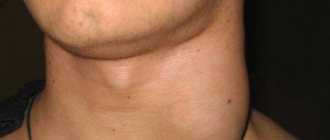
Lymph nodes are located shallow under the skin on the neck, under the arms, and in the groin. They increase in children most often on the neck during infections: colds, sore throats, etc. If the lymph nodes do not decrease after recovery from the infection, remain dense or continue to enlarge, the child should be examined by a pediatrician. You should not feel your child’s lymph nodes more than 2 times a day - this can make them even more swollen and painful.
THE DOCTOR'S CONSULTATION
See your doctor if your lymph nodes are enlarged:
- in a child under 12 months
- longer than 7 days
- and increased temperature
- several groups
- continue to enlarge or the surrounding skin changes
ATTENTION!
If the lymph nodes are enlarged in a child younger than 12 months, it is necessary to have the child examined by a pediatrician.
| ASK YOURSELF A QUESTION | POSSIBLE REASON | WHAT TO DO |
| Does your child have enlarged lymph nodes in the front and sides of the neck? Fever, stuffy nose, runny nose, sore throat, sneezing, dry cough? | ARVI (cold); angina; Infectious mononucleosis | Call a doctor. Give paracetamol to reduce fever. As your child's condition improves, check 1 to see if the lymph nodes are getting smaller. If the increase persists for more than 7 days, contact your pediatrician again (see also Fever, Runny nose) |
| Are the lymph nodes of the lower jaw enlarged? Does your child complain of pain in a tooth or anywhere in the mouth? | Inflammation of the tooth, gums, cheeks | Contact your pediatric dentist . He will examine the child and prescribe treatment (see Mouth pain) |
| Are the lymph nodes only enlarged in the groin or under the armpit? Is there swelling, redness, or tenderness in an arm or leg on the same side? | Infection (possibly bacterial) | Consult your pediatrician for advice . He will examine the child and prescribe treatment, which may include antibiotics. |
| Did swollen lymph nodes occur while taking medication, particularly antiepileptic drugs? | Side effect of the medicine | Make an appointment with your pediatrician . He will adjust the appointment |
| Did enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes occur after the child was scratched by a cat? Slightly elevated temperature, headache? General malaise? | "Cat Scratch Disease" | Contact your pediatrician . He will examine the child and prescribe treatment. Paracetamol can be given to reduce the temperature (see Cuts and abrasions) |
| Are the lymph nodes directly above the collarbone enlarged? Are the lymph nodes of other groups enlarged? | Infection; another disease requiring immediate diagnosis and treatment | Contact your pediatrician immediately . He will examine the child and prescribe the necessary examination and treatment. |
FOR INFORMATION
Lymphoid organs
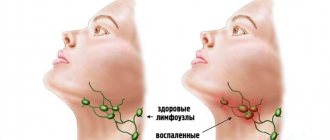
Lymphoid organs are the basis of the body's defense system in the fight against pathogenic bacteria and viruses. It consists of the spleen (the largest organ) and groups of small lymph nodes connected by lymphatic vessels through which lymph flows. Lymph nodes, located in the neck, armpits, groin and many other places, act as a barrier to the spread of germs. Lymph is a fluid containing large numbers of white blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow, then pass through the spleen and lymph nodes and then gain the ability to recognize foreign cells and microbes. Lymphocytes participate in the body's immune defense reactions. They produce antibodies that destroy or render harmless microbes; Antibodies remain in the blood for a long time and when the same microbes re-enter, they are able to fight them. When microbes attack the body, the lymph nodes become noticeably enlarged, as there are more lymphocytes and they actively produce antibodies.
Pediatrician appointment prices:
| TYPES OF MEDICAL SERVICES | Cost, rub. |
| Examination of a child by a pediatrician to obtain a certificate + certificate | 1950 |
| Visit of a pediatrician, consultation at home (Moscow) | 5400 |
| Consultation with a pediatrician at home for the second child | 1950 |
| Patronage for a newborn / gymnastics and swimming at home (1 session, pediatrician Kapina A.V.) | 6300 |
- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
Lymphadenopathy is an increase in size, as well as a change in the shape of one or an entire group of lymph nodes of various origins, without signs of inflammation.
