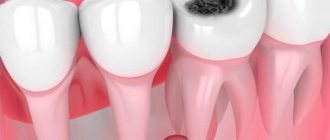
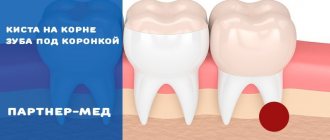
An inflammatory formation affecting the upper part of the tooth root is called granuloma. It is formed during the development of periodontitis. Tooth granuloma is tightly attached to the root, being the initial stage of a granular cyst (cystogranuloma), from which it differs, in fact, only in its slightly smaller size. If the formation is ignored and not treated, it will begin to increase.
Tooth granuloma: symptoms of the disease
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis based on an x-ray, where a darkening will be visible in the root area. Any darkening in the image is a sign of the presence of a cavity, but if a granuloma occurs, it means that periodontitis, which is chronic in nature, begins to develop.
For a long time, the tooth may not bother a person at all. Sometimes pain may occur when biting or when eating hot food: these are the first signs of the development of chronic periodontitis. An exacerbation of the disease is observed during periods of weakening of the body's immunity: then the pain intensifies significantly, which is especially noticeable when biting. During such periods, as a rule, the gums become swollen, and in the area of inflammation it becomes painful to touch.
What is the difference between a cyst and a granuloma?
There are other diseases in the oral cavity that are symptomatically similar to a cyst. Specifically, a granuloma is an outwardly swollen round projection in the root zone of a tooth. The doctor must correctly diagnose the disease, since the sequence of exposure, removal techniques, and pharmacology have significant differences. Granuloma is eliminated with the help of medications, as well as accompanying mouth rinsing with phytocomponents. The cyst has deeper roots and does not go away without surgery.
Why does granuloma appear on the root of a tooth?
At the tops of the roots, such formations can appear for several reasons:
- Poorly performed treatment of pulpitis. If caries is started, the affected cavity gradually becomes quite deep. When microorganisms enter the pulp, its inflammation begins, accompanied by acute pain, which may stop over time, indicating the death of the nerve.
But the development of the disease does not end: bacteria through the root canals extend beyond the boundaries of the affected tooth, as a result of which a focus of inflammation appears near the upper parts of the roots, called periodontitis. The further course of the disease can occur according to several scenarios, one of which is the formation of granuloma.
It is necessary to understand that a tooth with a granuloma does not necessarily have to be affected by caries, since the root can become inflamed near a tooth that has already been treated. If the doctor has not completely removed the tissues affected by caries by placing a filling on top of them, then there is a high risk of developing pulpitis with the subsequent formation of granuloma.
- Filling of root canals performed with violations. A granuloma that appears on the root of a tooth whose canals were filled some time ago indicates the unsatisfactory quality of the procedure performed. Due to inattention, haste or inexperience, the doctor could not fill the canals to the very top. Dentists often refuse to admit their own mistake, because in this case they will have to treat the tooth for free. Such unfortunate specialists can evade until the last minute, pretending that they do not understand the causes of pain, recommending taking a course of antibiotics.
Granuloma and cyst: what do they have in common?
To summarize, all granulomas are divided into simple and complex. The first type is characterized by a slight compaction of granulation tissue without the release of purulent exudate. Developed forms have a pronounced focus of inflammation and large sizes (up to 10 millimeters in diameter). Some experts do not share the concepts of cyst and granuloma. This needs to be sorted out. A classic granuloma does not have clear boundaries and shape, while a cyst is a capsule with purulent fluid, much larger in size, usually with less pronounced symptoms. On the other hand, a cyst is a developed form of granuloma, i.e., in fact, its more complex type.
Diagnosis of granuloma on the tooth root
At the early stage of development of the disease, it will not be possible to notice any visual changes. The first signs of pathology become noticeable as the size of the infected area and the amount of pus increase.
To treat the disease with therapeutic methods, it is necessary to examine the affected area in detail: a complete picture of the granuloma must be obtained, which will allow one to detect key signs of the disease that differ from other diseases.
When suppuration occurs, the gums become very red and swollen, and pain appears, which can radiate to the head area in general and the ear in particular. This is the first symptom that should make you wary.
