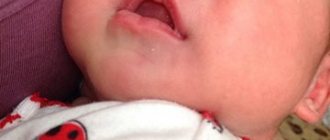
Reasons for the formation of bumps behind the ears
There are a number of health problems that can cause lumps and lumps to form behind the ears. It is most likely that this problem may occur with the following diseases:
- mastoiditis;
- otitis media;
- infection;
- abscess;
- lymphadenopathy;
- acne;
- fat cyst.
If you find any suspicious growths, for example, a ball behind the ear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Our clinic specialists are ready to conduct an examination, determine the causes of the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Diet for ear cancer
Diet for cancer
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: until recovery or lifelong
- Groceries cost: 2500 - 4800 per week
The diet of cancer patients should be as healthy as possible. It may seem quite specific to some people. The menu should mostly include:
- plant products - vegetables, fruits, legumes, herbs, cereals and whole grain baked goods;
- poultry and eggs;
- seeds, nuts and natural vegetable oil;
- seafood;
- milk and fermented milk drinks, cheeses and feta cheeses;
- drink green and herbal teas, freshly squeezed juices and compotes.
It is recommended to avoid red meat, sausages, smoked meats, fatty and spicy foods, alcohol, mayonnaise and other packaged sauces, confectionery, sweets, fast food and other products of questionable composition and quality.
Otitis media
Otitis media is another type of ear infection that can be of either viral or bacterial origin. This disease is characterized by the appearance of a lump behind the ear, which is quite painful and can cause swelling. This disease leads to a tumor noticeable even to the naked eye.
Treatment of such pathologies involves the use of potent antibiotics, which can not only alleviate the symptoms, but also fight the infection. Correct treatment can only be prescribed by an experienced doctor who will conduct a full examination to confirm the diagnosis.
General information
Oncology of the auricle is a less common type of pathology, however, we should not forget the threat it can pose. In 85-90% of cases, tumors are localized on the auricle and in approximately 10-15% the tumor is localized in the middle ear.
Among the most common benign tumors of the outer ear are fibromas and papillomas , and more rare ones are chondromas , lipomas and angiomas . Malignant formations are represented by sarcomas (oncology is more often diagnosed in children) and directly cancerous tumors ( carcinomas , melanoblastomas ), which are more susceptible to adults and elderly people.
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy is a secondary infection of the throat or ear that begins its development from the lymph nodes. These organ-like structures are small structures located throughout the human body, including the pelvis, armpits, neck and ears.
With the development of infectious diseases, the lymph nodes will become inflamed, which is the immune system’s reaction to the pathogens. The bumps located behind the ears will gradually increase in size. Therefore, if you suspect lymphadenopathy, you should immediately contact qualified specialists.
Classification
Depending on the degree of malignancy and the structure of formations on the auricle, they are distinguished:
- benign (fibromas, papillomas, chondromas, lipomas, angiomas);
- malignant (sarcoma, carcinoma, cancer itself and melanoma );
- tumor-like (cysts, atheromas, keloids, exostoses ).
According to its structure, ear cancer can be polymorphic cell, basal cell, squamous cell keratinizing and non-keratinizing, spinobasal cell and papillary.
Acne
Acne occurs as a result of clogged hair follicles and occurs mainly in teenagers. Once oil and dead skin cells accumulate in the pores, pimples or nodules can form. In some cases, neoplasms can be quite impressive in size, hard in structure, and quite painful.
In our clinic, you can make an appointment with an experienced doctor who will conduct an examination, tell you what to do if there is a lump behind your ear, and, if necessary, prescribe additional examinations.
Pathogenesis
Excessive growth and proliferation of cells during the formation of neoplasia usually involves structural elements of the skin, subcutaneous fat, cartilage, bone, vascular networks and nerve sheaths. The mechanism of development is based on malignant metaplasia.
Benign angiomas are considered the most complex, because in this case the tumor in the ear is represented by telangiectasias or repeating networks of veins and capillaries, which can have expansions in the form of cavities. They are prone to bleeding.
When the sebaceous glands are blocked on the earlobe, atheroma - an epidermal cyst of the sebaceous glands. It is usually encapsulated, smooth and round in shape, the contents of the thick mass contain fat, cholesterol , detritus and epithelium. It can grow over time, fester and break through.
