People turn to the dentist when they have any problems with the health of their teeth or gums. Pain in the tooth, swelling of the gums, increased sensitivity of the teeth, bad breath - all these phenomena can appear against the background of various dental diseases and, based on the nature of the disease, the specialist selects the optimal method of dental treatment.
Whatever method of dental treatment is chosen, its main task will be to preserve all the functions and aesthetics of the tooth. Below we will look at a variety of dental treatment methods that are used in modern dentistry and will also talk about complications that can occur when errors in treatment procedures were made by the doctor.
Methods and timing of modern treatment of dental diseases
Dental treatment in modern dental clinics is a whole series of special measures to stop the development of the inflammatory process, restore all useful functions, as well as the aesthetics of the dental unit. Most often, patients turn to dentists for the treatment of dental caries, which occurs in people of all ages and in a variety of forms - from the spot stage to deep caries, when the destruction of a unit has reached almost to the root. If caries was not cured on time or its treatment was carried out in violation of the rules, complications such as pulpitis and periodontitis arise. Treatment of these dental diseases is more complex; it is carried out in stages and involves at least 2-3 visits to a specialist’s office. The timing of dental treatment always depends on the complexity of the clinical case. For example, treatment of caries in the spot stage takes place in one visit
dentist, implantation and prosthetics are divided into several stages and the treatment period is maximum - from several months to a year. Do you want dental treatment to always proceed quickly and with a minimum of discomfort? Then attend regular preventive examinations at the dentist, because it has long been known that the best dental treatment is prevention!
Oral plastic surgery
The need for oral surgery may arise for various reasons, such as orthodontic or speech therapy. But most often this is due to the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases.
About 20 percent of people have a shallow oral vestibule. This is the space limited by the lips and cheeks on the outside, and the gums and rows of teeth on the inside. For the vestibule of the oral cavity, the normal depth is 5-10 millimeters. If the depth does not reach 5 millimeters, the dentist diagnoses a shallow vestibule of the oral cavity. Because of this, a number of dental problems arise (gum recession, periodontitis, and others). In an infant, this can lead to impaired sucking function. If a pathology is detected, the patient is recommended to undergo plastic surgery of the vestibule of the oral cavity, or, as it is also called, vestibuloplasty.
Endodontic dental treatment: when and how is it carried out?
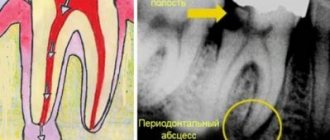
Endodontic dental treatment is used in practice if caries has destroyed the tooth and the inflammatory process has moved into the canals of the dental unit. When carrying out endodontic dental treatment, a specialist treats the canals: cleans the cavities from damaged tissue, rinses them with an antiseptic solution, and applies medicine. Typically, after these procedures, a temporary filling is placed on the tooth, and the patient is sent home to return to the dentist's office in a few days.
At the second visit, an x-ray of the diseased tooth is taken to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. If the inflammation has been stopped, the canals are treated with an antiseptic again, and then their space is filled with gutta-percha. The tooth treatment ends with the final restoration of the crown using a composite filling material.
Endodontic treatment must be carried out with high quality and using specialized modern tools: files that allow the canals to be expanded as needed, a microscope that allows the doctor to see the condition of the tissues and canals, an apex locator that shows the length of the tooth canals.
If root canal treatment is carried out incorrectly, errors are made in its technology - there are risks of serious complications that can lead to the loss of a dental unit.
Plastic surgery of tongue and lip frenulum
In addition to vestibuloplasty, plastic surgery of the frenulum of the tongue and lips is often performed in dentistry.
The pathological condition of the frenulum can lead to many problems and inconveniences, such as:
- problems with diction,
- interference with normal food intake,
- gap between the front incisors,
- gum recession,
- periodontitis,
- malocclusion.
- In infants there is a dysfunction of sucking.
