9466
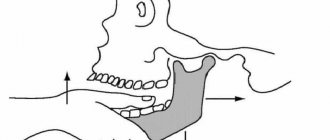
Full chewing and speech abilities are partly ensured by the normal development of the mandibular joint. It is he, due to his mobility, that allows him to carefully crush food and communicate freely through the speech function.
But when a pathological process starts in its structure (overload of the joint, violation of the integrity of the joint capsule, infection, etc.), undesirable consequences arise - the jaw clicks when chewing.
Causes of the problem
In the front of the skull, on the facial right and left sides, there are two temporomandibular joints (TMJ). Chewing, swallowing, and speaking abilities are supported by muscle structures and ligaments that surround each joint and connect the movable jaw to the bony frame of the head.
The formed apparatus allows the movable jaw to move sideways, open and close the mouth, and move forward.
The synchronization of the work of two joints is a sign of the correct functionality of the entire apparatus. If the functioning of one of the joints is impaired, the second one will also cease to perform its functions correctly.
TMJ pathologies are one of the most common problems that orthodontists have to deal with in their practice. Often such malfunctions are accompanied by painful sensations, clicking, crunching in the jaw or its jamming for a second.
In the absence of pain, a person gets used to the disturbance over the years and stops paying attention to periodically occurring sounds. But in vain, because a symptom can signal the beginning of the development of a serious disease.
Among the causes of TMJ dysfunction and the appearance of a crunch in the jaw, it is worth highlighting the following:
- A state of strong emotional and physical stress . In a frightening, irritating or threatening situation, the muscles surrounding the joint may contract spasmodically, inevitably displacing the joint head momentarily.
- Vocal activity, public performance of poetry and other literary works are the most common causes of jaw clicking in childhood.
- Medical errors in dentistry . The problem may arise due to a poorly ground filling, which affects the development of the bite, or due to the installation of an incorrectly fitted denture.
- Injury.
- Exceeding the norms of the intensity of the sports training program, which leads to muscle overstrain.
- Long-term absence of chewing teeth in the lateral regions.
- Weakening the tone of the masticatory muscles.
- Accelerated grinding of the upper layers of hard tissue on all teeth or in separate groups.
- Advanced forms of the carious process.
- Malocclusions.
The reasons for the development of malocclusion and the appearance of concomitant jaw clicking can be:
- Bad childhood habits (sucking foreign objects, supporting the cheek with one’s hand while sleeping, etc.).
- Diseases of the ears, nose and throat.
- Pathological enlargement of the nasopharyngeal tonsil, leading to breathing problems.
- Teeth grinding.
- Diseases of periodontal tissues and others.
In some cases, the reasons listed above are accompanied by other accompanying symptoms:
- swelling of the problem joint area;
- pain when chewing food;
- redness;
- difficulty moving the jaw.
If these signs appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
Classic symptoms of TMJ dysfunction:
- pain in the ears, neck, head or chewing muscles;
- ringing in the ears, congestion, hearing loss;
- feeling of overstrain of the masticatory muscles after waking up;
- migraine;
- clicking or crunching of the jaw when opening and closing the mouth;
- painful sensations when chewing hard food and opening the mouth wide;
- frequent jamming of the joint;
- weakness in the chewing muscles;
- improper closing of the jaws;
- loss of fixed bite height.
In advanced stages of TMJ disorders, it is difficult to determine the root cause of their development. Many patients consult a doctor not after the appearance of clicks in the jaw, but when there is a persistent state of pain.
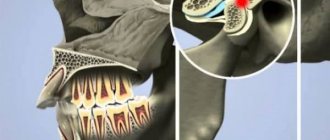
Structure of the TMJ (temporomandibular joint)
The temporomandibular joint consists of the following elements:
- head of the mandible
- mandibular fossa
- articular tubercle
- articular disc
- capsule and ligaments
The articular head is an ellipsoidal bone formation at the end of the condylar processes of the lower jaw.
An articular disc is a biconcave plate consisting of coarse fibrous connective tissue. It has an oval shape. Located between the articular surfaces, it isolates the articular head from the mandibular fossa, dividing the joint cavity into two floors (upper and lower), the disc is fused at the edges with the joint capsule.
Diagnostic measures
The doctor begins the search for the causes of crunching and clicking in the jaw by interviewing the patient and visual examination. The orthodontist palpates the lower jaw and mandibular joint and determines the type of bite.
In some cases, a consultation with a neurologist and a study of the motor and sensory functions of the trigeminal nerve system are prescribed.