Anatomy of the auricle
Epitheliomas (carcinomas) of the ear are localized at the top of the helix and begin with a warty nodule, which gradually enlarges and spreads over the entire auricle, gradually “corroding” it and causing overgrowth of the ear canal. A detailed study of neoplasia reveals atypical keratocytes (with deposits of keratin ), in which the process of normal cell maturation is distorted, starting from the spinous layer and ending with the upper layer of the epidermis. Tumor cells exhibit a high percentage of pleomorphism and numerous mitotic figures. In other cases, the oncological process immediately begins with the condition of an ulcer, which has limited edges and a tendency to spread in depth and breadth. Penetration of more than 4 mm and extension of 2 cm significantly increases the risk of malignancy. In both cases, regional lymph nodes are involved in the pathological process.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the ear
In children, sarcomas with round-cell, spindle-cell osteo-, angio- and melanosarcoma are more often found. The size and consistency may vary, the color from bluish to red.
The disease is usually characterized by a long-term benign course, which is replaced by rapid tumor growth, ulceration of the skin and exposure of bleeding masses, which then disintegrate. In some cases, a malignant ear tumor grows from the mesenchymal tissue remaining in the newborn in the supratympanic space.
Diagnostics
To find out the reason for the appearance of a lump on the jaw, a comprehensive examination is prescribed. First, the doctor examines and collects the patient’s complaints. If a patient has lymphadenitis, at the initial stage of the disease the following symptoms appear:
- slight enlargement of lymph nodes, their mobility;
- pain of the nodes on palpation, turning the neck (pain can radiate to the ear or other parts of the body nearby);
- general weakness;
- low-grade temperature ;
- decreased sleep quality;
With inflammation of the lymph nodes, accompanied by purulent processes, the patient has complaints of:
- increased pain when moving the jaw;
- redness of the skin in the area where pus accumulates;
- severe swelling of the lymph nodes, their pain even without pressure;
- temperature rise to 38 ºC or more.
In the last stages of lymphadenitis, the patient’s well-being deteriorates significantly: inflammatory processes spread to the neck and shoulders, fever appears, and bluish skin is observed at the site of inflammation.
Since, in addition to inflammation of the lymph nodes, there are other reasons for the appearance of lumps on the jaw, it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis based on the clinical manifestation of the pathology. Therefore, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used.
The patient is prescribed:
- blood test (general, advanced);
- bacteriological examination of mucus from the tonsils and upper respiratory tract;
- radiography of the jaw (in different projections);
- ultrasound examination of pathological formation;
- CT or MRI of the head;
- biopsy (if necessary).
Regardless of the mechanism of occurrence of a lump on the jaw, it is important to begin taking therapeutic measures in a timely manner. The earlier treatment is started, the lower the risk of complications.
Treatment methods
Even if a lump that appears in the ear area does not cause you any discomfort or pain, it is not recommended to delay going to the doctor. Untimely removal of atheroma leads to re-inflammation, as a result of which suppuration begins, swelling appears and the temperature rises. In such situations, long-term treatment is required and always with the use of antibiotics.
If the inflammatory process has already begun, surgical intervention is necessary, during which the cyst is opened and its contents are removed.
After the end of the inflammatory process, it is necessary to perform a second operation to remove the capsule. If this is not done and treatment is stopped after removing the contents of the cyst, the atheroma will periodically grow and become inflamed.
The tumor is removed under local anesthesia. During the operation, the surgeon makes a thin incision through which the capsule and its contents are removed. If you have to make a large incision, stitches are applied, which can be removed after 4-5 days. The sooner the atheroma is removed, the less noticeable the trace of the operation. After timely removal of the ball on the earlobe, virtually no traces remain.
In addition to surgical intervention, atheroma can be removed using laser or radio wave methods.
- Laser removal
If the ball that has formed in the earlobe does not exceed 5 mm in diameter, it is not necessary to remove it through surgery; it is quite possible to use a carbon dioxide laser. If the diameter of the lump is more than 5 mm, removal can be done using a combined method, which includes the use of a laser beam and a scalpel.
With this method of treatment, tissue injury is minimal and relapses occur less frequently. The main advantage of laser removal of atheroma is the short recovery period.
- Radio wave method
The use of radio waves to remove wen on the earlobe began quite recently. Since this method is the most gentle, it is better to focus on it. The atheroma is removed by the so-called “evaporation” of the cyst along with the capsule. The radio wave method means the use of high-frequency waves, the energy of which is concentrated on the corresponding electrode. The procedure does not involve heating the tissues or causing thermal damage. It is performed under local anesthesia.
The equipment used to remove a cyst allows you to kill cells only in the desired area. Thus, healthy cells are not exposed to radio waves. After removing the formation, a crust forms in its place, under which the wound heals.
Under no circumstances should you try to squeeze out the wen yourself. The blocked duct is so narrow in diameter that all attempts will not only fail, but will also cause the onset of the inflammatory process.