Abscess on the tongue - what is dangerous about an abscess in the mouth and how to remove it without consequences
Tongue abscess is a serious pathological condition, which is characterized by the appearance of a purulent neoplasm against the background of rapid spread of inflammation. In this case, the patient begins to experience severe malaise, the body temperature may rise sharply, and the organ itself will become swollen, which will result in problems with diction, eating, and even breathing. As part of the diagnosis, the doctor may suggest performing a puncture to find out more about the contents of the abscess. Today we’ll talk about the reasons why a purulent process can begin to develop, what accompanying symptoms are characteristic of this condition, and what methods of treating an abscess are used today.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of this disease are:
- An increase in acute, throbbing or aching toothache, intensifying with food intake;
- Experiencing a bitter taste or unpleasant odor in the mouth;
- Feeling of general weakness, headache, apathy, insomnia, lack of appetite;
- Increased tooth sensitivity;
- The gums become inflamed, there is swelling, redness, a small compaction or swelling filled with pus is formed;
- There is an enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes;
- As the infection develops, nausea appears and body temperature rises;
- Facial asymmetry may appear, the size of one cheek, lower or upper lip may increase.
It is important to know that an abscess that begins on one tooth, if left untreated, can spread to the next. If the outer shell cannot withstand and ruptures, the pus comes out, it becomes easier and the pain goes away, but there is a risk of purulent masses getting into healthy tissues and teeth, and the sad story repeating. Ignoring purulent seals in the oral cavity can lead to such dire consequences: tooth loss, death of jaw tissue, development of respiratory diseases (pneumonia, sore throat) and vision. This is also fraught with paralysis of the facial nerves, and the entire body is exposed to acute intoxication.
Features of a purulent abscess
An abscess on the oral mucosa is a kind of abscess, which is characterized by severe inflammation and the formation of purulent masses. Gradually, it leads to the death of living tissue, and in an advanced stage it is accompanied by a general deterioration in the patient’s condition and the appearance of severe pain during talking, chewing food and even breathing. Obviously, this pathology can provoke very serious consequences for the body as a whole, so under no circumstances should an abscess in the oral cavity be ignored.
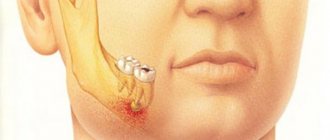
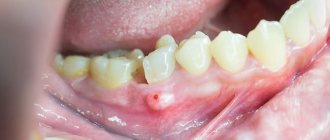
The photo shows a tongue abscess
An abscess of the root of the tongue, as, in fact, of any other part of this organ, is quite readily treatable, but requires an integrated approach to solving the problem. It is important to understand here that the sooner inflammation is detected, the easier and faster it can be eliminated. The pathology in question has a serious impact on the overall health and immunity, so do not hesitate with treatment.
Treatment
To get a complete picture of the disease, dentists use modern diagnostic methods, on the basis of which they select the optimal solution to this problem. These include radiography, ultrasound, sampling of purulent mass and their analysis, visual examination of the condition of the pharynx (pharyngoscopy). Based on the results obtained and studying the history of the disease, appropriate therapy will be prescribed.
Before visiting a doctor, you can alleviate your condition a little by taking painkillers and warm antiseptic solutions, but you should not put off visiting the dentist for long, because the process develops very quickly and does not go away on its own.
Treatment of an oral abscess is usually carried out using two methods:
- Surgical intervention Allows you to avoid most of the complications that may arise from an unauthorized breakthrough of a purulent sac. The operation is performed under local anesthesia by a dental surgeon, with the help of special instruments the abscess is opened, the wound is cleaned and drainage is placed, after the operation antibiotics, antihistamines, vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed;
- Medication Medications (Fluocinonide gel, Chlorhexidine solution, Ibuprofen) are prescribed only in the initial stage; timely consultation with a doctor and timely prescribed medications help avoid surgical intervention.
When the pus comes out, relief comes: there is no more pain, the temperature returns to normal, and the swelling disappears. The course of treatment ends with the necessary physical procedures: electropharesis with the addition of an antiseptic on the gums, UHF heating, and the procedure for silvering teeth affected by caries. Until the wound in the mouth completely heals, the patient must abandon hard vegetables and fruits in favor of soft cereals and liquid soups.
Reasons for the formation of an abscess on the tongue
Most often, the formation of a purulent focus on the body and the root of the tongue in particular becomes a consequence of mechanical or thermal effects. Damage opens a direct path for the penetration and spread of bacterial infection. As practice shows, the formation of an abscess is often preceded by injury to the mucous membrane with sharp fish bones.
“In my case, the abscess was generally the result of my passion for dried vobla! Once again I accidentally scratched the edges of my tongue, then it turned red, began to hurt, and one fine morning I discovered a small abscess on it. I was scared, of course, and immediately made an appointment with a doctor. Fortunately, everything worked out without surgical intervention. The doctor prescribed rinsing with chlorhexidine.”
