What is oral candidiasis?
Oral candidiasis (also called oral thrush) is an infection of the mouth caused by the yeast-like fungus Candida. These microorganisms are part of a healthy microflora, but under certain circumstances their reproduction disrupts the favorable environment and becomes a source of disease processes. Inflammation and plaque on the tongue, ulcers on the mucous membrane and discomfort in the mouth - this disease is called oral candidiasis.
Infants are most susceptible to this disease, but at this age it is treated faster and is tolerated almost painlessly. Oral thrush is often observed in adults after 50 years of age, when the immune system is already weakened. Oral candidiasis is less common in men than in women. Recently, the percentage of cases has increased significantly, which is associated with uncontrolled use of medications: weakening of cellular immunity increases the risk of oral candidiasis after antibiotics, or rather their improper use. Microbiology, the science of microorganisms, studies the essence of oral candidiasis. And she successfully copes with her task, at the moment this disease has been studied in detail, and doctors know all the methods of treating and preventing infection.
When should you make an appointment with a doctor?
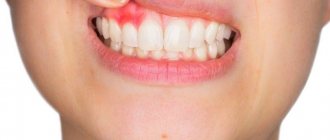
Swelling of the cheek is a symptom of an acute inflammatory process, in which you need to urgently seek medical help. Other reasons to visit a dental clinic are:
- redness and looseness of the gum tissue,
- bleeding when brushing teeth,
- constant metallic taste in the mouth,
- discomfort and pain,
- uneven height of the gingival margin,
- exposure of the necks of the teeth,
- discharge of pus from under the gums.
The temperature often rises, appetite disappears, and weakness occurs. These are symptoms of intoxication of the body.
Causes of oral candidiasis
A healthy person is still a carrier of fungi of the genus Candida, since they are part of the microflora and calmly coexist with other microorganisms without causing harm. But any change in the balance in the body can lead to rapid proliferation of bacteria and the development of disease. A weakened state of immunity plays a key role in the etiology of oral candidiasis, but any of these reasons can be the starting point for the onset of the disease:
- pregnancy;
- immunodeficiency states;
- infectious processes;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics or improper use of medications;
- injuries and damage to the oral mucosa;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- contact with an already sick person.
Causes of the pathological process
Inflammation of the gums and swelling of the cheek can develop due to tissue injury and the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the wound. Inflammation can lead to:
- pericoronitis,
- complex tooth extraction or other traumatic dental surgery,
- chipping of a tooth with the formation of a sharp edge that damages the gums,
- advanced caries and pulpitis,
- tartar,
- cyst,
- poor quality filling or prosthetics.
The inflammatory process develops faster in people with reduced immunity, diabetes, and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Also at risk are patients with complex malocclusions.
Diagnosis of oral candidiasis
Candidiasis (thrush) of the oral cavity can be detected during an examination by a dentist if the patient has characteristic complaints. The doctor examines the condition of the oral mucosa, examines scrapings, and carefully examines the hair and skin. If you have oral candidiasis, you also need a blood test to check your glucose levels and rule out diabetes. The sooner you detect the presence of this infection, the easier it will be to get rid of it, so you should not delay diagnosis just because the symptoms do not cause you discomfort.
Symptoms of oral candidiasis
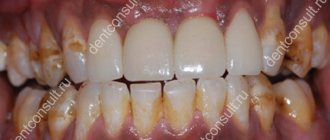
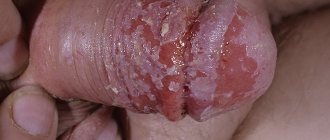
- Infection is characterized by the appearance of swelling and a whitish coating on the mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips, and tongue. When the plaque is removed, the surface bleeds, and the patient experiences a burning sensation.
- With oral candidiasis, the tongue and throat become sensitive, and any contact is painful for the patient.
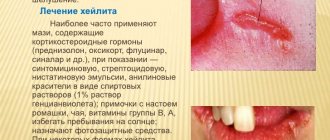
- Signs of oral candidiasis also include cracks in the corners of the lips and redness of the mucous membrane.
- Symptoms of oral thrush include severe dry mouth, a feeling of tightness of the mucous membrane, and roughness of the internal surfaces.
- Patients often complain of increased temperature due to oral candidiasis. Sometimes this disease is accompanied by the appearance of small ulcers on the inside of the lip and cheek mucosa, which are filled with pus and emit a characteristic odor of oral candidiasis.
