Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Dental prosthetics is a sequential multi-stage process. It is the high-quality implementation of each of them that leads to an excellent final result. There are main stages of prosthetics , some of them have their intermediate stages. They can also be clinical, that is, performed in a doctor’s office, and laboratory, in a dental laboratory. The main ones include: examination, preliminary treatment, prosthetics. The last stage includes the restoration of supporting teeth , their preparation, taking impressions, determining the closure of the jaws, fixing temporary structures, fitting and fixing permanent dentures and an adaptation period. Laboratory stages are carried out by a dental technician after taking impressions and determining occlusion (closing of the jaws). Before starting any treatment, it is necessary to draw up a treatment plan.
Oral examination
Any treatment process must begin with an examination. A preliminary examination allows you to determine the need for prosthetics, choose the optimal type of design and amount of work.
Examination of the oral cavity in dentistry Additional examination (instrumental, x-ray, etc.) provides information about the condition of the supporting teeth, periodontal tissue, bone tissue, the need for root canal treatment, and the possible presence of inflammatory elements at the tops of the root canals or in the bone.
This is an integral stage of successful prosthetics, as it allows not only to identify and eliminate hidden problems, but also to avoid possible complications in the future, after installation of the prosthesis .
Filling or crown: which option to choose?
The crown of a tooth refers to both its part located above the gum mucosa and an artificial structure in the form of a case, put on the natural crown destroyed by caries. The need for such tooth restoration arises after treatment of deep caries and pulpitis with the passage of root canals, and sometimes after mechanical trauma to the jaw and tooth.
Many patients are afraid of having a crown installed and beg the dentist to limit themselves to a filling. But if you fill a pulpless tooth, of which less than 50% of its own tissue remains, then it will most likely have to be removed very soon. After all, hard tissues after removing the pulp become very fragile and easily crack under load. Prosthetics after removal will become inevitable, but will cost much more.
Preliminary treatment
Dental treatment is an important point not only before prosthetics or implantation, but throughout life. Timely sanitation of the oral cavity preserves the health and integrity of the dental system, avoids possible complications, as well as the spread of infection throughout the body. Treatment of abutment teeth , hidden and obvious carious cavities, acute inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues or bones is mandatory before starting any prosthetics. This will allow not only to eliminate defects or diseases that have arisen in a timely manner, but also to extend the service life of the prosthesis. Also, some fixed structures require mandatory endodontic treatment.
Materials for the manufacture of prostheses
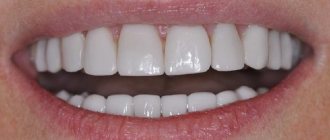
For permanent restorations, metals, ceramics and zirconium dioxide are used. Metal-ceramic crowns consist of 2 layers: a metal base, which is lined with a ceramic composition. Thick double walls require strong turning. Zirconium crowns are very durable, so the teeth need to be prepared minimally for them. New ceramic compositions, such as E-max, are quite durable and at the same time make it possible to choose the color of teeth of any shade.
The same materials can be used for conditionally removable prosthetics.
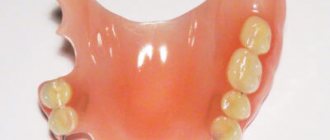
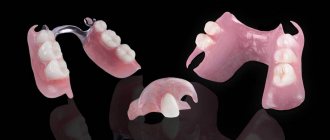
For removable dentures, the most important element is the base. The base is made from:
- Acrylic
- Acry Free
- Nylon
The hardest material is acrylic. Its disadvantages are microporosity and rapid wear. Acrylic contains substances that cause allergies. Pros: low cost and ease of processing.
Acry Free is a material that contains no allergens, it is softer and thinner than acrylic. It is easier to get used to such a product.
Nylon restorations fit comfortably in the mouth and do not cause allergies, but do not distribute the chewing load well enough due to their softness.
Metals and plastics are used for fastening elements of partial removable structures. And for the base - the same acrylic and plastics based on acrylic resins.