Anna Semenova, 43 years old, Omsk, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
Quite often, the oral mucosa is injured by sharp edges of teeth or crowns, as well as worn-out prosthetic structures and incorrectly adjusted orthodontic devices for correcting the bite. Patients suffering from periodontitis, ulcerative stomatitis, and acute tonsillitis are also at risk. In this case, pathogenic bacteria can spread from the source of chronic infection in the oral cavity. Thus, to date, experts in the field of dentistry have identified the following main reasons for the development of pathology:
- penetration of infection, staphylococci and streptococci,
- trauma to the mucous membrane,
- imbalance of oral microflora,
- dental diseases,
- glossitis,
- stomatitis,
- tonsillitis.
Trauma to the tongue can cause an abscess.
It should also be noted that quite often an abscess develops after a burn as a result of consuming too hot food or drinks. Infection can also appear through fresh scratches from hard foods or sores caused by eating spicy or salty foods.
Opening an abscess, phlegmon of the maxillofacial area
The frequency of development of abscesses and phlegmon of the maxillofacial area of the head is due to the high prevalence of chronic focal odontogenic and tonsillogenic infections, as well as infectious and inflammatory lesions of the skin and oral mucosa. Based on data on the localization of the infectious-inflammatory process in various anatomical sections, zones, regions, as well as spaces of the head and neck, their systematization is built. From the description of the topographic-anatomical structure of the areas of the face, the perimandibular and adjacent areas of the neck, one can see the complexity of their anatomy. There are many cellular spaces, numerous lymph nodes and vessels scattered throughout all areas of the face, an abundant network of arteries and veins with rich innervation of these areas.
The basic principle of treating inflammatory diseases is opening the source of inflammation and draining it. Complete drainage reduces pain, promotes the outflow of wound fluid, improves local microcirculation, which naturally has a beneficial effect on local metabolic processes, the transition of the wound process to the regeneration phase, reducing intoxication and interstitial pressure, limiting the necrosis zone and creating unfavorable conditions for the development of microflora.
The incisional drainage method of treating phlegmons and soft tissue abscesses is quite widespread to this day. It involves opening a purulent focus and open wound management in the postoperative period. The incisional drainage method is a classic one; in general, it determines the tactics for the treatment of acute purulent diseases of soft tissues and purulent wounds.
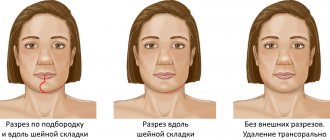
Opening of the purulent focus is carried out by external access from the skin, or intraoral access from the mucous membrane.
During the operation of opening an abscess (phlegmon), the skin, mucous membrane, and fascial formations above the purulent focus are dissected; the muscles are cut off, peeled off from the place of attachment to the bone of the temporal, medial pterygoid and chewing muscles (m. temporalis, i.e. pterygoideus mcdialis, i.e. masseter) or using a hemostatic clamp, the muscle fibers of the temporal, mylohyoid and buccal muscles (m. temporalis) are pulled apart , T. mylohyoideus, T. buccalis). The exception is the subcutaneous muscle of the neck (m. platysma) and often the mylohyoid muscle, the fibers of which intersect in the transverse direction. which ensures the wound gapes and creates good conditions for the outflow of purulent exudate. Loose tissue located on the way to the purulent focus, in order to avoid damage to the vessels, nerves, and excretory flow of the salivary glands located in it, is stratified and pulled apart with a hemostatic clamp.
Characteristic symptoms
The pathology is characterized by a fairly rapid pace of development. Based on where exactly the neoplasm is localized, experts distinguish between deep and superficial forms of abscess. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Surface view
In this case, an abscess occurs on the back of the organ. The person experiences acute pain during swallowing, which often radiates to the ear. As part of a visual examination, noticeable swelling of the mucous membrane can be detected; when touched, a compaction can be clearly felt. Such an abscess can open without outside help, but in any case professional treatment is necessary.
Deep view
This is a more dangerous form of pathology, in which purulent processes develop in the thickness of the tissues of the organ. Experts include the following conditions as associated symptoms:
- general weakness,
- poor appetite
- restless sleep due to constant painful sensations,
- tachycardia,
- heat,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- increased salivation,
- severe swelling of the organ, acute pain,
- blue mucous membranes, formation of gray plaque,
- the appearance of bad breath.
The main danger is that when an abscess develops, the tongue greatly increases in size. As a result, problems arise not only with speech, but also with breathing.
How is diagnostics carried out?
At the first appointment, the doctor is obliged to ask the patient about all the symptoms that worry him. He also needs to find out the circumstances under which the mucous membrane was injured. Next, the specialist sends the patient for blood tests, since the formation of an abscess usually causes a significant increase in the level of leukocytes and ESR.
