Discoloration of gums is a fairly common problem with which patients often seek help from a dentist. The seriousness of this disease lies in the fact that the blue color of the gums can indicate not only some dental disease, but also the presence of severe somatic pathologies. Diagnosing the disease at an early stage and promptly starting treatment is the key to quickly getting rid of the disease without developing any complications.
Important information about diseases and factors that cause blue gums in adults
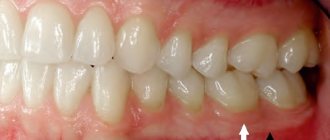
When blue gums near a tooth are discovered, or generalized (along the entire row) changes in the shade of the oral mucosa become noticeable, then there is no time for jokes. Many are beginning to wonder what this might be connected with. And we will tell you about the most common – dangerous and not very compelling reasons for this phenomenon.
The reasons for blue gums can be different.
Gingivitis: my gums hurt
The process, which is characterized by gum inflammation, swelling, redness and bleeding, is called gingivitis and is one of the most common periodontal diseases in both children and adults. Only 3% of people can boast of absolutely healthy gums. How to get into such a small percentage of lucky ones? The answer is simple - follow the necessary measures to prevent gum inflammation, regularly visit the doctor and not let even seemingly harmless signs of an incipient disease take their course.
Gingivitis is the last of all diseases in periodontology in which the inflammatory process can still be stopped. Next comes periodontitis, a disease in which inflammation spreads to other periodontal tissues. From this point on, treatment is based only on bringing the disease into remission and attempts to relieve symptoms as much as possible at the time of relapses, as well as in the future when it is necessary to resort to tooth extraction. Therefore, gingivitis in children and adults requires increased attention in order to avoid serious periodontal problems.
Possible dental causes
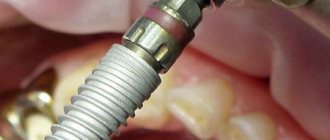
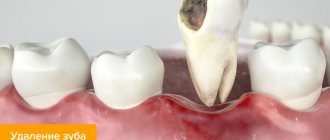
Some dental patients notice that they have blue gums after tooth extraction. Indeed, this is not uncommon. Often the phenomenon is caused by traumatic effects on tissues, vessels and capillaries during surgical procedures. And such a symptom may not necessarily occur only after root removal, but also after procedures such as anesthesia, incisions, suturing, and gum retraction. Changes in mucosal swelling can often be seen after the following operations: gingivectomy, vestibuloplasty, osteoplastic procedures, implant installation.
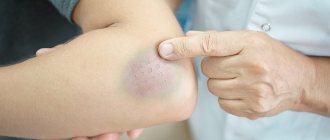
Important! After surgery, blue gums in an adult are most often discovered due to too large-scale intervention or traumatic actions of the doctor. And also if the patient has a history of various chronic diseases, for example, hypertension, diabetes, or poor blood clotting. In this case, there is a high risk of hemorrhages in the tissue and the formation of various hematomas.
If there is blue gum near a tooth, this may be due to other dental factors:
- poor-quality prosthetics: after installing structures that do not correspond to the anatomical characteristics of the patient, or are too “driven” under the gums, hematomas may form, since the tissues are compressed too much and cease to be properly supplied with blood,
- the presence of crowns with a metal component in the mouth: materials based on alloys of base metals can, over time, interact with saliva and oxidize, leaving blue gum above or below the tooth. Blue gums can even appear from a metal-ceramic crown,
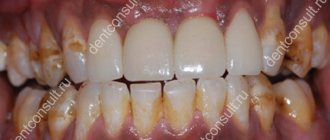
Gums may remain blue after whitening
- teeth whitening carried out by an inexperienced dentist, cosmetologist, or, more often, by the patient himself (for example, at home, using inappropriate means and folk recipes). In the process, a doctor or home “experimenter” may leave soft tissues without proper protection, apply too much product and not remove the excess, overexpose the composition and thereby provoke a burn,
- inflammatory periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease,
- purulent processes in the affected teeth, mucous membrane, bone tissue: for example, gumboil, enlarged cyst or granuloma, abscess, osteomyelitis,
- the presence of removable dentures in the mouth: at the initial stage, they can put pressure on the mucous membranes, injure and irritate them, and impair blood circulation in the tissues. During operation, such problems arise in the absence of timely corrections and against the background of inevitable atrophy of the jaw bone,
- complications after surgical interventions: for example, alveolitis after tooth extraction. This may also be inflammation of the tissue around the implant, indicating mucositis or peri-implantitis,
- cervical caries.
