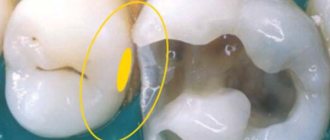
In what cases may the bone fail to take root?
The bone may not take root in cases where it becomes infected, including when the patient violated the schedule for taking antibiotics or did not follow the doctor’s orders.
Much attention is paid to food intake: the patient can simply, out of forgetfulness, bite into something hard, and his stitches will come apart, and the material and bone graft will become infected through the open wound.
The above accounts for 90 percent of cases
when the bone may not take root.
Are there any contraindications to bone grafting?
Of course, there are contraindications to bone grafting. These include
:
- various chronic diseases, incl. diabetes mellitus with high sugar levels,
- the period when the patient takes a number of drugs, including chemotherapy,
- in the period after chemotherapy, when the bone cannot be “touched” at all.
Features of hygiene after bone grafting
After bone grafting it is recommended
:
- use of special surgical toothbrushes,
- the use of toothpaste should be limited, and even better, use special toothpastes for post-surgical interventions,
The main thing when carrying out hygiene is NOT TO INJURY
area of bone grafting! You should try to eliminate contact with this area or reduce it to a minimum.
Preparation for surgery:
During the preliminary examination, the plastic surgeon decides together with the patient what result they want and can (depending on the initial data) achieve. The doctor evaluates the condition of the jaw, bone density, degree of deformation, discusses the intervention technique, and gives recommendations on preparing for plastic surgery. In special cases, the doctor may request an additional X-ray of the jaw or an orthodontist’s report. If a person smokes, it is advisable to reduce the number of cigarettes per day if possible - for faster and easier rehabilitation.
Chin reduction or enlargement, as well as other corrections, are performed under general anesthesia and the patient will need to undergo a comprehensive preoperative examination, including blood, urine, and ECG tests.
Advantages and disadvantages of bone grafting
In ancient times, the profession of “dentist” did not exist: if a tooth needed to be removed, people were wary of going to amateurs in the field of medicine who had tools suitable for such manipulations - to hairdressers and blacksmiths. Nowadays, it is possible to solve any dental problems painlessly, effectively and professionally, but for many, a “primal” fear awakens. Bone augmentation surgery is no exception.
Fear of the procedure can be a serious obstacle to restoring your full smile. If a patient needs bone grafting, it is important to understand the benefits that surgery provides, namely the restoration of full bone volume. This makes it possible to carry out implantation, which will subsequently solve deeper problems, namely, restore the aesthetics and functionality of the teeth. As for the disadvantages, they are associated with material costs (the operation is quite expensive), duration (the procedure delays implantation for at least 2-3 months), as well as difficult rehabilitation. In the first days after bone grafting, you may experience pain, swelling and bleeding. Symptoms can be easily relieved with local anesthetics and antiseptics. In addition, there are restrictions on flights, nutrition, and physical activity. According to statistics, the probability of serious complications after surgery is only 1-3%, and only if the patient is negligent about the recommendations of his attending physician, or the operation was performed unprofessionally.
With a competent and professional approach, the patient will not know what complications are after bone grafting. But the question is different - is it necessary to carry out this procedure if today there are implantation techniques that, with equally high results, allow you to do without bone augmentation? We successfully use methods of dental implantation with immediate loading - in 90% of all cases bone grafting is not required
Chin augmentation techniques:
If chin augmentation is necessary, several techniques can be used, depending on the tasks and the anatomy of the jaw.
Installation of an artificial implant:
Modern maxillofacial prostheses are made from elastic, but very strong, reliable and inert materials, so that the risk of an allergic reaction or rejection is minimized. Implants are available in different shapes and sizes, but they can be custom-made for a specific patient. The surgeon makes a small incision from the inside - from the mucous membrane, and forms a special pocket where the implant is tightly installed. The incision is sutured and no external traces of the operation remain. Similar to an implant, the patient’s own cartilage tissue can be used. It is usually taken from the costal or ear cartilage and is installed in the same way from the inside into the formed pocket.
Augmentation osteotomy of the mandible:
Chin correction can be performed using an osteotomy. In this case, a fragment of bone is cut off and moved anteriorly if the chin needs to be enlarged or repositioned from below when reduction is necessary. When an operation is performed on the patient's bone, the fragments are fixed with titanium plates, and the seam still remains invisible because it is located under the jaw.
