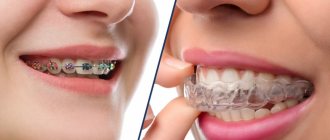
Unfortunately, not all dental defects are corrected with the help of braces, mouth guards and aligners. Quite often, patients experience pathologies, the elimination of which requires the use of more radical measures. This occurs in cases where the cause of malocclusion is not individual dental units, but a disproportion in the development of the upper and lower jaws.
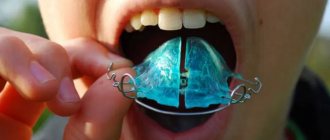
A palatal expander is an orthodontic device that is intended to correct abnormalities in the development of the upper jaw.
Design features of the palatal expander
A palatal expander is a metal orthodontic structure that has:
- support rings (crowns) - placed on molars;
- screw - designed to expand the device;
- wire arches - connected to supporting elements and a lock, creating a shock-absorbing effect of the structure.
Due to the constant pressure of the device on the lateral parts of the upper jaw, they quickly stretch.
How quickly does the upper jaw increase in size with FAGGA?
The FAGGA device allows you to increase the upper jaw by 6–10 mm in an average of 4–6 months. Each patient is unique, and it is very difficult to predict how the body will react to treatment in each specific case, so the orthodontist can give an approximate treatment period.
Commentary by orthodontist M.N. Ostroukhova: “After diagnosis, we can name the approximate terms of treatment, but they depend both on the individual characteristics of the body and on the patient’s compliance with all recommendations. In general, treatment times with this device are quite accurate if the patient visits the orthodontist on time and the activation of the device is not disrupted.”
Advantages and disadvantages of a palatal expander
Orthodontic construction has a number of advantages. These include:
- short active treatment period - it takes only a few weeks to correct the pathology;
- the ability to accurately predict the final result;
- expansion of the jaw does not entail a change in the position of the roots of the teeth, but allows them to remain in the same sockets without provoking;
- the design of the product is highly safe - the likelihood of injury to the oral mucosa due to device failure is excluded;
- high aesthetics - the device is invisible to others.
The negative points are the following:
- despite its high aesthetics, the palatal expander is a bulky orthodontic structure;
- the surface of the tongue is subject to a high probability of mechanical damage by the locking mechanism of the product;
- the adaptation period is accompanied by impaired swallowing function;
- presence of excessive salivation;
- pronounced articulatory disorders;
- the active period of treatment is accompanied by painful sensations.
Many patients are consoled by the fact that the discomfort associated with the use of a palatal expander does not have to be endured for long.
Features of orthodontic treatment with the FAGGA device
There are two phases of treatment. The first is the expansion phase of the palate, during which bone growth occurs. The second is treatment with braces to close the gaps between the teeth and create proper interdental contacts. An orthodontist performing treatment with the FAGGA device must have extensive knowledge and experience, and be able to combine various equipment in order to achieve a successful and lasting result of bite correction. Dial-Dent orthodontists are sufficiently qualified to carry out complex treatment and have experience working with various orthodontic equipment.
Indications and contraindications
The only indication for installing a palatal expander is a pathological narrowing of the upper jaw - micrognathia.
It can develop due to:
- genetic conditioning;
- disorders of fetal development in the embryonic period;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- consequences of rickets;
- disorders of mineral metabolism in the human body.
There are contraindications for using a palatal expander.
These include:
- asymmetrical crossbite;
- open bite of anterior teeth;
- the presence of skeletal jaw asymmetry;
- convex profile;
- inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues.
When is jaw expansion performed in adults and children?
Orthodontics recommends wearing fixed expanders or jaw surgery in cases where this is the only effective and safe option to correct the bite. The main indications for expanding the upper jaw or lower dentition are:
- Micrognathia is insufficient development of the jaw. The disease is often congenital or appears during a period of intense bone tissue growth. The causes of the disease are injuries, genetic predisposition, rickets, defects in bone formation, endocrine pathologies;
- Abnormal narrowing of the dentition, when correction is possible only through orthodontic treatment.
Preparatory stage and installation of a palatal expander
Having examined the patient and drawn up a plan for correcting the pathology, the orthodontist begins preparing the patient for the installation of an orthodontic product.
For this purpose the following is carried out:
- a thorough examination of the patient’s oral cavity and, if necessary, treatment of carious teeth;
- professional hygienic cleaning;
- increasing the distance between the supporting molars using separation rings installed for 7 days.
The palatal expander is installed using two methods:
- directly in the patient’s oral cavity;
- on a plaster model of the patient's jaw.
Support rings can be standard or custom made.
The orthodontic screw is selected by the doctor in accordance with the therapeutic task.
Installation of wire arches is carried out by fixing closed loops with locks of support rings.
