The inflammatory process of the periodontal soft tissues that occurs during complicated or improper teething is called pericoronitis. Inflammation during teething can occur in both adults and children, regardless of the location of the problem tooth, but most often pericoronitis of the wisdom tooth develops (it is also often called the “eight” or third molar).
Causes of inflammation and swollen gums during teething
The main prerequisites for the development of pericoronitis are:
- Mechanical injuries to the gingival tissue over the tooth germs due to hard foods, too hard toothbrushes, as well as due to other damaging factors.
- Long-term or difficult teething.
- Favorable conditions in the mouth for the accumulation of bacterial plaque and food particles under the gingival margin (insufficient hygiene, peculiarities of microflora in the oral cavity).
Swollen gums during teething are easily susceptible to traumatic influences, which leads to the development of inflammation. In this case, teething itself can be difficult for the following objective reasons:
- Dense bone tissue in the “eight” zone; bone compaction is most often formed because there are no milk teeth in this zone.
- There is not enough space for the “eight” in the dentition.
- Thickening of the gums and periosteum in the posterior part of the jaw is usually explained by the characteristics of embryogenesis.
Even one of these factors can cause the disease.
White spots on enamel: what are they?
More often, white spots appear on baby teeth, less often on permanent teeth. Experts divide them into two classes:
- carious - those that are associated with the development of caries;
- non-carious.
White areas on the enamel indicate its demineralization. A whitish line may also appear at the edge of the gums of the front teeth. In any case, consultation with a doctor is required.
Compared to permanent teeth, baby teeth are more susceptible to caries. Their enamel is thin and porous, which allows bacteria to easily penetrate inside. The disease progresses quickly, so in a short period of time there may be nothing left of the tooth. There is a risk of damage to the “successor” rudiments. These facts refute the opinion of some parents that there is no need to treat baby teeth, since they must be replaced.
Features and risk factors
During difficult and prolonged eruption, the tooth germ practically does not change its position, and a significant part of its chewing surface is covered with a flap of gingival or mucoperiosteal tissue, the so-called “hood”. The flap covering the tooth germ forms a kind of pocket in which food debris and bacterial plaque accumulate. A moist nutrient medium creates optimal conditions for the intensive reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, which, in turn, actively secrete waste products that are toxic to our body. This provokes the development of an infectious-inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the problematic tooth germ.
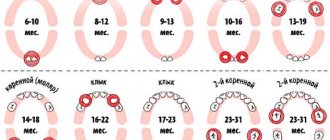
Most often, inflammation of the gums occurs when a wisdom tooth erupts in the lower jaw, which is due to the anatomical structure of the jaw and the lack of space for third molars. In modern people, the jaw arch is approximately 1-1.2 cm smaller than in our distant ancestors, but the size of the teeth has remained the same. This is why the “eights” are cut much later, when the body as a whole and the dental system in particular have already formed - and because of this, it is difficult for the new tooth to find the “right” place on the dental arch.
Since wisdom tooth pericoronitis is the most common type of disease, people over the age of 18 are primarily at risk (usually “eights” are cut at the age of 20-25, but for some this process can take up to 30 years) . As for pericoronitis in children, it usually occurs against the background of insufficient oral hygiene in a child or with infectious diseases of the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, stomatitis), which complicate teething in children and require treatment. Accumulations of plaque and hard dental deposits significantly increase the risk of developing the disease, so timely and regular removal of tartar can serve as a good preventative method.
Carious lesions
Caries is the most common dental disease. It is usually caused by poor oral hygiene. A white spot on the enamel is the initial stage of the carious process, which is easy to treat and does not require the use of equipment that is so scary for a child, such as a drill. If you palpate the problem area, you may feel roughness. By postponing a visit to the dentist, the enamel in the affected area becomes thinner, softens and begins to deteriorate.
Pericoronitis, symptoms and types
With pericoronitis, the symptoms largely depend on the form of the disease - acute or chronic. Acute pericoronitis is characterized by:
- Aching intense pain in the area of the cutting tooth, the pain intensifies under the influence of food and mechanical irritants (hygienic procedures, chewing, touching, etc.).
- Difficulty chewing food, complicated swallowing. A few days after the onset of inflammation, it becomes difficult to open the mouth and severe pain appears.
- Swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes, sometimes the lymph nodes become painful when touched.
- Externally noticeable swelling of the cheeks a few days after the onset of the inflammatory process.
- General deterioration in health - weakness, lethargy, prolonged low-grade fever (increased temperature to 37-37.5 degrees).
- Bad breath, which is caused by the decomposition of food particles and the active activity of microorganisms in the “hood” space.
Acute pericoronitis can occur in a serous (catarrhal) or purulent form: in the first case, the signs of inflammation are more pronounced, the pain is more intense, and there is no purulent discharge. In the second case, purulent exudate flows freely from the inflammatory focus, due to which tissue tension is somewhat reduced and the symptoms are less pronounced. A person may feel like their condition is gradually improving, when in fact the infection is simply spreading to other tissues in the mouth.
If treatment for acute pericoronaritis was not carried out or was carried out at home, the disease gradually becomes chronic: the severity of symptoms decreases, while exacerbations of pain and discharge of pus into the oral cavity are periodically observed. In this case, there is a high risk of developing severe complications.
Complications of the disease
In the case when treatment of the gums during complicated tooth eruption was not carried out, serious complications of the inflammatory process develop:
- Periostitis, or flux, is inflammation of the periosteum.
- Osteomyelitis - in this disease, inflammation affects both the bone tissue itself and the bone marrow, gradually leading to bone resorption. This can cause abnormal jaw fractures.
- An abscess when the infection spreads to nearby tissues. Purulent inflammation leads to the melting of muscles and fatty tissues with the formation of a large accumulation of pus.
