General information
Mycosis of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity ( stomatitis or thrush ) is usually a dysbiosis , it is provoked by yeast fungi and most often by the genus Candida. A fungal infection can affect both adults and children, regardless of gender, the main condition is the presence of severe illness or long-term antibiotic therapy, but most often it affects infants or elderly people who have a chronically weakened immune system , the functioning of other systems is not adapted or impaired, and organs.
It can occur as an independent pathology, be a secondary infection or a manifestation of other chronic diseases.
How it manifests itself
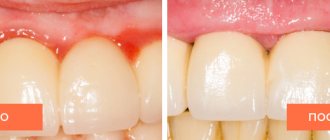
The disease is easily diagnosed, since its symptoms are clear and speak for themselves. Symptoms are the same in adults and children. The pathology develops according to the principle of dermatitis. The skin becomes inflamed, red, and mucous membranes swell. As the number of fungi increases, sores form. They are painful, covered with a white or yellowish coating. When trying to remove the latter, blood begins to flow.
Subjectively, the patient complains of:
- itching/burning on the affected areas of the tongue;
- pain when eating solid foods;
- bad breath;
- discomfort during a conversation.
Plaque found on mucous membranes consists of dead epithelial cells, fibrin, bacteria, and food microparticles. It can be located in small isolated areas or merge into volumetric circles. If measures are not taken in time to eliminate this symptom, the infection will spread to the throat and then to the internal organs.
The danger lies in the fact that candida multiplies very actively. They are able to penetrate into the deep layers of the mucous membranes of the mouth. Then the disease is difficult to treat, and the likelihood of relapse remains high.
As for the painful sensations that appear while eating, they are associated with severe tissue inflammation. The latter turn red and bleed. Any mechanical impact aggravates the situation.
If pain occurs when swallowing, it means that candidiasis has spread to the pharynx. A feeling of a lump in the throat indicates the appearance of voluminous film growths. This should not be allowed. The sooner treatment is started, the lower the risk of unwanted complications.
Other symptoms of candidiasis on the tongue
Other signs indicating the disease include:
- weakness, lethargy;
- increased body temperature;
- proliferation and enlargement of the papillae on the surface of the tongue;
- deterioration of taste or loss of the ability to recognize tastes;
- tissue swelling;
- decreased tongue mobility.
If these symptoms appear, you must make an appointment at a dental clinic.
Pathogenesis
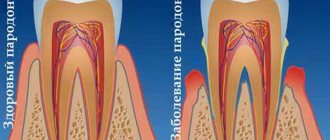
Yeast fungi in the human body are considered to be opportunistic microflora . They may be present in the microflora, and if the immune system is strong, then the fungal infection does not cause diseases, for example, urogenital, respiratory, skin, or, as in this case, the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Normally, in almost 70% of the population, yeast fungi are present in the resident microflora; they are inactive and do not cause candida or other fungal diseases. Reproduction usually occurs by budding and spores. Proliferation occurs not due to the departure of daughter cells from the mother cells, but through elongation and formation of a pseudomycellar tree. As a result of vital activity, toxic substances are released that weaken the human immune system.
Model of a fungus cell of the genus Candida
alcohol and drug abuse, oncology, and the use of contraceptives contribute to imbalance of the oral microflora and excessive proliferation of opportunistic fungi . Fungus in the mouth is most often a superficial disease that affects the mucous surface of the cheeks, the corners and borders of the lips, the back of the tongue, the palate, etc., but with significant spread and penetration into the bloodstream it can cause systemic chronic and generalized disorders.
In neutropenic or severely ill patients, candidal fungal infection can enter the bloodstream, where it causes widespread visceral dissemination. Generalized mycosis can lead to candida sepsis and even death.
How to eat during treatment
Candida fungi multiply very quickly if a person eats a lot of sweets. Therefore, until complete recovery you need to stop eating:
- sweets;
- ice cream;
- baking.
Any alcoholic drinks are also prohibited.
Meat lovers should give preference to turkey and chicken. Buckwheat porridge is very useful - it contains many B vitamins. In order not to further irritate or injure the mucous membrane of the tongue, you should eat warm and well-chopped food.
Classification
Mycoses are divided depending on the form of the course - mild and severe, acute and chronic; according to the type of changes, they can be acute pseudomembranous candidiasis (thrush), acute atrophic candidiasis , chronic hyperplastic candidiasis , candida-associated periodontitis , ulcerative-erosive stomatitis .
