Home ⁄ Periodontology (old page)
[113909]
Periodontology is a branch of dentistry that deals with the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of gums. The most common diseases encountered in periodontology are gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease. We recommend that you carefully care for your teeth and gums, and also undergo regular examinations by a periodontist. Don't delay visiting your doctor if you notice your gums bleeding when biting into hard foods or brushing your teeth. Any disease, including gum disease, is much easier to cure in the initial stage than when it is advanced.
Causes of periodontitis
The causes of periodontitis are divided into general and local. The first group includes diseases of diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states, pathologies of the blood system and other diseases that affect the condition of the periodontium. Some chronic diseases can also affect the occurrence of periodontitis, as well as cause complications in its course. The most common local causes of the development of periodontitis include the penetration of various microorganisms into the oral cavity. Also, the causes of periodontitis include traumatic factors associated with improper positioning of teeth, hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, malocclusion, etc.
Pathogenesis of periodontitis
Pathogenesis of periodontitis: in the early stages of the disease, the gums begin to bleed, dental ligaments weaken, plaque appears, the consistency of saliva changes - it becomes more viscous. With a rapidly progressing disease, tooth loss occurs as a result of destruction of the alveolar processes. During the acute period of periodontitis development, inflammation of the gums occurs, purulent masses are released from the periodontal pockets, an unpleasant odor is felt from the oral cavity, and the teeth begin to shift. The formation of fistulas on the gums, swelling and pain in the submandibular lymph nodes is possible. In the chronic form of periodontitis, against the background of periodic exacerbations of the disease, the development of microbial allergic reactions may occur.
Classification of periodontitis
The classification of periodontitis includes the following aspects:
- According to the degree of spread of the disease, local and general periodontitis are distinguished. In the first case, the affected area covers one or more teeth. In the second, it spreads throughout the jaw.
- Based on the form of the disease, periodontitis is classified into acute and chronic.
- Depending on the severity, periodontitis is classified into mild, moderate and severe.
Pain due to periodontitis
There may be no pain during periodontitis at the initial stage of the disease. Subsequently, as the disease progresses, pain appears in the gums, accompanied by redness, bleeding, change in shape, formation of a periodontal pocket, pulsation, and the appearance of bad breath. Pain with periodontitis can occur during brushing your teeth, as well as when biting and chewing food. In severe forms of the disease, pus may be released from the periodontal pocket, and an increase in body temperature may also be noted.
Acute periodontitis
Acute periodontitis can occur with acute or chronic trauma to the maxillofacial area. The main symptoms are sharp pain, bleeding gums, swelling and redness, and possible displacement of teeth. When infectious agents penetrate, a purulent inflammatory process may develop, which in turn causes an increase in the symptoms of the disease. Acute periodontitis requires urgent medical intervention in order to provide timely treatment and prevent the development of complications.
Chronic periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis is a consequence of the development of a disease such as gingivitis, which affects the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. As a result of the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms between the teeth and gums, pathological pockets are formed in them, the sizes of which range from three to more than five millimeters. The development of the inflammatory process that causes periodontitis can be provoked by a weakened immune system, the presence of caries, dental trauma, the influence of chemicals or medications. Periodontitis can also occur as a result of poor-quality fillings or dental prosthetics.
Exacerbation of periodontitis
Exacerbation of periodontitis is characterized by the occurrence of sharp and intense pain in the teeth and gums, which may be accompanied by an increase in temperature and a deterioration in general well-being. Due to increasing pain, the patient is unable to maintain oral hygiene, which in turn provokes the proliferation of bacteria and the appearance of plaque. The size of pathological pockets between the teeth and gums can reach five to six millimeters; there is also the release of purulent formations, redness and swelling of the gums. Exacerbation of periodontitis requires immediate medical attention. To avoid tooth extraction, it is necessary to immediately conduct a diagnostic study in order to ascertain as accurately as possible the nature of the inflammatory process, and undergo a course of comprehensive treatment.
Since ancient times, our grandmothers knew one simple truth: nothing gets rid of diseases better than our Mother Nature. Every disease has its own causes, and every plant perfectly eliminates the causes of the disease. Long observations and centuries of experience have brought to our attention many properties of plants, which often help faster and more effectively than many expensive medicines.
For example, if we consider the beneficial properties of oak bark, we can discover many wonderful features that help cope with many ailments, such as stomatitis, gingivitis, gumboil, uterine bleeding, remove bad breath, remove excessive sweating and prevent bedsores.
Clinical researches
Many experts note the high effectiveness of Asepta products. Conducted at the Military Medical Academy named after. CM. Kirov research has shown that products for individual oral hygiene of the Asepta series allow, within 6 months after the completion of complex treatment, not only to improve oral hygiene and reduce inflammatory processes in the gums by 55.37%, but also to reduce number of relapses of localized periodontitis.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment of chronic localized periodontitis of traumatic etiology in young people, it is advisable to include series products in the complex of treatment and preventive measures.
