Root canal filling
One of the most popular methods of dental treatment after pulp removal is root canal filling.
The procedure is necessary to strengthen the teeth and prevent infection from entering the root canals. Dentists at the Berezka clinic use new technologies when performing fillings and use reliable innovative materials as fillings. We offer our patients the best and safest methods to restore the integrity of the tooth.
MODE OF APPLICATION
Prepare the material at a temperature of 18-23°C on a glass plate with a metal spatula.
First, mix half of the powder with a full portion of the liquid for 15 seconds, then introduce the remaining portion of the powder, mix for 15 seconds until a homogeneous cement paste is obtained.
NeoDent cement is used in two consistencies:
To install an insulating lining and seal cavities: powder and liquid are mixed in a weight ratio of 2:1, which corresponds to 1 spoon of powder without top per 2 drops of liquid, the working time of the material at a temperature of 18-23°C is 1.5-2 minutes, higher temperature shortens working time and then it is recommended to knead the material on a chilled glass.
The final hardening time of cement is 6-7 minutes from the moment mixing begins.
For fixation of crowns, bridges, inlays and pins: powder and liquid are mixed in a weight ratio of 1.3-1.5:1, which corresponds to 1 spoon of powder without top per 3-4 drops of liquid, working time of the material at a temperature of 18-23 °C for 2 minutes, higher temperatures shorten the working time and then it is recommended to knead the material on a cooled glass.
The final hardening time of cement is 6-7 minutes from the moment mixing begins. Fixation is carried out using standard methods. After curing, remove excess material using appropriate tools.
Preparation for filling
Before filling the canals with filling material, the doctor must thoroughly clean them and prepare the cavity in a special way. This process takes place in several stages:
- Removal of affected tissue
Most often, the need for root canal treatment arises as a consequence of another pathological process, in particular caries. To destroy the source of infection and open access to the mouths of the canals, the dentist removes dead and diseased tissue using a bur.
Pulp removal
The pulp is the sensitive tissue of the tooth, a plexus of blood vessels and nerves located in the coronal part and inside the roots. The method of filling root canals involves removing the pulp using a special tool. Most often, this procedure, like the previous one, is performed under local anesthesia to eliminate pain and discomfort when removing the pulp.
Channel measurement
In order to perform a quality filling, the doctor needs to obtain the most accurate information possible about the properties and current condition of the canals. For this purpose, before treatment, as a rule, a targeted radiograph is performed. An important procedure is also measuring the length of the channels. The length is individual and depends not only on the size of the root, but also on the degree of curvature of the canal.
Mechanical restoration
Before filling, the canals are cleaned and expanded using special instruments. This is necessary to completely remove the affected tissue, as well as to more densely and evenly fill the canal cavity with filling material. Mechanical processing is performed using special thin tools - files. With the help of a file, the canal is passed completely, from the mouth to the apex.
Only after completing all the preparatory steps can the doctor proceed to filling.
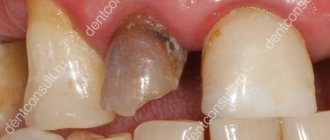
What to do if the crown falls off a tooth?
The development of secondary caries, consumption of sticky and hard foods, incompatibility of artificial products with dental tissues, accidental damage are the reasons why installed crowns fall out. What to do in such a situation? Rinse thoroughly, dry and place the prosthesis in a safe and cool place. Then contact a prosthetist for re-fixation, or to make a new structure. If this possibility is not expected in the near future, there are several ways to solve the problem yourself. Temporary fixation of dental crowns will help preserve the integrity of the tissues of the supporting teeth, maintaining their functionality and appearance.
Classification of filling materials: types and features
Elastic, this includes:
- non-hardening - intended for temporary filling of canals;
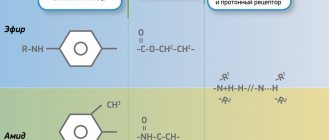
- hardening are endosealants or sealers, which are divided into: zinc-phosphate cements;
- products containing zinc oxide and eugenol;
- polymers with Ca hydroxide;
- glass ionomer agents;
- materials containing resorcinol-formaldehyde resin;
- calcium phosphate based products.
Primary solid means for canal filling are also divided into two main types:
- Fillers - suitable for filling the canal gap. This type includes primary hard materials - pins and hardening pastes.
- Sealers are hardening materials used to fill the space between the pins and the walls of the root canal. Designed to provide sealants for root fillings and are used in parallel with primary solids.
ISO requirements
Requirements for dental cements are established by international standards ISO 9917-2-95 and 9917-91. The regulated parameters depend on the purpose of the cement. So compositions for filling dental canals should have:
- working time , max., min. – no more than 20;
- hardening time , hour – no more than 72;
- fluidity , min., mm – not less than 20;
- solubility ,% – no more than 3;
- film thickness , microns – no more than 50.
Restoration mixtures must meet the following requirements:
- compressive strength , MPa – not less than 130;
- erosion , mm per hour – no more than 0.05;
- hardening time , min – 2-6.
General requirements for dental cements include biocompatibility with the human body and tissues, uniform distribution of pigments, absence of foreign impurities, homogeneity of consistency and some others.