“5 years after wearing a metal-ceramic bridge, my gums became blue, and they become exposed when I smile. It was very ugly. After that, she stopped opening her mouth wide at all. She hardly smiled. Complexed. And when the bridge cracked a few years later, the dentist suggested replacing it with zirconium dioxide so that there would be no blue discoloration. It cost me a lot more, but now everything looks very natural and doesn’t interfere with my smile.”
Marina Olegovna, review from the dental portal gidpozubam.ru
Blue gums after installation of metal-ceramic crowns
How to care for your gums after implantation
After dental implantation, it is recommended to completely abstain from eating and drinking for two hours. Next, for 2-3 weeks, nutrition should be gentle, without consuming solid, excessively hot or cold foods.
One of the most important rules is to regularly rinse your mouth with prescribed antiseptic solutions, chamomile or other ingredients recommended by your doctor.
It is preferable to chew on the side opposite the suture, however, this recommendation will be individual for each patient. During the first 24 hours after the installation of dental implants, it is not recommended to brush your teeth, but in more detail about how to care for your gums after implantation, the doctors of the Apex dental clinic will tell you at your consultation.
What internal diseases may the symptom indicate?
If you have blue gums, then the reason for this phenomenon is pathological changes occurring in the body against the background of various systemic diseases. Thus, due to diseases of the blood, heart, and metabolic disorders, blood vessels become thinner and capillaries become fragile, and internal local bleeding occurs.
Doctors say that a similar symptom sometimes occurs against the background of iron deficiency conditions, that is, with anemia. For kidney disease and thyroid problems. And in diabetes mellitus, when the processes of nutrition and tissue regeneration are disrupted, even minor traumatic injury can lead to the formation of long-term non-healing hematomas.
Classification
Depending on the preservation of gum tissue, there are 4 stages of gum recession:
- In the first stage, only the attached part of the gum decreases. The decrease in tissue volume is insignificant.
- The area of the attached gum is destroyed, but the bone and gum tissue are preserved, and tooth sensitivity increases.
- In the third stage, the outer surface of the tooth is exposed, and tooth sensitivity becomes painful.
- The tooth is exposed around the perimeter, including in the interdental spaces.
Receding gums are a gradual process. In most cases, it is caused by a specific dental disease. The gums become thinner and smaller, resulting in tooth mobility and loosening, which can lead to their loss.
Other factors leading to the problem
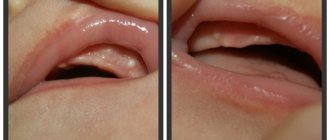
Another reason why an adult’s gums may turn blue is a burn. It is not difficult to get it if you eat too spicy foods, hot soups and sour drinks. A bad habit such as smoking can also contribute to this.
The symptom may indicate chemical burns, when delicate tissues are damaged due to the use of aggressive compounds unsuitable for the oral cavity. For example, alcohol, manganese, iodine, peroxide.
Very often, pathology occurs due to bruises and injuries received in the area of the maxillofacial apparatus. And the safest reason that can explain the blueness of mucous membranes is the consumption of drinks and dishes with food or natural dyes that give pigment to the teeth, gums and tongue. For example, blueberries, blackberries, soda pop, plum wine and plums. Fortunately, you can easily get rid of this problem by thoroughly cleaning your mouth with a brush and paste.
Consequences of a recession: what will happen if the problem is not solved
Almost all dental diseases, if ignored for a long time, first result in a loss of aesthetics, food getting into the spaces between the teeth, the development of an inflammatory process, mobility, and then the loss of teeth. And gum recession is no exception. As the thinning and loss of mucous membranes progress, the problems intensify:
- increased sensitivity and acute pain in the teeth in the area of the gingival margin develops,
- exposed areas of the root are more susceptible to caries, which quickly reaches the inside of the tooth and affects the pulp,
- the risk of developing wedge-shaped defects increases,
- gums become swollen and inflamed or, on the contrary, become unnaturally light, whitish,
- Plaque is deposited faster at the roots, which over time expands the periodontal pockets and, among other troubles, gives a putrid odor from the mouth.
If the problem is not solved, you can lose all your teeth - they simply will have nothing to hold on to.
Also, the recession has psycho-emotional consequences. When the gum contour loses its attractiveness, a person's smile begins to appear unhealthy and completely unattractive. In addition, the teeth lengthen because... their roots are now also “included” in the smile zone. Large gaps (tremas) appear because the roots of the teeth are narrower. All this creates serious psychological barriers to communication.
