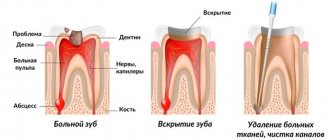
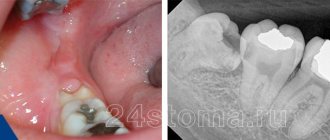
If something hurts somewhere, you should not endure the pain, but go to the doctor. If your neck hurts, radiates under your jaw, and in general the pain causes serious discomfort, then you can contact one of these specialists - a surgeon, neurologist
, dentist,
otolaryngologist
- or make an appointment with
a therapist
, who will refer you to the right doctor. An accurate diagnosis cannot be made based on the location and nature of the pain alone. Additional examinations may be required to help find the right solution and relieve you of painful discomfort. Pain in the neck and jaw occurs for a number of reasons, which can be divided into mechanical effects and acquired diseases and pathologies. If such pain accompanies you constantly, then it cannot be ignored. The lack of well-chosen treatment can result in a whole list of unpleasant consequences.
Content:
- Causes of pathology
- Signs of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes 1.1. First stage 2.2. Second stage 2.3. Third stage
- How to cure an enlarged lymph node in the submandibular area
- Prevention of the inflammatory process
Inflammation of the submandibular lymph node is one of the most common types of lymphadenitis.
Its development is caused by inflammatory processes occurring in the oral cavity and less often in other parts of the body. Often the problem occurs with advanced caries, pulpitis, gingivitis, and inflammatory lesions of the tonsils. It is also caused by throat diseases. Let's take a closer look at why the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and what should be done to normalize the situation.
Causes of pathology
If the lymph node changes its size, it can be assumed that a viral or bacteriological infection has spread. Taking into account the localization of the lesion, the doctor understands exactly where the source of the disease is located and which organs need urgent medical attention.
Among the dental provocateurs of enlarged submandibular lymph nodes:
- inflammation of the salivary glands;
- gingivitis;
- pulpitis;
- flux;
- stomatitis;
- alveolitis;
- periodontitis;
- deep caries;
- inflammation occurring under the crowns.
But the violation is not always associated specifically with dental diagnoses. Its reasons are:
- Respiratory diseases: pharyngitis, laryngitis, rhinitis.
- Pathologies related to the bone structures of the skull: damage to the bone structures of the lower jaw, damage to the temporomandibular joint, articular capsule.
- Infections: sore throat, measles, tonsillitis, otitis media, chicken pox, mumps. In all these cases, the lymphatic tissues swell a few days after the first symptoms of the disease appear.
- Specific pathologies caused by pathogenic pathogenic agents: toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea.
- Oncological neoplasms. Lymphatic tissue always reacts very sharply to tumor growth. Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes sometimes indicate the presence of a neoplasm in the area of the tongue, neck, or salivary glands.
- Autoimmune disorders. Always associated with disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Then, by mistake, lymphocytes begin to treat healthy cells as dangerous pathogens. They destroy them, causing inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Hyperthyroidism. With an exacerbation of this disease, the neck and cheek area swells, the lymph nodes become more voluminous.
In young children, parents may notice large round “balls” under the jaw during the period of active teething. This often causes an increase in body temperature. There is no need to be afraid of such symptoms. It is associated precisely with the inflammatory process provoked by the eruption of milk units. But, if the situation does not return to normal within three to five days, it is still worth showing the baby to a pediatric dentist, surgeon or pediatrician.
What to do if your jaw and neck hurt
The surest and most correct step is consultation with a specialist. You can start with a therapist who will examine you, collect anamnesis, make a preliminary diagnosis and give a referral to a specialist. For diagnosis, you may need to do an x-ray, ECG
, blood test, MRI, CT scan, etc., depending on what is the possible cause of your illness. When cancer is suspected, diagnosis and treatment are more difficult.
Massage treatments
Massage makes it possible to relax the muscles in the neck area, but it should only be prescribed and performed by specialists. Also, massage is often prescribed as a restorative procedure after an already completed course of treatment. Certain types of therapeutic and simple massage can strengthen the muscle corset and relieve tightness in different parts of the spine. Self-massage can also be prescribed to work out the neck muscles. But before this, a specialist must teach you how to correctly perform all massage exercises (stroking, kneading, rubbing, etc.), and also monitor the results.
Drug treatment
If the cause of pain is an inflammatory process, such as otitis or tonsillitis, then a whole range of medications is prescribed, the action of which is aimed at relieving the symptoms of a cold and getting rid of the virus, bacteria or infection that led to the onset of the disease. It is not safe to prescribe medication on your own. Depending on your condition and problem, taking medications may make the situation worse. For example, a number of medications under certain conditions cause enlargement of the lymph nodes, and this, in turn, is likely to lead to increased pain in the neck and jaw. Medication and other treatment methods are selected based on the problem. To treat the same sore throat, antiviral and antipyretic drugs are prescribed. If a patient is diagnosed with a temporomandibular joint disorder, surgery and physical therapy are considered.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are far from the best option for getting rid of neck and jaw pain, especially when these folk methods are prescribed independently. Tea with honey and plenty of warm drinks for colds and sore throats help to quickly overcome the disease, but do not cure. Only the methods of official medicine can cure a sore throat or other disease. If the problem is inflammation of the lymph nodes, then it is highly not recommended to use such a folk remedy as heating. This can lead to increased inflammation and serious spread. If you experience neck pain, do not try to solve the problem yourself; only a doctor, after a comprehensive diagnosis, will draw up a treatment plan and adjust it as your recovery progresses.