For accurate diagnosis, a number of research activities are used:
- biochemical blood and urine tests to determine the presence of inflammatory processes;
- ultrasonography;
- radiography;
- EMG – functional diagnostics of the state of muscle and nervous tissue, as well as neuromuscular transmission;
- arthroscopic surgical procedure (minimally invasive intervention to study various joint pathologies and diseases);
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Classification of pathology depending on its manifestations:
- The clicking sound occurs on one side of the jaw . The clinical picture indicates dysfunction of the lower jaw. In medical practice, a unilateral defect is more common.
- The lower jaw clicks on the right. The symptom indicates a malfunction of the TMJ in the area of the right chewing molars.
- The sound occurs near the left ear . Symptoms indicate joint dislocation or arthrosis. In advanced cases, partial hearing loss is possible.
If the sound occurs rarely and is not accompanied by discomfort, this phenomenon may be natural and physiological in nature. You should be concerned if the uncharacteristic sound is repeated frequently and is accompanied by inflammation or pain.
Why is a displacement of the midline of teeth dangerous and how to correct the defect.
Come here to find out how to correct a crooked jaw.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/chelyustey/sovremennyie-metodyi-ispravleniya-malenkoy-nizhney.html read what to do if a child is diagnosed with a small lower jaw.
Why does my jaw click when I open my mouth?
Most often, such clicking is caused by jaw arthritis. This pathology affects the cartilage layer of the joint or meniscus. Accordingly, the meniscus becomes thinner, the fibers become looser, and the cartilage can partially fuse with the articular head. As a rule, the clicks in this case are multiple, resembling a crunch.
The sound is formed as a result of the movement of the articular heads, which overcome the boundary in the form of folds of the cartilage disc. This crunch can be muffled, and therefore only audible to the person himself. Very often the jaw crunches when the mouth is opened sharply, when subluxation of the joint occurs. With some difficulties, but the jaw can be returned to its place. But sometimes this is impossible on your own - the patient is diagnosed with a dislocation, and here the help of a surgeon will be required.
Treatment methods
The method of eliminating problems with TMJ directly depends on the causes of the development of the pathology and the characteristics of its course. In combination with therapeutic measures, the patient may be prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, and anti-stress drugs.
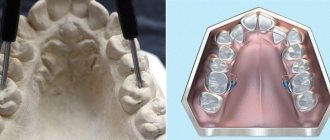
In some cases, to eliminate the problem, they resort to the use of fixing orthopedic structures, such as splints, plates, and mouthguards.
In case of serious problems, joint surgery is performed in the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery. Today, doctors use a number of techniques for the surgical treatment of TMJ disorders.
Minimally invasive technique
The surgeon injects a special solution into the joint structure, which will help remove the affected hard tissue cells.
Also, the effect of the drug is aimed at smoothing cartilage tissue and normalizing the production of synovial fluid for rapid restoration of the joint.
The essence of the procedure is the elimination of inflammation and stimulation of fluid production in the joint. The technique is effective for mild disorders.
Jaw arthroscopy
Jaw arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in maxillofacial surgery to treat damaged parts of the joint.
It is performed using a thin tube (arthroscope) that is inserted into the jawbone through a small hole in the soft tissue. A microscopic camera is attached to the device, which transmits a close-up image of the surgical field to the monitor.
Instruments for surgical procedures are inserted through the arthroscope. During the operation, the doctor may do the following:
- excise scars and thickened cartilage tissue;
- “model” the shape of the jaw bone;
- wash the joint and strengthen it;
- inject an anti-inflammatory agent into the area of inflammation.
After such an operation, the treated tissues are quickly restored.
Open operation
Open operations on the jaw bone are performed in case of serious traumatic injuries, the presence of a tumor and degenerative changes in the structure of hard tissues.
Of the existing methods of opening access to the joint, the Rauer incision is considered the most aesthetic. Although it is technically difficult to implement. The length of the incision, passing along the lower part of the zygomatic arch slightly short of the tragus of the ear, is about 3 cm.
The same incision is made from the end of the first cut perpendicularly downwards. As a result of using a scalpel, a triangular-shaped flap of soft tissue is obtained. It is retracted, part of the masticatory muscles is cut off from the zygomatic bone and free access to the joint is opened.
The procedure allows you to start regenerative processes.
Prosthetics – head replacement
The deformed area is replaced only after open surgery . During the manipulation, the head of the affected joint is completely replaced.
The correct distribution of the bone end parts is ensured by the laying of muscle and cartilaginous elements. The technique is used for advanced pathologies and disorders.
Retroalicular technique
The technique involves fixing the joint with special internal screws. The incision is made behind the ear. This approach is very convenient due to a good inspection of the required area.