During plastic surgery of the frenulum of the tongue, the latter is dissected, then the lateral edges of the mucous membrane are compared using transverse sutures to capture deep-lying tissues. Labial frenuloplasty is performed by making an incision around the frenulum, then the fibers are separated and displaced from the bone, after which sutures are placed
Is it possible to treat teeth without a drill?
Sociological surveys show: almost 80% of people are afraid to visit the dentist due to fear of having their teeth drilled. Not only children, but also adults are afraid of drills. If you are also afraid of the need to drill a tooth for its quality treatment, then it will be useful for you to know the following fact: if you seek dental care in a timely manner during dental treatment, you can completely do without a drill!
Fluoridation
If the examination reveals caries in the stain stage, then dental treatment may involve procedures aimed at remineralizing and strengthening the enamel. Tooth surfaces are covered with special gels containing high concentrations of fluoride and calcium and, of course, this treatment is absolutely painless!
Laser treatment
Another option for dental treatment without drilling is the use of laser radiation with a wavelength of a certain length. The laser beam heats and destroys tissues destroyed by caries, and after treatment it will be enough to rinse the area of manipulation with water. The innovative method of dental treatment has many advantages, including: high efficiency of the method; low risks of complications; additional antibacterial effect. The disadvantages include the fairly high price of laser dental treatment and a wide range of contraindications. It is also worth knowing that dental treatment with laser radiation will be painless only when caries has destroyed only the tooth enamel. If the destruction has reached the deep layers of dentin and pulp, before laser dental treatment, the patient is given anesthesia to eliminate unpleasant painful sensations.
Infiltration treatment method
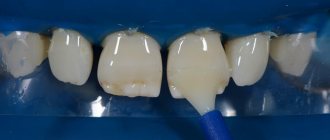
Dental treatment is carried out using Icon technology, which consists of treating carious cavities with a special polymer composition. The active substances in the composition uncouple and dissolve damaged tissue, the remains of which the doctor removes with an alcohol solution. Then the treated areas of the tooth are dried and treated with a polymer resin that fills micropores in the natural enamel coating of the tooth. The tooth treatment using Icon technology ends with the use of a polymerization lamp, which dries the applied composition. The advantages of this dental technique include: maintaining the integrity of the natural enamel coating for a long time, increasing the strength of tooth enamel; the ability to choose a polymer shade that exactly matches the tone of natural enamel; speed of dental treatment - the entire treatment process takes no more than half an hour; The treatment is painless and does not involve the risk of overheating of the tooth tissue.
Icon dental treatment technology is optimal for treating carious stains in the interdental spaces and is suitable for eliminating caries in children.
Ozone therapy
Another method of treating teeth without drilling is ozone therapy, which involves exposing carious cavities to ozone. The impact is carried out by a special device that converts oxygen into ozone. This gas destroys pathogenic microflora and carious bacteria. After treatment with ozone, the tooth is covered with a special gel and the treatment process ends.
Ozone therapy can be used not only to treat teeth damaged by caries. It is indicated for inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, inflammatory processes in the dental canals.
Features of the dental treatment process under a crown
Installing a crown does not guarantee 100% protection of the tooth from caries and other dental diseases. Some time after the installation of a prosthetic structure in the patient’s oral cavity, phenomena such as subsidence of the gums and exposure of the cervical part of the tooth may be observed. These phenomena create favorable conditions for the development of caries and the risks of developing carious lesions are especially high due to insufficient oral hygiene. Under the crown, not only caries can develop, but also pulpitis and periodontitis, and therefore if you have pain in a tooth on which a crown has been placed, you need to seek professional treatment urgently!
If the diagnosis reveals caries or an inflammatory process under the crown, tooth treatment will involve removing the orthopedic structure and carrying out all the necessary manipulations to stop the inflammation and save the tooth.
Note that caries under the crown often appears because errors were made during the manufacture of the prosthetic structure or during its installation. If the crown is adjacent to natural tissues with insufficient density, pathogenic microflora can easily penetrate under it. For this reason, it is important to choose a good dental clinic for prosthetics, which employs experienced and competent specialists.