For diagnosis, a blood test is required.
In order to identify the pathogen, bacterial culture is performed. The patient may also be referred for an X-ray examination, which will help detect the source of the infection, especially if there are complications. Competent diagnosis makes it possible to distinguish between diseases such as tongue abscess and Ludwig's tonsillitis, lymph node abscess, lymphadenitis.
Possible complications
The pathological condition under consideration, especially if the formation of an abscess occurs at the very root of the organ, is fraught with serious consequences for the entire organism as a whole. If treatment is not started in time, the abscess may well result in serious complications. Thus, in advanced stages it is often accompanied by purulent inflammation of the tissue - the formation of phlegmon, the occurrence of sepsis and severe intoxication of the body, and this, in turn, can lead to death.
Causes of paratonsillar abscess
As a rule, a paratonsillar abscess develops as a complication of tonsillitis or chronic tonsillitis. With tonsillitis, scars can form in the tonsils, preventing pus from leaving the lacunae (lacunae are natural narrow and highly branched cavities in the body of the tonsil). Pus that does not find a way out accumulates inside, from where it penetrates into the tissue surrounding the tonsil.
Treatment of tongue abscess
Conservative therapy involves taking antibiotics and rinsing with antiseptic agents, such as Furacilin or Chlorhexidine. However, such treatment can be effective only at the earliest stage of pathology development. If the situation is advanced, immediate surgical intervention will most likely be required. The dentist will perform an emergency opening of the abscess, thereby preventing further spread of the infection. If a purulent neoplasm has formed deep at the base of the organ, the doctor may perform an autopsy from the outside under the chin. After removing purulent discharge, the specialist will thoroughly rinse the cavity using antibiotics and proteolytic enzymes1.
In some cases, surgery is performed to remove the pus.
In the most advanced cases, when the patient is already experiencing serious breathing difficulties, a tracheotomy is performed. The patient is prescribed antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and antihistamines. To strengthen the body's defenses, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes and regularly rinse the mouth with antiseptics, including decoctions of medicinal herbs - chamomile and sage. It is important to understand here that the use of any pharmaceutical drugs and traditional medicine must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
What is an oral abscess?
An oral abscess is an acute inflammatory disease characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the tissues of the gums, tongue or cheeks. The abscess is accompanied by local swelling and hardening of soft tissues, severe pain on palpation, fever and general weakness. The disease is diagnosed by a dentist after a visual examination of the tissue, after which immediate surgical intervention is required: opening the abscess, followed by cleaning and taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
Oral abscess is one of the most common complications in the practice of dental surgery. It can be observed in patients of different ages. Untimely treatment can lead to the transition of inflammation to the chronic stage. Against this background, sepsis and phlegmon can develop. That is why, if the slightest symptoms of an abscess occur, you should immediately visit a dentist.
Prognosis and prevention
The success of treatment largely depends on how deeply the infection has spread and how quickly the person receives medical care. If an abscess is diagnosed in a timely manner, the likelihood of a favorable outcome will be at the highest level - the disease can be cured in just a couple of weeks. If the problem is neglected, the situation may result in the development of phlegmon and sepsis. To prevent the appearance of an abscess on the tongue, including relapses, it is enough to follow the recommendations of doctors:
- pay close attention to oral hygiene, brush your teeth and tongue twice a day,
- minimize the consumption of too spicy and salty foods,
- take care of the condition of the oral cavity, try not to injure the mucous membrane with foreign objects,
- in case of accidental damage, you should thoroughly rinse your mouth with water and an antiseptic solution, and also, just in case, consult a specialist to eliminate the risk of infection of the wound,
- strengthen the immune system - a healthy lifestyle, frequent walks in the fresh air, sports and proper nutrition,
- systematically visit the dentist for preventative care.
Preventive examinations with a dentist will help you avoid problems.
If you detect any suspicious changes in the condition or appearance of the oral cavity, you should definitely consult a doctor for advice. It is better to waste your time and go to a specialist than to undergo long and grueling treatment.
Home remedies
To speed up the wound healing process after treatment, you can resort to proven home methods. Here it should immediately be noted that their use is justified only if the attending physician has given his consent. Here are some reliable tips:
- rinsing with a light saline solution at the rate of 2 teaspoons per glass of water at room temperature,
- treating wounds with a solution of hydrogen peroxide or Chlorhexidine,
- applying a piece of ice to relieve acute inflammation.
Tongue abscess is a disease that is inevitably accompanied by very unpleasant symptoms. A general deterioration in health, high temperature, pain, problems with speech and breathing are only a small part of what the development of such a serious and dangerous phenomenon in an advanced stage entails. To prevent the situation from worsening, consult a doctor immediately when the first signs of pathology appear.
- Vernadsky Yu.I. Fundamentals of maxillofacial surgery and surgical dentistry, 2003.