Chin lipofilling:
In some cases, it is enough to visually enlarge the chin with lipofilling - using the patient’s own fat taken from the abdomen, thighs, buttocks or “double chin”, if any. A few injections and the face takes on the harmonious, desired shape. Also, lipofilling can be used to complement any type of correction, be it osteotomy or implant installation, if the surgeon considers it necessary to level out the resulting void or remove asymmetry.
Diagnostics
The main goal of any diagnosis is to identify the cause of the problem. And make a diagnosis. Likewise, the diagnosis of distal occlusion is designed to identify the cause of closure in the second class. In order to separate the flies from the cutlets during treatment, so to speak. That is, dental causes of closure are in the second class from non-dental (maxillary, skeletal).
The main diagnostic methods are:
- Analysis of TRG (teleradiogram) of the skull in a lateral projection. It allows you to clearly determine all the skeletal (jaw) nuances of the problem. Both with the position of the jaws and with their sizes.
- Analysis of plaster models of jaws (for this, casts are taken). It allows you to clarify the “dental” nuances: the size of the teeth, the length and width of the dentition, the features of the relationship (including closure) of the upper and lower teeth
Analysis of TRG (teleradiogram) of the skull in a lateral projection.
Analysis of plaster models of jaws.
It is not recommended to fall below this diagnostic “bar”. Below - just by eye. But this, as we understand, is not the best option.
Diagnostics is the first and key step in the treatment of distal occlusion. Do you want to know why it’s impossible to do without diagnostics?
Chin reduction techniques:
Chin reduction surgery (genioplasty) is most often resorted to by women due to dissatisfaction with the shape of the lower jaw or the presence of a skin-fat fold.
Reducing osteotomy of the mandible:
Osteotomy is also performed to reduce the chin. The “extra” bone fragment is cut off, polished if necessary, brought to the desired shape and repositioned with a posterior displacement using titanium plates. After surgery, the stitches are placed under the jaw.
Double chin liposuction:
To correct a double chin, liposuction is performed on the lower side of the jaw using a vacuum or radiofrequency method. Only a few punctures remain, which then quickly heal, and if there was no significant amount of subcutaneous fat, the skin quickly restores its elasticity, begins to fit tightly to the jaw and the face takes on neat features.
Preparatory activities
The general goal of preparatory procedures for mandibuloplasty is to reduce surgical risk and minimize the likelihood of postoperative complications.
Activities begin with an initial consultation, during which the doctor assesses the type and severity of functional and aesthetic disorders, listens to the patient about his problem, intentions and expectations from the operation, informs him about the features and possible results of the operation.
This is followed by diagnostics - facial anthropometry, X-ray studies in the necessary projections (OPTR, teleradiography, targeted images), CT. Based on their results, the volume of bone tissue in the surgical area, the nature of occlusion, and malocclusion are assessed. A treatment plan is drawn up.
If there are concomitant malocclusions that cannot be corrected during mandibuloplasty, the patient may be indicated for orthognathic surgery to correct them.
An important stage of preparation is computer modeling , the purpose of which is to select the optimal surgical strategy, predict its results, and determine the size of the implant.
Before operations, laboratory and instrumental examinations of the patient’s health are also carried out - urine and blood tests (general and biochemical), a coagulogram (to assess blood clotting), bacteriological studies for the presence of viral infections, an electrocardiogram, etc. If required, doctors from other countries are involved in the diagnosis specialties.
15-20 days before surgery, stop taking medications that affect blood clotting. NSAIDs may also be prohibited . It is important that the doctor knows about all medications the patient is taking. If among them there are those that negatively affect hemostasis, the doctor will inform the patient that their use should be stopped for a while.
The length of the preparatory stage is about 7-10 days.
How is the operation performed?
On the scheduled day, in the morning on an empty stomach, the patient enters the clinic, the surgeon performs preliminary markings in the ward, and they are sent to the operating room.
Depending on the technique used, the operation takes from 1 to 2.5 hours. Often, patients combine chin surgery with other facial interventions, which is convenient both from an economic point of view and in terms of recovery. After plastic surgery, the patient is put on a compression bandage and left for a day in the clinic under observation.