Signs of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes
How the disorder manifests itself depends on how far the disease process has progressed. If you do not carry out the necessary therapeutic measures, one stage will quickly pass into another.
First stage
The size of the lymph nodes changes very slightly, but the person already feels that they hurt when pressed. Discomfort occurs when turning the head. Body temperature often rises and a sore throat appears. A tickle or dry, unproductive cough is annoying. Pain occurs only on one side of the neck or on both sides at once. The first case is more likely if it is a viral disease.
Second stage
It is called “acute lymphadenitis”. Now the lymph node can be distinguished visually - it becomes convex and protrudes forward. Externally it resembles a subcutaneous ball. Its diameter reaches three centimeters, but can be more impressive.
The node is painful to the touch. Because of this, it is difficult for the patient to turn and tilt his head, and open his mouth wide. The mobility of the upper and lower jaw is significantly limited.
The pain may radiate to the cheek or ear. Body temperature increases. Overall performance decreases.
Third stage
Called purulent lymphadenitis. Here, the inflammatory process even affects structures adjacent to the lymph node. The patient complains of pain in the throat, collarbone, armpit, and head. The nerve endings of the teeth may become inflamed. Then acute toothache occurs.
Pus formed in lymphoid tissues consists mainly of necrotic cells. If it gets into the blood (and such a possibility always exists), the outcome can be extremely unfavorable, so the inflammatory process should not be started.
Patients can understand that the submandibular lymph node is inflamed and needs treatment as soon as possible by the following signs:
- the “ball” enlarges and becomes red or bluish;
- every day it becomes more dense and solid;
- the skin located above the lymph node takes on a red tint and is hot to the touch;
- the lower jaw area swells.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
The list of therapeutic measures is determined by the nature of the pathology:
- Fractures of the lower jaw
. A linear fracture of the body without displacement is an indication for double-jaw wire splinting. The patient is recommended a gentle diet. In the first days, painkillers are prescribed; for open injuries, antibiotics are used. - Purulent processes
. The skin around the outbreak is treated with disinfectants and alcohol solutions. Antibacterial drugs are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen. The treatment regimen includes anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, immunostimulants, and vitamin complexes. - Neuralgia
. The basis of treatment is anticonvulsant medications, which, to increase effectiveness, are combined with medications to improve microcirculation, antispasmodics, antihistamines and therapeutic blockades. - Dental diseases
. Host local events. According to indications, it is recommended to take antibiotics and analgesics. - Atypical prosopalgia
. Tricyclic depressants and anticonvulsants (both separately and as part of complex therapy) provide good results. For intense pain, botulinum toxin is injected to temporarily reduce sensitivity. - Stylohyoid syndrome
. NSAIDs, sedatives, blockades with corticosteroids and local anesthetics, ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone are prescribed.
How to cure an enlarged lymph node in the submandibular area
Therapy must be carried out under medical supervision. Its main goal is to eliminate the infection that caused the disorder. If the root cause of the condition is not established, it will not be possible to be completely cured.
If the problem is related to an oral disease, mandatory treatment is carried out. For severe inflammatory pathologies of internal organs, antibiotic therapy is carried out. For pathologies of a viral nature, patients are prescribed antiviral drugs.
If the examination reveals that pus has accumulated inside the tissues, it is drained using a drainage tube. Additionally, a puncture is taken to recognize the pathogen and understand whether the disease has a benign or malignant course.
As soon as the infectious focus disappears, the lymph nodes begin to shrink, stop hurting and gradually reach their normal state.
Prevention of the inflammatory process
To reduce the risk of developing lymphadenitis, you must strictly follow the recommendations:
- Have annual preventive examinations at the dental clinic. Treat all emerging oral diseases in a timely manner. Avoid caries and take care of your gums.
- Do not ignore the presence of infections and treat them. During therapy, strictly follow all medical prescriptions.
- For any damage to the skin, treat wounds with antiseptics. This minimizes the risk of contracting an infectious disease.
- If you feel unwell, consult a doctor and get laboratory tests. This simple measure allows you to detect violations at the earliest stages.
It is necessary to understand that using “grandmother’s” methods for inflamed lymph nodes is dangerous. So, under no circumstances should you heat the inflamed area or apply cold compresses to it. It is unacceptable to massage him or put pressure on him. All of these actions can make the situation worse. Then it will be much more difficult to reverse the disease.
Anatomy of the trigeminal nerve
The trigeminal nerve (5th pair) is a large mixed (sensory-motor) nerve, consisting of three branches :
- Orbital (n. ophthalmicus).
- Maxillary (n. maxillaris).
- Mandibular (n. mandibularis).
The mandibular ( MF ) is the third branch of the trigeminal, innervating the skin, mucous membranes of the organs of the lower jaw, and the muscles of the lower part of the face. Its location and parameters in the human body are individual and determined by anatomical features. The nerve trunk consists of 30-80 fibers, thickness is in the range of 3.5-7.5 mm, length - 0.5-2.0 cm.
The roots of the mandibular nerve transmit information from the lower part of the face and oral cavity: teeth, gums, tongue, outer part of the ear. Motor - innervate the masticatory and part of the facial muscles.
At the exit from the skull, the LF is divided into two branches:
1. Sensitive ( anterior ) - innervating the mucous membranes and skin:
- cheeks, chin;
- floor of the mouth;
- lower teeth, jaw;
- lower lip, back of tongue;
- salivary glands (sublingual and submandibular);
- parts of the outer ear.
2. Motor ( posterior ) - ensuring coordinated work of muscles:
- chewable;
- maxillohyoid;
- suprahyoid;
- palatal-curtain;
- eardrum.