From this article you will learn:
- why do gums bleed during pregnancy,
- what is pregnancy gingivitis,
- how to carry out treatment correctly.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
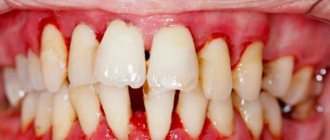
Inflammation of the gums during pregnancy is a process characterized by bleeding gums, as well as hypertrophy of the gingival papillae, which occurs due to an increase in the concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman. This condition is usually called the term “gingivitis in pregnant women”, and according to statistics, it is observed in 75% of women - for a period of 2 to 8 months. Most often, gingivitis occurs in the area of the front teeth, and it affects only the gingival margin at the necks of the teeth (including the gingival papillae).
Clinical studies show that more than half of all women with gingivitis during pregnancy already had a mild form of chronic catarrhal gingivitis at the beginning of pregnancy, which is practically asymptomatic. Thus, an increase in the content of estrogen and progesterone in most cases led to an exacerbation of pre-existing gingivitis, and was not the root cause of its development. We will tell you more about the causes of inflammation below, because... there are other factors to consider.
Chronic catarrhal gingivitis –
But pregnant women can experience not only gingivitis, but also a more serious gum disease, in which inflammation spreads from the superficial part of the gums to deeper tissues. This disease is called periodontitis, and with it there is destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth, destruction of the dental-gingival attachment, suppuration from periodontal pockets, and over time, tooth mobility also occurs. And this disease already indirectly affects the fetus, which requires mandatory treatment.
Content:
- Why do gums bleed during pregnancy?
- Signs of violation
- Types of gingivitis in pregnant women
- How to treat bleeding gums during pregnancy
- How to strengthen gums during pregnancy 5.1. Diet is the key to good health of the expectant mother and baby
- Why you need to treat gum disease
Bleeding gums during pregnancy is a fairly common problem.
Most often it is associated with hormonal changes, due to which local blood supply is disrupted and vascular tone decreases. What to do if your gums are bleeding and how to prevent the development of gingivitis. Let's talk about this in this article.
Causes
The formation of soft plaque on enamel during pregnancy occurs faster than usual, especially during toxicosis.
Because of these unpleasant sensations, women often replace full teeth brushing with a simple rinse. This causes inflammation, irritation, gingivitis and periodontitis.
The main causes of bleeding gums are as follows:
- hormonal levels change and the immune system weakens;
- the amount of bacteria in the oral cavity increases due to insufficient hygiene and mouth rinsing;
- softening of the gums occurs due to the production of progesterone, changes in the composition of saliva and lack of calcium.
Also among the causes of bleeding may be overly aggressive brushing of teeth, active use of toothpicks and floss, as well as irritating foods (spicy, salty, etc.).
People with low blood clotting rates encounter this problem more often than others.
Bleeding gums can also occur due to a person's physical characteristics and abnormalities in the oral cavity, such as malocclusion, insufficient frenulum length, crowded teeth and other factors.
Why do gums bleed during pregnancy?
There are several reasons for the violation:
- Hormonal changes, redistribution of metabolic processes. During pregnancy, immunity usually decreases. As a result, a woman’s body becomes very susceptible to viral and infectious diseases. The structure and composition of dental plaque changes. A jump in harmful microflora in the oral cavity is recorded. If at the same time a pregnant woman does not pay due attention to hygiene, bleeding of soft tissues quickly comes to the fore. It can lead not only to inflammation of the gums, but also to the destruction of the upper layers of enamel.
- Lack of calcium. This microelement is needed for the formation of the fetal skeleton. To avoid its deficiency, the expectant mother should eat properly and take a high-quality vitamin and mineral complex. If less calcium is supplied than necessary, the woman’s teeth are the first to suffer. The body gives all its reserves to the child. The first place he gets additional resources from is dental crowns. If the units begin to deteriorate, bleeding gums often occur. This is due to weakening of the dentogingival connections.
- Copious deposition of soft plaque. Pathogenic microorganisms multiply in it. If the soft accumulations are not removed in time, they will harden and begin to disappear under the gums. Then the problem of bleeding will appear.
How are treatment methods chosen depending on the stage of pregnancy?
