Teeth grinding, which is medically called “bruxism,” is a fairly common phenomenon. Many parents observe it in their children. Adults can also grind their teeth, but bruxism is much more common among children.
In most cases, children grind their teeth during night sleep, but you should know that experts distinguish not only the nighttime, but also the daytime form of this disorder. The latter is observed very rarely and indicates more complex problems that require a comprehensive examination of the entire body. But there is no need to panic. Doctors do not consider bruxism a disease, but attribute it to such phenomena as sleepwalking, snoring and apnea.
What can cause teeth grinding in a child? Let's figure it out.
Causes of bruxism in children
The presence of teeth grinding may indicate disorders in various organs and require the attention of specialists in various fields (from dentists, to neurologists, otolaryngologists, gastroenterologists and psychologists). Moreover, each of these areas of medicine names its own causes of the disorder:
- Psychology says that the root of the problem lies in nervous experiences, stressful or depressive states, and emotional overstrain.
All of these conditions can cause sleep disorders, which will provoke involuntary spasms of the masticatory muscles, accompanied by clicking and grinding of teeth.
- Neuralgia looks deeper and states that the presence of bruxism in children indicates disorders of the nervous system.
And this opinion cannot be discounted, since quite often teeth grinding is observed in combination with apnea (breath holding during sleep), tremor and even epilepsy. Involuntary tension in the masticatory muscles also occurs during inflammatory processes affecting the motor neurons of the trigeminal nerve. In these cases, bruxism signals the possible presence of some serious disorder in the activity of the nervous system.
- Dentistry explains the disorder by malocclusion and medical errors made during dental treatment or when installing braces or crowns.
Any of the above reasons can lead to tooth deformation and damage to the enamel, as a result of which the upper and lower rows of teeth begin to cling to each other, making unpleasant sounds.
- Gastroenterology names helminthic diseases as possible causes.
Scientific studies do not prove the fact that the unpleasant sounds made by teeth during sleep are associated with the presence of any protozoa in the body. But at the same time, medicine confirms that helminth parasitism causes a deficiency of B vitamins, which can lead to disorders of the nervous system, accompanied by teeth grinding. If you suspect a child has bruxism, it would not hurt to take bacteriological tests, at least to make sure that it is in no way connected with gastroenterology.
You should know that the causes of this specific disorder may be different in the daytime and nighttime forms. We propose to consider each of them in more detail.
Possible complications
With prolonged bruxism, the following pathologies may develop:
- disease and dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
- restriction of jaw movement;
- constant pain in the temples, shoulders, neck;
- hypertrophy of the masticatory muscles, which visually changes facial features;
- gingivitis;
- persistent sleep disturbances;
- oral fibroids;
- cervical arthrosis;
- damage to mucous membranes under dentures;
- scalloped tongue;
- lichen planus.
Daytime and nighttime bruxism in children - the main differences
Grinding of teeth during the daytime may indicate that the child is experiencing emotional stress. Experts tend to consider this form a bad habit, not a pathology. Accordingly, constant monitoring of one’s actions helps to get rid of it. In order to teach this to a child, it is better to contact a professional psychologist - he will suggest special methods and exercises.
Interestingly, many children begin to grind their teeth during the day at a very early age, as soon as they have the opportunity to squeeze the teeth that have erupted in the upper and lower rows. These actions should not be mistaken for manifestations of bruxism. The baby is simply getting used to having teeth in his mouth. Teeth grinding and grinding at the age of about a year only indicates the child’s interest in his body and its capabilities.
At night, bruxism is an involuntary condition characterized by the following symptoms:
- periodic repetition of attacks of teeth grinding, grinding or clicking, lasting for 10-15 seconds;
- increased breathing and heart rate, increased blood pressure;
- headache, toothache or painful chewing sensations that occur in the morning;
- lethargy, dizziness, tinnitus, loss of strength during the daytime;
- bleeding and inflammation of the gums, cracks in tooth enamel, loosening or destruction of teeth (in some cases, their premature loss), bite defects.
In cases where bruxism in a child is accompanied by bleeding gums, we can recommend the use of ASEPTA gum gel with propolis. It helps relieve pain, has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, and strengthens soft tissues.
What happens if the disease is not treated?
As already mentioned, isolated cases of bruxism do not pose a health hazard. But regular grinding can cause irreparable harm. Consequences:
- abrasion of tooth enamel;
- increased tooth sensitivity;
- chipping, crumbling, destruction and, as a result, loss of dental elements;
- development of caries;
- injury to the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks and lips;
- damage to the temporomandibular joint;
- gastrointestinal diseases (due to impaired chewing of food);
- the appearance of chronic fatigue syndrome;
- constant headache;
- dizziness;
- facial asymmetry.
Why is night bruxism dangerous?
Should parents worry and take some measures if their baby grinds his teeth in his sleep? Yes, if:
- Child's age over 7 years
Most often, teeth grinding during sleep occurs in young children, and by the age of seven it usually goes away without a trace. If the child has already gone to school, but the problem remains, it’s time to take measures to eliminate it.
- A large number of repetitions of this condition are recorded or attacks last more than 15 seconds
In these cases, unpleasant sounds made by teeth during sleep may indicate serious disorders in the activity of the nervous system. The sooner the diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, the greater the chance of avoiding the disease becoming chronic.