The following methods can be used to make an accurate diagnosis:
- use of classical x-rays;
- the use of radiovisiography or, in simpler terms, computer x-ray.
In the picture, the affected area looks like a dark spot with a clear border in the upper part of the tooth. The size of the spot indicates the following:
- 5-8 mm – the probability of having a dental granuloma is high;
- more than 8 mm – formation in the form of a cyst.
In rare cases, a large granuloma, up to 1.2 cm in size, may occur. Therefore, X-rays may not be enough for diagnosis: it is recommended to perform a biopsy of tissue cells from the area affected by the disease.
In most cases, granuloma is discovered during treatment of other dental diseases: the doctor may pay attention to increased swelling and swelling of the gums. In addition, the bone tissue near the top of the tooth may also bulge.
An increased risk of developing granuloma is observed in patients with crowns and pulpless teeth. Such people are advised to undergo regular examinations in order to promptly identify any changes affecting the gums and teeth.
Classification of granulomas and forms
In medicine, granulomas are classified according to several criteria: etiology, pathogenesis and morphology. Specific varieties are collected in a separate group. In the group according to the criterion of etiology there are types of established and unidentified etiology: infectious and non-infectious. The latter include dust granulomas, drug-type granulomas and neoplasms around foreign bodies. Pathogenesis group: immune and non-immune. The first type includes epithelioid cell granulomas. Non-immune ones occur due to toxic factors and acute infections. The morphological group is divided into two main groups: mature and epithelioid cell. According to the morphology of granulomas, there is the formation of a diffuse-type granulomatous infiltrate and the formation of tuberculoid-type granulomas.
Main types of granulomas
In medical practice, there are many types of neoplasms of this type. They can be single or multiple. It is not always possible to see the beginning of their formation, since pathogenic cells are located deep in the layers of the dermis. Granuloma in children and adults can appear and disappear without treatment. This should justify the need for gentle therapy in the future. Granulomas of the following type are most often diagnosed in children and adults:
- ring-shaped;
- pyogenic;
- tuberculosis.
Tooth granuloma: treatment
Usually treatment is only therapeutic in nature, but its strategy may vary depending on whether the canals have been filled before.
- If the canals have not been filled, the tissues affected by caries are drilled out, and the old filling is removed. This is required to carry out high-quality mechanical treatment of the canals, which are expanded and treated with antiseptic agents. If the granuloma is small (formations up to 3 mm are considered such), then the canal is sealed immediately. If the size of the granuloma exceeds 3 mm, the treatment period increases, since it is necessary to put a medicine into the canal, which includes potassium hydroxide - this substance leads to a decrease in the granuloma or even to its complete disappearance. A temporary filling is placed for the period the medication is placed (approximately 2-3 weeks). Then a repeat x-ray is taken, which should clearly show a significant reduction in the inflammatory formation. If the dynamics are obvious, the canals are sealed and a permanent filling is placed.
- If the canals have been filled, then the first stage of treatment is their unsealing. The further sequence of actions is similar to that described in the previous paragraph. The only thing is that if there is a crown on the tooth, it will have to be removed, and after the treatment is completed, it will have to be made and placed again. Some patients do not want to spend money on re-installing a crown: the solution is to perform a root resection operation, when the upper part with the granuloma attached to it is cut off through a small incision in the gum.
COMPLICATIONS
Untreated granuloma leads to:
- To complete loss of a tooth. This happens due to complete destruction of the root. As a result, soft tissues are drawn into the inflammation process, in which pus accumulates.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw.
- Formation of a dental cyst.
- Cancerous tumors.
- Infection of other organs and the development of sinusitis, pyelonephritis and infectious myocarditis.
- If pus gets into the skull, meningitis, encephalitis and inflammation of the peripheral nerves may begin.
- The appearance of migratory granuloma. Manifests itself in the form of protrusion of the facial skin. The disease also appears in the form of abscesses and fistulas in different places.
Granuloma between tooth roots: treatment with antibiotics
The number of people putting off visiting a doctor until the last minute is large. There are many reasons for this: fear of pain (although modern means of anesthesia make it possible for the patient to feel nothing at all during treatment procedures), lack of free time, and reluctance to part with money. But all these reasons and excuses come to naught when the pain becomes unbearable, becoming chronic. As practice shows, as soon as a person does not sleep for a couple of nights, the issue of the need to visit the dentist is resolved by itself.