A person has about 600 lymph nodes. Normal sizes are up to 1 cm. The cervical, axillary, inguinal, and intra-abdominal lymph nodes are more often enlarged. Playing a protective role, lymph nodes are among the first to stand in the way of the spread of infections and other foreign antigens (allergens, tumor cells, etc.).
Until a child reaches 12 years of age, the lymphatic system is considered immature, although its formation begins in the early prenatal period. This explains the high incidence of lymphadenopathy among pediatric patients.
Among the causes of enlarged lymph nodes, infectious diseases occupy first place, then systemic diseases of connective tissue, and blood diseases.
Fortunately, lymphadenopathy of a specific tumor nature in children makes up no more than 10% of the total morbidity. A malignant form of the tumor process, which predominates in childhood, is lymphosarcoma. Rarely, enlarged lymph nodes in children occur with severe allergic reactions and helminthic infestations. You need to know that the use of a long course of certain antibiotics and antifungal drugs can provoke the development of a generalized form of lymphadenopathy, the signs of which gradually disappear after discontinuation of the drugs.
Infectious causes of enlarged lymph nodes are varied - these are:
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- fungi;
- parasites.
Infectious diseases that most often occur with enlarged lymph nodes:
- viral (Epstein Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, other herpetic viruses, measles, rubella, viral hepatitis, HIV);
- parasitic (toxoplasmosis, etc.);
- chlamydial infection;
- mycoplasma infection;
- fungal diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria, tick-borne borreliosis, listeriosis, yersiniosis, etc.);
- mycobacterial (tuberculosis).
If an infectious cause of enlarged lymph nodes is suspected, an epidemiological history is important:
- contact with domestic animals (for example, cats);
- eating undercooked meat, raw water;
- going out into nature;
- swimming in ponds;
- visiting exotic countries.
If lymph nodes are enlarged, you should contact the following specialists:
- infectious disease specialist;
- hematologist;
- surgeon;
- oncologist (if necessary).
Services and prices
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an infectious disease specialist
2,200 rub.
Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with an infectious disease specialist
2,100 rub.
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatric surgeon
2,200 rub.
Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatric surgeon
2,100 rub.
Ultrasound examination of lymph nodes
1,300 rub.
Isaev Andrey Aleksandrovich Head of Department, pediatric surgeon Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 43 years
Dear patients! For your convenience and prompt provision of all the information you need, we ask you to leave your request during the clinic’s opening hours.
Pediatricians:
Avzalova Daria Evgenevna
Pediatrician, neonatologist
Experience: 18 years Reviews: 7
Call to home
Barzenok Tatyana Arsenyevna
Head of the pediatric department, pediatrician of the first category
Experience: 28 years Reviews: 17
Make an appointment Call at home
Belousova Elena Sergeevna
Pediatrician, nephrologist
Experience: 18 years Reviews: 14
Make an appointment Call at home
Bykov Mikhail Viktorovich
Pediatrician of the highest category, ultrasound diagnostics specialist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Experience: 25 years Reviews: 3
Make an appointment Call at home
Kazakova Liliya Valentinovna
Pediatrician, neonatologist, head of the breastfeeding consultant service
Experience: 28 years Reviews: 31
Make an appointment Call at home
Sedova Maria Sergeevna
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist
Experience: 20 years Reviews: 30
Make an appointment Call at home
Sergienko Tatyana Yakovlevna
Pediatrician, pediatrician on duty at the pediatric hotline
Experience: 39 years Reviews: 21
Make an appointment
Lymphadenopathy in children: key diagnostic points 03/21/2016
Lymphadenopathy in children: key diagnostic points
Larisa Anatolievna Peresada, pediatric hematologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, receives consultations at:
Children's clinic, Kyiv, st. Tatarskaya, 2-E
Children's clinic on the Left Bank, Kyiv, st. Dragomanova, 21-A
Lymphadenopathy is a condition of hyperplasia (enlargement) of lymph nodes. This term is a preliminary diagnosis that requires further clarification during clinical and laboratory examination and dynamic observation.
