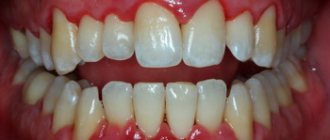
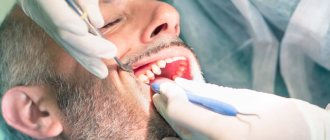
Hyperesthesia is hypersensitivity of tooth enamel, manifested by short-term pain when exposed to external stimuli. Most often, symptoms are observed on the front teeth, which react painfully to biting, hot or cold. Increased sensitivity may manifest itself to sweet and sour foods, and discomfort occurs when brushing your teeth. Hyperesthesia must be combated, and the sooner treatment begins, the better. In advanced cases, the enamel is completely destroyed, and the affected teeth have to be removed. Let's try to figure out how to relieve increased sensitivity of teeth, what means are used for this, and how you can prevent the development of the disease.
Causes of tooth sensitivity
Hyperesthesia is the result of thinning or damage to the tooth enamel and its hard tissues, which leads to exposure of the tubules of the dentinal layer, which directly communicate with the pulp and nerves of the tooth. As a result of this, the slightest external impact on the tooth and its exposed tubules causes pain and discomfort.
Thinning or damage to tooth enamel occurs under the influence of internal and external factors. The main causes of this pathology are the following disorders and diseases.
- An unbalanced diet, depleted in vitamins and minerals.
- Hormonal disorders or uncontrolled use of hormone-containing drugs.
- Frequent infectious diseases.
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Chronic stress or nervous disorders.
- Malocclusion.
- Abuse of foods high in acids.
- Use a toothbrush with stiff bristles.
- Do-it-yourself teeth whitening with dubious preparations.
- Pathological increased abrasion of tooth tissues.
- Wedge-shaped dental defects.
- Caries, periodontitis, pulpitis or erosion of tooth enamel.
- Bad habits - smoking, chewing hard nuts, grinding teeth, etc.
- Previously performed dental procedures - whitening, tartar removal, filling, prosthetics, etc.
In order to effectively relieve increased tooth sensitivity, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the pathology. Only by eliminating it can you get rid of pain, discomfort and other unpleasant sensations.
Summary
- If hypersensitivity occurs, avoid drinks and foods containing acids (fruits and fruit juices, wine, etc.).
- If you have previously used whitening toothpastes, stop using them, because... with a high probability, hypersensitivity is caused precisely by their use.
- Consult your dentist about the cause of sensitivity - it may be caused by caries or exposed tooth necks. Remember that caries in the form of a white spot is a reversible form of caries, and if you undergo remineralization therapy on time, you will not only get rid of increased sensitivity, but also prevent the destruction of this area of enamel.
- If there are dental deposits, they must be removed, followed by a course of remineralization and/or deep fluoridation.
- Maintain proper oral hygiene - cariogenic microflora in the cavity, feeding on food debris, produces acids that wash calcium from the enamel and lead to the appearance of both hypersensitivity and dental caries. Check out the link above for comprehensive hygiene tips, as well as videos on proper brushing and flossing techniques.
Sources:
1. Higher professional education of the author in dentistry, 2. Personal experience as a dental therapist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. The European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry (USA), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry. Textbook" (Borovsky E.).
Symptoms of sensitivity
The main sign of hyperesthesia is short-term toothache, which appears when eating cold, hot, sour, sweet, spicy food or when brushing your teeth. In this case, the pain can be mild and manifest itself in the form of minor discomfort, or it can be acute, very strong and throbbing. In both cases, it is felt for only a few seconds, after which it subsides and passes without a trace.
The pain that occurs with severe sensitivity can be local and affect only one or a few teeth, or be generalized - felt in most teeth or in all at once, which indicates the presence of caries, periodontal disease or exposure of the neck of the tooth.
According to clinical manifestations, it is customary to distinguish between three degrees of increased sensitivity of teeth.
- I degree – reaction of teeth to external temperature stimuli.
- II degree – reaction to temperature and chemical stimuli.
- III degree – reaction to temperature, chemical and tactile stimuli.
Pain is a constant companion of hyperesthesia and its main symptom. And even if it goes away for a while, and the patient can calmly eat cold, hot and other irritating foods, this does not mean that tooth sensitivity has gone away by itself. In this case, a peculiar period of remission has simply begun, which does not at all negate the mandatory treatment of the pathology.
