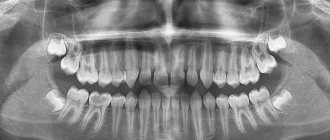
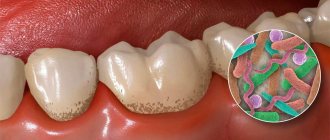
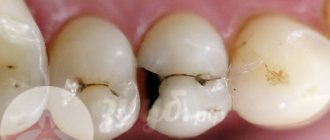
The most important area of dentistry is the prevention of dental caries.
It is necessary for children, teenagers and adults.
After all, routine prevention of dental caries is the shortest path to a healthy smile, for which there are now available means and effective methods.
According to the methods of influence, the prevention of dental caries differs into primary and secondary.
But in general, it represents a set of measures to prevent the occurrence of diseases, their relapses and complications. It begins with a visit to the dentist, which is necessary at least every six months.
Methods for preventing caries
Conventionally, methods of caries prevention can be divided into household and professional. Household methods include time-tested and proven methods that are passed down from generation to generation. They do not require any energy expenditure, but they do need regularity. Professional prevention includes various hygiene procedures and timely treatment of caries. They also distinguish endogenous prevention, which is aimed at strengthening teeth from the inside, and exogenous, when all actions are carried out locally. So how can you stop dental caries?
Primary or endogenous prevention of caries
Proper nutrition is important in preventing tooth decay. This is not only about giving up chocolate and cakes, but also soda and concentrated juices. You should not eat sour apples, as they disrupt the acidity of saliva. It is better to replace them with hard, raw carrots, which clean your teeth almost better than a good specialized paste. It wouldn’t be a bad idea to nibble on Japanese horseradish – wasabi – from time to time. Japanese scientists have found that it blocks the growth of carious microbes.
Paradoxically, kissing is a great way to defeat tooth decay. When we kiss, the gums are massaged and salivation becomes more intense, and along with it, the acid-base balance is evened out.
If you have a tendency to develop caries, it makes sense to consult a specialist for recommendations on taking vitamins. Russian scientists have found that the demineralization of enamel is affected by a deficiency of vitamin C. During the experiment, it was found that those who were attacked by caries had a decrease in its content in the body several months before. In addition, vitamin D also increases the resistance of teeth to caries, since calcium is easily absorbed with it. Don't forget about such a useful element as fluorine. It has a pronounced anti-caries effect.
How to reduce the adverse effects of carbohydrates on teeth
Fermentation of carbohydrates under the influence of microbes leads to the production of organic acid, which destroys tooth enamel and contributes to the development of caries. It is impossible to completely stop eating carbohydrates, but it is quite possible to reduce the intensity of their influence on the development of caries. The following measures will help with this:
- Reducing the amount and, most importantly, the frequency of eating carbohydrate foods, so that the teeth come into contact with carbohydrates as little as possible.
- In some cases, your doctor may recommend switching from sugar to sweetener substitutes.
- Reducing the time carbohydrates spend in the mouth. This can be achieved in two ways: do not eat the sweet dish last, and be sure to rinse your mouth after eating.
- Avoid eating sweets at night and between meals.
If any of the recommendations are violated, to reduce the risk of caries, you need to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth.
Secondary or exogenous prevention of caries
As already mentioned, exogenous prevention is characterized by a local effect on the teeth. Good cleaning should occur at least twice a day using dental floss and an antibacterial mouth rinse. If you are the owner of dentures, then you cannot do without using an irrigator. You need to brush your teeth for at least 4 to 5 minutes.
How to brush your teeth properly to prevent tooth decay:
- The method of brushing your teeth should combine horizontal, vertical and circular movements.
- Brush movements should be short and circular. Make sure that the long bristles remove plaque from under the gum line and between the teeth.
- The head of the toothbrush should be at an angle of 45°.
- Brushing your teeth should take at least 5 minutes.
- It’s not just your teeth that you need to brush – plaque on your tongue is just as much a breeding ground for germs as dental plaque.