Possible associated symptoms
Typically, blue gum above or below a tooth is not the only symptom that something is wrong. Typically, people with a similar problem note other warning signs:
- mucous membranes swell and begin to bleed, may move away from the necks of the teeth,
- itching and soreness in the gums occurs: the discomfort intensifies with pressure, any mechanical impact, while eating food,
- a nearby tooth hurts, it can also become mobile,
- body temperature rises,
- there is a strong foul odor coming from under the gums, pus may be released,
- Plaque intensively accumulates on the necks of teeth.
Symptoms
Changes in gum color are usually accompanied by the following complaints:
- pain when brushing teeth and chewing food;
- itching;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- periodontal bleeding;
- accumulation of abundant plaque on the teeth;
- formation of tartar.
Symptoms depend on the cause of the disease and on the individual characteristics of the body. Eliminating the cause of gum discoloration is the first thing to start treatment with.
When does it make sense to go to the doctor?
Of course, in any unclear situation this will be the best solution. However, many people prefer to wait a few days, observe the condition of their blue gums and evaluate their overall health. And this is not prohibited if you do not have a rapid increase in body temperature and positive dynamics are observed.
In what cases should you urgently consult a doctor?
In cases where blue gums persist for longer than 3-5 days, with severe pain, high fever, loss of appetite, a change from a local process (when the gums turn blue in the area of 1 tooth) to a generalized one (the pathology spreads to neighboring elements of the row, increases in size, grows ) you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment and relief of edema
First you need to find out the cause of the tumor, since each case requires its own treatment to avoid deterioration.
Periodontitis in the acute phase
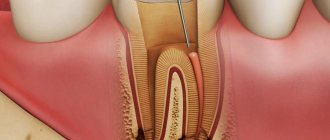
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the bone, which is associated with the fact that an infection has entered the root canals of the tooth and began to spread into the bone. If immunity is lowered, then bone inflammation goes from chronic to worsening. The amount of pus increases. Swelling and pain in the gums occur.
Periodontitis can occur both in a tooth that has been treated and filled, and in a tooth that has never been treated. In a treated tooth, it can occur due to incomplete cleaning of the tubules.
When this disease worsens, the following symptoms occur:
- A diseased tooth experiences swelling in the gum;
- The appearance of a fistula and purulent discharge;
- Pain on palpation and biting;
- Lack of reaction of the diseased tooth to high and low temperatures, to sweet foods;
- Presence of caries;
- Fever.
Swelling and pain occur due to suppuration and disappear when the pus is released. But the inflammation still goes to the bones, so a visit to the doctor is necessary.
How to treat
First, the diagnosis is clarified by the doctor. An x-ray is taken. Further treatment is of three types:
- Conservative: pus drains through the root canals, and then the canals are filled;
- Surgical: the tooth is removed and the socket is cleaned;
- Combined: the tooth is treated, an antiseptic is applied under the temporary filling, and a special incision is made to release the pus.
The choice of method depends on the location of the tooth, its condition, the course of the disease, prospects for tooth restoration, and the patient’s health status.
At home you also need to carry out the following procedures:
- Rinse with a solution of salt and soda;
- Take an antibiotic if prescribed by a doctor;
- Take anti-inflammatory drugs.
What not to do:
- Do not heat the tumor site;
- Take an antibiotic if it has not been prescribed by your dentist;
- Do not mix painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Gingivitis, periodontitis in the acute stage
Gingivitis differs from periodontitis in that the latter is an inflammation of the gums that turns into inflammation of the bone tissue, while gingivitis is a simple inflammation of the gums.
With these two diseases, your teeth should not hurt.
Causes of diseases:
- Tartar;
- Caries;
- Bad fillings;
- Incorrectly placed orthopedic structures;
- Malocclusion.
Gingivitis has an acute and chronic nature. Periodontitis is a chronic disease; there are periods during which the disease worsens.
Exacerbation may occur due to:
- Gum injuries (pricks and cuts from sharp objects);
- The presence of foreign objects in the gum pockets (bones, pieces of food, chipped tartar);
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections;
- Diabetes;
- Reduced immunity;
Symptoms
In the acute stage, gingivitis has symptoms such as:
- The occurrence of swelling and pain in the gums or jaw near a group of teeth;
- Pain when eating and brushing teeth;
- Gum bleeding due to hard foods or toothbrushing;
- Blue or red gums;
- With pressure - pain occurs;
- The gums are so swollen that they cover part of the teeth.
Periodontitis has similar symptoms, with the difference that it also reduces the height of the partitions between the teeth and their pattern becomes unclear, and the tooth roots are exposed.
