Content
hide
1 Why is it important to treat baby teeth on time?
2 Features of filling baby teeth in children
3 Is silvering teeth an alternative method?
4 Cost of filling baby teeth
5 Technical points
6 Why is it necessary to fill teeth?
7 More about anesthesia
8 What to do if you don’t want to fill your baby teeth?
Caring for children's teeth is an acute and problematic issue. How many things violate children's oral hygiene: frequent consumption of sweets, violation of a healthy diet, irregular teeth brushing. The result is diseases of baby teeth, unpleasant symptoms and, of course, a visit to the dentist. This is stressful for both adults and children.
Parents worry about the baby, but the child is simply afraid of unpleasant and unfamiliar sensations. Fortunately, in modern dental clinics, doctors find an approach to a young patient, creating a friendly atmosphere so that the child does not regard the treatment as something scary.
It is under such conditions that filling of children’s baby teeth takes place, if parents make the right choice of a medical institution. In addition, delaying filling is an extremely dangerous undertaking, from which nothing good will come. Dental pathology affects all organs and systems, leading to complications and impaired formation of permanent teeth.
Why is it important to treat baby teeth on time?
Sanitation of the oral cavity and filling of baby teeth is necessary in order to eliminate inflammatory processes, the growth of bacterial flora, and also to create normal conditions for the formation of a healthy bite and full-fledged permanent teeth.
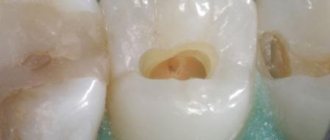
Caries of primary teeth is a problem that needs to be addressed immediately. It is necessary to carefully examine the child's teeth in good lighting. You can do this during hygiene procedures. You should pay attention to spots, light areas on the enamel, violations of its integrity, black spots, and gum pathology. These minor symptoms indicate that there is an increased risk of infection spreading into deep tissues.
The most common and at the same time erroneous opinion is that baby teeth do not need to be treated, because they will fall out anyway. But while the child is sick, his entire body suffers, the immune defense is disrupted, the digestive system malfunctions, deep tissues are involved in the process, as well as permanent teeth that will not fall out and will serve the person for the rest of his life. The focus of the pathology spreads the infection throughout the body; secondary complications may occur throughout the body, because germs and bacteria are spread along the bloodstream.
Price
It is possible to seal the grooves on the chewing surface of the 6th, 7th, 8th teeth of the permanent dentition from the age of 6 years. The cost of the procedure is significantly lower than the cost of regularly changing dental fillings. At the Novostom clinic, you can also carry out deep fluoridation when the fissures mature. The cost of the procedure is 220 rubles. The price of sealing depends on several circumstances:
- what fissures are to be treated, how accessible they are for visual inspection;
- what diagnostic methods will be needed;
- what materials are used to seal.
The cost of sealing with fissurotomy at Novostom clinics is 2,200 rubles.
The article was prepared by an expert:
Gomonova Ekaterina Nikolaevna
Children's dentist
Make an appointment
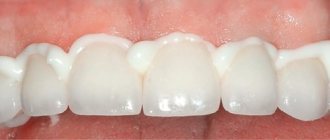
Features of filling baby teeth in children
Modern pediatric dentistry has a variety of tools, equipment and materials that make fillings high-quality and long-lasting. The most commonly used is composite. This material has the property of self-hardening. A composite complex with glass ionomer cement is also used. This filling material adheres well to the surrounding tooth tissues, is resistant to external factors, and lends itself well to working with tools.
Technical points
In general, filling teeth follows the same principle as installing fillings in permanent teeth. The only caveat is that the filling material is deliberately installed for a certain time, since the tooth itself will fall out over time. Another point - during filling, the doctor works with the diseased and adjacent tooth to prevent the spread of the infectious process.
In order to cure caries of primary teeth, the dentist uses the following techniques:
- manual tissue preparation is used. The use of machinery is required if the cavity is deep enough and manual processing is not enough;
- treatment with chemicals that eliminate the source of destroyed tissue;
- ordinary processing, which involves the use of a drill.