The first trimester of pregnancy is associated with the risk of spontaneous abortion, so during this period interventions should be as necessary, and the indications for them are acute pain or severe swelling of the gums. Tartar can also be removed, but it is still better to postpone this manipulation for a while. In the second trimester, you can carry out complex treatment, including professional cleaning and taking antiseptics. And in the third trimester, a visit to the dentist should be as short as possible, so you should limit yourself to only hygiene procedures.
Signs of violation
If your gums bleed during pregnancy, you can assume the presence of gingivitis. During different periods of pregnancy, this disease manifests itself in different ways. Typically a woman complains about:
- inflammation and swelling of soft tissues;
- bleeding even with minor mechanical stress;
- feeling of constant itching;
- transformation of the gingival papillae - they cease to be pointed and become dome-shaped;
- pain when chewing solid foods;
- elevated body temperature.
There are three forms of gingivitis:
- Light. Only the gingival papillae are damaged.
- Average. The inflammatory process has spread to the gums.
- Heavy. The entire gum is inflamed.
The disease can affect one or more teeth, or affect the entire dentition. In any case, treatment must be carried out as soon as possible.
Symptoms of gingivitis
Among the first signs of gingivitis are the following unpleasant symptoms:
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- bleeding when eating solid foods and when brushing your teeth;
- the appearance of a specific taste in the mouth;
- discomfort, itching and pain in the gum area;
- change in the shape and size of the gums.
In the first stages, the problem affects only the very edge of the gums (papillae); in advanced cases, the symptoms of gingivitis are very pronounced and affect the entire surface around the teeth.
Gingivitis comes in several varieties; it can be in just one jaw or spread to the entire area around the teeth.
In some cases, a portion of the skin may need to be removed or a difficult and painful procedure will be required to clean out the so-called gum pockets.
Types of gingivitis in pregnant women
Taking into account the dominant symptoms, the disease is classified into three types:
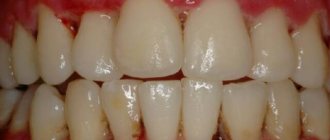
- Catarrhal. There is abundant deposition of a yellowish coating. It can be easily removed from dental crowns. The gums swell and hurt. Blood comes out of them infrequently. If you press on the tissue, severe discomfort will occur. With catarrhal disease, the entire gingival surface is inflamed.
- Hypertrophic. It appears no earlier than the twentieth obstetric week. Inflammatory reactions affect the lower jaw, tissues in the growth zone of incisors and molars. Gum pockets form. They are depressions located at the border of the gum and tooth root. The first one becomes inflamed, causing its size to increase.
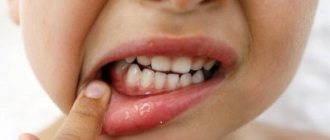
- Ulcerative. The most dangerous type of disease. It is the result of severe health problems. May occur starting in the first trimester. The situation is aggravated if the pregnant woman is under stress for a long time. The woman suffers from itching, burning, swelling, and extensive ulcers.
Diet of the expectant mother
For the health of the unborn child and good health, women need to monitor their diet. It is recommended to eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, fresh herbs and vitamins.
But an excess of vitamins can be dangerous, so it is advisable to consult with your doctor and, if necessary, prescribe a suitable diet, taking into account individual characteristics.
A low-carbohydrate diet has a beneficial effect on the condition of the body as a whole. Spicy and fatty foods that can irritate the mucous membranes in the mouth should be avoided.
It is very important to compensate for calcium deficiency. Sauerkraut, blackberries, onions, kiwi, and broccoli are especially useful for ginginitis.
How to treat bleeding gums during pregnancy
Therapy for bleeding gums during pregnancy is aimed at:
- elimination of symptoms of the disorder;
- strengthening soft tissues;
- removal of plaque and stone;
- removal and prevention of further spread of the inflammatory process;
- overcoming pain symptoms.
The first thing the doctor does is perform professional oral hygiene. An ultrasonic scaler is used for this. It carefully cleanses plaque from each tooth, smoothes the enamel surface and even brightens the smile by one or two shades.
After professional hygiene, the pressure of tartar on the gums is eliminated. This alone may be enough to save the patient from increased sensitivity and bleeding.