The service life of acrylic restorations is about 3 years, Acry Free and nylon restorations are 5 years. Dentures are replaced for several reasons. This could be a breakdown, an allergy, or a desire to replace an old design with a more modern one. The main thing is that removable structures do not stop bone loss. The relief of the oral cavity changes, the gums sag, and the restoration no longer fits.
Stages of dental prosthetics
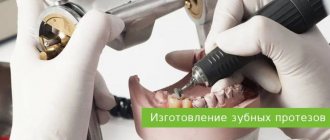
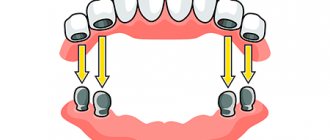
Rarely does dental prosthetics happen in a single stage; generally, it is a sequential, multi-stage process. After preliminary endodontic treatment, it is necessary to restore the supporting teeth using inlays or pins. Then the doctor prepares (grinds) them to create a place for the prosthetic structure, takes impressions from both jaws and the prosthetic area, and determines the color of the artificial teeth. A very important step in prosthetics is determining the occlusion (the relationship of the jaws), which allows you not to interfere with the prosthesis during chewing. The impressions are sent to the dental laboratory. This is a kind of information for a dental technician about the shape and size of the teeth, the anatomical features of the prosthetic bed, the location and type of structure. Based on the impressions obtained, the dental technician casts diagnostic and working models from plaster, which are an exact copy of the teeth, and in the case of complete edentia, the gums. Next, the structure itself is modeled with wax and the prosthesis itself is created using various methods and techniques. Sometimes during its manufacture it requires checking, fitting and fitting. The finished structure is fixed in the oral cavity. In some cases, additional correction of the prosthesis is required during the adaptation period.
Care of cast dental prosthetic structures
Regardless of what percentage of teeth are replaced by a bridge or hidden by cast dental crowns, oral hygiene must be maintained. To clean teeth and cast dentures, use regular toothbrushes, toothpastes, and dental floss. In addition, dental rinses have shown good results in oral care. They help effectively remove dirt from teeth, tongue and hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity. If you do not trust store-bought and pharmacy dental hygiene products, you can use an aqueous solution of salt and soda or infusions of medicinal herbs to rinse your mouth. Brushing your teeth is done at least 2 times a day, and rinsing your mouth after every meal.
In addition, after installing cast dentures for teeth, there are some restrictions that need to be taken into account. It is necessary to give up bad habits associated with the oral cavity: biting your nails, grinding your teeth and opening packages with your teeth is prohibited.
You need to be careful when handling solid food: caramel, bones and cartilage, when chewed, can damage the material and deform the prosthetic structure of the teeth. After installing a cast prosthetic structure for teeth in the oral cavity, the attending physician will give more detailed recommendations on how to care for it. It is not for nothing that the casting of dental prosthetic structures from noble and non-precious materials is so popular among dentists and their patients. Installing such structures for dental prosthetics improves the appearance of the oral cavity, improves the quality of life, and does not require excessive financial costs.
Stages of dental prosthetics with metal-ceramics
process of metal-ceramic dentures begins with the preparation of previously prepared abutment teeth and obtaining a two-layer impression.
Bridges They are removed with special elastic masses, which allows the dental technician to accurately convey information about the shape, size and location of the teeth and the orthopedic structure.
Next, temporary crowns or bridges are fixed onto the prepared teeth in order to temporarily restore the cosmetic defect and prevent changes and displacement of the tissues of the prosthetic bed. Central occlusion is determined - the nature of the closure of the teeth of both jaws. All received data is transferred to the dental laboratory. At the next visit, the solid metal frame of the prosthesis is fitted and the color of the ceramic veneer is determined and sent back to the laboratory for ceramic veneering. On the third visit, the doctor fits and temporarily fixes the finished metal-ceramic prosthesis . Sometimes at this visit the prosthesis is fixed with permanent cement. Temporary fixation allows, if necessary, to adjust the prosthesis during the adaptation period.
Fixation of dentures
Fixing agents are used only if removable dentures are installed, since they allow the structure to stay more firmly in the oral cavity and also have a shock-absorbing effect, reducing irritation of soft tissues. Most of these products also have antibacterial properties.