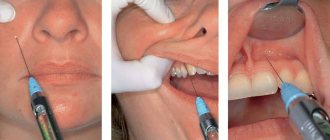
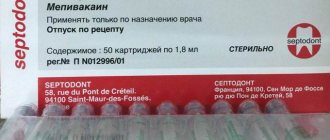
Of course, when filling teeth, anesthesia is used so that the child does not feel pain and the doctor feels comfortable working. It is important to choose the right anesthetic, administer a sufficient amount, and be careful with dosages.
Treatment of a baby tooth is a more rational choice than tooth extraction. Preservation of the jaw area plays a role in the formation of the bite, ensures normal chewing function, diction, and facial contours. Extraction is carried out only in a number of cases when this method is the only one possible. The choice of treatment method is decided by the attending physician on the basis of diagnostic data, as well as based on the characteristics of the young patient’s oral cavity.
Types of fissures
The doctor chooses a sealing technique based on the type of groove. They are:
- open type. Fully visible during visual inspection, allowing non-invasive intervention;
- deep and narrow, which makes it impossible to examine the bottom, walls and qualitatively fill them with sealant without invasion.
Non-invasive
They are sealed without using a drill. The procedure takes about 5 minutes. Some features of the procedure arise in connection with the choice of material for sealing.
Invasive
Using a drill allows the doctor to:
- see how much caries has spread;
- guaranteed to fill the grooves with sealing material.
Why is it necessary to fill teeth?
The main problem that causes the need to fill baby teeth is caries. This is an infectious process that is caused by pathogenic bacteria and negatively affects the structure of the tooth, corroding its tissue. The peculiarities of the oral cavity are that it contains extremely aggressive flora and any infectious process occurs at a high speed. This once again shows how important it is to consult a doctor in a timely manner, or even better, to visit him as part of preventive examinations.
It’s not for nothing that children are told how harmful sweets are, especially at night. Sweets contain increased amounts of glucose, which is an excellent basis for the development of bacteria. Food debris lingers in hard-to-reach areas of the teeth and spaces between them. During the night, bacteria accumulate there, the waste products of which eat away the enamel and damage the teeth. Add to this missed brushing of teeth, reduced immunity, and you’re done – caries of baby teeth.
If caries progresses, neighboring teeth shift, deformation of the dentition occurs, and the bite and function of the teeth are impaired. At the same time, the germination of permanent teeth is disrupted - there is no room left for them due to displacement. In addition, the permanent tooth grows in place of the milk tooth, and if there was a source of infection there, it will grow in the appropriate condition.
More about anesthesia
Local anesthesia is not required in all cases. It is used only when caries is deep or medium. If it is necessary to numb the area being treated, the dose is carefully calculated, the sensitivity of the injection site is first reduced, and then the drug is administered. It is important to consider the patient's age and weight when choosing the dosage and concentration of the drug.
What to do if you don't want to fill your baby teeth?
Of course, you can do without installing a filling. But you will have to worry about this in advance. If the process is started, it is better to listen to the opinion of the attending physician and thereby save the baby from unpleasant consequences. How to avoid caries?
- Even while the fetus is gestating, the mother can improve the condition of its future teeth. To do this, it is worth enriching your diet with calcium, fluorine and phosphorus. the increased content of these microelements covers the expenses of the mother’s body and is the basis for the formation of the child’s skeleton and teeth;
- Once children's teeth are mature, they require daily care. This is important for removing food debris and removing harmful acids that destroy enamel. It is worth choosing special brushes and pastes that enrich the enamel with minerals and are gentle on teeth and soft tissues;
- The choice of paste should be made together with the pediatric dentist. In principle, until the age of 2, the toothpaste is not used, and instead of a brush, a device is used that is put on the finger and cleans the teeth. Next, you should consult a doctor and he will select care products based on the patient’s characteristics;
- Taking care of your teeth should become a habit for your baby. Parents can play with this and talk about the benefits of hygiene in an accessible form. Visits to the doctor should be treated in the same way. You should not scare your child with an evil dentist, to whom they will take him if he does not brush his teeth. Visiting a doctor is not a punishment, but a common procedure that you need to get used to since childhood;
- Parents should control baby food, the presence and quantity of sweets in it. It is better to replace sweets and chocolate with natural delicacies and fruits in moderation;
- Preventative visits to the dentist will consolidate the effect of proper dental care and allow for early diagnosis of pathology.