The main causes of lymph node hyperplasia in children can be grouped into the following groups:
- infectious, which in turn are of a viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic nature,
- associated with a malignant disease (leukemia, lymphoma, solid tumor metastases),
- as part of immunological disorders: hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, Kawasaki syndrome, as well as in autoimmune diseases: autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, sarcoidosis, congenital immunological defects,
- congenital metabolic diseases - storage diseases (for example, Niemann-Pick disease, Gaucher disease),
- associated with taking certain medications (phenytoin, hydralazine, procainamide, isoniazid, allopurinol, dapsone).
In the process of differential diagnosis, it is fundamentally important for the doctor to answer a number of questions. Are the lymph nodes really enlarged? Are we talking about localized or generalized lymph node hyperplasia? Does the process progress over time? Is there evidence to support an infectious etiology? Is there a suspicion of a malignant process? For example, the location of the lymph nodes - supraclavicular - always gives reason to suspect a malignant etiology. The most common task in pediatric practice is the need to distinguish the infectious from the malignant nature of lymph node hyperplasia. For this, there is a certain step-by-step algorithm, since it is not clinically possible in all cases to distinguish the age norm of the post-infectious state of the lymph nodes.
So, the signs of typical physiological lymph nodes under the age of 10 years: palpable in the cervical, submandibular, inguinal areas, size less than 1 cm (submandibular less than 2 cm), soft-elastic consistency, mobile, painless.
In children, the infectious etiology of lymphadenopathy is found in most cases. In this case, both a local infection and a systemic infectious process can lead to enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Signs indicating the infectious nature of the condition:
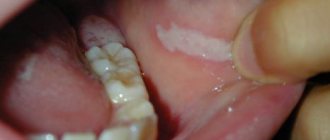
- visible local entrance gates of infection (teeth, tonsils, aphthae on the oral mucosa, traces of scratching in allergic dermatitis, other skin lesions),
- local pain/hyperemia (redness),
- there is an indication of a systemic childhood infection (for example, rubella, scarlet fever).
The primary assessment, as already mentioned, is to identify the location of enlarged lymph nodes. It is important to determine whether the lymph nodes of one group are hyperplastic or whether the process is widespread. In children, the neck area is most often involved. In this case, bilateral (two-sided) damage to the lymph nodes of the neck is characteristic mainly of viral etiology (adenovirus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, herpes virus type 6, HIV), and a similar picture can occur with streptococcal sore throat. Acute unilateral damage to the lymph nodes in the neck area is predominantly characteristic of the staphylococcal nature of the disease, while the entrance gate of infection is the tonsils.
Subacute (chronic) course of the disease occurs, for example, with cat scratch disease, atypical mycobacteria, tularemia (which is rarely remembered, but there are currently facts of registration of this disease in Europe).
Auxiliary for diagnosis are a hemogram (general blood test) + ESR, determination of C-reactive protein, as well as ultrasound of the lymph nodes. Both blood tests and ultrasound images have their own characteristics during the inflammatory process.
One of the stages of the differential diagnosis algorithm is the prescription of antibacterial therapy, which is justified and appropriate for hyperplasia of the cervical group of lymph nodes. With an infectious etiology, the undoubted effect occurs within 10-14 days. This situation is interpreted as lymphadenitis.
The average observation period usually lasts 2 weeks. This time is enough to determine whether regression has occurred, whether the condition remains unchanged, or whether the disease is progressing.
If there is no positive dynamics on your own or after antibiotic therapy, or it is initially difficult to explain the hyperplasia of the lymph nodes with a clear infectious cause, the algorithm provides for the expansion of diagnostic measures. These include:
- determination of the level of LDH (lactate dehydrogenase), ferritin, uric acid in the blood, because an increase in these parameters may be indirect markers of a neoprocess;
- in-depth search for infectious agents that sometimes cause a subacute/chronic state of lymph node hyperplasia (with an appropriate history and clinical picture!) - examination for Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes virus type 6, as well as bacteria that cause cat scratch disease, brucellosis;
- HIV testing - if lymphadenopathy persists for more than 1 month;
- Mantoux test;
- Ultrasound + Dopplerography of the involved group of lymph nodes;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray of the chest organs.
Here is an indicative diagnostic scheme, which is subject to correction in each specific case.