How does dental hypersensitivity manifest?
A person will immediately recognize that tooth sensitivity has increased. The main symptom is acute short-term pain lasting 10-30 seconds. Pain may occur locally or affect the entire dentition.
Doctors distinguish three stages of hyperesthesia:
- The first is tooth sensitivity to hot/cold;
- The second is a reaction to changes in acidity: sweet, salty, spicy;
- Third, teeth react to any irritants, including light touches.
Treatment at home
At home, you can use special medicinal varnishes, gels, powders or foams that help restore the protective properties of the enamel. Depending on the form of release, these products are applied to the surface of the teeth or used to prepare a solution for rinsing.
- Varnish Bifluoride 12.
- Fluocal gel or solution.
- The drug Fluorlak.
- Powder for preparing Remodent solution.
- Strontium chloride paste 75% or its 25% rinse solution.
- 10% calcium gluconate solution.
- Dental gel Tooth Mousse.
- Dental cream MI Paste Plus.
These products help reduce tooth sensitivity caused by internal disturbances in the body and slight thinning of tooth enamel. These medications can only be used after prior consultation with a dentist.
Treatment
If a doctor has diagnosed a patient with hypersensitivity, treatment is usually prescribed depending on the cause of the disease, as well as the degree of its development. In modern dentistry, there are many techniques, so treating sensitive teeth is usually not difficult for a dentist.
With grade 1 hyperesthesia, complex surgical or therapeutic treatment is usually not required. Sometimes it is enough to carry out a course of dental fluoridation, which consists of 10-15 sessions of applying applications of calcium and fluoride salts to the diseased tooth.
When treating stage 2 and 3 diseases, application of applications is sometimes not enough; it may be necessary to cover the enamel using modern filling materials.
If the cause of hyperesthesia is a carious process, it is necessary to prepare the tooth, clean the cavity from tissues affected by caries and put a filling.
If the cause of the disease is receding gums as a result of inflammation of periodontal tissue and exposure of the cervical areas, it is necessary to carry out surgical treatment, during which the gums are lifted and cover the neck of the tooth.
With increased tooth wear, sensitivity cannot be reduced using simple therapeutic methods; orthodontic treatment aimed at correcting the bite may be necessary.
When treating a generalized form of hyperesthesia, it is necessary to simultaneously prescribe drugs to normalize phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the patient's body. For this, the dentist usually prescribes calcium glycerophosphate preparations, as well as multivitamin complexes, which should be taken throughout the course of treatment for hyperesthesia.
If increased sensitivity persists after filling, it is necessary to check the quality of the filling. If the filling is placed incorrectly, its edges do not adhere tightly to the tooth enamel, and food debris can get into the resulting gap, causing pain. In this case, it is necessary to refill the tooth. Sometimes sensitivity after caries treatment may indicate the presence of a chronic inflammatory process inside the tooth pulp.
If you experience tooth sensitivity after cleaning or whitening, this may indicate thinning tooth enamel. If there are no other carious and non-carious diseases, a good effect in the treatment of hyperesthesia can be achieved using electrophoresis procedures with a solution of calcium glycerophosphate. Another new and effective remedy is to coat the enamel surface with a special varnish containing calcium and sodium fluorides. Thanks to these measures, it is possible to get rid of sensitivity for a long time.
Whitening sensitive teeth should be done with extreme caution, only in a specialized clinic after consultation with an experienced specialist. After all, during the whitening process, tooth enamel can also become thinner and more sensitive. The doctor must select the most gentle whitening technology, as a result of which the enamel will not be damaged.
Dental sensitivity and braces are also interconnected; sometimes patients experience increased sensitivity after removing braces; to eliminate this sensitivity, a course of applications of calcium and fluoride salts, as well as coating the surface of the tooth enamel with varnish with calcium and sodium fluorides is usually sufficient.
If sensitivity occurs after brushing, it is necessary to use special toothpastes with a high content of fluoride and calcium. Today you can choose a good pasta, but you should entrust this matter to professionals. No one can select a toothpaste specifically for your teeth better than a dentist.
Toothpastes and rinses
You can also reduce tooth sensitivity at home using special toothpastes and rinses.
- Oral-B Sensitive Original.
- Sensodyne-F.
- MEXIDOL dent Sensitive.