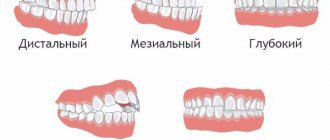
Treatment of mesial occlusion
With mesial occlusion, in contrast to distal occlusion, the opposite situation is observed - the upper jaw lags behind the lower jaw in size ( Class III according to Engle).
External signs of mesial occlusion:
- protruding massive chin
- concave face profile
- retraction of the upper lip and protrusion of the lower
- enlarged lower third of the face
To treat mesial malocclusion, orthodontists use additional devices:
- Face masks
- Various rods fixed to micro-implants
We talked about microimplants above, so all we have to do is tell you what face masks are.
Face mask
A face mask is a structure with support points in the chin and forehead area.
It allows you to secure elastic rods and create a force that stimulates the growth of the upper jaw and promotes the displacement of individual teeth.
In childhood, to treat mesial malocclusion, a face mask is used together with a face bow. When treating adolescents and adults, a face mask is used in conjunction with braces.
The mask can be easily removed and put on without the participation of a doctor. It fits securely, but active activities and sports training while wearing a face mask are prohibited.
The effectiveness of treatment, and therefore the period of wearing a face mask, depends on compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. On average, treatment using a face mask takes 2-4 months when worn 10-16 hours a day.
Oral hygiene when using the device
The presence of any orthodontic structure in the oral cavity requires the patient to pay increased attention to the condition of the teeth and mucous membrane.
To avoid the development of diseases caused by the accumulation and development of pathogenic microbes on the palatal expander and teeth, it is necessary to use the following hygiene products:
- toothbrush and toothpaste (twice a day);
- use of rinse aid;
- removing food debris using toothpicks, floss, brushes;
- The presence of an irrigator will facilitate the care of the orthodontic product.
Changing the size of the jaw is a physiologically and morally very complex process. If it is not possible to avoid it, then strictly follow the orthodontist’s instructions - this will help shorten the active therapeutic period.
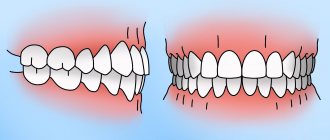
Treatment of distal bite
With a distal bite , the upper jaw is pushed forward and the lower jaw is shifted back. The cause of the pathology is the underdevelopment of the lower and/or overdeveloped upper jaw.
External signs of distal bite:
lips do not close at rest; the lower lip falls under the upper teeth; the convex profile of the face; the chin looks small; the mental fold; the shortened lower third of the face is pronounced;
With this structure of the maxillofacial region difficulties arise with biting and chewing food, the chewing load on the teeth is incorrectly distributed, problems with diction, pain and disturbances in the functioning of the temporomandibular joint, breathing problems and various ENT diseases are possible.
For more information about the causes of distal bite, read the article Why, When and How to correct malocclusion
Depending on the inclination of the maxillary incisors, two subclasses of distal bite are distinguished:
The upper incisors are inclined towards the upper lip, class II, subclass 1 of the Angle classification
The upper incisors are inclined towards the palate II class, 2nd subclass of the Angle classification
The main goal of orthodontic treatment for distal occlusion is to restrain the growth of the upper jaw and stimulate the development of the lower jaw.
, additional orthodontic devices are used together with the brace system
- Herbst apparatus
- Facebow
- Palatal clasp and palatal expander
- Various rods fixed to micro-implants
Herbst apparatus
Herbst appliance - holds the lower jaw in a forward position, but does not interfere with opening the mouth and chewing food.
Despite its intimidating appearance, the Herbst apparatus:
- does not require long and painful habituation
- not noticeable to others because it is attached to the lateral teeth
- allows you to eat your usual food
- does not complicate oral hygiene
- gives good results in the correction of jaw anomalies
- can be installed together with a bracket system
Thanks to constant wearing , treatment using the Herbst apparatus gives results in 6-10 months. To consolidate the treatment results, it is necessary to wear a retention device for several years.
Facebow
A facebow is used in conjunction with braces if the following is required:
- movement or stabilization of the back molars while correcting the position of the front teeth
- normalization of the position of molars when removing the front teeth (in case of increased crowding)
The device consists of an intra- and extra-oral arch, which are made of medical stainless steel. Arches differ in the method of fastening :
- on the neck
- on the head
- on the neck and head
The method of attachment of the facebow depends on the orthodontic problem that the device helps solve.
Due to the bulkiness of the design, you need to use the facebow with increased attention:
- It is recommended to wear the device while you are awake
- You can only sleep with the device installed on your back
- Do not wear the device during sports activities
You need to wear a facebow 10-12 hours a day. The treatment period is several months.
