In children after birth, rashes are often physiological; they should not cause much concern to parents. The skin adapts to its new habitat - without water, which is often accompanied by some problems. As a result, the influence of any negative factors can cause a skin rash.
The first children's medical center offers the services of qualified pediatric dermatologists in Saratov. The Center’s specialists aim not only to rid your child of the external symptoms of the disease, but also to find and eliminate the cause that caused it. This is very important, because if the cause of the disease is not eliminated, it can recur again and again, taking a chronic course.
Molluscum contagiosum in children
Molluscum contagiosum is more common in children than in adults. Children up to one year old practically do not get sick with molluscum contagiosum. This is due to the fact that in the first year of life the child’s circle of contacts is small: the child moves in a limited space, often specially prepared for him and under the strict supervision of adults, without trying to come into contact with other children. But as soon as a child begins to actively communicate and independently explore the world, the threat of becoming infected with molluscum contagiosum increases sharply.
The peak incidence of molluscum contagiosum in children occurs between the ages of 2 and 6 years. Immunity at this age is still weak. Children become infected through toys or dirty hands. The virus penetrates the skin in the place where the integrity of the skin is damaged - through wounds, abrasions, cracks. Children's skin is delicate and sensitive, and the activity of a preschool child is great. As a result, numerous microtraumas occur, opening the way for infection. Cases of infection with molluscum contagiosum while swimming in the pool have also been described.
From 6 to 10 years, the incidence of molluscum contagiosum decreases. Instilling household hygiene skills is of great importance. The sooner your child starts taking care of clean hands, the better.
Description of the disease
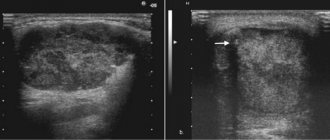
Atheroma is one of the relatively harmless tumors due to the fact that it does not transform into a malignant neoplasm.
However, there is a risk of significant increase in size, so medical attention is required in all cases. Teenage children are more likely to experience this problem. Boys and girls get sick about the same. The main reason why parents first turn to a surgeon is the presence of a visually noticeable tumor.
The atheroma itself is a small capsule filled with pasty contents. It is sebum, which, due to blockage of one or more glands, did not come out, but remained in the subcutaneous tissue.
Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum
The incubation period of the disease ranges from two weeks to several months, but most often the rash appears on the 14-15th day.
At first, single rashes appear, then there are more of them. Molluscum contagiosum can affect any area of the skin except the palms and soles. In children, exposed areas of the arms and legs, as well as the face and neck are most often affected. In adults, the genital area and the inner thighs are most often affected.
In the typical form of the disease, the rashes are located only in one anatomical area; in the generalized form, they spread throughout the body.
Rash
The elements of the rash look like protrusions (papules), firm and painless to the touch, pink or flesh-colored, with a pearlescent top. In the center of the papule there is a small depression, from which, when pressed, a white pasty mass is squeezed out. Papules have a round or oval shape, the size usually varies in the range of 2-5 mm, but sometimes the nodules merge, and then such formations can reach a diameter of 1 cm or more.
More about the symptom
Itching
In some cases, the rash is accompanied by itching, which intensifies when scratching. Under no circumstances should papules be scratched, as this can lead to a bacterial infection. The presence of a bacterial infection is indicated by redness of the skin around the papules, swelling, and suppuration.
More about the symptom
Questions
- Which doctor treats atheroma in children?
A pediatric surgeon is involved in identifying and treating atheroma in children. - Is it possible to cure atheroma without surgery?
Sometimes in the early stages of the disease the surgeon chooses a wait-and-see approach. In 20-35% of cases, atheroma can resolve on its own. However, if the capsule is formed and the tumor is large, it will not be possible to do without surgical intervention. - How dangerous is atheroma in childhood?
Atheroma is a relatively safe tumor. It does not become malignant, rarely becomes complicated and is not accompanied by the development of permanent defects. However, this does not eliminate the need to consult a pediatric surgeon. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis and select treatment. In addition, atheroma can sometimes become inflamed due to the addition of bacterial flora and cause a deterioration in the child’s well-being. - Is it possible to play sports after surgery?
After surgical removal of atheroma, it is recommended to refrain from active activities for 2-3 weeks. This will allow the tissues to fully heal and recover.
Methods for diagnosing molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum can be confused with manifestations of other diseases, including serious ones such as syphilis or cancer. Also, the activity of the molluscum contagiosum virus increases with a decrease in immunity, so in 20% of cases molluscum contagiosum accompanies HIV infection. This means that when rashes appear that correspond to the description of molluscum contagiosum, a medical examination is required to rule out such options.