After surgery, the joint can be loaded immediately, but only slightly.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the exact causes of jaw clicking includes a number of measures:
palpation on both sides of the temporomandibular joint;- anatomical studies of occlusion;
- neurological diagnostics, including the trigeminal nerve;
- Ultrasound and x-ray of the area with pathology and tissues near it;
- a general blood test, which is required to check the absence of inflammatory diseases;
- facial electromyography;
- dental examination, even if not a single tooth hurts;
- MRI is prescribed in advanced cases and when there are no metal structures installed in the patient’s oral cavity;
- collecting information about what the patient complains about when the jaw cracked for the first time.
How effective is therapeutic exercise?
After eliminating the causes of the disease, the doctor prescribes restorative exercises to the patient, or rather a set of exercises that will help improve the functionality of the masticatory muscles.
Joint exercises are performed after thermal preparation of muscle structures with a warm compress. The duration of the manipulation is no more than 10 minutes.
Good results can be achieved with the following exercises:
- Move your movable jaw forward and backward 10 times in each direction.
- Move your jaw first to the right and then to the left with your lips parted. Repeat at least 10 times.
- Press the chin area with your hand and try to forcefully lift your jaw up. The duration of the movement is at least 1 minute.
- Try pushing your jaw forward for 1 minute, pressing with your fingers on both sides of the chin.
How to treat arthrosis of the jaw?
Treatment for arthrosis of the jaw joint varies depending on the causes of the disease. Its purpose is:
- restoration of mobility of the lower jaw;
- suppression of degenerative and dystrophic processes in the joint.
As a rule, the doctor prescribes analgesics and recommends wearing a splint - an elastic, removable mouth guard that distributes the load on the jaw. The selection of an individual splint (based on an impression), palatal plate or other orthodontic device for arthrosis of the jaw joint is carried out for relaxation in case of muscle hypertonicity or maintaining a healthy position of the TMJ. If the splint is not enough, a specialist may prescribe a Botox injection. Then permanent dentures are created for the patient, which help support the joint affected by arthrosis and correct the bite. Also, with arthrosis of the lower jaw, selective grinding of teeth can be performed.
Treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint involves a moderate change in habits. Patients should avoid eating solid foods, frequent vocal exercises, and chewing gum. Therapy for arthrosis of the jaw joint requires lifelong limitation of mechanical loads and regular visits to the dentist or gnathologist. Preventive courses of physical and pharmacotherapy are carried out at least 2 times a year. It is important to minimize stress and physical strain. The further the disease progresses, the softer the food should be - until the patient switches to purees, cereals, soups and juices.
It is considered optimal to start treatment at stage 1 or 2. In advanced cases of arthrosis of the jaw joint, only surgical intervention can help the patient.
Osteoarthritis of the jaw joint - which doctor should I contact?
The first step if you suspect arthrosis of the jaw is to consult an orthodontist or gnathologist. They will give the patient a referral for an x-ray, and will also determine whether there are any malocclusions or dental contact problems. You may also need to consult a prosthodontist.
If the cause of the disease is primary diseases, in parallel with a specialized doctor, narrow specialists participate in the treatment of jaw arthrosis - for example, a rheumatologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, psychotherapist or otolaryngologist.
Drug treatment of jaw arthrosis
Treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint with medications is usually carried out in a hospital setting. At home, patients can take painkillers, use warming and analgesic local drugs, and also take chondroprotectors.
To relieve inflammation and improve jaw mobility, patients take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) intravenously or orally - for example, ketoprofen, ibuprofen, paracetamol, nimesulide. For topical use, ointments and gels are recommended - finalgon, nicoflex, voltaren, butadione and indomethacin. In the absence of allergies, preparations based on medical bile and bee venom are used. Muscle relaxants, such as mydocalm, help relieve spasm in arthrosis of the jaw joint.
For severe pain, in addition to glucocorticosteroids (hydrocortisone), injections of opioid analgesics are prescribed - for example, tramadol, trimeperidine.
If there are injuries or foci of infection in the body, treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint is accompanied by antibiotic therapy in the form of injections of cefazolin, metronidazole, cefuroxime.
For better regeneration of cartilage and synovial fluid, it is recommended to take chondroprotectors - for example, artracam, Dona or Movex.
Drug therapy for arthrosis of the jaw joint is carried out 2-3 times a year as prescribed by a doctor. The administration of drugs is often combined with physiotherapeutic techniques - for example, in the form of electrophoresis with novocaine, lidase and iodine, Trilon ointment.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of jaw arthrosis
Physiotherapy in combination with properly selected medications and orthodontic devices helps eliminate pain without surgery, even at the 3rd stage of arthrosis. Therefore, the following physiotherapeutic techniques are used to treat arthrosis of the jaw joint and rehabilitate patients.