Additionally, the woman is prescribed gels, rinses, ointments or solutions designed to stop the inflammatory process and activate regeneration reactions. Most often these are compositions based on plant extracts. In any case, the dentist should select medications taking into account the “interesting” position of the patient.
What measures are prohibited during pregnancy?
- Use arsenic.
- Carry out dental prosthetics and teeth whitening procedures.
- Use anesthesia (for pain relief, gentle agents are used that do not contain adrenaline).
Situations where doctors may forget about a patient’s pregnancy due to inattention are quite possible. Therefore, it is very important for the woman herself to monitor the actions of the dentist and specify each drug that is supposed to be introduced into her body. If the sensations are too painful, you can resort to anesthesia. The stress of a pregnant woman can cause more harm to the unborn child than the use of an anesthetic drug.
How to strengthen gums during pregnancy
To avoid unpleasant dental symptoms and have a healthy and beautiful smile during pregnancy, you must follow these recommendations:
- Brush your teeth two to three times a day with a high-quality brush and toothpaste. If your gums are prone to bleeding, preference should be given to soft bristles and anti-inflammatory hygiene products.
- Use floss and dental rinses that have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Take a vitamin and mineral complex selected by your doctor. It will not allow vitamin deficiency to develop and will prevent calcium deficiency.
- Do not eat large amounts of sweets and baked goods. Do not eat toffee or caramel.
- Avoid drinking too hot or, conversely, cold drinks and foods. They worsen the condition of the enamel and irritate the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
- Pay maximum attention to a balanced diet.
Diet is the key to good health of the expectant mother and baby
Let's dwell more closely on the importance of dietary nutrition. Scientists have proven that dental plaque appears many times faster if you eat a lot of sugar. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the amount of this product in the daily diet.
To maintain immunity, you should eat non-acidic vegetables and fruits. Particular attention should be paid to sources of vitamins B, D, A, ascorbic acid - broccoli, kiwi, blackberries, onions, apples, peaches, bananas, carrots, tomatoes.
Clinical researches
Analysis of the results of clinical studies revealed the significant effectiveness of Asepta products for moderate periodontitis. The use of Asepta mouth rinse turned out to be quite effective. In addition, no phenomena of mucosal irritation or brown staining of fillings were recorded. This indicates that the use of this rinse for a two-week period provides an obvious clinical effect in the absence of negative side effects.
Sources:
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Why you need to treat gum disease
Some expectant mothers put off treatment for bleeding gums. They think that this problem can be dealt with after childbirth. This attitude towards the disease is incorrect. Only with good immunity can the body independently cope with inflammation and prevent its rapid progression. In all other cases, competent dental therapy should be carried out.
Under the influence of pathogenic microflora, which actively spreads when gingival tissue is damaged, the epithelium begins to collapse. If at the very beginning this process is reversible, then it will be quite difficult to correct the situation.
At some point, the pathogenic flora that has spread spreads to the periodontium. It gets damaged. This is manifested by tooth mobility. If you do not start treatment even with such symptoms, you can lose some units at a young age.
Doctors know of cases where the infection has affected the jaw bones. Then an irreversible change in the facial skeleton occurs, and fistula tracts are formed.
Don't start gingivitis. After undergoing professional hygiene and simple drug treatment, you will recover very quickly.
Therapy
| Service | price, rub. |
| Primary consultation and examination with a doctor | For free |
| Initial consultation with an implantologist, orthodontist, orthopedist (orthopantomogram is required) | For free |
| Examination by a doctor with prescription of medication | 500 |
| Help for antenatal clinics, hospitals, sanatoriums | 500 |
| TREATMENT OF CARIES | |
| Treatment of caries “without drilling” ICON technology – 1 tooth | 2500 |
| Treatment of caries (filling, anesthesia, lining) | 2400 — 3800 |
| Treatment of deep caries (filling, anesthesia, x-ray, lining) | 3000 — 4500 |
| Artistic tooth restoration (frontal group of teeth) | 4700 — 6350 |
| Restoration of a chewing tooth (filling, anesthesia, x-ray, pin) | 3000 — 4650 |
| NERVE REMOVAL – CANAL TREATMENT (depulpation) is carried out in two visits, payment in stages | |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 1-canal tooth, without the cost of a filling | 3700 — 4800 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 2-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 5700 — 6800 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 3-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 7700 — 9800 |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a 4-channel tooth, without the cost of a filling | 9700 — 11000 |
| Installing a seal | 2800 — 3200 |
Initial consultation is free.