Signs of oral candidiasis in HIV diseases are slightly different from traditional ones. In this case, the infection spreads quickly and immediately becomes acute, and plaques and plaque appear not only in the mouth, but also in the genital area. With HIV, thrush of the oral mucosa is difficult to treat, so even with minor symptoms it is better to visit a doctor and check your health.
Flux symptoms
Clinical manifestations of acute periodontitis/periostitis are quite characteristic. Flux manifests itself as sharp pain in the tooth area, intensifying even with light pressure on it. Swelling and redness of the lips, cheeks, enlarged gums, and the tooth is often mobile.
There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, and sometimes fistulas on the gums. A characteristic sign of gumboil is the appearance of independent pain, weak at first, then intensifying, becoming pulsating and tearing. Its difference from pain with pulpitis is that it is strictly localized and becomes sharp when pressing on the diseased tooth, especially in the form of tapping. The closing of teeth is so painful that many people refuse to eat even liquid food.
Clinical manifestations of acute periodontitis/periostitis are quite characteristic. Flux manifests itself as sharp pain in the tooth area, intensifying even with light pressure on it. Swelling and redness of the lips, cheeks, enlarged gums, and the tooth is often mobile.
There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, and sometimes fistulas on the gums. A characteristic sign of gumboil is the appearance of independent pain, weak at first, then intensifying, becoming pulsating and tearing. Its difference from pain with pulpitis is that it is strictly localized and becomes sharp when pressing on the diseased tooth, especially in the form of tapping. The closing of teeth is so painful that many people refuse to eat even liquid food.
It is also possible to increase body temperature to 37.5-38.0°C. Severe pain and difficulty eating food force the patient to see a dentist within the next few hours from the moment of illness.
Chronic form of periodontitis
In chronic forms of periodontitis, a different picture is observed. The most formidable and insidious in its course and possible complications is chronic granulating periodontitis and exacerbation of its course. The pain reaction is mild, but often in the vestibule of the oral cavity, in the projection of the apex of the root of the affected tooth, a fistula periodically opens with small purulent discharge.
When the fistula is closed during periostitis, swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane in the area of the flux and pain when pressing on the diseased tooth are possible. Chronic granulating periodontitis is diagnosed based on a comparison of clinical manifestations with X-ray data, which shows destruction of the periodontal gap and changes in the jaw bone in the form of “tongues of flame” in the area of the apex of the tooth root. The purulent process in the medullary spaces of the jaw adjacent to the periodontium leads to the spread of infection over a considerable distance.
The vital activity of pathogenic microflora during the long-term existence of a chronic pathogenic focus ultimately leads to odontogenic chronic sepsis. This provokes the emergence, formation or exacerbation of chronic infectious diseases of the heart, liver, kidneys and other organs.
The presence of such infectious foci can dangerously affect the course of pregnancy at any stage; complications such as infection of the female genital area, miscarriage, and disruption of the formation of fetal tissue occur.
Classification of oral candidiasis
This disease is usually divided into several types, each of which has its own characteristic features. Experts distinguish between acute and chronic oral candidiasis.
Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis
Characteristic of infants with weakened immunity. Oral candidiasis, or oral candidiasis, can be triggered by a previous infectious disease or gastrointestinal disorder. The disease is transmitted through a pacifier or dishes; the disease manifests itself in the form of a light or grayish coating on the mucous membrane. At the initial stage, plaque is painlessly removed; with the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx, it thickens and spreads in the oral cavity. It is almost impossible to remove plaque on the tongue without causing bleeding.
Acute atrophic candidal stomatitis
Accompanied by peeling of the integument, dryness and burning of the mucous membrane, it is painful for the patient to eat and touch the infected area. With this form of oral candidiasis, the infection can spread further - to the larynx, pharynx and even the esophagus.
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis of the oral cavity
It is characterized by a change from a whitish coating to a grayish-yellow one, after removal of which slight bleeding occurs. Along with plaque, plaques and thickenings appear that cannot be cleaned off or removed; they go away on their own during the treatment process.
Chronic atrophic candidiasis of the oral cavity
It is diagnosed when inflammation spreads to the skin and cracks appear in the corners of the mouth. In this case, the tongue becomes a shiny, rich pink color, and the vessels are clearly visible on it. Then the infection spreads to the internal organs. This type of oral candidiasis can occur due to improper installation of dentures, plates and crowns, which rub and injure the mucous membrane.