Price issue
As a rule, the cost of mandibuloplasty indicated by clinics in their price lists includes all costs associated with the operation:
- initial and subsequent examinations;
- expenses associated with the patient's stay in the hospital (food, provision of a robe, towel, slippers, hygiene kit);
- anesthesia and the operation itself;
- dressings;
- postoperative procedures and rehabilitation monitoring.
The cost of the operation is influenced by the type and complexity of the surgical intervention, the technology used, the general health of the patient, which may require additional procedures, the pricing policy of the clinic and its location.
In general, the entire mandibuloplasty procedure may require the patient to pay from 100 to 250 thousand rubles. In some cases, even more.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Recovery period:
Mentoplasty is a low-traumatic operation, but requires care in the postoperative period. During augmentation surgery, it is important to allow a pocket to form that will tightly hold the implant. Therefore, the pressure bandage must be worn for about three weeks. At this time you need to sleep on your back, limit facial movements, and do not go to the sauna. Within three days, the patient may experience pain, especially when chewing, notice hematomas and swelling, which will then go away on their own. If stitches are applied, they are usually removed within 7-10 days. If access was made through the oral mucosa, you need to follow a diet - do not eat hot, very cold, spicy, and in any case avoid solid foods.
Is it possible to perform bone augmentation at the same time as dental implantation?
New implantation technologies make it possible to perform two processes at once in one procedure, but first you need to determine the feasibility of this approach. Professionals often divide the work into several stages:
- Removal of a tooth.
- Bone grafting.
- Implantation.
But there are two pitfalls here. Firstly, not all clients are ready to go through the operation 3 times. Secondly, dividing the process into several stages is advisable only in cases of severe bone loss. To determine the appropriate method of performing the procedure, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the client and conduct competent diagnostics.
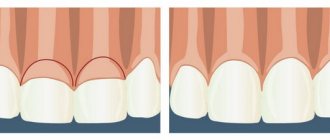
When to expect results
Before and after correction of micrognathia
The achieved cosmetic effect appears approximately 6 months after surgery. The shape of the chin improves significantly, its contours and size change, and the face as a whole becomes more proportional. The photos below before and after mandibuloplasty allow you to evaluate the effectiveness of modern methods of correction of the lower jaw.
Comprehensive correction of face shape for dysgnathia class III according to Engle
View as an album on VK
I think that with specific examples it will be easier for me to explain, and for you to understand , what changes and through what operations can be achieved for various facial deformities . In this case, the patient has class III dysgnathia according to the Engle classification . What does it mean? This means that the upper jaw is “lag behind” the lower jaw in its development . And now the teeth are closing incorrectly . But we are more interested in understanding how improper development of the jaws affects the appearance of the face . So, let's start the analysis.
Indications
Mandibuloplasty can be prescribed in the presence of the following defects of the lower jaw:
Before and after chin correction
- congenital deformations or imperfections (for example, a massive, noticeably protruding or, conversely, underdeveloped chin);
- acquired deformities (can occur after injuries or curvature of the lower jaw);
- noticeable asymmetry of the chin;
- malocclusion.
The patient's aesthetic preferences may also be an indication for surgery. Separately, it is necessary to highlight the indications for bite correction. Often, such defects develop in children as a result of sucking a pacifier or thumb after reaching the age of three. However, they can also be congenital.
Correction of such defects surgically can be prescribed in cases where there are significant deformations of the jaw, the correction of which is impossible through traditional orthodontic treatment. The main indications for plastic bite correction are:
Changing the shape of the chin
- lateral frontal bite;
- severe chin dysplasia with noticeable facial asymmetry;
- frontal open bite.
Surgery is considered necessary if the patient has:
- difficulty chewing;
- problems when biting;
- position of the tongue between the teeth when swallowing;
- difficulty speaking;
- incomplete closure of lips.
As a result of surgical correction of the bite, the jaws are set in the physiologically correct position, and the teeth come into maximum contact with each other when they are closed.
A little history
In Russia, bone grafting of the lower jaw began to be used in the mid-20th century. Then a one-stage plastic surgery was performed using a bone graft based on the outer plate of the rib. As for plastic surgery in general, it was recognized as an independent specialty by the Russian Ministry of Health only in 2009. Today, many advanced mandibuloplasty techniques are used, including the use of implants based on innovative materials that do not cause rejection by the body.