The localization of fungi can be on the tongue, on the cheeks, on the lips, in carious cavities and root canals, on the tonsils, in the corners of the mouth, or affecting the entire surface area of the oral cavity.
Fungus on tongue
The pathological effect of various infectious agents on the tissues of the tongue causes glossitis . One of the manifestations of glossitis may be the loss of the ability to determine tastes. Significant contamination also leads to the formation of ulcers, the sensation of blood in the mouth, and spread to the tonsils and pharynx.
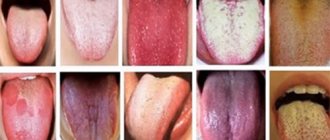
Different types of candidiasis on the tongue
Fungus on the tongue, photos of various types of damage to the epithelial layer (atrophic, hyperplastic, all-membranous and thrush), clearly demonstrates how varied the symptoms of glossitis can be. At the first signs, you should contact your dentist for a consultation.
Fungus on lips
The course of mycoses on the lips is usually chronic and most often manifests itself in redness. Unpleasant symptoms can occur even in people with fairly strong immunity, but more often in patients with diabetes , tuberculosis or AIDS .
Fungus on lips
Other symptoms may include slight swelling of the lips, burning, peeling, and a white coating as in the photo of fungus on the lips. The existing crusts are grayish in color, have raised edges and a tightly attached center, and differ in size. If you try to tear off the crust, a bleeding wound will open. In general, the pathology causes discomfort and pain.
The mucous surface of the inner part and red furrow of the lips may become thin, cracked, and tense. This is a fairly rare separate disease, also called cheilitis .
Treatment of tongue candidiasis
The treatment regimen is selected taking into account the factor that provoked the development of the disease. The main goal of therapy is not just to destroy pathogenic flora, but also to strengthen the immune system and improve the functioning of the stomach and intestines. If this is not done, the likelihood of relapse will remain high.
If the disease is caused by long-term antibiotic therapy, taking hormones or steroids, as is most often the case, you need to reduce the dosage of drugs from these groups and at the same time start using antifungal tablets. B vitamins and immunomodulators have an excellent effect on the body during the treatment of tongue candidiasis.
Medicines used for candidiasis
It is impossible to get rid of fungi of the genus Candida that have multiplied on the mucous membranes of the tongue without medications. Medicines should:
- relieve inflammation;
- activate regeneration processes;
- reduce pain;
- destroy fungi;
- heal ulcers;
- reduce swelling.
For this purpose, dentists prescribe the following pharmacological groups:
- Antifungal. They act by destroying the cell membranes of the pathogen. They are manufactured in the form of tablets and capsules for oral administration.
- Antiseptics for mouth rinsing. They destroy viruses, fungi, bacteria, and create conditions for the restoration of healthy microflora.
- Gels and ointments with antifungal activity. Used strictly locally. They treat the surface of the entire tongue. They help remove swelling, minimize itching and burning. Excellent healing of existing wounds.
- Antiseptics in the form of aerosols. Very convenient to use. Suitable for use in public places. Characterized by a wide spectrum of action.
When treating candidiasis in the tongue, it is important to use exactly the drugs prescribed by the doctor. There is no need to exceed their dosage, as this may cause the opposite effect.
Traditional methods of combating oral candidiasis
If you really want to supplement drug therapy with herbal remedies, it is permissible to use:
- decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs;
- alcohol tincture of propolis;
- soda solution.
These products should be used while rinsing the mouth.
Causes
The cause of fungus in the mouth is an imbalance of microflora and the pathogenic effect of prevailing conditionally pathogenic yeast fungi. The most common pathogens of the genus Candida are Albicans, krusei C, parapsilosis, tropicalis, pseudotropicalis, lusitaniae, dubliniensis and glabrata.
Infection can occur from the outside - during the passage of the birth canal, through sexual contact, kissing and everyday interactions with a sick person. Chronic microtraumas from the edges of teeth, poor dentures, serious illnesses, reduced immunity (including those caused by AIDS), chaotic use of antibiotics, excessive use of antiseptics, and the virulence of the pathogen also contribute to the penetration and growth of yeast fungi in the mouth.
