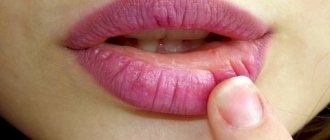
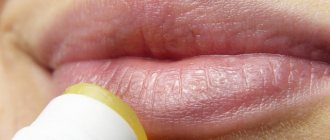
Cheilitis is an isolated inflammatory process in the area of the mucous membrane, skin and red border of the lips. Outwardly it looks like swelling with redness and peeling of tissue. It can be an independent disease or a symptomatic manifestation of other pathologies. Sooner or later, almost every person encounters it, but at a young age the disease is noticeably milder, recurs less often and has no complications. In older people, due to a weakened immune system, periodic relapses of cheilitis can cause malignant tissue degeneration.
Causes
Cheilitis is a polymorphic and multifactorial disease that can be triggered by infections, physical and chemical environmental factors, as well as internal characteristics of the body. Among them:
- constant exposure to the open air - inflammation and peeling of the lips occurs when chapped by hot or cold air, excessive insolation;
- the presence of chronic diseases with skin manifestations of symptoms - various types of dermatitis, psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, lichen planus, syphilis, etc.;
- allergic reactions of the body - mainly with food allergies;
- tissue irritation from regular exposure to chemicals, including medications (for example, nasal drops);
- various neurological disorders, severe stressful situations, depression, constant anxiety;
- endocrine abnormalities - primarily hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus.
Main causes of the problem
If your lips are peeling, it is important to find out the reasons for this condition. This will affect the further outcome of treatment. The key reasons for peeling skin on the mucous membrane of the upper or lower lip in children and adults are:
- Avitaminosis. This reason most often affects the peeling of the mucous membrane in winter and spring.
- Development of an allergic reaction.
- Infectious processes in the oral cavity.
- Unfavorable climatic conditions. If the mucous membrane in the oral cavity peels off, the cause of this problem may lie in the effects of wind and cold air on the sensitive epidermis in the lip area. This factor also includes increased water hardness, which negatively affects the condition of the mucous membrane in children and adults.
- Diseases of internal organs. Such ailments include: diabetes mellitus, pathological processes in the oral cavity, herpes.
- Bad habits - smoking, constant licking of lips, excessive coffee consumption.
- Dehydration of the body. Sometimes the mucous membrane may suffer from a lack of fluid in the body.
Before carrying out any treatment, it is important to find out why the problem appeared, and then improve the appearance of the lips with the help of certain measures.
Types of cheilitis
Manifestations of cheilitis may vary depending on the type and cause of the disease. There are:
- Exfoliative cheilitis - manifested by peeling of the red border of the lips, with rare areas of burning and dryness of the lips themselves.
- Exudative cheilitis - symptoms of the disease are supplemented by swelling and severe pain. The skin in inflamed areas may become covered with baked crusts, which greatly complicate the patient’s life.
- The glandular form affects the minor salivary glands. Their congenital or acquired proliferation is observed, followed by infection with bacteria. In this case, the source of infection can be caries, periodontitis or banal plaque. Outwardly it manifests itself as the formation of cracks on the surface of the lips, which begin to become wet over time.
- The allergic form occurs under the influence of household, cosmetic or food irritants (often this is lipstick). There are characteristic manifestations of allergic cheilitis in musicians who play wind instruments and in those who like to chew pencils. This type of inflammation is characterized by severe swelling, often with the formation of blisters, as well as itching, severe redness and burning.
- Meteorological cheilitis develops under the influence of weather conditions (wind, sun) and is manifested by burning, itching with small weeping blisters, in place of which erosions and ulcers form over time.
- The atopic form manifests itself as a symptom of dermatitis or neurodermatitis. Manifests itself in the form of redness and ulcers in the corners of the lips.
- The hypovitaminosis type of the disease is formed in response to a severe lack of vitamins, mainly vitamins A, C, B2. A characteristic burning sensation affects the surface of the lips, mouth and tongue. The mucous tissues take on a swollen appearance, cracks on the lips peel and bleed.
- Macrocheilitis is a response to damage to adjacent nerves (facial nerve neuritis), while itching and swelling from the tongue can spread to other parts of the face.
Attention! With a long course, there is a high probability of inflammation degenerating into a malignant neoplasm. This is especially typical for the meteorological form, which, in the absence of proper treatment, is often complicated by precancerous diseases.
Perioral dermatitis: symptoms
Symptoms of this disease are small round or oval-shaped papules located primarily around the mouth and on the chin. In some cases, papules, as mentioned above, can be found on the wings of the nose, on the bridge of the nose, on the temples and cheeks, as well as around the eyes. In some cases, papules may be filled with clear fluid.
