disease, antibacterial or antimycotic drugs are prescribed. To destroy bacterial microflora in the oral cavity, the following can be used:
- "Tantum Verde". It has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect and also reduces pain. The active substance is benzydamine hydrochloride. Available in the form of a spray, lozenges, and solution. You need to take the product every three hours;
- "Orasept." The active ingredients are phenol (fungicidal and antifungal action) and glycerin (relieves irritation). Available in spray form;
- "Yox." Contains povidone-iodine, allantoin, levomenthol, due to which it has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. The drug is active against gram-positive and gram-negative cocci, protozoan viruses, and yeast. Available in solution and spray;
- "Chlorhexidine." Has a bactericidal effect. So, rinse the mouth with a 0.5% solution for 30 seconds, then spit out the liquid.
If dysbiosis of the oral cavity has developed due to a fungus, then the drug “Candide” is prescribed, the active component of which is clotrimazole, which has an antimycotic and antibacterial effect. The product destroys mold and yeast-like fungi, gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The solution is used to wipe the affected areas of the mucous membrane.
In severe cases of the disease, the doctor prescribes narrow-spectrum drugs that are aimed at combating a specific type of bacteria. So, when staphylococcus is detected, macrolides or pyobacteriophage (Josamycin, Clarithromycin) are prescribed, enterococci are destroyed with macrolides, penicillins, nitrofurans (Furazolidone), drugs nalidixic acid, sulfonamides will get rid of Proteus, and for Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Gentomycin is indicated.
Also, treatment of oral dysbiosis involves the use of prebiotics and probiotics. Prebiotics stimulate the development of beneficial microflora. They are not digested or absorbed in the stomach and intestines, but are broken down by the microflora of the large intestine, that is, they are food for bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Prebiotics include di- and trisaccharides, oligo- and polysaccharides, amino acids, peptides, polyhydric alcohols, enzymes, fatty acids, antioxidants and others.
Biotics can be naturally or artificially synthesized
Natural prebiotics are found in cereals and bran, seaweed, vegetables, fruits and dried fruits, leafy greens, and dairy products (lactulose and lactose). They love beneficial bacteria and inulin contained in garlic, onions, bananas, chicory, and wheat. Synthesized prebiotics can be purchased at the pharmacy (Duphalac, Normaze, Laktofiltrum).
Probiotics contain live beneficial bacteria that prevent the development of pathogenic microflora. Pharmaceutical preparations may contain one strain of bacteria (lactobacteria, bifidobacteria) or several types of microorganisms that enhance each other’s effects. Probiotics include “Acilact”, “Bifidumbacterin”, “Lactobacterin”, “Linex”, “Polibacterin”, “Hilak forte”.
Products are available in capsules, tablets, powders, suspensions, and suppositories. The duration of their intake varies depending on the generation of the probiotic (from 4 weeks to 7 days). “BioGaia” is effective for oral dysbacteriosis. This medicine contains lactobacilli. It is used sublingually (placed under the tongue or chewed), which means it has only a local effect.
Live microcultures are also found in kefir, yoghurt, curdled milk, kumiss, cottage cheese, buttermilk, quick-ripening cheese, sauerkraut and other drinks prepared using starter culture or enzymes. More than 10 types of beneficial bacteria are involved in the production of kefir; fermented baked milk and yogurt contain mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria, acidophilus bacilli; 1 gram of cheese contains almost 100 million beneficial bacteria.
When treating oral dysbiosis, it is necessary not only to increase the consumption of foods containing beneficial probiotics and prebiotics, but also to exclude fast carbohydrates, fast food, fatty, fried and salty foods from the diet.
The more sweets a person eats, the more yeast-like fungi attach to epithelial cells, which means it is more difficult to get rid of them
Experts' opinion
Asept products have proven effectiveness. For example, multiple clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Traditional medicine
Folk remedies will help get rid of oral dysbiosis:
- homemade curdled milk. You need to boil a liter of milk and add a few pieces of dried black bread to it, leave to infuse in a warm place for a day. Use yogurt within a week;
- strawberries Berries stimulate salivation, which leads to the release of substances that destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Thus, conditions are created for the reproduction of obligate microflora;
- bloodroot. Potentilla decoction has soothing, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. A spoonful of the dried plant is poured with two glasses of boiling water and boiled for half an hour. You need to drink the decoction twice a day before meals.
To prevent the development of dysbiosis, it is necessary to monitor oral hygiene, adhere to a healthy diet, and promptly treat gastrointestinal diseases. Since doctors consider medication use to be the main factor in the development of pathology, the use of antibiotics, hormonal and antiviral drugs should be monitored by the attending physician. If drug therapy is long-term, then prophylactic administration of drugs based on bifidobacteria and lactobacilli is advisable.