Medical Internet conferences
Scientific supervisors: associate, Ph.D. Petrova A.P., ass. Venatovskaya N.V.
Relevance. All over the world, there is an annual increase in the number of people suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and hepatobiliary system [5]. The overall morbidity rate of the population of the Russian Federation in the class “Diseases of the digestive organs” increased from 99 per 1000 population in 1996 to 112 per 1000 population in 2010 [2,8]. At the same time, early diagnosis of these diseases is currently a priority medical and social task due to the fact that in the absence of timely treatment they often develop into more severe, chronic, incurable forms. Therefore, assessment of the general patterns of structural and functional reorganization of various parts of the digestive tract when pathological processes occur in them has great diagnostic and prognostic significance [1,6,13]. As you know, the oral cavity is a kind of mirror of the body. Changes in it reflect the patterns of the pathogenesis of systemic pathology and are caused by the etiological, pathogenetic, morphological and functional integration of all systems of the human body [14]. The results of numerous clinical studies in this area indicate that when the function of the gastrointestinal tract organs is impaired, damage to the oral mucosa is simultaneously observed, and there is also a risk of an unfavorable course of the existing chronic inflammatory process [4,10,18]. This relationship is explained by their anatomical and physiological proximity, common innervation and humoral regulation [11]. Therefore, knowledge of the characteristic pattern of manifestations of certain general somatic diseases in the oral cavity, in particular gastrointestinal diseases, and the ability to diagnose pathology is the most important professional quality of a dentist. This would greatly help in identifying systemic diseases at their earliest stages so that the patient can be referred immediately to an appropriate specialist.
Purpose: to find out whether there is a correlation between diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and their indirect manifestations on the oral mucosa.
Tasks:
1) study the anatomical and physiological structure of the oral mucosa, as well as identify similarities with the structure of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract;
2) determine which symptoms are more often observed in the oral cavity in patients with concomitant pathology of the digestive organs;
3) establish the relationship between changes in the oral cavity and specific gastrointestinal diseases;
4) identify the complex of morpho-functional disorders in the oral cavity characteristic of gastritis and gastric ulcer.
Materials and methods. An examination of the oral cavity of patients from the gastroenterology department who were undergoing treatment at the Road Clinical Hospital in the city of Saratov was carried out. The study involved a group of people with gastritis and gastric ulcer, consisting of 19 people aged from 43 to 66 years, of which 15 were men and 4 women. A literary review of periodicals, scientific papers, and library sources in Russian and English on the topic of diagnosing pathology of the gastrointestinal tract in the oral cavity was also carried out, and some clinical studies in this area were analyzed.
Results and discussion. The oral mucosa is a complexly organized system that has its own distinctive features. It consists of the following components:
1) multilayered squamous epithelium, in which several layers are distinguished: basal, spinous and, in the area of the hard palate, gums, cheeks along the line of closure of the teeth, granular and horny;
2) own layer;
3) submucosa (with the exception of the mucous membrane of the tongue, gums and hard palate).
The blood supply to the oral cavity is carried out mainly by the maxillary artery, which gives off the following branches: the inferior alveolar artery, the buccal artery, the posterior superior alveolar artery, the infraorbital, and the descending palatine. The veins accompany the arteries and flow into the internal jugular vein system. The outflow of lymph is carried out into the regional lymph nodes: mental and submandibular. Innervation of the oral cavity is provided by the II and III branches of the trigeminal nerve, as well as by the branches of the nasopalatine, buccal, lingual, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.
SOPR functions:
1) secretory;
2) buffer;
3) barrier (the ability of the epithelium of the oral mucosa to keratinize, immune protection of the mucous membrane);
4) reflexogenic;
5) selective permeability;
6) regenerative.