How to recognize a fungus - symptoms of the disease
Currently, experts identify several of the most common types of fungal infections of the tongue, each of which is characterized by its own symptoms. Let's take a closer look at these types:
- pseudomembranous, acute form: most often affects newborns and adults with seriously compromised immunity. A whitish coating appears on all surfaces of the oral cavity, including the cheeks, gums and throat; visually it resembles traces of cottage cheese or milk,
- pseudomembranous chronic: develops in patients with AIDS, as well as against the background of infections that have developed resistance to antibiotics. The symptoms are similar to those described above, the person may also experience pain when swallowing,
- atrophic, acute form: usually develops after prolonged use of antibiotics, often found in diabetics. In this case, swelling of the tongue is observed, the mucous membrane becomes covered with cheesy discharge, the person feels an unpleasant burning sensation, and the corners of the lips dry out and become covered with small cracks,
- atrophic chronic: as practice shows, this form is usually encountered by people with dental prosthetic devices. Active reproduction of microorganisms often begins under the palatal covering of the structure, and a distinctive symptom is the fact that the tongue acquires a rich red tint,
- erythematous: a chronic form, which is characterized by inflammation of the entire oral mucosa, including the throat, as well as the formation of a whitish coating,
- hyperplastic: accompanied by the formation of a dense coating in the form of plaques, but in this case it is not white, but practically merges with the natural shade of the tongue. Slight redness may be detected along the edges.
How to treat the pathology is determined by the attending physician, and before prescribing therapy, he needs to find out what specific form of pathology he is dealing with. To do this, the specialist conducts a visual examination and sends the patient for tests.
Symptoms
Oral fungus has a pathological effect, which consists of damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, on the red border of the lips (otherwise called cheilitis) and in the corners of the mouth. Damage to the mucous membranes in the mouth when the patient is in a weakened condition or after long-term antibiotic therapy can lead to acute catarrhal stomatitis .
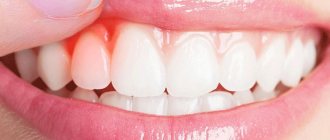
Pathology usually manifests itself in the form of a hyperemic or even bluish surface of the mucous membranes and the formation of single white plaques. They look like they are glued on. The fungus in the mouth, the photo of which is presented below, initiates chronic atrophic changes in the structure of the epithelium.
Fungus in the mouth
In addition, in addition to white plaque, crusts and redness, white papules, unpleasant local symptoms may occur in the form of itching, changes in taste, pain and burning.
Plaque on the tongue of fungal origin - why candidiasis appears and methods of combating it
Fungus on the tongue is not such a rare phenomenon, and the development of such a pathological condition is provoked by yeast fungi of the genus Candida. They are present in the body of any person and do not harm him until a certain point. But as soon as the immune system weakens and fails, the fungus will immediately begin to multiply and ultimately can lead to the development of candidiasis (thrush). Today we’ll talk about what a fungal infection of the tongue is, what symptoms are typical for it, and what treatment methods are used today to get rid of this unpleasant disease.
Tests and diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, microscopic examination of crusts and other biological tissues, fluids or scrapings is carried out, depending on the location of the pathology. As a result, fungal mycelium is detected. It is quite important to identify the causative microorganism (PCR diagnostics, ELISA, cultural inoculation with quantitative monitoring can be used for this), since various types of fungi can exhibit resistance to antifungal drugs.
Additional studies include checking for gastrointestinal pathologies, diabetes mellitus and leukemia .
Carry out differential diagnosis:
- with eczema - characterized by the formation of weeping surfaces after the opening of the blisters, redness and swelling are more pronounced;
- with leukoplakia , manifested by the development of plaques and opacities of areas of the epithelium;
- with allergic, streptococcal stomatitis, cheilitis and other similar lesions of a different nature.
Candidiasis
Cervical cancer
Diabetes
HIV
Thrush
18782 July 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Candidiasis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Candidiasis is an infectious disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. It is caused by the active proliferation of fungus on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, genital and internal organs and on the skin.
All representatives of the genus Candida belong to opportunistic microorganisms, that is, they are constantly present in the normal microflora. But with a decrease in immunity, changes in hormonal levels and for a number of other reasons, these fungi can begin to actively colonize the mucous membranes and skin.
The most common members of the genus are Candida albicans and C. tropicalis. In 90-95% of cases of urogenital candidiasis, C. albicans is the dominant pathogen.
The first contact with fungi of the genus Candida occurs during the passage of the child through the birth canal. However, the medical literature describes cases of detection of these microorganisms in amniotic fluid, which indicates the possibility of a vertical (transplacental) transmission route. Transmission of the fungus of the genus Candida also occurs through breastfeeding, skin contact between the child and the mother, and through household and food routes.