Classification of sealers (endosealers)
The classification of sealers includes, of course, not only newer materials, but also those that are no longer used in modern dentistry or are used in budget appointments. But for the historical aspect, and for general development, it would be nice to orientate ourselves in them.
Sealers are divided according to their consistency and combination of properties into:
- Plastic;
- Filers are primary solid.
Plastic sealers include non-hardening sealers and hardening sealers in their group. Currently, non-curing sealers are not used. Firstly, it is quite difficult to qualitatively fill the space between the dentin of the canal and gutta-percha, so as not to remove the material beyond the apex of the root, secondly, this group of materials has the super ability to dissolve under the influence of moisture, and at the end we have a poor-quality root canal filling, a newly developed pathological process.
A wide range of materials is included in the group of plastically hardening materials, including:
- Sealers based on resorcinol - formaldehyde resin;
- Sealers based on phosphate cement;
- Sealers based on epoxy resins;
- Sealer based on zinc oxide and eugenol;
- Sealer as an adhesive system;
- Polymer sealer with calcium hydroxide;
- Sealers based on silicone resin.
Sealer based on resorcinol - formaldehyde resin
Here you won’t open America to anyone - sealers based on resorcinol and formaldehyde resin are not used, because:
- A sealer based on resorcinol - formaldehyde resin has a high shrinkage, therefore, loss of high-quality sealing;
- Tooth staining pink;
- Formalin not only has a toxic effect on the body, but is also carcinogenic!
There's plenty to choose from
The TOP 5 best adhesives and cements that can be used for self-fixation of crowns at home include:
- Corega;
- Protefix;
- Fittydent;
- The president;
- ROCS.
Coreg contains only components that are absolutely safe for health. It is possible to buy it at a regular pharmacy for $2.5. Gives fixation for up to 24 hours. But there is a high risk of being quickly washed off with water and easily dissolved by exposure to food and drinks.
Protefix, at a cost of $4 to $6, reliably fixes the prosthesis for a period of 10 to 12 hours.
- not very convenient to dose;
- small amount of content;
- requires storage in a vertical position to avoid leakage of the composition.
Fittident adhesive is not for people with highly sensitive teeth (causes discomfort). After allowing the glue to dry slightly on the prosthesis, you can
alleviate discomfort. It has a viscous consistency and requires application to an exceptionally dry surface. With a price of $2.5-3.5 and reliable fixation, it has a drawback - it is not sold everywhere.
The fixation agent President, which costs from $2.7 to $3.5, has an undoubted advantage, forming a dense film that prevents food from getting under the prosthesis. But the fixation can be weakened by hot food.
ROCS glue, a joint Russian-Swiss production, costs about $3.7, gives fixation for up to 12 hours and at the same time provides the necessary freshness of breath.
The canal is sealed with phosphate cement
+7
- home
- Services
- Therapeutic dentistry
Unsealing a root canal previously treated with phosphate cement/resorcinol-formaldehyde method.
Removing old fillings from root canals is called disobturation. During this manipulation, cleansing is carried out from the crown of the tooth to its apical part. In this case, expansion is carried out first with special devices of smaller diameter with their gradual increase in order to achieve complete and effective cleansing of the root canals.
severe pain in the treated tooth;
development of an inflammatory process in the tooth;
lack of filling of additional root canals;
unsatisfactory condition of the filling.
Disobturation is a rather complex procedure that can be carried out by two methods: chemical and mechanical.
With the mechanical method, special equipment is used. The filling is crushed into several fragments, drilled out, and its remains are removed by rinsing or other devices.
The chemical method uses special substances: pastes, gels, solutions. When they are applied to the filling, it softens. Then cleaning is carried out with special tools.
How is deobturation performed with phosphate-cement/resorcinol-formaldehyde fillings?
First, a special solvent is placed into the opened dental canal and left there for several days.
mechanical processing of the chamber and the entrance to the tooth canals;
placing a cotton swab soaked in a special sealing liquid into the cavity;
placing a temporary filling.
A few days later, during the second visit to the doctor, the temporary filling is removed and the remaining filling is removed from the root canals. At the end, the cavity is washed, dried, degreased and subsequent filling is carried out.
Temporary fixation technology
At the preparatory stage, the surgical field and orthopedic structures that are to be fixed are dried and isolated from saliva. Degreasing of working surfaces is not required. Temporary cement is mixed taking into account the manufacturer's recommendations. In the future, the fixation technique - using the example of temporary acrylic crowns on eugenol-free cement - looks like this.
- Temporary cement is applied with a spatula to the cervical part of the temporary crown.
- Under bite control in habitual or central occlusion, the orthopedic structure is fixed in the oral cavity.
- After the time specified by the manufacturer, the temporary cement is removed.
- If work is carried out in support of a dental implant, a rubber dam is used to protect the latter.
- The final stage is x-ray control to check the effectiveness of cement removal.
- Fixation is completed by control of occlusal contacts.
- The patient receives recommendations on the rules for caring for the structure (they are practically no different from the case of installing fixed structures on permanent cement, with the exception of replacing dental floss with a dental brush).