Cream for fixing dentures
These include:
- fixing creams, gels, adhesives - they are applied to the surface of the prosthesis adjacent to the patient’s tissues, strictly according to the instructions (some are applied only to dried mucosa); Please note that creams and gels have different durations of action: the widely advertised Corega cream lasts 3–4 hours, Rocs cream lasts up to 12 hours (optimal duration), and Lacalut - 24 hours; You should also keep in mind that some fixatives contain zinc, which has a good anti-inflammatory effect; but with prolonged use of such drugs, an overdose of zinc occurs, which is harmful to the body, therefore zinc-containing fixatives can only be used in courses of 3 to 4 weeks with long breaks;
- powdered products - sprayed onto the surface of the removable dental prosthesis, then the product is put on in the usual way and lightly pressed against the gums and palate;
- strips of fabric - designed to tightly fix a removable denture in the absence of teeth and make it more comfortable to wear.
An orthopedic dentist will help you choose the right fixation agent.
Stages of dental prosthetics with inlays
Ceramic inlays are a type of microprosthetics, which is a modern alternative to conventional fillings. They fill previously prepared cavities in the teeth, restoring their shape and function. The indication for ceramic inlays is the ability to save a tooth with significant destruction of its coronal part (up to 65%).
At the initial stage of tooth preparation, the doctor removes all tissue destroyed by the carious process and, if necessary, carries out endodontic treatment. After the tooth is cured, an impression is taken and sent to the laboratory, where a ceramic inlay is made . At the next visit, the finished structure is fixed to the tooth using special cement. Ceramic inlays have high strength and durability, and are color resistant to food coloring. They are also highly aesthetic.
What do patients say?
Patient reviews of partially removable laminar dentures are ambiguous. Some patients report severe discomfort when wearing products (gums hurt, impaired diction appears) at the stage of getting used to the design. Most patients manage to get used to the dentures after 2 months of wearing them regularly.
Patients who chose nylon products praise their appearance and note the plasticity and softness of the material. Cases of complications have not been described by patients.
Considering the characteristics of plate products, dentists advise using them as temporary structures until it becomes possible to install fixed dentures.
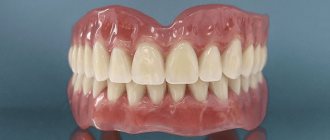
Stages of dental prosthetics with complete edentia
The production of a complete removable denture begins with an examination of the patient’s oral cavity, diagnosis of the condition of the dental system, and selection of a suitable design. The first impression is taken with a standard impression tray. Depending on which design is chosen, the impression mass is selected. The impressions are sent to the laboratory, where a dental technician casts plaster models and makes a wax base with occlusal ridges and custom impression trays.
On the second visit, using these trays, the doctor takes functional impressions, and using rollers, determines and fixes the occlusion. All information is transmitted to the dental technician. He makes the future prosthesis from wax with acrylic (plastic) teeth .
On the third visit, the structure in the oral cavity is checked, occlusion, fit, and the appearance of the patient’s face are assessed. The doctor makes the necessary notes and corrections and transfers the future design to the laboratory. The dental technician finally models the wax structure, plaster it into a cuvette where the wax is replaced with plastic. Next, he grinds and polishes the finished prosthesis.
At the next visit, the prosthesis is handed over. Finished structures are fitted, fit, occlusion and aesthetics are checked. The doctor will tell the patient how to use and care for the new prosthesis. During the adaptation period, additional corrections are possible.
What is a plate prosthesis made of?
To begin with, let us recall the general requirements for the material:
- No impact on the oral mucosa and the body as a whole;
- Aesthetics;
- High strength, low abrasion;
- Preservation of shape during use;
- Easy to care for;
- No unpleasant taste or smell;
- Must be repairable;
- Must be technologically advanced.
Plate dentures consist of a base (foundation) and artificial teeth. Also, in case of partial absence of teeth, support-retaining elements (clasps) .
The base is made from:
Acrylic plastics
Plastics are polymers that represent a large group of high-molecular compounds obtained chemically from natural materials or by chemical synthesis from low-molecular compounds. One of the properties of polymers is their high manufacturability, the ability to be molded under heat and pressure and stably retain their given shape, which explains their widespread use in orthopedic dentistry. Plastics are made from powder and liquid.
