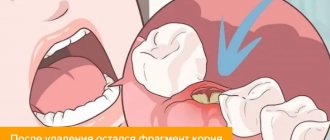
After tooth extraction, the state of the dental system changes, the chewing load is redistributed, the bone tissue in the resulting gap is stabilized, and the hole is overgrown. All changes occur gradually, but over time the consequences manifest themselves in the form of bone atrophy, changes in the bite and subsidence of the gums. Is it possible to place an implant immediately after removal? Only an experienced specialist will answer the question, since it directly depends on the patient’s health condition. What implantation methods do modern dentistry offer and when can a dental implant be installed? Let's take a closer look.
Implantation methods after tooth extraction
Dental implantation after extraction is carried out according to two protocols:
- One-stage - involves installing an implant immediately into the socket of the extracted tooth. There are techniques that allow not only the installation of an implant, but also the fixation of a crown on it.
- Delayed - requires complete healing of the hole and restoration of bone tissue after removal. The bone is restored in 2-5 months depending on the health of the patient. Only then is implantation carried out.
Questions and answers
— What to do if swelling occurs after tooth extraction and implantation?
Swelling is a normal reaction after any implantation protocol, because... This is a surgical type operation. The dentists of our clinic always provide consultations and give instructions to patients on how to act before surgery.
— Differences between immediate and delayed implantation (Briefly)
| One-step | Deferred | |
| Restoring aesthetics in 1 day | The implant can be loaded with a temporary crown, which is removed from the bite. | The only way to restore the beauty of a smile is to attach a removable denture to the adjacent teeth. |
| Jaw bone resorption | Doesn't happen, because the implant is installed immediately. | Does not occur if implantation is carried out within six months after the removal of a dental unit. |
| Restoring bone volume | Not required or can be performed simultaneously with implant installation | If the atrophy process has already begun in the bone, an osteoplasty procedure will be needed before restoring the teeth. |
| Formation of the gingival margin | Required before installing a temporary crown | Performed before installation of an orthopedic prosthesis |
| Cost of services | Acceptable | In the future, higher than one-stage (due to the need for more procedures) |
— Is it possible to implant an artificial root after tooth and cyst removal?
A cyst is a new formation that can reach a diameter of 0.9 to 3 cm. It is usually located at the very edge of the tooth root. In most cases, the formation can be cured with medication.
But in later stages, the cyst can lead to loosening of the root. At the same time, the periodontal tissues are in an inflamed state, which makes it impossible to carry out immediate implantation (the risk of rejection increases to almost 100%).
Experienced dentists recommend waiting for complete recovery and installing the implant using a delayed protocol.
— Why is implantation called the best method of restoring teeth? (Comparison with alternatives)
Installation of a dental bridge.
Involves preparation (grinding) of adjacent units. A bridge is secured to these teeth, covering the gap. Used when 1 to 4 teeth are missing.
How is implantation different?
In case of implantation, it is possible to restore one, several in a row (or several scattered ones), as well as all teeth in the jaw. No turning of adjacent units is required.
Removable prosthesis.
It is used when most or all teeth in the jaw are missing. Can be attached to remaining teeth using special hooks. With complete edentia (the absence of all teeth), the prosthesis is held in place by adhesion forces and may fall out. Also, the removable orthopedic design does not prevent jaw bone resorption, which requires relining the prosthesis every 5 years.
What are the advantages of implants?
They prevent the development of bone tissue atrophy due to the fact that they evenly distribute the load across the entire jaw. The structure cannot fall out.
| Expert, author of the article: Akhtanin Evgeniy Alexandrovich Dental surgeon, implantologist 13 years of implantation experience Material updated: October 11, 2022 |
When it is possible to perform implantation - the doctor chooses after a complete diagnosis
It is necessary to study the condition of the bone tissue, its size and density. Based on the results, the doctor makes a decision - delayed or immediate implantation. Our Center is equipped with diagnostic equipment, so results can be obtained within 15 minutes . But this is only a preliminary assessment; the final decision is made after tooth extraction.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
What happens if you don't restore a tooth?
While eating, the load is evenly distributed over the entire upper and lower row and is transferred to the bone tissue. This stimulates its trophism, ensures normal density, as well as reliable fixation of natural roots.
Single or multiple defects in a row lead to the fact that certain areas of the jaw remain without load. The slowdown in trophism provokes gradual resorption of the bone. It loses volume and becomes less dense.