When contacting a dermatologist, the doctor will examine the patient, make a diagnosis and suggest a treatment method.
Inspection
In most cases, the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is made by a dermatologist based on the results of an examination of the patient.
PCR diagnostics
Since HIV often accompanies molluscum contagiosum, PCR diagnostics for HIV can be prescribed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Serological blood test
When molluscum contagiosum is detected in adults, a serological blood test is prescribed to identify sexually transmitted infections (hepatitis B and C, HIV, syphilis, etc.).
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Pediatric mammology
Hello, dear parents!
Allow me to introduce myself: Sergey Vladimirovich Kaplunov – I am a pediatric surgeon and pediatric oncologist. And today I would like to talk with the parents of my potential patients aged 0 to 18 years on such a very rare topic as pediatric and adolescent mammology. The relevance of this topic is due to the fact that parents do not know who to contact with this or that problem that has arisen in such a sensitive and intimate area, and doctors - pediatricians, gynecologists and ordinary pediatric surgeons are not fully aware of all the variants of pathology that can occur in the area of the mammary glands in children of different ages, and therefore cannot prescribe qualified treatment.
Let me look at breast problems in children according to the age at which these situations may arise.
But first, just a little bit of anatomy: both girls and boys have rudiments of glandular tissue located immediately under the nipple area - so from these tissue rudiments in adolescence, girls will develop glandular tissue of the mammary gland, and in boys these rudiments of glandular tissue will develop. the tissues will normally remain in their rudimentary form.
I. Newborn period. During this period, the so-called “sexual crisis” often occurs, one of the manifestations of which is engorgement (swelling, thickening, increase in volume) of those same rudiments of mammary gland tissue due to the passage of female sex hormones (estrogens) from the mother to the newborn child (sometimes it can even be released scanty secretion from the nipples) – usually this condition can be observed on the 3rd – 10th days of the child’s life, followed by a slow decrease in the severity of tissue engorgement in the nipple area.
But when infections penetrate through the thin and therefore easily vulnerable skin of a baby, against the background of this transient and physiological state, purulent-inflammatory diseases such as mastitis of newborns and necrotizing phlegmon of newborns (which is often localized in the area of the anterior chest wall) can occur.
Already in the neonatal period, parents may notice various developmental anomalies associated with the mammary glands in the child, such as:
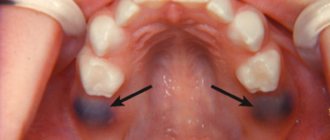
atelia - absence of a nipple (absence of a nipple can be a symptom of syndromic pathology - an anomaly in the development of all tissues of the chest wall on the side of the missing nipple);
polythelia - an increase in the number of nipples: most often there is one additional nipple (on one side), which is located along the so-called “milky line” (from the armpit to the groin area), as a rule, the additional nipple is smaller in size (the nipple itself is also reduced and the surrounding areolar area of the skin) – a vestigial appearance
II. Girls in the period from 9 months to 1.5 years. During this period of life, female children sometimes experience a “second wave” of tissue engorgement in the area of the future mammary glands and, as a rule, this condition occurs precisely in those girls whose mothers continue to feed them breast milk. This condition is explained by the fact that hormonal changes occur in the mother’s body associated with the resumption of the cyclic production of sex hormones (as before pregnancy).
III. Pre-adolescence in girls. Often, mothers are concerned about the fact that the first signs of the beginning of the formation of mammary glands in girls begin at 8–9 years of age. This very often looks like a one-sided thickening (engorgement) of tissue in the retro-nipple area, measuring no more than 1 cm (“pea-sized”) on one side. On the opposite side, such engorgement is either absent or less pronounced. So this unilateral engorgement of the tissue under the nipple (girls complain of some tactile pain in this area) can be perceived by parents as a tumor (neoplasm) or as premature development of the mammary gland. However, we must remember that tumor diseases at this age in the area of the future mammary glands in girls are extremely rare, and the asymmetry of the beginning of the growth of the mammary glands in the first few months is not a sign of pathology starting from 8-9 years of age. Moreover, it has been noticed that more often it is the tissue of the future mammary gland on the left that begins to swell. The development of glandular tissue of the mammary glands often occurs not smoothly, slowly and gradually, but spasmodically. And, as a rule, a noticeable increase in mammary gland tissue begins only from 10 to 12 years of age - at this age, tissue development occurs more or less symmetrically.