However, many people try to cure granuloma on their own using strong antibiotics, which is basically impossible. Antibiotics may be prescribed to relieve inflammation and stop the formation of pus, but nothing more. But the action of antibiotics may not affect pathogenic microorganisms located in the root canals, and it is the infection in their unsealed areas that is the only reason for the formation of granulomas.
If a patient comes to the doctor with a suspicion of granuloma, and the doctor, driven by some of his own considerations, does nothing, recommending taking antibiotics, it is better not to delay time, but to immediately contact another dentist. Some doctors simply do not like to re-treat someone’s poorly treated teeth, since repeating the same operations takes much more time, while others, if the patient comes back again, do not want to admit that they made a mistake, which for them is tantamount to realizing their own lack of competence.
How to cure granuloma in a child
The causes of granuloma annulare in children are unknown. Scientists believe that type 4 cellular immune reactions and pathologies of tissue monocytes are involved in the formation of the disease. Sometimes clinical manifestations of the disease are observed after prolonged sun exposure, insect bites, injuries, or vaccinations.
The development of granuloma annulare is a benign process characterized by the formation of nodules or papules that form a kind of ring around areas of unchanged skin. Rashes of yellowish-brown, flesh-colored or bluish color are located in the form of single or multiple lesions. Typical localization is the dorsum of the hands and feet. The lesions can merge, forming rings.
Children often experience spontaneous regression of rashes. If the process is widespread or the rash bothers you (itching, pain), treatment is prescribed. Granuloma in a child can be cured using ointments with corticosteroids and intralesional administration of hormonal drugs. PUVA therapy and pulsed laser are also successfully used.
Tooth granuloma: surgical treatment
If therapeutic treatment does not help, then surgery comes into play: the operation is performed in the presence of a destructive process affecting the gums, and anesthesia (both general and local) is used to carry it out.
There are several surgical treatment options.
Root resection
Elimination of granuloma occurs in several stages:
- a passage to the top of the tooth opens by peeling off the gum shell;
- the root canals are cleaned and subsequently filled with medicinal substances;
- excision of the granuloma is carried out;
- the area is filled with synthetic fabrics;
- the tooth is filled.
On average, the operation takes about an hour.
Hemisection
If a tooth has many roots, then this procedure is prescribed (if there are complications that prevent the root from being saved).
The treatment procedure includes:
- removal of roots under the crown;
- filling the empty space between the roots with a special dental product;
- installation of a crown;
- monitoring the condition of the tooth using x-rays.
The method is simple, while the functionality of the tooth is preserved. If necessary, some time after the procedure, the patient can resort to prosthetics, provided that the root system remains healthy.
Cystotomy
The method is used when removal of large granulomas is required.
To implement it:
- a channel is created between the affected area and the oral cavity, through which pus absorbed by tampons is removed;
- after cleaning, the cavity is treated with antibacterial agents;
- sutures are placed;
- the cavity, free from suppuration, is filled with bone cells.
Urgent dental care for the development of purulent inflammation
We already wrote above that dental granuloma develops asymptomatically for a long time and this form is called chronic. But if a person experiences severe stress, catches a cold, a malfunction occurs in the immune system of his body - the granuloma will turn into an acute form, in which purulent inflammation can begin to actively develop. Its signs are excruciating pain that does not subside after taking pharmaceutical painkillers, swelling of the gums and cheeks, and increased body temperature.
Naturally, with such symptoms, you need to urgently contact the dentist to get emergency help. Treatment will depend on where the pus is located and accumulates:
- If the pus is in the granuloma itself, then assistance to the patient will consist of opening the tooth to ensure the outflow of pus through the root canals;
- If there is swelling on the gum and cheek, this indicates that the pus could go into the mucous membrane or periosteum and then the doctor will have to make an incision in the gum to drain it.
If you go to the dentist with a granuloma of a tooth that is completely destroyed, it would be advisable to remove such a tooth. But at the same time, it is important that the tooth extraction procedure is carried out efficiently and not only the tooth is extracted, but also the granuloma. If the tumor remains in the socket, alveolitis may develop - a rather serious and unpleasant complication.