The color of the papules, depending on the stage of the disease - exacerbation or remission - can vary from pale pink with a bluish tint to bright red. In some cases, papules are accompanied by hyperemia (general redness) of the skin, or may not cause a change in skin color. A distinctive feature of this type of dermatitis is considered to be a characteristic (light) strip of healthy skin around the mouth, which can be up to 4 mm wide. In turn, the localization of papules can be different - from single formations to groups of several pimples with clearly defined edges. In the case of a large number of papules located nearby, the skin becomes rough, which is felt well when touched.
Also, symptoms of perioral dermatitis, especially during an exacerbation of the disease, may include:
- dryness and tightness of the skin;
- skin itching;
- burning.
However, in a large number of cases, patients do not observe or experience any additional concern with dermatitis.
The sooner you start treating oral dermatitis on the face, the easier and faster it will be cured. That is why, when you detect the first signs of a possible disease, you must seek advice from a dermatologist.
.
Initial appointment
An initial appointment with a specialist involves a thorough examination of the patient, as well as drawing up a preliminary medical history (recording complaints, symptoms, concomitant diseases), which allows making preliminary assumptions regarding the cause of the disease. Additionally, tests and other diagnostic measures may be prescribed to clarify the clinical picture and understand how to treat oral dermatitis on the face.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this type of dermatitis is necessary as a way to differentiate from diseases with similar manifestations - eczema, herpes simplex, rosacea, etc.
Diagnostic measures in this case include:
- dermatoscopy: allows you to assess the general condition of the skin, the degree of development of pathology through a thorough examination of neoplasms;
- scrapings of skin material from the affected areas: bacterial culture of the test material makes it possible to determine the presence and type of infection (for example, candida);
- Allergy tests for staphylococcus and streptococcus: also allow you to determine the sensitivity of the skin to these agents and identify their presence.
Treatment plan
If the tests confirm the initially suspected diagnosis of oral dermatitis, the treatment prescribed by a specialist will be comprehensive (using ointments and other medications, as well as diet) aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the disease on the face.
The impact on perioral dermatitis on the face when developing a treatment regimen involves two successive stages leading to the gradual disappearance of the rash:
- At the first stage, it is necessary to completely abandon cosmetics (primarily decorative cosmetics) and ointments with corticosteroids. The latter are most often recommended to be discontinued gradually, reducing the dose and quantity, otherwise the so-called “withdrawal syndrome” may occur, which leads to an exacerbation of all existing symptoms - redness, swelling of the face, burning, itching. At this stage, it is most often assumed to use antihistamines (which relieve itching and burning), as well as herbal medications to relieve local inflammation. Additionally, reflexology can be used, which is an effect on active points on the skin of the face, either by simple pressure or with the help of special needles, to reduce the unpleasant manifestations of dermatitis.
- Second stage: after the acute phase of the disease passes, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, which are designed to destroy the infection and are selected taking into account the infectious agent. Antibiotics are taken only under the supervision of a doctor, who has the ability to adjust their composition and dose taking into account the patient’s body’s reaction to them. Particular care should be taken when treating oral dermatitis during pregnancy: in this case, taking antibiotics is contraindicated, and full treatment is possible only after the birth of the child (normalization of hormonal levels is also important). During pregnancy, only partial relief of the symptoms of the disease - burning, itching, etc. - is possible with the use of medications that are safe for the fetus. The same applies to therapeutic measures for dermatitis in children: treatment in this case can only be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, otherwise it can harm the child’s health.
In addition to the described methods of influence, the patient may be recommended:
- strengthen the immune system and take vitamins;
- establish intestinal microflora;
- adhere to a diet: a diet for this type of dermatitis involves avoiding fried, fatty and spicy foods, increasing the amount of vegetables and fruits consumed, and preferring boiled rather than fried foods. During the period of taking antibiotics, you must completely abstain from alcohol.
Treatment result
Most often, if you follow medical recommendations, it is possible to cure perioral dermatitis. In some cases, a course of treatment is assumed rather than a one-time treatment. In this case, taking antibiotics can usually last quite a long time (several weeks), and the overall course of treatment can last from several months to a couple of years.
Prevention
Because dermatitis is a multifactorial disease with an unidentified underlying cause, preventive measures include the following:
- careful use of cosmetics, primarily foundations, as well as ointments based on corticosteroids;
- compliance with personal hygiene measures;
- strengthening the immune system (taking vitamins, reducing psychophysical stress, etc.);
- proper nutrition with plenty of fruits and vegetables;
- monitoring the state of the digestive system;
- control of hormone levels, especially during pregnancy.