- There are signs of tooth decay or gum inflammation
If you do not take action in a timely manner, you may face much more serious problems: gum disease, premature loss of baby teeth, and malocclusion.
Bruxism becomes especially dangerous when baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. It can cause diseases that will lead to the loss of permanent teeth at an early age.
Doctors do not consider bruxism a health-threatening disorder, especially if we are talking specifically about nighttime teeth grinding. It usually goes away with age without any treatment.
If you want to help your baby cope with the problem before he outgrows it, then first consult a dentist.
Diagnosis and treatment of bruxism in children
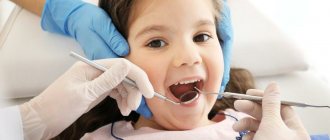
The fact that a child suffers from teeth grinding is noticed by the parents themselves or close relatives. But to confirm the diagnosis, a special polysomnographic study is required. It allows you to record the presence of involuntary contractions of the masticatory muscles and is important for excluding epilepsy, as one of the possible hidden causes of the disorder.
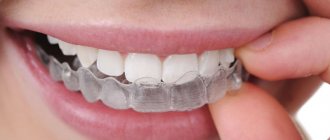
A dentist can also determine the presence of burxism. To do this, an examination of the oral cavity is carried out, and if necessary, a bruxchecker is used - a special mouth guard, selected individually. It is inserted into the mouth while you sleep at night, after which it is given to the dentist for examination. Based on the nature of the damage to the mouth guard, it determines the places where the teeth are subjected to the greatest load during sleep.
Since it is extremely difficult to accurately determine the cause of the disorder, an integrated approach to its treatment is most effective.
Let's talk in more detail about the methods of treating bruxism in children, used by specialists in various branches of medicine:
- psychotherapeutic – meditation, auto-training, relaxation training, reducing stress levels, mastering self-control techniques, etc.;
- dental – consultations with specialized specialists (periodontist, orthodontist), correction of bite defects and correct selection of braces, timely replacement of deformed fillings;
- medications - taking calcium, magnesium, B vitamins, sedatives and hypnotics, Botox injections and other medications that help reduce the activity of the masticatory muscles;
- physiotherapeutic: relaxing massage, facial gymnastics, compresses.
For those who are trying to decide for themselves the question of how to treat bruxism in children, the following measures can also be recommended:
- wearing protective overlays on the teeth (mouthguards), which prevent the contact of the upper and lower teeth in the event of involuntary closure of the jaws during sleep;
- additional load on the jaws before bedtime: invite the child to chew an apple or carrot an hour before bedtime; sometimes chewing gum is also used for this;
- warm compresses on the cheekbones for 10-15 minutes twice a day to help relieve pain;
- self-control - teach your child to ensure that when the mouth is closed, the upper and lower teeth do not touch.
If you observe frequent and prolonged bouts of bruxism in your child, be sure to consult a doctor. Among the serious consequences of this disorder, doctors identify damage and premature loss of teeth, hearing impairment, and the appearance of asymmetry in the face. Don't wait for them to appear.
Therapy methods
Treatment of a disease is primarily aimed at eliminating the causes that caused it. For example, if bruxism is caused by neurological problems, then the neurologist prescribes appropriate medications. The dentist takes symptomatic measures. These include wearing a special plastic mouth guard placed on the lower jaw at night. It is designed to prevent teeth from rubbing against each other. Treatment of caries and periodontal disease (if any) is also carried out. If occlusal defects are present, orthodontic therapy is prescribed.
How to avoid the disorder - prevention of bruxism in children
Remember that most often, involuntary closing of the jaws during sleep is observed against the background of stressful situations. Try to ensure that the baby grows up in a comfortable psychological and emotional environment.
In cases where stress could not be avoided (this could be entering kindergarten, forced separation from one of the parents, the death of a grandmother or grandfather), try to mitigate its consequences as much as possible. Be especially attentive and tolerant of your child during such periods.
To prevent nighttime bruxism, make sure your child is calm before bedtime. Instead of watching cartoons or a computer game, invite him to read, or do puzzles or mosaics. Stop active games at least an hour before bedtime. Try to spend at least half an hour before bed with your child, this will allow him to relax and fall asleep peacefully. Quiet walks in the fresh air are also very useful in the evening. They not only help create a favorable emotional background, but also contribute to the health of the body as a whole.
Monitor your child's nutrition. Try to keep his food healthy and varied. Be sure to keep your jaws busy by letting your baby chew on hard vegetables and fruits. This kind of “charging” is especially useful an hour before going to bed, just don’t forget that after it the child should brush his teeth. Select the brush and toothpaste according to the baby’s age. If the child is still very young, ASEPTA Baby gel toothpaste, designed specifically for delicate baby teeth, is perfect. And for those who are already 4 years old, we can recommend ASEPTA Kids toothpaste. It helps to carefully care for the oral cavity during the period of growth of baby teeth and their replacement with permanent ones, ensuring oral health.
There is no need to panic if your child begins to grind his teeth in his sleep, but carefully assess the degree of the disorder and the possible threat to the baby’s health, visiting specialists if necessary. Timely medical consultation will help avoid worsening the problem and the development of more serious ailments.