The service is provided
Zohiri Khoja Zakirovich Therapy, orthopedics
Branch: Pavshinsky, 17
Make an appointment with a specialist
Osipova Irina Gennadievna Therapy, general dentistry
Branch: Pavshinsky, 17
Make an appointment with a specialist
Gum diseases
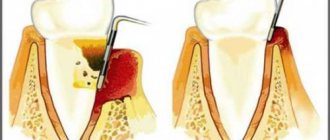
Periodontium is a whole complex of tissues surrounding the tooth. The gums, which everyone can see, are covered with mucous on top, underneath there is a muscular-ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth; between the teeth you can see the gingival papilla. Beneath the soft tissue is bone, which contains the roots of the teeth.
Let's consider the most common diseases of the soft tissues of the oral cavity:
- Gingivitis
. Perhaps the most well-known cause of gum inflammation, both during pregnancy and outside of it, is gingivitis. In essence, this is an acute inflammation of the gum edge, affecting the gingival papillae located in the interdental spaces. The most common symptoms of gingivitis are bleeding and soreness of the gums (especially during brushing), redness and swelling of the tissues (sometimes with noticeable hypertrophy of the gum margin), sometimes accompanied by bad breath. - Periodontitis
. This disease usually occurs in the absence or untimely treatment of gingivitis. If the gums are very swollen during pregnancy, it is quite possible that the pathological process has reached the stage of periodontitis, that is, the ligamentous apparatus (periodontal) surrounding the teeth gradually began to deteriorate. In addition to redness and bleeding of the gums, looseness of the tissues appears; when you press on them, sometimes a discharge with a putrid unpleasant odor appears; a space is formed between the tooth and the gum - a periodontal pocket. In advanced cases, tooth mobility appears. - Periodontal disease
. Unlike gingivitis and periodontitis, the cause of periodontal disease is not inflammatory, but degenerative processes. With periodontal disease, the gums practically do not change color, except in cases where periodontal disease is also accompanied by gingivitis or periodontitis. The gums may be absolutely “quiet”, but the edge of the gum is significantly lower than normal. Due to this, the necks of the teeth are exposed (normally this part of the tooth is not visible, since it is covered by the gum), teeth become sensitive to cold (since there is no enamel in the neck area), the teeth become mobile, and eventually begin to fall out. Periodontal disease is a disease that is associated with age-related changes in tissues. Previously, only older people suffered from it, but now periodontal disease has become much younger. More and more often we meet young people and middle-aged patients who already have all the signs of periodontal disease. People often call the above-mentioned gingivitis and periodontitis periodontal disease, which is wrong: these are fundamentally different diseases that require different approaches to treatment. - Stomatitis
. Unlike the above-mentioned diseases, stomatitis can develop not only on the gums, but also in any area of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. This is an infectious and inflammatory disease, manifested by redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of ulcers or aphthae, severe pain, sometimes bleeding of the affected areas, and profuse salivation. There are several reasons for the appearance of stomatitis: exposure to irritating factors, allergic reactions, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, fungal, bacterial and viral infections. In all cases, the appearance of stomatitis indicates a decrease in immunity, both local (in the oral cavity) and general. - Periodontomas
. This group includes all kinds of benign periodontal tumors: fibromas, cysts, and so on. As a rule, they require surgical treatment, which in pregnant women is always postponed until delivery and is carried out as planned.
In addition to the above-mentioned common ailments, there are also idiopathic periodontal diseases, which we will not consider due to their rarity.
During pregnancy, gingivitis and stomatitis are most often diagnosed. They are completely curable and go away completely without a trace if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all recommendations.
Current promotions!
Implantation in installments regularly
The promotion operates regularly and applies to patients who require implantation.
Main causes of gum disease
The main cause of gingivitis is the presence of soft microbial plaque and hard supragingival and subgingival dental plaque that occurs due to insufficient oral hygiene. If you do not start treatment in time and only “suppress” the symptoms of gingivitis with all kinds of “medicinal” pastes, gels and rinses, the inflammation can affect the periodontium, that is, develop into periodontitis.