Choosing a clinic for filling baby teeth is a responsible decision for parents. Contact those institutions that use modern technology and medications and employ qualified pediatric specialists. And for the child, the atmosphere and the sensations that he experiences during a visit to the doctor are important.
Types of cements
Dental cements and other filling compounds are used in the treatment of permanent and primary teeth in the form of fillings, linings, obturation materials and sealants.
They are classified according to their basis, and can be of the following types:
- Mineral cements. They are made on the basis of phosphoric acid, which is why they are called “phosphates”. These include zinc phosphate, silicate and silicophosphate compounds.
- Polymer cements. They use organic acid as a base, usually polyacrylic acid. This group includes polycarboxylate and glass ionomer cements.
- Oil-based formulations. The main material of this group is zinc oxide-eugenol cement.
- Water-based materials (water-based dentin).
Phosphates
They include three main types of materials: zinc phosphate, silicate and silicophosphate cements.
Zinc phosphate consists of two components - powder (a mixture of Zn oxides (75-90%), Si, Ca, Al, F, Mg) and liquid (orthophosphoric acid).
Advantages of zinc phosphate composition:
- Harmless to the pulp.
- Good adhesion to fabrics.
- Low thermal conductivity.
- Radiopacity.
Flaws:
- low strength;
- large shrinkage during curing;
- instability to saliva;
- difference in color from natural fabrics.
Silicate cements. The powder is a carefully ground aluminosilicate glass (oxides of Si, Ca, Al, F). The liquid, like all fluorides, is phosphoric acid.
Currently, this type of material is rarely used. In no small part due to the irritating effect on the pulp, which is especially important for children's teeth. There are other disadvantages as well.
Silicophosphate cements. A mixture of both zinc phosphate (40%) and silicate (60%) cements. They surpass silicate cements in strength parameters.
Positive properties:
- non-toxic to pulp;
- good adhesion;
- sufficient strength.
Flaws:
- solubility in saliva;
- bad aesthetics.
For the treatment of baby teeth, the brands “Infantid”, “Lactodont”, “Beladont” are mainly used.
For moderate and superficial caries, due to the low toxicity of silicophosphate cements to the pulp, insulating spacers do not need to be used.
At what age should you start caries prevention in children and what measures are taken.
Visit here to learn more about the indications for photodynamic therapy in dentistry.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/zubyi/chasto-diagnostiruemyie-patologii.html we will consider commonly diagnosed dental pathologies in children.
Phenolates
This class of materials includes Ca(OH)2-salicylate (chelate) and zinc-eugenol cements. The latter consist of zinc oxide and eugenol, which react upon curing to produce zinc eugenolate.
Eugenol (clove oil) – found in the aerial parts of the eugenia plant, has bactericidal, antiseptic and analgesic properties.
The main advantage of zinc-eugenol cements is their anti-inflammatory and odontotropic (dentin-forming) properties.
Flaws:
- low mechanical strength;
- high solubility in oral fluid;
- incompatibility with composites;
- pulp irritation (potential allergen).
Calcium hydroxide cements consist of two pastes. The first includes Ca(OH)2, the second contains substances that provide hardening. Their advantages include:
- beneficial effect on the pulp (it can be coated without a gasket);
- ease of preparation and use;
- fast curing.
Flaws:
- low hardness;
- solubility in case of seal failure.
Phenolates can be used to treat primary teeth. However, interest in them among pediatric dentists has disappeared due to the emergence of new, better materials.
Polycarboxylates
Polycarboxylate cements are intermediate between mineral and composite. Manufactured on the basis of polyacrylic acid. They consist of powder (specially processed zinc oxide with the addition of calcium and magnesium salts) and a binding liquid – polyacrylic acid.
Positive properties:
- low toxicity to the pulp , due to which no gasket is required when filling mammary units;
- good adhesion (chemical bond with dentin and enamel);
- biocompatibility with dental tissues.
Flaws:
- insufficient strength;
- solubility in oral fluid (therefore not used for permanent fillings).
- limited preparatory and working time (mixing - no more than 20-30 seconds, installing a seal - no more than 2 minutes).