These microorganisms produce endotoxins and enzymes that cause cell death and tissue necrosis, which enhances the adhesive (attachment to cells of the mucous membranes or skin) ability of the fungus and ensures penetration into tissue.
Overproduction of these and a number of other substances determines the pathogenicity of representatives of the Candida family.
Causes of candidiasis
- Exogenous (external) factors facilitating the penetration of fungi into the body:
- occupational hazards leading to frequent skin damage;
- prolonged exposure to a warm and humid environment;
- violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes.
- Factors leading to a decrease in the body's resistance:
- presence of chronic diseases;
- long-term use of drugs that disrupt the natural microflora;
- unbalanced diet;
- frequent stress, disturbances in sleep and rest patterns.
Risk factors for developing candidiasis
- Metabolic disorders (hypovitaminosis), diseases of the immune system (HIV infection), endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, etc.).
- Long-term use of certain drugs: hormonal contraceptives, systemic glucocorticosteroids, broad-spectrum antibiotics, cytostatics.
- Long stay or living in an area with high humidity and temperature, comfortable for the circulation of fungal spores in the environment.
Classification of the disease
Based on the localization of the process, the following are distinguished:
- Urogenital candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of the oral mucosa.
- Superficial candidiasis.
- Interdigital candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of periungual ridges and nails.
- Candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Urogenital candidiasis (UGC)
– a widespread disease: according to medical statistics, about 75% of women of reproductive age have registered symptoms of UGC at least once.
There are acute and chronic forms of urogenital candidiasis, candidiasis of the vulva, vagina and other urogenital localizations.
In some cases, when diagnosing, a clarification is used: complicated or uncomplicated UGC, which reflects the number of exacerbations per year and the severity of the disease. Symptoms of female urogenital candidiasis
- The appearance of white-yellow cheesy or creamy discharge from the genital tract. The intensity of discharge may increase before menstruation, which is associated with changes in hormonal levels.
- Unpleasant sensations, itching in the genital area, often aggravated by sexual intercourse or urination.
- Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina, the presence of damage to the skin of the genital organs (cracks, microtraumas).
- In the chronic course of UGC, dryness of the mucous membranes of the genital tract develops.
Symptoms of male urogenital candidiasis
- Redness, swelling, discomfort in the genital area.
- Whitish discharge of a cheesy structure from the genital tract.
- Pain and burning during sexual intercourse and urination.
Superficial candidiasis
can be erythematous (the main symptom is reddened areas of the skin with a weeping surface) and vesicular (the formation of papules, vesicles and pustules in the affected area - inflammatory elements located in the superficial layers of the skin). The lesion begins with large folds of skin, gradually spreading to other areas of the body. In the depths of the folds, weeping occurs (separation of serous exudate through the smallest defects of the epidermis), a violation of the integrity of the skin contributes to the addition of a secondary infection.
Interdigital candidiasis
localized in the space between the fingers. In this case, redness of the skin is noted, followed by the appearance of bubbles in transparent contents. The disease spreads quickly in close groups (in kindergartens, schools, etc.).
Oral mucosal candidiasis (OCOR)
Oral candidiasis causes discomfort, especially when eating - burning, pain, dryness. Depending on the location of the process, several forms of oral candidiasis are distinguished.
Often, CSOPR and the gastrointestinal tract accompanies immunodeficiency conditions: HIV infection, acquired human immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or congenital immunodeficiency (for example, with T-lymphocyte pathology). In the presence of these diseases, candidiasis occurs with the most severe symptoms, is difficult to treat, and is aggressive in nature.
The most common manifestation of CSOPR is candidal stomatitis, which mainly affects infants and adults with weakened immune systems.
With this pathology, the oral mucosa turns red, swells, and whitish films with a cheesy consistency appear on it. In the initial stages of the disease, plaque is easily removed. As the disease progresses, the films become denser, are difficult to separate, and when removed, the bleeding mucous membrane is exposed.
With candidal stomatitis, the tongue may be affected, which is manifested by redness of the back of the tongue, the appearance of plaque and desquamation of the epithelium. These symptoms are accompanied by severe pain in the affected area when talking, eating, and palpating the tongue.