Most often, changes in the mucous membranes are nothing more than a reflection of the internal problems of the whole organism. The oral mucosa shows early signs of many infectious and non-infectious, acute and chronic, specific and nonspecific processes [12]. Quite pronounced changes in the oral cavity are observed, in particular, in pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. In patients with diseases of the oral mucosa, diseases of the digestive organs are diagnosed in 75% of cases [15]. It is worth noting that the relationships studied in this article are due to the morphofunctional similarity between the oral mucosa and the gastrointestinal tract.
It is known that the receptor field of the mucous membrane reflexively affects the underlying parts of the digestive tract. However, there is also an inverse relationship. The oral mucosa is an effector field of the reverse influence of “pathological” reflexes from a number of internal organs [9]. At the same time, symptoms in the oral cavity allow for early diagnosis of this pathology even before the development of severe manifest forms. Studies of the initial part of the digestive tract with concomitant gastrointestinal pathology conducted by clinicians have shown that changes in the oral mucosa, as well as their severity, are closely related to the form, severity and duration of the underlying disease [7,16]. Moreover, certain pathological changes can be observed in almost all structures of the oral cavity. Patients with concomitant pathology of the gastrointestinal tract may complain of pain, itching and burning of the tongue, dysgeusia in the form of a sour or bitter taste in the mouth. Objective symptoms include: 1) coating on the tongue; 2) violation of the relief of the tongue; 3) swelling of the mucous membranes and tongue; 4) paresthesia; 5) ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa; 6) change in color of the mucous membrane.
Tongue disorders rank first in terms of occurrence in gastrointestinal pathologies. Often these changes are noticed by patients themselves. The appearance of the tongue has significant diagnostic value, since it may indicate a hidden gastrointestinal pathology. Most often, plaque is found on the tongue, the severity of which depends on various reasons. The state of the language matters here. Normally, as well as with hypertrophy of the papillae of the tongue, the plaque is dense and quite pronounced. With papillary atrophy, on the contrary, it is absent or insignificant. The reason for the formation of plaque is a disruption of the physiological process of keratinization and desquamation of the epithelium of the oral mucosa, which is observed in pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, the severity of self-cleaning processes, the composition of the microbial flora and the hygienic status of the oral cavity undoubtedly also play a role.
Plaque on the tongue is usually found with gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, enterocolitis, and gastric neoplasms. Moreover, during an exacerbation, it is pronounced and covers the entire back of the tongue or mainly its posterior sections. The color of the plaque is grayish-white, but under the influence of pigment-forming microorganisms, food chromogens, and medications, it can take on a different color. However, during the period of remission or during the treatment of the underlying disease, it is possible to completely free the tongue from plaque. Subjective sensations are often not observed, but with an abundant, dense coating, patients note a feeling of awkwardness and dullness of taste perception. It should be noted that plaque can also be detected in other diseases, in particular infectious ones, as well as in healthy people in the morning.
The second most common symptom of diseases of the digestive system is a disorder in the papillary apparatus of the tongue. In persons with hyperacid gastritis, hyperplastic glossitis is observed, in which the papillae are well defined, the tongue is covered with a dense coating and is somewhat swollen. In patients with gastric and duodenal ulcers, only the fungiform papillae hypertrophy, which rise above the surface in the form of bright red dotted formations. Hypoplastic glossitis is manifested by atrophic changes in the papillae, absence of plaque, and the size of the tongue is slightly smaller than average. With pronounced atrophy of the papillae, the tongue takes on a “varnished” appearance, which is often observed with gastritis, peptic ulcers and gastroenteritis. In this case, atrophy of the papillae of the tongue causes a number of subjective sensations in the patient: burning, tingling, feeling of awkwardness, pain when eating. Along with trophic disorders, impaired absorption of vitamins, their breakdown in the intestines, as well as reduced synthesis of vitamins B1, B2 and PP play a significant role in the pathogenesis of the described changes.