Particular attention is paid to lymph nodes more than 1.5 cm in diameter, dense on palpation, especially if they are accompanied by the so-called B-symptoms. It should be clarified here that B-symptoms include: a) profuse night sweats, b) an increase in temperature over 38°C, c) a decrease in body weight by 10% or more within 6 months. Such symptoms can be recorded with tuberculosis, AIDS, invasive intestinal diseases (amoebiasis, for example), and Hodgkin's lymphoma. As a rule, in such situations there is no time for observation, and it is advisable to perform an open biopsy of the lymph node for diagnostic purposes.
In addition, there are cases when lymph node hyperplasia is accompanied by changes in blood tests - anemia and thrombocytopenia. If autoimmune diseases and congenital immune defects are excluded, a bone marrow puncture is necessary for diagnostic purposes.
The review does not list all, but the most common causes of lymphadenopathy. It is also important to remember that the knowledge and clinical experience of the doctor is sometimes more important than the pedantic implementation of the schemes, and the diagnosis for each patient may have individual characteristics.
Based on materials from the German Society of Pediatric Oncology and Hematology:
Minisymposium on infectious diseases in children (University Hospital Bern, Switzerland, 2012)
Management of Lymphadenitis Minisymposium Infectiologie 25. October 2012.
Diagnostics
To establish the true causes of enlarged lymph nodes, you need to undergo a comprehensive diagnostic examination in a clinical setting. First of all, it is necessary to conduct a thorough history taking to establish the cause of the enlarged lymph nodes in the child. Next, a study is carried out to determine the presence of tumor formations, skin lesions, and the presence of inflammatory processes.
In our medical network clinics in Makhachkala, various types of laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out. To identify the causes of lymphadenopathy in children, specialists usually conduct a set of diagnostic examinations, which includes:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- general urine analysis;
- X-ray of the chest area;
- ultrasound examination of internal organs;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- lymph node biopsy with histological and cytological analysis.
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor makes the diagnosis based on external symptoms and accompanying complaints of the patient. Most often, the disease affects the glands on both sides. Sometimes the symptoms of the disease practically do not appear, except for inflammation of the salivary glands. Once ill, a small patient may refuse to eat, he may experience dry mouth and inflammation behind the ears.
The child is hospitalized only in case of complications or an epidemic. At home, the patient must be isolated from family members for 10 days and kept in bed.
It is necessary to adhere to a dairy-vegetable diet, grind food to reduce pain when swallowing, eat in small portions and drink plenty of warm teas, decoctions, and fruit drinks. You should avoid sour juices and fatty foods.
Doctors often prescribe:
- antipyretic,
- antihistamine,
- vitamins.
Gargling with a soda solution and dry warm compresses applied to the throat area are indicated. To relieve pain, you can tie a warm scarf around your neck and make a warm oil compress with heated vegetable oil.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes physical therapy, for example, ultraviolet radiation, diathermy. In severe cases, intravenous detoxification therapy with glucose solution is prescribed.
You can get a referral for them and undergo them at the children's clinic or at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic in Moscow Central Administrative District at the Baumanskaya metro station.
Prevention
To avoid mumps, a vaccination is necessary, which is done in any children's clinic according to the vaccination calendar, that is, after a year, often together with the measles and rubella vaccine. However, if a child has a decrease in immunity, for example, with leukemia, then the vaccine is contraindicated. Vaccinations for small allergy sufferers are given with special care. Normally, vaccination should be carried out under the supervision of an allergist.
Prevention and treatment of lymphadenopathy in Makhachkala
The essence of treatment for lymphadenopathy is to identify and treat the underlying disease. For example, if the pathology of the lymph nodes is caused by a bacterial disease, then a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed. If the cause of lymphadenopathy is a viral infection, then antiviral treatment is carried out accordingly; in case of oncology, a complex of antitumor measures, etc. When choosing a treatment regimen, the doctor is guided by the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and the results of the examination. Self-medication is strictly prohibited. And the use of folk remedies is possible only in agreement with the attending physician. special measures to prevent lymphadenopathy in children . But the following will help minimize the likelihood of developing lymph node pathology:
- active lifestyle;
- good nutrition;
- increasing immunity;
- outdoor games;
- preventing frequent colds.
Parents are also required to take care of the child’s health, including timely visits to the doctor.