Treatment of oral thrush
The treatment of this disease is carried out by the dentist, although he may seek advice from a therapist, immunologist or endocrinologist. To get rid of this disease, there are many medications, from which a specialist will choose the one that is right for you. Do not forget that different medications are used to treat oral candidiasis in adults and children. Also, to speed up recovery, you should follow a special diet that your doctor will prescribe; it is important for restoring the mucous membranes after candidiasis of the mouth and throat. Many patients neglect visiting a specialist and prefer advice from those who have already encountered this infection, as well as traditional methods. Such behavior is extremely dangerous; oral candidiasis cannot be treated based on reviews on forums or recommendations from friends. This can provoke unforeseen complications and cause serious harm to health. The doctor will accurately determine the cause of your disease and prescribe a drug that is suitable for your physiological characteristics. Read more about the treatment of oral candidiasis in the article.
Why do my gums or cheeks swell?
In most cases, swelling of the gums or cheeks is caused by purely dental reasons:
- Flux
During gumboil, the gums become swollen and painful, and the temperature rises. The development of a tumor begins with an ordinary carious cavity. It gets infected, which eventually leads to tooth decay. Pus accumulates and begins to look for a way out. The cheek swells greatly and a white spot appears on its surface. Without treatment, a fistula forms in this place, and the cheek turns into a huge purulent wound. If you do not seek help from a doctor in time, blood poisoning may occur.
- Removal of a tooth
This operation inevitably involves damage to soft tissue, and swelling is a natural phenomenon. After a while it subsides. If this does not happen, and the gums swell more and more, then you need to urgently visit a doctor. Causes of severe swelling can be:
- a large accumulation of pus,
- incipient periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum),
- infection in the wound.
If you notice swelling of the cheeks and gums, or tissues of the oral cavity, then you need to consult a dentist.
The doctor will determine the exact cause, begin treatment or refer you to another specialist.
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
By leaving a request on the site, you consent to the processing of personal data
Make an appointment
Initial consultation with a dentist
For free!
- Inflammatory infiltrate
It usually occurs against the background of pulpitis or periodontitis. Pus begins to accumulate in the soft tissues, which causes the appearance of phlegmons and abscesses. It is considered a very dangerous disease because it can lead to big troubles.
- Periodontal disease
Swelling is accompanied by aching or sharp pain. There is no conservative treatment; surgical intervention is necessary. Often it is necessary to remove some teeth and install dentures.
- Teeth chips
The sharp edges of a destroyed tooth begin to scratch the inner walls of the cheek, which leads to inflammation and severe swelling.
- Wisdom tooth growth, pericoronitis
The eruption of the figure eight often leads to inflammation of the gingival hood. Swelling, as a rule, extends to both the cheek and gum.
- Carious teeth
Advanced caries often causes not only the gums to swell, but also the tonsils and cheeks. After eliminating the cause, the swelling gradually goes away. Folk remedies are useless here; urgent medical help is needed.
- Cyst
Depending on the type of cyst, its shape, and location, the doctor decides on conservative or surgical treatment. In some cases, a consultation with an oncologist may be required.
- Gum disease
Swelling is one of the main signs of inflammation of periodontal tissue. Without treatment, the disease quickly becomes chronic and difficult to treat. There is a high chance of losing a tooth.
In addition to the reasons listed, swelling of the gums and cheeks can be caused by:
- inflammation of the facial nerves;
- pathologies of the maxillofacial skeleton;
- allergies;
- disruption of the immune system;
- inflammation of the submandibular and parotid lymph nodes as a result of an infectious disease;
- malignant neoplasm;
- facial injury;
- diseases of internal organs, such as the heart;
- eye diseases;
- blood pathologies.
Prevention of oral candidiasis
The occurrence of this disease is a very unpleasant and painful phenomenon, fortunately, it is quite easy to avoid by following the recommendations. One of the main causes of infection is weakened immunity, so the basic rule for preventing the disease is to treat any disease at the right time and take medications strictly as prescribed by the doctor. To avoid candidiasis of the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx, hygiene, visiting a good dentist, professional ultrasonic cleaning and other preventive measures will help. Oral candidiasis in women is often due to hormonal imbalance; if you have symptoms of the disease, you should pay attention not only to the affected area, but also to the condition of the body as a whole.