Salivation is a natural physiological process that occurs throughout a person’s life. Special glands located in the oral cavity are responsible for it.
They are capable of producing about 2 liters of saliva per day. Sometimes the amount of saliva produced increases sharply, which significantly affects the quality of life. This is especially common in childhood.
Increased salivation in a child can be caused by various reasons, both natural and pathological. To understand this issue, it is necessary to consider what role saliva plays in the life of a child’s body.
Functions of saliva
Firstly, it is involved in the digestion of food, making it softer and helping it move through the esophagus. The enzymes contained in saliva are capable of breaking down starch and fats. Thus, food enters the stomach already partially digested.
Secondly, saliva plays a protective role, preventing the mouth from drying out and having a bactericidal effect. It helps to wash away food debris, and with it bacteria. Saliva neutralizes many acids and alkalis, protecting tooth enamel from their aggressive effects. It is also able to strengthen the enamel, nourishing it with important microelements (fluorine, phosphorus, calcium).
Thirdly, it helps make teething less painful by reducing inflammation in the gums. And finally, in the first months of a baby’s life, saliva has a special viscosity, which makes breastfeeding easier during natural feeding.
How to avoid irritation from saliva on a child’s face and neck
The most common reason why a baby drools is teething. How to prevent the formation of rashes, pimples and red spots on the baby’s cervix, chin, neck:
Saliva coming from the mouth collects under the pacifier and causes irritation on the chin.
- promptly blot saliva and wash the skin with boiled water;
- change bibs and blouses more often;
- if a one-month-old baby is drooling, a clean diaper should be placed at the head of the crib to absorb liquid;
- lubricate your face, neck, chest with baby oil or cream.
To feed your baby, prepare food that does not damage the gums, has a soft structure, and has a viscous consistency.
Causes of increased salivation in children
Excessive drooling is scientifically called hypersalivation. In children, there are clearly visible age periods when it can occur most intensely.
Important! There is a distinction between true and false hypersalivation.
True hypersalivation is caused by malfunctions of the salivary glands, and false hypersalivation (also called reflex) in childhood is associated with more serious disorders in which swallowing saliva becomes less frequent.
For example, if the sensorimotor arc malfunctions, the interaction between the brain and the oral cavity is difficult. The child's number of spontaneous swallows is reduced, which creates the appearance of profuse drooling. Depending on the age, the causes of increased salivation in children may be different.
Causes of drooling can be physiological and pathological
Baby care
Excessive salivation requires increased care from parents. Mothers stock up on handkerchiefs or soft napkins to wipe the newborn's mouth and chin.
Even with constant wetting of the chin, dripping drool causes redness, peeling, and a rash on the skin around the mouth and on the chin. Knowledgeable mothers advise using baby cream and lubricating irritated areas several times a day until the skin is restored.
Your doctor will tell you which creams and ointments to relieve irritation on your child’s skin. You need to lubricate delicate skin with the prescribed products very carefully, in a thin layer, so as not to cause even more irritation.
Newborn period
In newborn babies, salivation is normally absent due to the underdevelopment of the salivary gland apparatus. However, often a mother may notice how, in the first hours of a child’s life, a colorless liquid, very similar to saliva, is actively secreted from his mouth.
Most often, this is how amniotic fluid comes out, which the baby managed to swallow while passing through the birth canal. Normally, this phenomenon should stop a few hours after birth. If drooling continues longer, it is better to inform your pediatrician (neonatologist) about this in order to exclude serious health problems.
How to help muscles?
Exercises for the speech apparatus are useless while the muscles are too relaxed or, conversely, tense. Therefore, before classes you should massage the facial, neck and shoulder muscles. First of all, these are light strokes; sudden movements cannot be made. Lay your baby down so that his head is on your lap, at right angles to your chest. Movements are made with both hands on both sides of the face simultaneously in the following directions:
- from the middle of the forehead to the temples;
- from eyebrows to hairline;
- from the middle of the forehead along the cheeks to the neck and shoulders;
- from the earlobes through the cheeks to the nasal wings;
- from the corners of the mouth, first to the middle of the upper lip, then to the middle of the lower lip, then to the wings of the nose.
If the muscles are very tense, then the movements should be very light all the time, but if they are relaxed, then vigorous kneading and gentle stroking should be alternated.
This is general advice for parents of children with dysarthria. Specific sets of games and exercises and medications, if necessary, are selected only by a speech therapist and a neurologist, based on the characteristics of the child’s condition.
Publication date: 10/03/2019. Last modified: 01/13/2020.
Drooling at 2–3 months
At the age of about 2 months, a baby may experience profuse salivation, caused by the fact that the salivary glands finally begin to work at full capacity. It is at this age that a child may need his first bib to protect his clothes from getting wet.
The mother also needs to very carefully monitor the condition of the child’s skin, especially the area around the lips and chin. Excessive saliva can irritate baby's delicate skin. To prevent this from happening, it is recommended to lubricate the area around the mouth with baby cream or Vaseline.
Inflammation of the submandibular salivary gland
Closer to 3 months, children become active explorers of the world around them and taste everything. They put fingers, toys and any other objects at hand into their mouths.