Also, with gastrointestinal diseases, patients experience swelling of the tongue and mucous membranes. This condition often does not cause suffering to the patient and is diagnosed by a doctor accidentally during a routine examination of the oral cavity. However, with severe swelling, patients note a feeling of awkwardness, an increase in the size of the tongue, and biting of the cheeks and tongue. Upon examination, tooth marks are revealed on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue. In patients with concomitant pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, edema is confirmed by the McClure-Aldrich blister test, which also helps to identify sick individuals without visible edematous changes in the mucous membranes and tongue and makes it possible to establish the presence of hidden edema, which can serve as an important diagnostic sign in early stages of the disease. Swelling of the tongue and mucous membranes is a characteristic symptom of chronic intestinal pathology: colitis, enterocolitis and is detected in more than 80% of cases. This condition is determined by a violation of the absorption and barrier functions of the intestinal epithelium. In addition, water imbalance also plays a certain role.
Paresthesia of the tongue often occurs in patients with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes a burning sensation and tingling sensation can be observed without visual changes in the tongue. The taste buds of the tongue perform a sensory function and are the effector, end link of the gastrolingual reflex. It is known that normally their number is in correlation with the functional state of the digestive tract. The maximum activity of the receptors is observed on an empty stomach, and after eating, their demobilization is observed. This occurs as a result of centrifugal impulses from the interoreceptors of the stomach to the exteroreceptor apparatus of the tongue and is realized as a normal reaction in healthy people. Some disturbances in taste sensitivity are observed in almost all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, with peptic ulcers, several types of functional mobility impairment are noted: there is no demobilization of taste buds after eating; there is a perverse reaction - an increase in the level of mobilization of taste buds after eating; a reaction similar to that observed in practically healthy people [3]. The described disorders are a consequence of changes in the normal reflex relationships of the receptor fields of the tongue and stomach as a result of disorders of the secretory and motor functions of the stomach, which is characteristic of peptic ulcer disease. Decreased taste sensitivity to bitter and sweet is often characteristic of stomach cancer.
Ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa are nothing more than the result of trophic disorders that occur as a result of pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. This position is confirmed by numerous clinical observations indicating a combination of aphthous stomatitis with diseases of the large intestine, as well as experimental studies on its modeling. With experimental gastritis and enterocolitis, predominantly desquamative and then erosive-ulcerative glossitis develops. And irritation of the large intestine provokes the development of aphthae-like changes in the mucous membranes.
A change in the color of the mucous membrane also indicates gastrointestinal diseases. It has been established that the color of the mucous membrane depends to a certain extent on the type, duration and severity of the underlying disease. Catarrhal stomatitis, manifested in the form of areas of hyperemia or cyanosis, is observed with gastric ulcers, colitis, enterocolitis. In case of complications of gastric ulcer by bleeding, pallor of the mucous membranes is noted.
In our study, we examined a group of patients from the gastroenterology department of the Road Clinical Hospital in the city of Saratov, consisting of 19 male and female people aged from 43 to 66 years with gastritis (6 patients) and gastric ulcers (13 patients). The following results were obtained: patients with gastric ulcer (in the acute phase) complain of burning - 69%, tingling of the tongue - 54%, impaired taste perception - 69%. Objectively: hyperemia of the mucous membranes - 85%, the tongue is covered with a whitish-gray coating - 100%, hypertrophic changes in the fungiform papillae of the tongue are noted - 92%, as well as changes like rhombic glossitis - 15%. According to literary sources, all identified changes in the organs of the oral cavity are in one way or another characteristic of gastric ulcer in the acute phase. Patients with hyperacid gastritis complain of distortion of taste sensations - 33%, the presence of a metallic taste in the mouth - 16%. Objectively: swollen, hyperemic mucosa of the vestibule and the oral cavity itself - 83%, there is a change in the relief of the tongue like a “varnished” type in some patients - 33% and like hyperplastic glossitis in others - 50%, a grayish coating on the back of the tongue - 83% ( Table 1). Note that all the identified changes in the oral cavity of patients with gastritis, with the exception of rhombic glossitis, are also characteristic of this pathology and were described above based on data from a literature review. However, in our study, the sample consists of only 19 people, so it is not possible to transfer the results obtained to the general population and talk about a direct relationship between the identified changes in the oral cavity and a specific pathology due to the low representativeness of the sample. Moreover, at the moment, in the available literature sources, no reliable information has been found on a strict correlation between certain changes in the morpho-functional state of the oral cavity and specific diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. However, in the literature there is a lot of information that there are manifestations in the oral cavity that are more or less characteristic of certain gastrointestinal diseases, which is confirmed by the results of our study.