Compensatory mechanisms ensure the displacement of the remaining teeth. The chewing load is distributed unevenly, which leads to protrusion and accelerated wear of the antagonists. The units move towards the defect where the bone is less dense. Due to the weakening of the ligamentous apparatus, they become mobile.
The visible results of these processes are bite defects, enamel abrasion, and changes in facial contours. Functional inferiority of a number, as well as problems with chewing food lead to chronic gastrointestinal diseases. The severity of the described changes depends on the length of life without teeth.
Atrophic processes are irreversible. It is impossible to slow them down with removable dentures. Only implantation can stop the loss of spongy bone, since it restores trophic processes in the jaw.
Indications and contraindications for immediate implant placement
Indications
- Mechanical damage to the root - fracture, dislocation
- Restoration of frontal units
- Therapeutic treatment did not bring results
- Sufficient bone volume
- No contraindications
Contraindications
- Deficiency, looseness of bone
- Inflammation at the root apex
- Enlarged socket after removal
- Inflammatory processes of the oral cavity, gum pathologies
- Reduced immunity, systemic diseases
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding period
Implantation methods
How long after surgery can a permanent implant be placed? The answer to this question depends on the type of implantation. In addition, the type of implant affects the method of its installation: transgingival, patchwork, or in the socket immediately after tooth extraction.
There are different types of surgery:
- one-stage;
- one-step;
- two-stage.
Regardless of the method, it will take time for the pin to heal. This usually takes from 2 to 6 months. At this time, the patient wears a removable denture, which is fixed on adjacent teeth or a provisional crown on the implant. The temporary structure is then replaced with a permanent zirconia crown. Let's look at each method in more detail.
One-step method Single or multiple dental defects are eliminated in one visit to the dentist. The method of implant installation is transgingival. The doctor makes a puncture through which he screws a pin into the deep tissues of the jaw. Due to the fact that the procedure is minimally invasive, a temporary crown can be placed in just a few days and replaced with a permanent one after 3-5 months.
There are 4 technologies that are used within this method:
- Basal. Used when there is insufficient bone tissue. Implants are fixed not in the spongy layer, but in the basal layer of the jaw, which is practically not subject to atrophy. This procedure is performed only if three teeth are missing in a row, otherwise there is not enough space for implants.
- All-on-4. Four implants are installed - two frontal and two lateral. Next, removable or fixed dentures are attached to them. The technology is not suitable for jaw bone atrophy.
- All-on-6. Six implants are fixed. Two are in the frontal zone, and four are in the lateral region at the site of the chewing teeth. Then dentures are installed on them.
- Complex. In this case, different types of implants and implantation technologies are used. Suitable for non-standard situations, for example, when the patient needs to have his front and molars installed.
Two-stage method Used when there is a risk of complications. The installation method is patchwork. This means that the gums are peeled away to gain access to the bone. A bed for the implant is formed in the jaw, a pin is inserted and the gums are sutured. The artificial root remains without load for a period of 3 months. At this time, the patient wears a removable denture, which holds onto the adjacent teeth and does not load or loosen the pin.
There are 2 options for implementing this method - classic and beam.
- Classical. A bone bed is formed, a pin is installed in it, which is closed with a plug, and the gum is sutured for 3-6 months. Then the gum is opened, the plug is removed and a gum former is installed for a month. Afterwards the implant is placed.
- Beam. 2 or 4 implants are installed in the most favorable areas of the jaw. 3-6 months after the operation, the implants are combined with a metal beam, onto which the prostheses are subsequently fixed.
Regardless of the chosen method, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of bone tissue - density, height, width. The pin survives if the bone is of sufficient size - more than 10 mm. If there is not enough bone tissue, then an implant with the selected size and shape that can cope with the chewing load will not be installed.
How to do dental implantation immediately after extraction
After a tooth is removed and an implant is immediately placed, the process of osseointegration occurs faster. The hole with the artificial root begins to heal, the blood clot turns into bone tissue that surrounds the implant in the early stages of healing. This promotes accelerated osseointegration of the implant with the jawbone, ensuring reliable fixation and stability.
Stages:
Diagnostics
Full diagnostics, choice of design in the absence of contraindications.
Tooth extraction, artificial root installation
Local anesthesia or sedation is used. A bed is formed in the hole, an implant is installed, and the space around is filled with osteoplastic material. After the procedure is completed, the gums are sutured. A temporary removable prosthesis is installed. Engraftment lasts 4-6 months.