The baby's body becomes acquainted with new microflora, which leads to increased secretion of saliva, which performs a protective function. At this age, increased saliva production can also occur against the background of an acute respiratory disease.
Breathing through the nose becomes difficult, and the child has to breathe through the mouth. This causes the nasopharynx to dry out and reflexively release a larger amount of saliva than usual, which moisturizes the air and disinfects it.
Is fist sucking harmful?
Often parents try to wean their child off this habit because they are concerned about his bite and the quality of his future teeth. Some displacement of the teeth is indeed possible if the child chews his fist, fingers and other objects very enthusiastically. But this only affects baby teeth and does not affect the molars.
Applying mustard, pepper and other tasteless substances to your fingers or fist is not the best idea, as it will cause stress and will not help wean your child off the habit. It is better to just leave the child alone and let him do what his body requires.
22.11.2017
- Share:
Teething period
Teething usually begins around 6 months of age. The child becomes whiny and irritable. The process of tooth extraction is accompanied by pain and the formation of wounds on the gums. They can greatly disturb the baby, bringing him a lot of suffering.
Salivation helps make pain less intense: saliva has an anti-inflammatory and calming effect. Teething is greatly extended over time and sometimes lasts up to 2 (and even 3) years.
Important! Increased salivation up to 2 years of age is most often caused by natural causes and is physiological.
Why is that bad?
- ✓ Excessive salivation can irritate the skin of the chin and perioral area, causing the child to develop a rash and bothersome irritation.
- ✓ Excess secretion gets on clothes and surrounding objects, the child may feel discomfort, just like the people nearby.
- ✓ Children over 3 years of age may experience psychological discomfort from such a problem. Peers may make fun of him, laugh, the child will be embarrassed by drooling, withdraw into himself.
The concept of “bad” in this case is somewhat contradictory, since in most cases there is no serious threat to the baby’s health. However, anyone would prefer not to have such a problem. Why?
- ✓ Excessive salivation can irritate the skin of the chin and perioral area, causing the child to develop a rash and bothersome irritation.
- ✓ Excess secretion gets on clothes and surrounding objects, the child may feel discomfort, just like the people nearby.
- ✓ Children over 3 years of age may experience psychological discomfort from such a problem. Peers may make fun of him, laugh, the child will be embarrassed by drooling, withdraw into himself.
Increased salivation after 5 years
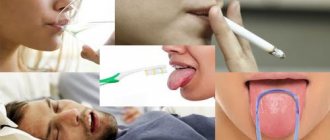
If a symptom bothers a child at an older age, after 5 years, then this may be a cause for concern on the part of the parents. There are a number of reasons why saliva is produced in large quantities:
- inflammation in the oral cavity (stomatitis, gingivitis, candidiasis);
- infections of the upper respiratory tract and nasopharynx (for example, with adenoids, copious amounts of saliva are produced at night and prevent the baby from sleeping);
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, duodenitis, pancreatitis);
- helminthic infestations;
- poisoning with drugs, as well as toxic substances and household chemicals (a life-threatening condition - requires immediate medical attention);
- diseases of the nervous system (especially with damage to the central nervous system, some forms of cerebral palsy, congenital malformations).
If there is increased drooling of any etiology, it is best to show the child to a doctor. Only he will be able to determine the true cause of the symptom and, if necessary, prescribe additional examinations.
When to see a doctor
It is not always safe for a baby to drool and bubble at 2 months. Often the appearance of such a symptom can mean the onset of a serious illness.
How much should a 6 month old baby eat?
If you notice the following signs, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is inflamed. If ulcers, wounds and erosions are visible on the tongue, then you should immediately begin qualified treatment.
- The sockets on the gums become inflamed during teething.
- Helminthic infestations. Helminths release toxic substances and waste products into the body, which causes saliva production to increase.
- Inflammatory processes of the ENT organs: otitis, sinusitis.
- Poisoning with toxic substances: mercury, lead, chemical pesticides.
- Traumatic injuries increase the secretion of the salivary glands and disrupt their activity.
- Infectious diseases. In this case, hypersalivation is auxiliary in nature, thus the body gets rid of pathogenic microorganisms. Often the temperature also rises, a runny nose, cough, and redness in the throat appear.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Streptococcal sore throat.
- Epiglottitis is swelling of the epiglottis. An ambulance must be called.
- Cramps.
For hypersalivation, anticholinergic drugs are prescribed:
- Atropine;
- Spasmolitin;
- Tifen;
- Diprofen.
Important! All medications should be taken with caution. If the remedy is chosen incorrectly, it will cause hypersalivation and more serious consequences. If surgery or radiation is required, you should be aware that this can lead to deviations in the form of caries and facial asymmetry. All decisions regarding treatment are always made thoughtfully, and the most appropriate method is selected based on the individual characteristics of the child and feasibility.
In some cases, treatment requires speech therapy massage, since hypersalivation makes it difficult to pronounce sounds.
If the cause of salivation is physiological, then it does not require medical intervention and goes away on its own after some time. In the case of pathology, the underlying disease, which was the result of hypersalivation, should be identified and a course of treatment carried out.