When the first signs of the disease appear, you should not wait long, you must seek advice from a specialist, undergo an appropriate examination and begin therapy, since in order to achieve the best results, treatment of oral dermatitis must begin as early as possible - in this case it can be cured in a relatively short time .
You can make an appointment with a specialist at the Energo clinic either by phone or by using a special form for registering patients on the clinic’s website.
Take care of your beauty and health!
Diagnosis of cheilitis
There are no specific laboratory tests to detect cheilitis. All diagnosis of the disease is carried out by visual examination. To determine the causes of inflammation, diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract may be prescribed for the presence of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Additionally, allergy tests are performed to exclude food allergies.
General laboratory tests allow you to check the condition of the body and determine the possible causes of cheilitis:
- low levels of vitamins due to hypovitaminosis can provoke exfoliative cheilitis;
- bacterial cultures of smears and biopsies are performed in patients with immune system disorders in the absence of results from the treatment;
- testing for markers of HIV infection, herpes, the presence of fungal or bacterial microflora, respectively, allows us to identify the viral, bacterial or fungal causative agent of cheilitis;
- a blood test for anemia, ESR are required to assess general health;
- examination of the function of the thyroid and pancreas for endocrine pathologies.
On a note! Cheilitis tends to be chronic with periodic relapses. Self-healing without medical supervision is almost impossible, so try to pay attention to such a “minor” problem and consult a specialist. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a general practitioner or attending dentist. In some cases, consultation with an allergist, infectious diseases specialist, dermatovenerologist or gastroenterologist may be required.
Treatment
Different forms of cheilitis differ in their approach to treatment. Collectively, the impact may include:
- correction of the psycho-emotional sphere - a neurologist prescribes sedatives, tranquilizers, a psychologist or psychotherapist conducts appropriate psychotherapy;
- physiotherapy - treatment with laser, ultrasound, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis is prescribed locally; they relieve irritation and accelerate tissue regeneration;
- drug symptomatic therapy - non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed; in case of severe inflammation - hormonal drugs;
- immunotherapy – strengthen the immune system by taking immunomodulators and immunostimulants;
- vitamin therapy - taking vitamins A, C, group B (mainly vitamin B2) is of great importance;
- surgical treatment – typical for glandular cheilitis with enlargement of the salivary glands; Both laser ablation with a surgical laser and direct removal of areas of the gland are used;
- antiallergic therapy with antihistamines.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe diet therapy with the exclusion of foods that provoke allergies or chemical irritation of tissues (spicy foods, saltiness and marinades). When staying outdoors for a long time, it is imperative to use special protective equipment.
Contour plastic surgery with Surgiderm 24XP
But not in all cases, dry lips can be dealt with only with the help of cosmetics or correction of nutrition and habits. If you have age-related dryness, and as a result, loss of fullness, volume and wrinkles on your lips, we advise you to use the possibilities of contouring.
Several injections of Surgiderm 24XP will help correct excessively thin or asymmetrical lips and fill them with moisture from the inside. The drug is based on high-viscosity hyaluronic acid, so the filler is perfect for creating volume.
Prevention
The main prevention of cheilitis is maintaining a healthy lifestyle and timely treatment of any infectious and allergic diseases. Basic list of measures:
- Eat right - a balanced menu should contain an abundance of fruits, vegetables, herbs, nuts, fish, and high-quality dairy products.
- Reduce the use of cosmetics - try to choose hypoallergenic formulations and constantly monitor the skin's reaction.
- Dose your exposure to open wind or direct sunlight.
- Protect your lip skin from physical and chemical damage.
- Take vitamin and mineral complexes periodically in courses (after consultation with your doctor).
- Give up bad habits.
- Seek medical advice promptly if you have characteristic symptoms.
Remember: your health is the greatest value, and constant monitoring of its condition is very important to maintain the body’s performance, especially in old age.
Lips peel from the inside
This problem is much less common than detachment of the upper part of the epidermis on the outside of the lips. However, it also brings severe discomfort and requires close attention. The skin in the mouth may peel due to:
- Allergic reactions (to new toothpaste, medications, food).
- Dental ailments (tartar, periodontal disease, gingivitis, caries, etc.).
- Previous burns (thermal or chemical).
- Serious diseases (autoimmune diseases, cancer, infections). With oncology, some area of disturbance may appear in the mouth, which bothers the person constantly (it does not hurt much, but does not heal). And infectious and autoimmune diseases usually manifest themselves as serious health problems, pain, large ulcers and other symptoms that are difficult to ignore.
The sudden appearance of skin peeling in the mouth is a reason to quickly consult a doctor. This is a rather atypical symptom that should not be ignored.