But an increase in the size of the mammary glands in girls under 8 years of age - “thelarche” - requires the attention of both parents and a doctor! Thelarche can be isolated (i.e., only an increase in the size of the mammary glands without the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics) or as one of the symptoms of premature sexual development. Premature sexual development of a girl requires, first of all, the exclusion of hormone-producing tumor processes (most often in the ovaries) and a careful detailed examination by an endocrinologist! False thelarche can be mistakenly mistaken for true thelarche (proliferation of glandular tissue of the mammary gland) - this is an increase in subcutaneous tissue in the area of future mammary glands due to adipose (and not glandular) tissue. This condition usually occurs in overweight girls, and in diagnosing this condition, the key diagnostic role is assigned to an ultrasound specialist.
IV. Teenage years. This period accounts for the maximum amount of various pathologies, because during this period the greatest activation of the development of glandular tissue of the mammary glands occurs. Let's look at just a few of the problems.
The growing mammary gland requires the most gentle approach to itself in order to avoid problems with breastfeeding in the future associated with the presence of scars on the skin and inside the breast tissue, which will interfere with the formation and release of milk and the very process of feeding the baby. In such cases, there is an equally effective alternative to surgical treatment - a puncture type of treatment, which does not leave any scars behind!, is less painful, there is no need for general anesthesia and long-term painful dressings. The choice of treatment method for a purulent process in the mammary gland (surgical or puncture or even conservative) is, of course, a matter for an experienced specialist and depends on each specific clinical situation. The main rule for parents is to contact a specialist early with inflammatory changes in the mammary gland area in a teenage girl.
The most common tumor in the mammary glands in teenage girls is fibroadenoma - a benign tumor! Cancerous tumors of the mammary glands in children under 18 years of age (carcinoma, lymphoma, sarcoma) are a rare situation.
It is believed that fibroadenoma is a hormonally dependent tumor, the development of which depends on the reaction of breast tissue to the increasing concentration of estrogen in the growing female body. Often, fibroadenomas can be multiple, ranging in size from 5 mm to 5 cm (sometimes they occupy most of the breast tissue - leaf-shaped or phylloid fibroadenoma).
The only method of treating breast fibroadenoma is a surgical approach - operations in this case (especially in adolescents) should be organ-preserving and aesthetic in nature. Incisions and sutures are made using cosmetic techniques, and only the tumor is removed without involving surrounding healthy tissue.
In this informational article, I focused only on some of the most common problems that can arise in the mammary glands, mainly in girls. A separate topic is the occurrence of tissue proliferation (increase) in the area of the mammary (mammary) glands in boys - this is especially relevant (emotional, cosmetic, social aspects) in adolescence: the so-called gynecomastia. There are also a number of nuances and differences here. This topic will be discussed in the next information article.
Kaplunov S.V.
pediatric surgeon, pediatric oncologist of the highest category
Make an appointment
Make an appointment
Treatment methods for molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum should be treated by a doctor. You should not try to remove papules yourself - this can lead to bacterial infection.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum depends on a number of factors, primarily on the stage of development of the disease, the severity of symptoms and the state of the patient’s immunity. The following methods can be used:
Instrumental removal
Papules can be removed instrumentally, followed by treating the wound with antibacterial agents.
Credestruction
Cryodestruction is the removal of papules using exposure to low temperatures. Papules are treated with liquid nitrogen. Tissues treated in this way freeze and die.
Radio wave removal
Molluscum contagiosum papules can be removed using the radio wave method (using the Surgitron apparatus) and using a laser.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is the effect of high-frequency current on papules. It is popularly described as “cauterization with electricity.” At the moment of discharge, a local strong thermal effect occurs, the tissues coagulate, which virtually eliminates the risk of infection at the treatment site.
Conservative treatment
The course of treatment for molluscum contagiosum may include conservative treatment with ointments and creams, as well as taking antiviral drugs (if the affected area is large).
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Signs of mastitis in newborns
- when touching the mammary glands, the baby cries;
- as a rule, the infection penetrates into one of the glands (much less often it affects both), due to which the mammary gland becomes denser, the baby develops severe pain when touched;
- in the area of infection the skin turns red;
- The baby’s body temperature rises to 39 °C;
- the child cries when he is swaddled or changed;
- the baby refuses to breastfeed and becomes lethargic;
- later, pus accumulates at the site of infection; when pressure is applied to this area, the child screams very loudly and experiences pain;
- with purulent mastitis, pus may spontaneously (without pressure) be released from the nipples of a newborn.