It should also be remembered that changes in the mucous membranes often reflect the essence not of “pure” pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, but of other disorders of the body that have developed secondarily [17]. Therefore, determining the primary etiological factor that caused the development of certain changes in the oral cavity is one of the key points in the professional activity of a dentist in relation to the diagnosis of the disease.
The need for anesthesia before dental treatment
Anesthesia during dental treatment is not always necessary, but only in cases where the destruction has affected the deep layers of dentin. There are nerve endings in the deep layers of tooth tissue, and therefore any manipulation in this area can cause significant pain to the patient. To eliminate discomfort during dental treatment under such circumstances, anesthesia is administered before the start of the treatment process, selected individually. The anesthetic is administered by injection, but there is no need to be afraid of an injection: modern syringes have ultra-thin needles that allow you to administer the medicine quickly and painlessly.
For patients with a high pain threshold, anesthesia can be given not only before dental treatment, but also before such activities as professional cleaning of dental surfaces and whitening. Typically, topical anesthesia is chosen. General anesthesia is used in dental treatment
extremely rarely - mainly before complex and lengthy operations. It is worth knowing that general anesthesia has a number of contraindications and therefore, before choosing this anesthesia technique, the patient must undergo a series of tests.
Specifics of dental treatment in the smile area
The front teeth are included in the so-called smile zone and therefore, when treating them, the aesthetics of the final result of the treatment process is fundamental. To restore an anterior tooth, the dentist must have experience in selecting shades of light-curing composites, recreating the natural shape of the tooth, and all the natural irregularities of its surface.
If the tooth located in the smile area is healthy, but there are aesthetic defects, the use of veneers may be a treatment option. Veneers are miniature plates-onlays that are glued to the surface of the teeth and ideally mask defects such as curvature of teeth, unsightly shape, darkening of the enamel, and interdental spaces. If a tooth is destroyed by more than fifty percent, restoration with a crown is indicated. A pin that is used by some specialists for severe tooth destruction
Installation is not recommended. A large filling will not withstand the load that is inevitable during chewing processes and will fall out or break off, along with part of the tooth. If the root part is affected when the filling is broken, the tooth will have to be removed. In the area of the front teeth, prosthetics made from durable and aesthetic materials are recommended: ceramics, porcelain, zirconium.
Types of pathologies of the oral mucosa
- Mechanical damage that can occur when the mucous membrane is exposed to poorly installed fillings, dentures and other solid objects, including solid food. The damage appears as scratches and may bleed.
- Thermal injuries occur when eating very hot food or drinks. A whitish spot appears at the burn site, from which the skin begins to peel off.
- Chemical injuries occur when eating hot, spicy foods, or when taking certain medications.
Symptoms that may indicate the need for dental treatment
If you are worried about tooth pain, even if it is mild and appears from time to time, this is a clear reason to see a doctor and undergo professional dental treatment. The sooner you contact a specialist, the less likely it is that the treatment will be complex, protracted and painful. The following symptoms may also indicate the need for urgent dental treatment: The appearance of dental hypersensitivity; sharp, unpleasant odor from the mouth (if hygienic procedures for caring for the oral cavity are carried out on an ongoing basis); bleeding, swelling of gum tissue; problems with opening/closing the mouth; the appearance of spots, irregularities on the dental surfaces, and changes in the shade of tooth enamel. Remember that a timely visit to the dentist for tooth treatment is the only way to save the tooth. And your teeth are better than any, the most modern dentures!