Gingivitis of microbial etiology is the most common cause of the generalized form of periodontitis. And local forms of this disease, affecting areas only near one or two teeth, arise mainly due to traumatic factors (occlusion characteristics, defects in old fillings, exposure to dentures, and so on).
Why do gums bleed during pregnancy?
If a woman has sore gums during pregnancy, most likely there is an inflammatory process due to gingivitis or periodontitis. Unfortunately, during this period all diseases develop much faster. If before gingivitis manifested itself only as slight redness, then during pregnancy the gums already “bleed” (as our patients say), swell, hurt, and secrete exudate.
Gums hurt and bleed during pregnancy, primarily because bacteria aggressively multiply in the oral cavity, the inflammatory process becomes more intense due to changes in hormonal levels. As a result, chronic diseases become more active, changes occur in the composition of saliva, immunity sharply decreases, and normal blood supply to the gums is disrupted. The impact of toxicosis cannot be discounted.
But the main reason for gum inflammation during pregnancy is a change in eating habits. And this is not only the desire to eat sweet, starchy and sour foods, but also the diet in general. Many women in this position have an increased appetite: they practice frequent snacking throughout the day, usually in the form of buns, cookies, and cakes.
Food debris gets stuck between the teeth, and if they are not removed immediately after eating, the digestion process starts (acid begins to act). A fertile nutrient medium causes increased proliferation of bacteria, which a weakened immune system and saliva of altered composition are unable to suppress.
Bacteria release waste products, inflammation appears - and your gums become red and swollen: this happens very quickly during pregnancy. In the place where food constantly remains between the teeth, the gum first becomes loose and inflamed, the inflamed soft tissues no longer adhere tightly to the tooth, and a so-called periodontal pocket appears. Food gets into it, which again helps to intensify the inflammatory process directly inside the soft tissues, that is, between the gum and tooth. Over time, hard deposits (“tartar”) form in the periodontal pockets, which subsequently prevents the periodontal tissues from normalizing; recovery is impossible without the help of a dentist.
It cannot be said that only women who neglect brushing their teeth and using dental floss “bleed” their gums during pregnancy, but for them this process occurs much faster and more aggressively.
Photos of the dental offices of the clinic Our Dentist in Krasnogorsk
(images are clickable)
How does the disease develop during pregnancy?
Most women's gums begin to bleed already during the first half of pregnancy, at 2-3 months. During this period, pregnant women often have swollen gums (due to swelling of the marginal part and gingival papillae), the mucous membranes turn red and then take on a bluish tint, and pain is observed (especially when brushing teeth). This form of gingivitis is called catarrhal.
During this period, many women begin to spare themselves, that is, brush their teeth less and less. As a result, the situation gets worse: soft microbial plaque accumulates faster, making the symptoms of the disease even more pronounced.
In the second half of pregnancy, complaints that the gums are swollen become even more common. This is not surprising: the catarrhal form of gingivitis, which occurred earlier, is complemented by the hypertrophic one. Over the teeth, including the front teeth, unsightly formations appear in the form of swelling and growths (granulations). This is not only not beautiful, but dangerous. Granulations contain billions of bacteria, they are abundantly supplied with blood, which means they are a source of infection, blood from which enters almost all organs and systems of the body.
Gingivitis itself is unpleasant, but not critical for a pregnant woman. But the source of infection located in the oral cavity becomes chronic, which means it already affects the entire body, although the mother may not directly notice it.
Another thing is worse: as mentioned above, gingivitis without adequate treatment can turn into periodontitis, and this is not only pain, odor, bleeding and discomfort, but also a direct path to early tooth loss. And the more widespread the process, the more microorganisms and their toxins are constantly in the mother’s body.
If a pregnant woman’s gums become inflamed, it means that pathological processes have begun. But they can be stopped by contacting a dentist or periodontist in time, and the sooner the better.
Treatment of gum disease during pregnancy
The reason that gums bleed during pregnancy in most cases is the catarrhal form of gingivitis, which develops against the background of insufficient oral hygiene when eating habits change. An additional provoking factor is changes in hormonal levels and decreased immunity.