Examples of brands: Carbocement, Adgesor-CarbofinePoly-F-Plus.
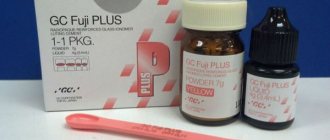
Glass ionomers
Glass ionomer cements (GIC) are one of the main materials for the treatment of primary teeth. They are used to close carious cavities of all classes, and are also used as spacers when using composite materials.
Glass ionomer cements are polycarboxylates (based on polyacrylic acid).
GIC consists of a filler in the form of aluminosilicate glass powder (Si and Al oxides + Al, Ca and Na fluorides + Al phosphate) and a liquid ionomer – polyacrylic acid.
Ionomers are substances containing ionic groups that have an electrical charge. Due to the attraction of differently charged particles to each other, the binding function of polyacrylic acid is realized.
Some brands of GIC contain polyacrylic acid in powder form, which is mixed with aluminosilicate glass. In this case, to prepare the composition, the powder is mixed with distilled water.
An example of brands of chemically cured glass ionomer cements is “Cemion-F”, “Stomafil”.
GICs have a number of unique positive properties that make them very popular among pediatric dentists:
- Strong chemical bond with dentin and enamel of milk and permanent teeth.
- Good adhesion to most other materials.
- Cariesstatic (enamel strengthening) and bacterial effect due to the presence of fluoride.
- Biocompatibility , no toxicity.
- Coefficient of thermal expansion close to tissue.
- Good edge seal and low volumetric shrinkage.
Certain subtypes of GIC (“hardened”, “aesthetic”, “quick-hardening”, etc.) have special properties (compressive strength, color similar to dental tissue, etc.) that exceed the parameters of classical GIC. But the superiority of one property comes at the cost of deterioration of another. In particular, aesthetic GICs have lower strength.
Disadvantages of the GIC:
- relative fragility;
- insufficiently high abrasion resistance;
- slow hardening;
- insufficient aesthetics.
For the treatment of caries in primary teeth, it is recommended to use hardened GIC. Compomers, which contain GIC as an integral part, have even higher qualities. They will be discussed in more detail below.
Acrylates
These are polymer materials consisting of particles (powder) of polymethylacrylate and liquid (methacrylic acid ester).
Due to the toxic effect of unreacted monomer on the dental pulp, acrylates are not used today not only in children (they are generally contraindicated for them), but also in adults.
Composites
Composites are composite materials containing inorganic filler (quartz, porcelain flour, barium glass, etc.) and polymer resins (BIS-GMA, UDMA, D3MA, TEGDMA).
Since they contain more than 50% filler, composites are also called filled polymers. To form a chemical bond between the filler and the resin, the former are treated with special substances - silanes.
Composites can be either chemical or light cured. The latter are used more often.
There is no clear opinion on the possibility of using composites for filling baby teeth. Some experts are against this because of the danger of toxic effects on the pulp. Others willingly use them when treating children, arguing that to preserve the pulp you just need to follow a special filling technology.
The advantages of composites include:
- high strength and wear resistance;
- low shrinkage;
- good aesthetics;
- ease of use;
- maintainability.
Among the disadvantages, as already noted, is the risk of negative effects on the pulp, which increases due to the thin enamel and dentin of primary teeth.
Compomers
Compomers are a subtype of composite materials consisting of carboxylated methacrylate resin (matrix) and glass ionomers (filler).
In form, these are one-component pastes that polymerize with light. They combine the positive properties of glass ionomers and composites.
Their advantages:
- ease of use;
- good aesthetics;
- color fastness;
- cariesstatic effect due to fluoride;
- high adhesion of chemical nature;
- biocompatibility with RP tissues;
- possibility of various color solutions.
Flaws:
- lower strength and wear resistance than composites;
- worse polishability.
Despite the reduced mechanical properties compared to composites, they are quite sufficient for primary teeth. A contraindication may only be individual intolerance to individual components. Compomers can be used to fill temporary elements of cavities of any class.
Colored fillings made from compomers are very popular among children; they create motivation for dental treatment. In addition, thanks to the color, it is easy to control the wear process of the filling.
From the video, learn about the features of colored fillings used in children's dental treatment.