The main manifestations of diseases of the oral mucosa
There is a common name for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa - stomatitis. When the pathological process is localized on the tongue, they talk about glossitis, on the gums - about gingivitis, on the lips - about cheilitis. A characteristic manifestation of stomatitis is the appearance on the oral mucosa of foci of redness, blisters, erosions (afts) or ulcers covered with plaque. These lesions are most often detected on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard palate, and tip of the tongue. Often there is pain at the location of erosions and ulcers, enlargement of nearby lymph nodes, and sometimes an increase in body temperature. The average duration of the disease is 7-14 days. Stomatitis can recur with decreased immunity, poor diet, hypovitaminosis, infectious diseases, and exacerbations are more common in spring and autumn.
How is dental treatment performed in dentistry: an overview of the main stages
Unfortunately, most patients ignore dentists' advice on the importance of regular visits to the doctor and preventive examinations and therefore see a specialist with advanced caries, acute pain, and the presence of many different oral diseases. Therefore, dental treatment will always begin with diagnosis, and will also include the following stages:
Examination and treatment plan
An appointment with a doctor begins with an examination of the oral cavity, as well as prescribing a number of diagnostic tests for the patient. This will allow you to identify all existing dental and oral health problems and create a detailed treatment plan.
Professional sanitation of the oral cavity
It is recommended to begin dental treatment only after high-quality sanitation of the oral cavity, during which all types of plaque are removed from the dental surfaces.
Treatment
If a patient consults a doctor with medium or deep caries, dental treatment cannot be done without drilling. Using a drill, a specialist will remove all tissue damaged by the disease and create a cavity for installing a filling. Pulpitis and periodontitis imply a more complex treatment regimen, which includes canal treatment, antibiotic therapy, and some types of surgical interventions. The treatment method is selected based on the characteristics of the clinical case. The treatment of the tooth ends with the final restoration of its crown using photopolymer filling materials.
Percussion (tapping)
Percussion with tweezers or a probe handle along the crown of the tooth allows you to determine the location of the area affected by inflammation. Any examination begins with healthy teeth; for this purpose, the edges responsible for cutting and chewing reflexes are tapped on the top and sides of the crown.
The process of tapping teeth (percussion)
A good idea of where the source of inflammation is located is given by the relationship between the nature of the pain and the direction of the blow: periodontitis is detected with a horizontal blow, damage to the root nerve can be determined with a vertical blow. Thanks to this technique, the doctor has the opportunity to identify the place where there is pain and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Are complications possible after dental treatment, what could they be?
For some time after dental treatment, the patient may be bothered by a slight aching pain, which usually occurs during the process of chewing food. In this case, there is no need to sound the alarm, such pain is not a complication: it is observed after treatment of deep caries due to the pressure of the filling on the pulp and will go away in a few days without taking any medications, on its own.
But if the tooth hurts severely and the discomfort does not disappear after taking painkillers, you should go to the doctor urgently! This symptom indicates the preservation and continuation of the active development of the inflammatory process in the tooth. Usually the cause of such a complication is poor quality of primary dental treatment. At Uni Dent dentistry in St. Petersburg you can undergo dental treatment of any complexity.
Our clinic offers patients modern dental treatment methods, innovative equipment, sensitive and experienced staff, and doctors who regularly improve their qualifications abroad. Trust the health of your teeth to professionals - come to Uni Dent dentistry in St. Petersburg!
Prevention of oral diseases
- visit the dental office at least once a year;
- organize a special diet, in which lean meats, fish, fresh vegetables and fruits should predominate;
- rinse your mouth with special compositions after each meal;
- Strengthen your immune system and avoid colds.
To avoid any problems with teeth and oral cavity, you need to regularly visit the dentist and carry out preventive maintenance.