Prosthetics
After osseointegration of the implant with the jaw bone, the gum is opened, and a gum former is fixed to the implant for 10-14 days to create a gum contour. Then the former is replaced with an abutment, and a crown made from the impression is installed.
In rare cases, it is possible to fix the crown to the implant immediately after its installation. At the same time, the crown is removed from the bite so that the implant does not move during chewing. This method is recommended for the anterior parts of the jaw in order to quickly restore the defect. Not suitable for lateral use due to active chewing loads.
Re-prosthetics for severely damaged teeth
Every dentist in his practice very often encounters the task of repeated dental prosthetics. And as a rule, after removing old structures, a thin stump of a tooth that has been aggressively treated for a crown is discovered. This is due to outdated principles of prosthetics, when there was no talk of adhesive fixation.
Repeated prosthetics are caused by a number of problems awaiting the doctor, such as: root caries and violation of biological width, lack of ferrule effect, as well as complete destruction of the stump.
The question arises, how can one predict recovery and accurately outline a treatment plan for the patient before removing the old structure?
The answer is simple - this cannot be done for sure! Therefore, in my practice I apply the principle of “diagnostic autopsy”. Patients with such a clinical situation, after being informed of possible treatment options, are offered a diagnostic visit, after which a final decision will be made whether to preserve or remove the tooth.
What does a “diagnostic autopsy” consist of: old structures are removed, the condition of hard tissues, effect ferrules and periodontal tissues is assessed, as well as the possibility of their restoration. Temporary structures are made for the patient using the key made before the old structures were removed and further actions are discussed.
Let's look at the stages of treatment using a clinical example.
Photo 1. Metal-ceramic crowns connected together were previously installed on teeth 1.1, 2.1. Probing revealed overhanging edges of the crowns, as well as a deep subgingival location of the crown border on tooth 1.1.
Photo 2. Before removing the crowns, a silicone key was made.
Photo 3. After removing the old structures, the condition of the root and stump of the teeth was assessed. A violation of the biological width is also visible.
Photo 4. The remains of the composite and areas of carious lesions were removed with a bur. An ultrasonic nozzle was used to clean the cervical area of the teeth. CBCT shows normal endodontic status. Therefore, retreatment of the canals would be required only in the case of depressurization on the endoaccess side. An attempt to extract such a volume of pins is fraught with excessive thinning of the root and, as a consequence, the impossibility of preserving the teeth.
Photo 5. To restore the biological width, as well as enhance the ferrule effect, surgical lengthening of the crown part of the teeth was performed. Gingivoplasty in area 2.1 and gingivosteoplasty in area 1.1. After suturing, temporary restorations were made using a silicone key for 2 weeks.
Photos 6, 7. After 2 weeks, the stumps were restored with Core composite after sandblasting with aluminum oxide. Impressions were taken for laboratory temporary restorations.
Photo 8. Condition of soft tissues at the time of fixation of temporary single structures made of CAD/CAM composite.
Photos 9, 10. Condition of soft tissues after 1 year of wearing temporary structures.
Photo 11. The CAD/CAM system allows you to repeat the formed perigingival contour of temporary restorations in permanent structures, which is undoubtedly a big advantage and ease of use.
Photo 12. Immediately after fixation of ceramic crowns made of solid milled press ceramics, tooth 1.2 was temporarily restored with packable composite in a layer-by-layer technique, for financial reasons of the patient.
Subsequently, it is possible to make an exact copy of a ceramic veneer for tooth 1.2 by comparing digital scans before and after preparation.
Photos 13, 14. Follow-up examination after 1 week. The structural, functional and aesthetic parameters of the teeth are restored, and a healthy gum condition is achieved.
Advantages and disadvantages of one-stage dental implantation
pros
- One operation is performed, waiting time is reduced
- Simplified installation process
- Minimal loss of mucous and bone tissue after surgery
- If the technology is followed, the percentage of successful operations is 99.6%
Minuses
- Contraindicated in chronic inflammation, diseases
- Not performed if there is insufficient bone
- Strict rehabilitation period, frequent visits to the implantologist
For a favorable outcome, entrust the operation to a surgeon with extensive experience in this protocol.