If you have had a tooth with a granuloma removed, you must properly care for your teeth and oral cavity after this operation. You should:
- Temporarily stop drinking too hot food/drinks, alcohol, smoking;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia of the body and for this purpose do not visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, be sure to dress according to the weather;
- Eliminate stress and physical activity;
- Eat soft and warm foods for a week, trying not to chew on the side of the jaw on which the extracted tooth was located.
Be sure to take all medications and carry out all procedures prescribed by your doctor! If, within 3-4 days after the removal of a tooth with a granuloma, pain and swelling do not go away, contact the clinic immediately. The persistence of pain and swelling may indicate that the inflammatory process continues for some reason.
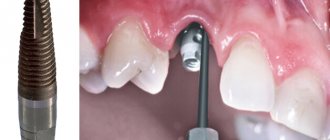
After tooth extraction during the treatment of granulomas, prosthetics and dental implantation are carried out no earlier than six months later. Such a pause in treatment is necessary for the complete restoration of all tissues in the area of tooth extraction.
Measures to prevent granuloma after an extracted tooth
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of the disease. They include:
- high-quality cleaning of teeth and gums on a daily basis;
- timely treatment of bleeding gums;
- regular visits to the dentist at least once a year (it is better to do this twice);
- replacing toothbrushes (old brushes accumulate bacteria that can provoke the development of the disease);
- contacting the dentist at the slightest pain associated with the gums or teeth;
- treatment of caries, periodontitis and pulpitis - quite often these diseases are the catalyst for the development of granuloma;
- the use of medicated toothpastes and herbal decoctions for rinsing;
- eating foods rich in calcium and other trace elements.
Features of prevention
The main condition for the prevention of dental granulomas is timely assistance from a dentist when caries occurs. You should not allow severe tooth decay or the development of pulpitis. The peri-root tissues are healthy until the pulp becomes inflamed. Therefore, if symptoms of caries or pulpitis appear, it is important to immediately consult a doctor.
Endodontic treatment also increases the likelihood of developing periodontitis. Therefore, it is better to eliminate caries in the early stages and avoid the need for root canal filling. If this is unavoidable, it is important to carefully choose a dental clinic - the professionalism of a specialist will help eliminate possible mistakes and prevent complications.
Complications after granuloma at the site of an extracted tooth
Lack of timely treatment and hope that the disease will go away on its own is fraught with serious consequences. Among the most common complications it is worth highlighting:
- development of periodontitis and further formation of a fistula;
- the occurrence of alveolitis is a consequence of the presence of an inflammatory process;
- formation of purulent flux;
- suppuration of the perimaxillary tissue;
- entry of pathogenic bacteria into the lymph nodes, from where they penetrate the cardiac system and internal organs (kidneys, liver and brain);
- development of facial asymmetry;
- the emergence of new foci of infection;
- infection of the body due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the blood vessels.
Timely removal of granuloma is a guarantee to avoid unpleasant health consequences.
How to make an appointment with a dermatologist
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist using the special form “Make an appointment with a doctor” - just enter your data so that the administrator can call you back and coordinate the time of the visit. During the consultation, the doctor will examine the clinical picture, prescribe tests if necessary, and select treatment. You can make an appointment with a dermatologist using the number. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) has a convenient location at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10. Nearby there are metro stations: "Mayakovskaya", "Tverskaya", "Novoslobodskaya", "Belorusskaya", "Chekhovskaya" .
Causes of granuloma
The reasons for the occurrence of this type of formation can be different, the main ones are:
- damage to the body by infectious diseases (syphilis, typhoid fever, typhus, tuberculosis);
- collagen diseases (rheumatism, scleroderma);
- drug effects;
- diseases caused by dust (silicosis, talcosis, asbestosis);
- dental diseases.
The mechanism of granuloma formation can be divided into 4 stages:
- A collection of young cells prone to phagocytosis (a process by which cells take up and digest particulate matter).
- Active proliferation of formed phagocytes.
- Transformation of phagocytes into epithelial cells.
- A collection of epithelial tissue that forms a granuloma.