How to treat
Periodontitis and gingivitis are treated by a dentist.
First, the doctor removes hard-soft deposits and polishes exposed roots and teeth. Then he examines the fillings, corrects them, and removes areas causing injury. Then the dentist removes foreign bodies and treats the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions. After this, the doctor applies anti-inflammatory drugs to the bandage.
It happens that in some cases toothbrushing, cleaning of roots and bones from stone, and suturing of tissues when they are detached and damaged are required. Here the doctor has the right to prescribe antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and antiseptics.
At home the patient should:
Lipoma
- Rinse the mouth with salt and soda (solution);
- Brush your teeth with special pastes;
- Treat the gums with anti-inflammatory drugs.
Abscess (periodontal)
A periodontal abscess is an inflamed area that has boundaries, in which pus accumulates under the gum. Outwardly, it looks like a formation on the gum in the form of a ball. Can be quite large.
Causes
The most common causes for this type of disease are the following:
- Accumulation of pus and its release;
- Injury of a deep nature due to a foreign object, due to which an infection entered the tissue.
Symptoms
The symptoms will be:
- A round swelling forms on the gum;
- The fabrics are elastic;
- When pressing, pain occurs and the movement of fluid inside is felt;
- Nearby tissues and cheeks swell;
- Body temperature rises.
How to treat
An abscess is treated in different ways. If it appears due to injury, then it is opened surgically, the pus is removed, and drainage is installed. If the abscess is due to periodontitis or periodontitis, then these diseases are treated first.
After the operation, you need to drink antibiotics, which the dentist will prescribe, and also take antihistamines, painkillers, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
If you suspect an abscess, then you urgently need to go to the dentist in order to prevent the risks of developing phlegmon and sepsis. There is no need to treat the abscess yourself, or heat it.
Other diseases
About ten percent of gum tumors are other diseases: precancerous, cancer, HIV infection, diabetes, hormonal disorders, etc. The symptoms of these diseases will be similar, but only a specialist will be able to accurately recognize the disease.
If you have discovered a gum tumor, contact the Onco.Rehab clinic to find out the cause of its appearance and timely treatment. Our qualified specialists will help you!
What can dentists offer in the fight against gum pathologies?
When a person discovers blue gums, he probably asks the question: what to do? The first step is to see a dentist. The doctor will examine your mouth and identify possible problems.
If the cause is poor-quality or incorrectly installed crowns or dentures, they will need to be adjusted or replaced. In case of dental diseases and detection of purulent processes against this background, it may be necessary to open, drainage and antiseptic treatment of tumors, clean the root canals, apply medicated pads and install a sealed filling at the end.
In case of periodontal inflammation, a specialist will definitely prescribe comprehensive treatment[1]. It is aimed at eliminating symptoms, restoring gum tissue and preserving teeth, which, in advanced stages of periodontitis and periodontal disease, can become loose and fall out. What procedures will be required: professional oral hygiene to remove bacterial plaque, anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy for gums in the form of rinses, lotions, antibiotic therapy. Some patients are also prescribed plasma lifting and periodontal gels with growth factors.
Expert opinion
Marina Igorevna Tarabanovskaya
Specializations: Dentist-therapist, periodontist
Experience: 10+
“In case of periodontal diseases, it is important not only to undergo treatment, but also to adjust the lifestyle that the patient usually leads. It is necessary to follow a certain diet, stop smoking, and purchase a suitable brush, toothpaste and mouthwash for daily hygiene. And be sure to undergo professional hygiene and examination by a dentist at least twice a year. Otherwise, the pathology will constantly worsen, and the patient risks losing all his natural teeth ahead of time.”
Traditional medicine tips
Many medicinal herbs have proven themselves to be excellent in the fight against inflammation in gum tissue. Infusions and decoctions are made from them, which are then used to rinse the mouth several times a day. Antiseptic plants that additionally have pronounced anti-inflammatory properties include chamomile, sage, and oak bark. Some sources provide recommendations for treating the mucous membrane with aloe juice or honey to relieve pain. In order to restore soft tissues after an incorrectly installed orthopedic structure, stimulation of blood circulation is required. A decoction of nettle leaves, as well as propolis ointment, helps with this.
Chamomile infusion is great for rinsing
It is important to understand that any folk recipes can be used only after consultation with the treating specialist. Otherwise, you can provoke the development of a serious complication and only make everything worse. And certainly traditional medicine cannot become a full-fledged alternative to drug therapy. The use of medicinal plants is justified only as an additional measure.