Products for the prevention of dental caries
Toothpaste against caries, or anti-caries, helps strengthen mineral dental tissues and prevents the formation of plaque due to the fluorine, phosphorus and calcium compounds introduced into the composition. The anti-carious effect of toothpastes is explained by the fact that topically applied fluorides increase the resistance of enamel to adverse effects. Penetrating into the enamel structure, fluorine creates a more durable fluorapatite system, fixes phosphorus-calcium compounds in hard dental tissues, and also suppresses the growth of soft plaque microflora. Anti-caries paste is most active during the period of enamel maturation, and later its effectiveness decreases significantly. Therefore, it is most reasonable to use anti-caries toothpastes in childhood to prevent caries in children.
Unlike toothpaste, a toothbrush can significantly improve or, if chosen incorrectly, worsen your oral health. For example, regular manual brushes with stiff bristles are not suitable for people with problem gums. Such brushing will only increase the colony of harmful bacteria and increase gum bleeding. The same can be said about electric toothbrushes, which also drive plaque under the gums, which leads to a serious inflammatory process. Today, the most effective way to prevent caries is to purchase a brush with ultrasound, which not only gets rid of plaque, but also destroys harmful microorganisms.
Clinical researches
ASEPTA toothpastes are clinically proven effective. For example, clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
In addition, clinical studies have proven that regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA ACTIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 60%, improve the overall condition of the oral cavity by 44% and reduce inflammation by 33%.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Modern prevention of caries
While strictly following all the rules of oral hygiene, do not forget to visit the dental office twice a year. No matter how hard we try to brush our teeth thoroughly and regularly, it is still not enough. Only professional hygienic cleaning can completely remove plaque and get rid of tartar. In addition, as a local prevention of caries, the hygienist performs a dental remineralization procedure. It allows you to restore the mineral composition of dental tissue and increase its resistance to caries. Typically, this procedure is part of professional hygiene and is recommended before and after teeth whitening at home or in the dentist's office.
It is especially important to seal teeth in time to prevent dental caries. Since 1984, in the USA, and later in our country, sealants have been used that delay the development of caries by closing the fissures and blind pits of the tooth. The procedure for sealing fissures is completely painless and is usually carried out in childhood and adolescence.
Correcting malocclusion and crooked teeth is one of the important components of professional caries prevention in adults and children. It has been proven that malocclusion and crowding of teeth, uneven load on them provokes the carious process and creates favorable conditions for its development.
The most effective and at the same time simplest way to prevent dental diseases is proper and regular dental and oral hygiene. By following simple, but systematic, rules, you can avoid many troubles with your teeth. But do not forget that caries is an internal signal of a failure of the body as a whole. As they say, healthy teeth in a healthy body!
The role of nutrition in preventing dental caries
One of the effective measures to combat caries is the correct approach to nutrition. The tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive to the lack of certain food components. In particular, a lack of protein in the diet prevents the accumulation of calcium and disrupts the structure and strength of enamel. At the same time, foods that are too fatty increase the permeability of the enamel, which increases the likelihood of the formation of carious lesions.
An excess of refined carbohydrates (sweets, flour products, sugar) in the diet not only reduces the resistance of teeth to the development of caries, but also weakens the immune defense, which is also a risk factor.
To prevent caries, it is important to adhere to the following dietary recommendations:
- A sufficient amount of protein must be present in the daily diet;
- eat foods containing vitamins C, D and group B;
- be sure to eat foods rich in calcium and phosphorus (milk, cheese, eggs, fish, broccoli, legumes), as well as fluoride-containing foods (sea fish, Georgian tea);
- it is necessary to limit the consumption of foods rich in “fast” carbohydrates, eat as little sweets, cakes and refined sugar as possible;
- Avoid sticky products: they can remain on the surface of tooth enamel for up to an hour, contributing to its demineralization for a long time.
The nature of your diet directly affects the condition of your teeth. A rational, fortified, balanced diet is an effective method of non-drug prevention of caries.