This condition is extremely dangerous for a child. Therefore, at the first symptoms of mastitis, you should consult a pediatrician or call an ambulance. If help is not provided in time, the pus can melt the tissues near the mammary gland and penetrate into its other parts. This condition can lead to a diagnosis of phlegmon of the chest wall - purulent inflammation of fatty tissue. More serious conditions that mastitis in a newborn can lead to are sepsis and generalized infection (spread of infection throughout the body), which threatens the life of the child.
For a newborn girl, mastitis is more dangerous than for a boy: if the acini (components of the mammary gland) die during the disease, connective tissue appears in their place. In this case, when the girl grows up, her breasts will most likely develop asymmetrically. And during breastfeeding, an adult woman runs the risk of serious lactostasis (milk stagnation), which will be difficult to cure without surgery.
Prevention of lactostasis in women
To avoid the manifestation of the disease, the following measures must be taken:
- Choose the right comfortable underwear that will not compress your breasts.
- Put your baby to the breast correctly and in a timely manner. At each feeding, you should give the baby one breast at a time. Make sure that milk flows out evenly in all lobes (change the baby’s position more often during feedings).
- Avoid injury and hypothermia.
- In case of excessive lactation, you should gently express a small amount of milk, achieving not complete emptying, but only softness of the breast.
- At the first signs of lactostasis, try to “decant” this mammary gland yourself.
- Limit sleeping on your stomach.
Many mothers who are just starting breastfeeding are susceptible to lactostasis. It is important to follow preventive measures to prevent this unpleasant phenomenon from occurring, as well as to be able to identify lactostasis in a timely manner and seek help from qualified specialists.
Features of breast swelling
Physiological mastopathy or engorgement of the mammary glands is the physiological condition of a child’s breasts, in which they increase in size. Usually the mammary glands are enlarged evenly, occasionally there is unilateral enlargement. An increase of up to 3 cm in diameter is considered normal if there is no redness or changes under the skin or on its surface.
Sometimes grayish or milky-white contents may be released from the mammary gland ducts; its composition is comparable to that of colostrum.
Typically, breasts begin to enlarge on the second day after birth, and gradually decrease from the end of the first week, but they completely disappear by the month. Such mastopathy does not require any treatment; you should not press the breasts, trying to remove milk from them, apply compresses with ointments, especially like Vishnevsky ointment, camphor and others, which is widely recommended on the Internet.
Swollen breasts do not cause any discomfort to the child, they are not treated in any special way, only with strong magnification can a clean, dry and sterile bandage be applied. It is necessary to protect the breasts from friction with clothing.
However, many parents are worried about breast enlargement and begin using bandages, squeezing out milk, secretions and fiddling with the swollen breasts, unwittingly introducing microbes into the cracks of the papillae. They penetrate deep into the chest and cause the development of a serious complication - neonatal mastitis. If its onset is neglected, the course of the disease can be severe, even fatal. How to distinguish the onset of mastitis from physiology?
How is mastitis treated in newborns?
Clinical guidelines for the treatment of neonatal mastitis state that before prescribing therapy, it is necessary to establish the stage of development of the disease.
If this is the initial (infiltrative) stage, then treatment of mastitis in a newborn is recommended:
- special ointments applied to the bandage;
- ultraviolet irradiation or UHF, which has a detrimental effect on bacteria;
- compresses with magnesium to relieve swelling and pain;
- compresses of dimexide with saline as an antiseptic;
- alcohol compresses;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- suppositories or syrup with paracetamol to relieve pain and fever;
- Treatment of neonatal mastitis can be enhanced with broad-spectrum antibiotics.
However, all of the above actions can be effective until a purulent focus has formed in the gland. If it occurs, the newborn will most likely require surgery, during which the pus will be removed and the cavity will be washed. After surgery, a bandage with a hypertonic solution will be applied to the wound. In addition, the doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
How to prevent mastitis in a newborn
- take care of your baby’s skin correctly, prepare the baby’s first clothes in advance: wash them with a special baby powder and be sure to iron them (this must also be done during the entire first month after discharge from the hospital);
- when, as a result of a hormonal crisis, the child’s mammary glands become engorged, do not touch or put pressure on them, and under no circumstances squeeze out their contents;
- dress the child in accordance with the temperature regime, do not overheat his body;
- On the eve of giving birth, get rid of long manicures and carefully treat your nails.