Alternatives
Single or segmental row defects can be eliminated using alternative methods - removable or bridge dentures. However, their use is possible only after complete tissue healing. Removable orthopedic devices do not stop bone atrophy; fixed bridges slow down the process, but do not completely eliminate it. 3-4 months after the operation, the alveolar ridge decreases, gum recession occurs, which is especially noticeable in the incisor area.
The use of removable structures is accompanied by unpleasant sensations as a result of rubbing soft tissues, and also reduces the patient’s quality of life due to restrictions on the use of solid foods.
Is it possible to place an implant if a tooth has been lost for a long time?
Whether it is possible to place an implant if the tooth was removed a long time ago is decided only by the surgeon after a complete diagnosis. Already 3 months after removal, the bone is so absorbed that it may not be enough to install an implant and augmentation will be required. The recommended implantation period is no later than 2-3 months.
In case of bone atrophy, osteoplasty is performed:
- Guided bone regeneration . Most often performed on the lower jaw, bone materials, biomembranes, and bone growth stimulators are used. It is used if the width and height of the patient’s bone is not enough for implantation. If bone tissue atrophy is insignificant, it is possible to perform NCR simultaneously with the installation of implants. Otherwise, it is carried out in a separate preliminary stage. It takes 3-4 months for the grafted material to fuse with the bone.
- Sinus lift. Intervention in the bone structure of the upper jaw in the area of the maxillary sinuses. Using instruments, tissue is punctured to raise the bottom of the sinus. The resulting space is filled with osteoplastic material. The operation can be closed or open. A closed sinus lift is performed for minor bone atrophy simultaneously with the installation of implants. Open - for moderate and critical atrophy in a separate stage.
Examples of work “Before” and “After”
Restoration of chewing teeth - basal implantation (March 2012)
Case: absence of chewing teeth in the lower jaw.
Basal implantation of posterior teeth
Case: absence of all chewing teeth in the lower jaw.
Basal implantation of posterior teeth
Case: the patient complained of the inconvenience of a removable denture in the area of the chewing teeth in the lower jaw.
Restoration of chewing teeth with ROOTT implants
Case: absence of three chewing teeth in the upper jaw Work: three one-stage ROOTT implants and a metal-plastic bridge with three crowns were installed.
Price
The Center for Private Dentistry Dr. Levin provides a case payment system.
- When implanting Nobel Biocare PMC Select or Groovy, the cost includes the surgical stages, including the design model, surgery, anesthesia, and all necessary procedures. The price is indicated taking into account the preparatory stage.
- Removal is paid separately, the price includes surgery, inflammation relief, socket rehabilitation, consumables, anesthesia.
- The case for installing a metal-free zirconium dioxide crown includes all stages - impressions, manufacturing, installation.
- Sinus lifting and any bone tissue augmentation operations are paid separately.
Operation stages
1. Consultation
The doctor listens to the patient, determines the condition of the teeth, gums and the advisability of implantation, and answers the patient’s questions.
2. Diagnostics
The patient is sent for an x-ray. A 3D computed tomography (CT) scan is performed. Helps to exclude contraindications and assess the volume and condition of bone tissue.
3. Preparation
They organize treatment of dental pathologies (if they are diagnosed), and carry out professional cleaning of the oral cavity.
4. Installation of implants
After anesthesia, the implants are implanted using the method of detaching the gum flap, followed by suturing the gums (with a two-stage protocol) or fixed through a puncture (with a one-stage implantation).
5. Prosthetics
If the operation is organized in 2 stages, 2-6 months after the implantation of titanium roots, the patient is fitted with permanent dentures with crowns made of zirconium dioxide or metal ceramics. While the bone is fused with the implants, the patient wears a temporary removable denture. In a one-stage protocol, the installed artificial roots are loaded with an adaptive prosthesis 2-3 days after surgery. Re-prosthetics with permanent structures are organized after a year.
Alternative options for tooth restoration after extraction
After removal, doctors recommend restoring the tooth in a short time. This is caused by bone tissue atrophy, which begins in the absence of chewing load, which complicates recovery in the future.
If for some reason the patient is not ready for implantation, alternatives can be offered:
- Bridge prosthesis. It is a non-removable structure of interconnected crowns. For installation, two supporting teeth are depulped (nerve removal, canal filling) and ground down for crowns. At the same time, the load on the support increases, mobility develops, which is why the bridge will need to be replaced. The bridge structure is not able to completely prevent bone tissue atrophy, but it prevents rarefaction, displacement, and curvature of the dentition. The rate of bone atrophy and the development of mobility depend on the patient’s health.