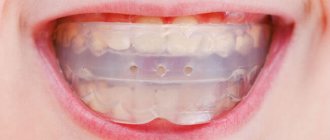
Palatal clasps and expanders
These orthodontic appliances are used to stabilize the position of the first molars (in the case of extraction treatment) and expand the maxilla in patients with anterior crowding and a narrow jaw.
The devices have a similar design and in the video we will demonstrate the operation of the palatal expander.
Immediately after installation, the devices may cause inconvenience and impair diction, but after quick adaptation, this ceases to bother you.
Microimplants
It is not always possible to set the correct direction of tooth displacement using only the “shape memory” effect of the metal arch of braces.
You will learn about the principles of operation of braces in the article Why, When and How to Correct an Overbite
In such cases, it is necessary to install additional rods. Sometimes other teeth can be used as a support for attaching the rod.
But if the rod cannot be attached to the supporting tooth due to the danger of its mixing or it is necessary to apply efforts in a direction where there is no natural support, orthodontists use micro-implants.
- Orthodontic microimplants are small in size
- Installed under local anesthesia
- Painless and non-traumatic installation procedure takes no more than 5 minutes
- Microimplants do not fuse with bone tissue and are easily removed after treatment
Installation process
The Marco Rosa apparatus has four elements that are used to fix it to the jaw. Two rings (left and right) that fit on the molars, and two legs (also left and right) that rest on the fangs.
Installation is performed in the following sequence:
- A week before installing the device, separating rubber bands (separation rings) are inserted between the supporting painter and adjacent teeth, which create a gap for installing metal rings on the painters. On the day of installation of the plates, these elements are removed before the start of the procedure.
- All teeth are cleaned with a rotating brush and toothpaste.
- Prepared cement is applied to the rings of the apparatus.
- The device is inserted into the mouth, the rings are put on the molars and pressed all the way with the instrument. The paws should be located on the occlusal surface of the canines. Excess cement is removed.
- The interdental spaces in the area where the rings are fixed are cleaned with thread.
- A composite is applied to the fangs at the point of their contact with the paws to fix the paws. Excess composite is removed.
- The junction is irradiated with light (to polymerize the composite).
This completes the installation of the plate..
In the video, watch how the Marco Ross apparatus is installed.
How the FAGGA device is made
After the orthodontist’s calculations and selection of the FAGGA device for treatment, the patient’s dental system is scanned. The scan result and the orthodontist’s order are sent to the laboratory, where an individual device is manufactured.
Dial-Dent cooperates with a laboratory in Canada. An analysis of various manufacturers has shown that such cooperation guarantees the highest quality and safety for patient health. The laboratory uses the best materials and strictly adheres to technology at all stages of manufacturing the FAGGA device. Transferring scan data and the finished device to Dial-Dent does not take much time, thanks to properly configured logistics and modern digital technologies.
All the pros and cons of the technique
The Marco Ross device demonstrates almost one hundred percent successful results due to a number of features:
- High efficiency due to the fact that expansion occurs along the unfused median palatal suture.
- Complexity of impact. Along with the expansion of the jaw, the symmetry and aesthetics of the face are restored, the nasal passages are expanded (nasal breathing becomes easier), speech and swallowing are normalized, and mesial occlusion is eliminated.
- Short wearing period when using rapid expansion.
- Inconspicuous when worn.
- Elimination of treatment with braces or, in extreme cases, its significant relief.
- Easy ability to set the expansion rate (the screw can be turned to a larger or smaller angle, daily or intermittently).
- Possibility of use in primary and mixed dentition , when the correction of any dental anomalies is most effective.
- Simplicity and elegance of the design , bright color of the base plates, attractive to the child (creates motivation and eliminates the baby’s anxiety).
The only disadvantages include discomfort after activation and the need for long-term retention. But these features are characteristic of all orthodontic devices without exception.
General overview
The full name of the Ross apparatus is plate-type, non-removable, mechanically operating, single-jaw. The device consists of the following elements:
- Hyrex screw with guides on both sides. Serves to create an expanding force.
- Rings for temporary molars. Provide fixation of the device on the supporting teeth.
- Metal feet. They rest against temporary fangs, creating points of application of force to the dentition, additional to the rings.
- Plastic base (plate), consisting of two parts. Combines all components into a single design.
The device bears the name of its developer. It is made from a plaster model, molded according to an impression from the child’s upper jaw. Costs about 10,000 rubles.
The use of the device allows you to expand the upper jaw along the median seam by 10-13 mm, increase the length of the upper jaw arch, eliminate mesial occlusion, and achieve normalization of a number of other functions of the dentofacial apparatus in children aged 5-11 years.
Depending on the tasks being solved, the Ross apparatus can be modified, in particular, equipped with dental onlays.