Advantages:
- Affordable price;
- Simple manufacturing technology (various color and size combinations are possible);
- Short production time for the prosthesis;
- Easy to care for.
Flaws:
- With prolonged use of the structure, the material begins to release special substances that can cause a local allergic reaction;
- Acrylic plastics are porous compounds. With poor oral hygiene and poor-quality care of the prosthesis, it becomes contaminated with microorganisms, which helps to reduce local immunity. And this can cause the development of inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa;
- Possibility of injury to the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Nylon
Nylon removable dentures
Nylon is an elastic material.
Advantages:
- Hypoallergenic;
- High aesthetics (complete imitation of natural teeth and gums);
- In case of partial absence of teeth, the supporting teeth are not treated;
- The flexibility of the material ensures a short adaptation period and also has the least mechanical impact on the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Easy care;
- When used carefully they last quite a long time.
Despite the significant positive qualities, nylon prostheses have their disadvantages :
- The fixing elements do not transfer the load to the remaining teeth. As a result, the mucous membrane takes on the chewing load, which leads to gradual periodontal damage and further inflammatory process;
- The absence of a rigid frame leads to the fact that chewing pressure is distributed unevenly. Subsequently, this leads to atrophy of the bone tissue of the jaws;
- For technological reasons, nylon prostheses are not polished. This design absorbs and retains foreign odors;
- Frequent adjustments are necessary;
- High price.
The material for the base is selected based on the individual characteristics of the body and the condition of the oral cavity.
Stages of prosthetics with veneers
Veneers are thin ceramic plates that are fixed to the front surface of previously prepared teeth and allow them to correct cosmetic defects, change shape, size and color.
Crowns and veneers The first stage, as with any prosthetics, is a survey, examination and
diagnosis of the oral cavity .
If necessary, X-ray and laboratory tests are performed. A very important stage is planning future structures, taking into account not only the condition of the teeth and oral cavity, but also the gender, age, and character of the patient. The shape of the face, the gingival margin and smile line, and the individual characteristics of the teeth are assessed. The size of the veneers is predicted and calculated. A photographic record is being taken. The doctor models the future restoration on a computer using a special program and demonstrates the result to the patient. At the next visit, the teeth are prepared, starting with cleaning their surfaces from plaque. The required shade of filling material is selected. Under anesthesia, the front surface of the teeth is prepared and the required amount of enamel is removed. The next step is taking impressions. Based on the dental impressions obtained, a plaster model is cast in the laboratory to obtain an exact copy of the patient’s teeth, on which the dental technician makes future veneers. After the doctor has prepared the teeth, temporary veneers . A dental technician, using computer systems, special scanners, sensors and ovens, produces structures strictly according to the specified parameters.
At the next visit, the doctor tries on the finished structures. If necessary, adjustments are made, deficiencies are eliminated, and the bite is checked. Veneers are fixed to the teeth using special cement.
Why do they grind down a tooth for a crown?
The dentist must remove part of the tissue to form a stump of a certain shape:
- a ledge is formed at the edge of the gum, on which the crown will be placed in the future;
- The edges of the tooth should remain almost parallel, and not cone towards the chewing edge.
The service life of the artificial crown largely depends on the quality of preparation and compliance with these two conditions. If there is no smooth and even ledge, its edge will not adhere to the tooth, but will hang over the gum, forming a gap. Soft plaque will accumulate around, and colonies of pathogenic microflora developing in it will cause caries and gum inflammation.
If the tooth stump takes a cone-shaped shape after filing, it will be difficult for the dental technician to produce a functional structure that can withstand the chewing load. This is fraught with depressurization (or decementing) of the crown. Residues of food and soft plaque with microflora will penetrate under it, which will eventually lead to its loss.
Preparation for the crown of a living, non-pulpless tooth should be carried out with plenty of cooling. After all, overheating of the tissues will cause inflammation of the pulp, which may appear after the installation of the crown. Due to the need to treat pulpitis, it will have to be removed and redone after treatment of the canals.