- Cellulitis is the next stage of a purulent process after an abscess, which does not have clear boundaries. Such purulent inflammation is a serious threat to the patient and is treated in a maxillofacial hospital.
These complications are usually difficult to treat, require a serious systemic approach and can lead to irreversible consequences. Therefore, if a person suspects he has pericoronitis, treatment should begin without delay in order to prevent the condition from worsening. You need to be especially careful if gum inflammation occurs during teething in children, since the children's immune system is still immature, the body's resistance to infections is lower and the process quickly becomes more severe.
Preventive measures
It is important to provide your child with proper dental care. Immediately after the first incisor appears on an infant, it is necessary to thoroughly clean it with a special brush-finger 2 times a day. It is necessary to ensure proper oral care even before teething begins. For this purpose, wipe the gums with a sterile piece of gauze soaked in boiled water. Other preventative measures:
- limiting the consumption of sweets, confectionery, carbohydrate foods, acidic foods and drinks;
- regularly visit the dentist with your child - at least 2 times a year, ideally - every 3-4 months;
- Give your baby vitamin complexes after illnesses and during periods of active growth - only as prescribed by the pediatrician.
It is important for the expectant mother to follow a diet and not take medications without the doctor’s approval.
Pericoronitis, treatment in children and adults
It should be noted right away that for pericoronitis, treatment at home can only reduce the symptoms of inflammation, but not solve the problem. Therefore, all home methods (rinsing with antiseptics, applying anti-inflammatory ointments, etc.) can only be used as a way to relieve inflammation during the eruption of wisdom teeth and reduce pain - this is a temporary measure before visiting the dentist.
In a dental clinic, in case of complicated teething, treatment will depend on whether the problem tooth should be preserved or whether it should be removed. If preserved, the doctor performs surgical excision of the “hood” under local anesthesia. This eliminates conditions for the accumulation of food and the growth of bacteria, and also facilitates teething. After excision of the “hood,” the patient is prescribed antiseptic therapy (rinses, baths) and, if necessary, antibiotic therapy.
In cases where tooth extraction is indicated due to their incorrect position on the jaw, lack of antagonists, or insufficient space for full eruption, the doctor immediately removes the problematic tooth and prescribes antiseptic therapy to the patient.
In some cases, at the initial stages of the inflammatory process, conservative therapy can be preliminarily applied - local treatment with antiseptic rinses and the introduction of an iodoform tampon into the “hood”. However, local therapy does not always give a positive result; moreover, it is appropriate only at the initial stage of the disease; in other cases, surgical intervention will be required.
When it comes to teething in children, treatment is always aimed at preserving the teeth (except for those cases when dystopia is clearly expressed and the doctor sees that preserving is useless).
How to reduce discomfort?
Methods to reduce discomfort during teething are different and their effect is individual. Often used:
- special anesthetic gels containing various local anesthetics (Dentinox, Kalgel, Bobodent and others);
- teethers (various models made of soft plastic, filled with water), which reduce discomfort but do not injure the mucous membrane;
- in case of severe anxiety and pain, the use of painkillers with ibuprofen and paracetamol (suppositories or syrup) in an age-appropriate dosage is allowed;
- the use of anti-inflammatory decoctions of medicinal herbs - treating the gums with a soda solution, a decoction of sage, chamomile or oak bark.
Diagnostic features
History of the disease Pericoronitis sometimes looks like a completely different disease of the oral cavity - for example, its symptoms can be confused with periodontitis (inflammation of the peri-apical tissues of the oral cavity) or pulpitis (inflammation of the dental pulp). The pain in these diseases is very similar, and periodontitis is often accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the gums. One disease can be distinguished from another by the following signs: with pulpitis there is no pain when opening the mouth and no noticeable swelling of the gums, and periodontitis develops only at the tops of the roots of fully erupted teeth. You also need to pay attention to the presence of a characteristic “hood” - a photo will help you assess how it looks with pericoronaritis.
Eliminating white spots on teeth: what you can do at home
If the problem lies in an excess or deficiency of fluoride, you may need to change the water or install a filter that will remove this element. For fluorosis, toothpastes purchased for a child should not contain fluoride.
If a child is one year old and already has white spots on his teeth, his diet needs to be adjusted. It is important that in addition to breast milk, the diet contains foods containing calcium and vitamins, such as cottage cheese and vegetables. If the baby is on artificial nutrition, you should make sure that he does not fall asleep with a bottle in his mouth. Remains of sweet milk formula can trigger the development of so-called bottle caries.
It is also necessary to pay great attention to oral hygiene. Parents should take care of their teeth first. And when the baby becomes more independent, you need to teach him the basic rules of hygiene. Your doctor will also give you recommendations for care.
Prevention
In some cases, especially when it comes to inflammation of the gums during teething in children, preventive measures will help prevent the disease: careful regular oral hygiene, timely removal of tartar and soft deposits, visits to the dentist for diagnostic examinations at least once every six months.
If pericoronitis is caused by the anatomical features of the structure of the dental system and the lack of space for the lower “eights” on the dental arch, preventive measures will only smooth out the course of the inflammatory process (due to timely cleaning of the oral cavity from bacterial plaque and food particles that create favorable conditions for inflammation) and identify the problem in time (subject to regular dental examinations).
White spots on a child’s teeth: a simple defect or an alarming symptom
All parents want to see their child happy and healthy. Therefore, it is important to carefully monitor the condition of his body. For any alarming symptoms, a causative factor must be found. Attentive attention to oral health is one of the main conditions for ensuring good health for the baby. If you notice white spots on your child's teeth, there is no need to panic, but you should not let the problem take its course. More often it indicates the beginning of the development of caries, but it can also manifest itself for other reasons. The dentist will help you cope with the problem.