Smokers, more often than other types of CSOPR, develop chronic hyperplastic candidiasis, accompanied by the formation of white, merging plaques that rise above the surface of the hyperemic mucosa.
With this pathology, the consistency of saliva changes: it becomes viscous and foaming; there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, a gray or white coating on the mucous membrane. In 10-40% of cases, this clinical form of candidiasis becomes malignant (i.e., becomes malignant).
Older people most often develop a chronic atrophic form of oral candidiasis. The mucous membrane turns red and swells. The lesion is often localized under dentures, which causes pain.
Candidal cheilitis and candidiasis of the corners of the mouth mainly occur in children and the elderly. The lesion is usually bilateral, with the formation of red, painful cracks in the corners of the mouth, covered with an easily removable white coating or scales. With a long course of the disease, a bacterial infection may occur.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
The diagnostic search algorithm for candidiasis of any localization includes taking material from the affected area, followed by microscopy and culture to determine the type of fungus and its sensitivity to antimycotic (antifungal) drugs.
In order to diagnose conditions that lead to a decrease in immunity, a general blood test is used;
Prevention
There are a number of preventive measures to prevent the development of fungus in the oral cavity, these include:
- regular visits to the dentist, at least 2 times a year;
- taking medications that strengthen the immune system and following a healthy, nutritious diet;
- compliance with the rules of oral hygiene - cleansing plaque with toothpaste and rinses 2 times a day;
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- minimal consumption of foods high in sugar and yeast, these include baked goods and other bakery, confectionery products, beer, etc.
How to avoid getting sick
Preventive measures include following simple rules:
- balanced diet;
- elimination of traumatic effects on the tissues of the tongue;
- taking an antifungal drug during a course of antibiotics and hormones;
- course use of immunomodulators;
- maintaining oral hygiene;
- timely treatment of emerging dental diseases.
People who take care of their dental health and visit the dentist twice a year are much less likely to experience tongue candidiasis. This is a proven fact. Therefore, do not ignore your doctor’s requests to come for preventive examinations.
In children
In infancy, oral mycosis is usually caused by Oidium albicans and is called thrush. Small children under one year old require special attention, because fungus in the mouth and other mucous membranes of babies can occur as a result of:
- breastfeeding or passing through the birth canal of an infected mother;
- violation of hygiene standards - use of unsterile utensils, things, household items, etc.;
- sexual contact, for example, oral sex;
- excessive consumption of sugars, for example, during artificial feeding.
Despite the fact that thrush in children tends to return, it is easier to tolerate than in adults and can be treated, in more rare cases it can provoke a fungus on the tonsils in a child, enter the body along with food during swallowing and provoke intestinal dysbiosis .
Causes of yeast glossitis
In most cases, the disease is a consequence of a weakened immune system. Therefore, more often than others, people who have suffered some kind of serious illness encounter it. Pathology also develops due to dysbiosis resulting from long-term antibiotic therapy, taking hormones or immunosuppressants.
Other reasons include:
- ulcerative glossitis/stomatitis not treated in a timely manner;
- frequent mechanical damage to the mucous membrane covering the tongue;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- liver dysfunction;
- disruption of the normal quantitative relationship between different fractions of blood proteins;
- thyroid diseases;
- oncology;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking;
- deficiency of potassium in blood plasma;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Tongue candidiasis also occurs as a result of direct contact with a carrier of the infection. This refers to the transmission of the disease during kissing, when using shared utensils. In newborn children, the cause of pathology is the passage of a sick mother through the birth canal.
Diet for fungus in the mouth
Antifungal Diet
- Efficacy: no data
- Terms: 3-6 months
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles. in Week
In addition to complex antifungal treatment, patients are strongly recommended to follow a strict diet consisting of foods without vinegar, sugar, yeast and alcohol. in vitamins and strengthening the immune system is also recommended The menu should include bananas, onions, garlic, asparagus, chicory, olive oil, seafood, legumes, and buckwheat.
Diet for candidiasis on the tongue
Compliance with certain dietary restrictions is an important point in treatment. For example, experts strongly recommend avoiding products with yeast. Too spicy and sour foods provoke irritation of the oral mucosa, which can cause an unpleasant tingling sensation and even pain. During recovery, doctors advise eating mainly liquid and warm food. In this case, spices and acid-containing foods will have to be excluded for a while.
You need to return to your usual diet gradually. For three months you will have to give up sweet and fatty foods, carbonated water, mushrooms, as well as confectionery and alcoholic drinks.