- Removable dentures . They represent a structure made of artificial gum with soldered crowns, attached to adjacent teeth with hooks. The supporting teeth are ground down if the fastenings are metal. The prosthesis has a range of mobility and requires careful care, since food particles can get under it. Removable dentures do not stop atrophy, but they do prevent displacement of adjacent units.
Implantation prevents all problems, including bone atrophy. An implant is an artificial root on which a crown is placed. Neighboring teeth are not ground down or damaged. The chewing load is maintained. The survival rate of dental implants is 98%. Implantation is considered the most reliable way to prevent bone resorption.
What are the features of implantation of chewing teeth?
- When implanting molars, more attention is paid to restoring their functionality and less to aesthetics, since these teeth do not participate in the formation of a smile.
- To recreate molars, large-diameter implants are used that are specially selected for the wide bone in the back of the jaw. Such structures can withstand maximum loads (up to 180 kg).
- Preference is given to one-stage implantation methods, which allow you to restore chewing function in the shortest possible time.
What is the best way to restore lost teeth?
An implant is the replacement of a lost natural tooth root with an artificial one. The restoration process does not involve neighboring teeth, and the new tooth is functional and looks natural. Installing a dental implant is the best way to regain the integrity of the dentition and prevent tissue atrophy.
A little bit of our advertising and let's continue:
clinics of the German Implantology Center are advanced dentistry in Russia, our doctors are recognized experts not only in the country, but also abroad. We use only rated materials, premium implants. Our priority is quality and an individual approach to each patient. Come for a consultation, tell us about the problem. Together with your doctor, you will choose a method to eliminate it that will give the desired result and will be financially feasible for you.
Sinus lift
Bone atrophy occurs when teeth are lost due to reduced weight bearing. When the roots of the teeth are missing, the bone cells do not experience pressure and are no longer saturated with nutrients. Gradually, the soft layers of bone dissolve, the bone becomes thin, and the gums collapse.
It is impossible to fix the pin in a short and narrow bone. Therefore, before implantation, the dentist may prescribe a sinus lift to the patient - an operation to restore the volume of bone tissue in the upper jaw in the place of the missing tooth.
Types of surgery
There are two types of sinus lift: closed and open.
- In the first case, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. First, the doctor makes a small hole in the bone of the upper jaw, then lifts the bottom of the maxillary sinus, fills the resulting space with bone material and sutures the wound. This type of operation is suitable for bone volumes of 7 to 8 mm.
- In the second case, the operation is performed through the bed created for the implant without additional incisions. Using a special surgical instrument, the dentist lifts the bottom of the maxillary sinus and introduces osteoplastic material that fills the missing volume of bone tissue. This type of surgery is suitable for bone volume less than 7 mm.
Sometimes pin implantation is carried out simultaneously with bone tissue augmentation. The procedures are combined if the bone is of sufficient thickness and its height is at least 7 mm, that is, with a closed sinus lift.
The open type of operation is more difficult and the risk of complications is higher. In this case, implantation is carried out after the rehabilitation period. As a rule, after six months, when the recovery period of soft and bone tissues is completed.
Contraindications
Like any surgical operation, sinus lift has contraindications. The operation cannot be performed in the presence of diseases of the ENT organs during the period of exacerbation, treatment of oncology in the head and neck area, blood clotting disorders, diseases of the immune system and after a heart attack.
Before performing a sinus lift, it is necessary to undergo an examination for the presence of contraindications. If the risk of complications is high, then it is better to refuse the operation and choose another type of dental prosthetics.
When to insert an implant immediately after extraction
- If there is inflammation;
- fistula, granuloma, cyst;
- against the background of diseases of the mucous membrane;
- with insufficient bone volume or pathological changes;
- if the removal was performed carelessly (severely injured hole) and more.
Contraindications also include systemic diseases :
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- oncology;
- mental disorders, depression;
- allergy to anesthetics;
- weakened immunity due to viral and bacterial infections;
- tuberculosis;
- HIV, syphilis;
- hemophilia and other blood diseases;
- chronic diseases at the acute stage, etc.
Sometimes situations arise when one-stage implantation is not completed. In this case, the operation is completed after extraction. The implant installation procedure is postponed for some time to allow the wound to heal. Next, treatment is performed according to the classical protocol.