- Rembrandt Sensitive.
Pastes to reduce tooth sensitivity should be used during hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity, 2 times a day, morning and evening. To achieve a positive result, it is better to use them in a course – 1 – 2 times a year.
Important to remember! Therapeutic pastes, like varnishes, gels, powders and foams, are effective only in the absence of dental diseases.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
Diagnostics
If hypersensitivity is suspected, special diagnostic methods are used:
- Probing
. Examination using dental instruments. Determines the reaction to tactile and tactile tests. - Thermometry
. Most often they are exposed to a jet of cold air under pressure. - Chemical irritants
. They are used quite rarely; it is easier to ask the patient if there are reactions to sour or sweet foods. But if used, then use a solution of glucose and citric acid. - Electroodontometry
. The higher the threshold for reaction to an electric discharge, the less sensitive the teeth. - Pain scale
. The patient is asked to rate the intensity of sensations on a numerical scale (1-5) or on a color-numeric scale (from green to red, from 1 to 10)
Treatment with folk remedies
You can also reduce tooth sensitivity using traditional methods. The following medicinal herbs and remedies are suitable for these purposes.
- Oak bark decoction for rinsing.
- Infusion or decoction of chamomile.
- Warm solution with 3 drops of natural tea tree oil.
- Warm salt solution for rinsing.
- Regular chewing of propolis.
- Regular use of warm fresh milk, which is kept in the mouth for 15 - 20 minutes.
Any folk remedy for tooth sensitivity should be used only if the enamel is slightly thinned. If there is a serious degree of pathology, you must immediately contact your dentist.
Treatment at the dentist
In most cases, hyperesthesia is caused by dental diseases. Therefore, it is not possible to get rid of the problem using home remedies or traditional medicine advice. In this case, home measures only aggravate the course of the pathology and lead to the progression of dental diseases.
You should not postpone a visit to the dentist even if there are minor manifestations of pain due to external stimuli. Modern medicine has effective methods for treating any dental ailment. After a thorough diagnosis of the condition of the teeth, an experienced specialist will accurately determine the cause of increased sensitivity and carry out the necessary treatment. This may be the elimination of wedge-shaped tooth defects, treatment of caries, periodontitis, pulpitis or erosion of tooth enamel. In the absence of serious diseases, the dentist can perform a competent procedure for remineralization of teeth, which will strengthen tooth enamel and relieve hypersensitivity.
Hypersensitivity is not a dental disease, but rather a symptom indicating the presence of dental disease. And the sooner you contact a specialist, the greater the chance of maintaining the health and integrity of your teeth.
Causes
The causes of dental hyperesthesia can be very diverse, ranging from mechanical damage to the surface of tooth enamel and ending with general disturbances in the functioning of the human body. The most common causes of enamel hyperesthesia are:
- damage to tooth enamel by short-term exposure to organic or mineral acids;
- exposure of dentinal canals as a result of carious and non-carious lesions of teeth;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system as a result of pregnancy or menopause;
- disturbances of phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the human body;
- previously suffered general or neuropsychological diseases of the human body;
- exposure to ionizing radiation on the human body;
- habit of eating a lot of sour berries, fruits, juices, fruit drinks.
Sensitive tooth enamel occurs when the dentinal tubules become exposed for one or more reasons and a variety of irritants affect the sensitivity of the pulp. In this case, even simple inhalation of cold air or brushing your teeth can cause painful sensations. Teeth in the cervical area are especially sensitive, because the enamel is thinnest there, and if the gum moves away from the tooth, it almost immediately begins to react sharply to various irritants.
Separately, we should dwell on the mechanism of hyperesthesia. As you know, dentin is penetrated by many tiny tubes - the so-called dentinal canals, in which there are processes of nerve cells that are connected to the pulp. Dentinal tubules are filled with fluid that is in constant motion. Any change in the speed of fluid movement causes a pain reaction. If the enamel is thinned, this leads to exposure of the dentinal tubules, and under the influence of various irritants, the speed of fluid movement in the dentinal tubules constantly changes, causing acute short-term pain, as a result of which the patient complains of very sensitive teeth.
Teeth sensitivity after whitening
The appearance of hyperesthesia after the whitening procedure is a fairly common complaint from patients. As a rule, this is associated with the use of aggressive abrasive “miracle products” or low-quality preparations based on hydrogen peroxide. Both of them wear away tooth enamel and cause increased sensitivity to irritants.