How to treat gums for pregnant women in this case? The complex of measures for the treatment of gingivitis includes three main components:
- Removal of hard deposits
(“tartar”). It was once believed that during pregnancy exclusively manual mechanical methods of removing deposits were indicated. Now the opinion of periodontists on this matter has changed dramatically: ultrasonic cleaning has come to the fore. It is absolutely safe (remember: a woman undergoes an ultrasound scan at least three times during pregnancy) and is less traumatic than mechanical cleaning. In the absence of contraindications, Air Flow technology is also used to remove pigment plaque. This allows you to further prevent the formation of tartar. Professional hygiene for pregnant women (in full) can be carried out at 10-12 weeks of pregnancy. In the first trimester, you should also visit the dentist for a medical examination and, if necessary, gentle cleaning with a brush and paste. - Anti-inflammatory therapy
. Therapy, usually lasting 10 days, is prescribed after removal of deposits. It includes antiseptic rinses and applications with special medicinal gels. Decoctions and infusions of herbs that do not contain alcohol (for example, chamomile, eucalyptus, sage, oak bark), chlorhexidine solution, and fluoride-containing compounds that simultaneously strengthen teeth are used as rinses. All procedures are carried out two or three times a day, after brushing your teeth: first brushing your teeth, then rinsing (at least a minute), and finally application (that is, you just need to smear the gums with gel). - Training in oral hygiene rules
. The doctor gives recommendations regarding the choice of toothbrush and toothpaste, and teaches how to properly use dental floss and irrigator. The condition of teeth and gums throughout pregnancy and after it depends on compliance with his recommendations.
You should not self-medicate; there are a lot of articles and advice on the Internet on how and with what to treat this or that form of stomatitis, gingivitis or periodontitis. It is important to remember that even the best and most useful article cannot replace a visit to the dentist. The doctor not only examines the oral cavity, but also asks the pregnant woman the “right” questions aimed at identifying risk factors in her specific situation.
The doctor can assess when, why and how often professional hygiene is necessary. Is just cleaning and recommendations enough or is it necessary to polish teeth (fillings) to eliminate traumatic factors, as well as the risks of increased formation of dental plaque.
When conducting an examination, the dentist must pay attention to the condition of the periodontium, and if there are periodontal pockets, he will promptly treat them and, possibly, treat them, which is almost impossible to do at home.
Mild forms of gum disease can resolve spontaneously after childbirth and the feeding period, when the body has fully recovered and normal immunity has returned. However, practice shows that during nine months of pregnancy and another six months to a year of lactation, the gums are no longer just “slightly inflamed,” but have undergone serious pathological changes, which means that the process has become chronic, which is a more serious disease, so you should postpone going to The dentist shouldn’t wait until later.
Severe forms of periodontitis may even require surgical treatment, which is a serious intervention. It is not performed during pregnancy, postponing the operation until planned delivery, but this does not mean that treatment is not necessary during pregnancy. The doctor selects conservative treatment methods to reduce symptoms and curb the process.
Prevention of gum inflammation in pregnant women
To avoid gum inflammation during pregnancy, you need to undergo a complete sanitation of the oral cavity at the planning stage.
During pregnancy, you need to follow a dietary regime and try to avoid constant snacking. After any meal, you must brush your teeth and use a irrigator. It is better to choose a brush and paste according to the dentist’s recommendations.
Dental floss and an irrigator will be faithful assistants in the fight for the health of teeth and gums: a special device for washing the interdental spaces and other hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity. It also massages the gums perfectly, but it is important not to overdo it.
Remember that professional teeth cleaning during pregnancy is carried out at least once every 3-4 months. Come to the “Our Dentist” clinic for a free consultation, without expecting clinical manifestations of diseases of the teeth and gums: preventive measures are always preferable to therapy, and even more so, surgery, from all points of view!
Your calls are always welcome! 8 915-367-04-47 - call, make an appointment, come for a free initial consultation, and Our Dentist will become yours!
Dear patients! All prices on the site are valid only at the time of publication. The specialist will inform you about the exact cost and scope of necessary procedures after consultation.
Author of the material: Chief Dentistry Doctor “Our Dentist” Oleg Nikolevich Sharmay.