Sources:
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Useful properties of oak bark
Oak bark has a wide range of useful characteristics, it perfectly heals wounds, is a natural antiseptic, anthelmintic, and actively inhibits the growth of pathogenic bacteria. The oak bark itself contains tannins, which have an astringent effect, resins, various acids, proteins and pectin, which actively help restore the protective functions of the body and restore the skin.
Oak bark, like the tree itself, is a powerful and unshakable natural protector of humans from various diseases.
When the human body is weakened, as a rule, the immune system is the first to suffer. When protection weakens, the first thing that suffers is the mucous membranes. The eyes begin to water, which leads to various complications; the nasopharynx is susceptible to attacks by various bacteria and microbes, which also leads to diseases. An unpleasant odor appears in the mouth, and when brushing your teeth, blood appears on the toothbrush. All this suggests that it is necessary to take measures to prevent diseases.
What to do if you have gum disease
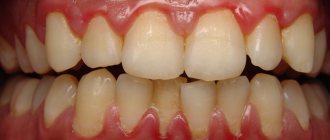
When the gums become inflamed, they become red and very painful. Pustules appear that are caused by various bacteria. Inflammation of the gums often leads to tooth loss, a disease called periodontal disease. In order to strengthen the gums, you need to purchase oak bark and make a decoction, which you need to rinse your mouth with during the day.
Can I use natural remedies?
As an addition to treating gums with a rinse, pregnant women can use herbal decoctions on the recommendation of their doctor. For inflammation, women are advised to pay attention to the following remedies while expecting a baby:
- decoction of oak bark;
- decoction of lingonberry leaves;
- infusion of chamomile;
- decoction or infusion of calendula flowers;
- sage tea.
An excellent helper for a pregnant woman's gums will be Asepta Fresh mouth rinse with chamomile and witch hazel extract. This product is perfect for daily protection of teeth and gums from plaque, and also preserves the natural whiteness of the enamel, soothes the gums and prevents the occurrence of caries. Asepta Fresh mouth rinse does not contain alcohol, dyes or antiseptics and can be recommended without restrictions on the period of use.
Preparing a decoction for rinsing
The decoction is prepared quite simply:
You need to take 2 teaspoons of crushed oak bark, pour it with two glasses of water, boil, reduce the heat and simmer over low heat for about 5 minutes. Then the broth must be set aside until it cools completely. Strain the mixture and pour the medicinal part into a jar. Mouth rinsing should be done 3 to 5 times a day. It must be remembered that treatment must be carried out for 3 days, even if after the first rinse there is a noticeable improvement, rinsing must be continued. In advanced stages of gum inflammation, such procedures should be carried out for up to one week. Every day it is necessary to prepare a new decoction, so the treatment will be more effective and bring more benefits.
Treatment of stomatitis
In addition to toothache and gumboil, stomatitis is a common oral disease. This is a fairly common disease among children, since parents are not always able to be vigilant and remove dirty hands or a dirty toy from the child’s mouth in time. Stomatitis causes high fever, purulent ulcers are observed in the oral cavity, which hurt terribly and cause a lot of trouble not only for the baby, but also for his parents. In order to get rid of this disease, you need to brew 2 teaspoons of oak bark, add a teaspoon of medicinal chamomile or calendula, pour it all over with three glasses of boiling water and boil in a water bath for 5 minutes. Then cool the broth, strain and begin rinsing your mouth.
For tiny children, the problem of rinsing is quite relevant; parents should not give up the folk remedy, they just need to treat every wound in the mouth with this decoction. After some time, the baby will feel a little better, the main thing is not to give up and do everything quickly and collectedly. Treatment of stomatitis with oak bark will be more effective, since there are no proven remedies for children, and those medicines that are used everywhere are prescribed to children from the age of seven.
Can rinse aids be used?
According to dentists, during pregnancy it is permissible to use mouth rinses with extracts of medicinal herbs and medications. The components of these drugs act at the local level and do not enter the general bloodstream.
Doctors also advise giving preference to non-alcoholic rinses during pregnancy, since such products do not pose a danger due to the adverse effects of alcohol on the mucous membranes. Non-alcoholic products are ideal as a preventive measure and will help avoid gum problems in the future.
As a rule, for inflammation of the gums, on the recommendation of the dentist, the following types of rinses are used during pregnancy:
- Fluoride-containing
- when the balance of the bacterial flora of the oral cavity is disturbed. - Herbal
– for minor inflammations. - Cetylpyridinium chloride products
are necessary to treat and stop the growth of plaque. These rinses are also used for severe inflammatory reactions. - Rinses with antiseptics
should be used short-term, no longer than 30 days (1 month). Such drugs are prescribed in difficult dental situations, with severe suppuration and abscess formation. - Desensitizing agents are recommended for use in case of increased sensitivity of teeth and gums