Teeth whitening is a dental procedure. Therefore, it should be carried out by professional dentists. They will tell you in detail how to prepare your teeth for whitening, how to care for your mouth after the procedure, and will carry out the necessary whitening using safe preparations and techniques.
Complications
Like any disease of the oral cavity, hypersensitivity has dangerous consequences. In advanced conditions, teeth can be lost as a result of caries or periodontitis. Even if the teeth are intact, hyperesthesia leads to a violation of the diet. Patients tend to exclude many foods and chew food poorly. This leads to the development of somatic diseases and can cause vitamin deficiency.
The most severe complication is inflammation of the pulp
– neurovascular bundle, which is often called simply “nerve”. This is a difficult disease to treat and can lead to pulp removal. This, in turn, deprives the tooth of nutrition and makes it fragile.
Sensitivity of teeth after filling
Increased sensitivity may appear after the filling is placed. This is due to the use of 38% phosphoric acid during the procedure. It is used to treat the surface of the tooth at the site where the filling is applied to achieve reliable fixation of the filling material. But, unfortunately, this acid makes tooth enamel porous, exposing the tubules of the dentinal layer. Therefore, in order to avoid unpleasant painful sensations after filling, it is recommended to strictly follow all the recommendations of the treating dentist - they will help restore the protective functions of the enamel.
Tooth sensitivity during pregnancy
The appearance of hyperesthesia during pregnancy is the first sign of thinning of tooth enamel due to a lack of vitamins and essential minerals. In this case, you need to review your daily diet in favor of foods high in vitamin D, C, calcium and magnesium. It is also necessary to limit the consumption of foods that contain large amounts of acids. And in order to prevent the development of possible diseases, you should consult a dentist or have your teeth remineralized.
Enamel demineralization
The enamel is 97% composed of hydroxyapatite crystals, a small amount of water (2–3%) and organic substances (1–2%). Over the course of a lifetime, it can wear out and break down for various reasons.
Demineralization is a process in which enamel loses useful minerals (primarily calcium), on which its integrity and strength depend.
Demineralization has two main causes.
- Poor oral hygiene, in which bacteria multiply and produce acid that destroys enamel.
- Excess carbohydrates in the diet are a breeding ground for bacteria.
At first, changes in the condition of the enamel are not noticeable, but if plaque is not removed in time, whitish spots appear (early stage of caries), and then full-fledged caries. Then just go to the dentist.
At the white spot stage, caries can still be prevented. To do this, you need to saturate the enamel with minerals, which will increase resistance to acids. You can strengthen your enamel both at home and in the dentist's office.
Sensitivity of teeth to cold and hot
Painful symptoms when eating cold or hot food are the first sign of hyperesthesia. In this case, we are talking about the first degree of hypersensitivity, which can be caused by thinning of tooth enamel or more serious diseases, for example, caries. Therefore, you should not put off visiting the dentist. For minor problems, he will recommend effective home remedies to reduce sensitivity. And if there is a disease, he will provide adequate dental treatment.
Prevention and recommendations from dentists
In order to avoid the occurrence of increased tooth sensitivity and its unpleasant symptoms, the following simple recommendations should be followed.
- Balance your diet in favor of foods high in vitamin D, C, calcium, magnesium and phosphorus.
- Strengthen your body's immunity.
- Monitor the formation of correct bite in children.
- Limit consumption of foods high in acids.
- Use medicated toothpastes and soft-bristled brushes.
- Do not attempt to whiten your teeth on your own.
- Regularly remove tartar and hard deposits from your dentist.
Increased sensitivity of teeth is classified as a pathology that is much easier to prevent than to eliminate. To do this, you need to regularly, 1 – 2 times a year, undergo a preventive examination with a dentist. A specialist will be able to identify possible dental problems and provide timely treatment. Your teeth will be healthy and will not cause pain when eating your favorite foods.
Author: Elena Grunina Dentist-therapist, endodontist. Work experience more than 9 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Indications for strengthening enamel
- Caries at any stage.
- Baby teeth.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
- Discomfort or toothache while eating.
- Condition before and after teeth whitening.
- Orthodontic treatment (braces).
- Chips, scratches and cracks on teeth.
- Bite abnormalities and, as a result, pathological abrasion.
- Long-term drug therapy.