- ultrasound (10-20 sessions);
- laser therapy (14 sessions);
- microwave therapy (UHF - 10-12 sessions);
- electrophoresis (10-12 sessions);
- phonophoresis;
- mud therapy;
- myogymnastics;
- massage of masticatory muscles;
- balneotherapy (including paraffin therapy and ozokerite);
These procedures improve nutrition of the affected joint, normalize metabolism and activate the processes of natural regeneration of bone and cartilage tissue. With fibrotic changes in tissues, physical therapy helps to soften them and increase the range of motion of the jaw. Also, this type of treatment relieves inflammation, has an analgesic effect and serves to prevent complications of arthrosis of the jaw joint.
Therapeutic exercise for arthrosis of the jaw joint
Therapeutic exercises for arthrosis of the lower jaw help maintain facial mobility, speech intelligibility, improve innervation of the affected area and reduce the impact of the disease on other organs and systems. With hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, it helps to stretch the ligaments and relax the jaw, and also strengthens the jaw apparatus. This promotes proper distribution of the load, and therefore slows down the progression and reduces the symptoms of arthrosis of the jaw joint. Myogymnastics does not replace wearing a mouthguard, but significantly enhances its effect.
- Press your tongue against the hard palate and allow your jaw to drop freely as you relax the muscles in your lower face.
- Place your thumb on the affected joint (in front of your ear) and, keeping your tongue against the roof of your mouth, place your index finger on your chin. Lower your jaw halfway, overcoming the gentle resistance of your index finger. Shut your mouth. Repeat 6 times, and then begin to lower your jaw completely (also 6 times).
- Raising your shoulders and chest, tuck your chin in so that a “double chin” forms under it. Hold for 3 seconds, then repeat (10 times).
- Place your thumb under your chin and gradually open your mouth completely, against the gentle resistance of your finger. Then grab your chin with your thumb and index finger and repeat the exercise - this time closing your mouth (10 times).
- With the tip of your tongue in the center of your palate, open and close your mouth.
- Grasp a small object with your front teeth and slowly move your jaw from side to side. Then repeat the exercise with back and forth movements. As your range improves and the exercise becomes easier, increase the thickness of the object.
What you can do at home
Eliminating the symptoms of the disease at home can only temporarily improve the patient’s condition. For timely diagnosis, it is advisable not to delay visiting a doctor.
In situations where clicking or pain occurs unexpectedly, you can reduce the severity of the disease and improve your overall well-being with the help of traditional medicine:
- Cold . A cloth is moistened with cold water and applied to the painful area for 10 minutes. After an hour, the procedure is repeated until relief occurs. The compress is effective for inflammatory processes in the joint.
- Warm . Hot water is poured into a bottle-type container. The container is wrapped in cloth to avoid burns and applied to the joint. The procedure reduces muscle tension due to arthrosis.
- Medicinal herbs . Decoctions of fennel, calendula, oregano or burdock help relieve inflammation and reduce pain.
To reduce the chewing load, it is recommended to temporarily abandon hard and rough foods and give preference to soft foods. Opening your mouth wide is also extremely undesirable.
TMJ dysfunction syndrome
This entire triad of symptoms is called “TMD syndrome (temporomandibular joint dysfunction). This syndrome is too difficult to treat; unfortunately, one doctor alone cannot cope with such a situation. A comprehensive treatment is required, in which doctors such as a gnathologist, orthopedist, orthodontist, and sometimes a surgeon will take part. That is why it is very important to consult a doctor with the first signs in order to prevent the disease in time.
Soreness
Often, compression in one or two joints leads to changes in the structure of hard tissues (arthritis, arthrosis). This condition is always accompanied by pain.
The disease most often occurs as a result of infection, which over time can cause purulent melting of the bone.
Arthritis can also develop due to traumatic injury to the lower jaw. If untreated, the disease leads to joint immobility (ankylosis) after fusion of bone, cartilage and fibrous structures. The condition can only be treated surgically.
In the catarrhal and purulent stage, the primary task of the surgeon is to ensure the outflow of exudate. In this case, a sling-shaped bandage or an orthodontic structure in the form of a plate is often used.
Further treatment is based on medication, physiotherapy and exercise therapy.
In what cases is expansion of the dentition indicated and what devices are used.
In this publication we will talk about the shortening of the dentition and the correction methods used.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/formyi/slivshiesya.html all the most important things about the treatment of fused teeth.
Prevention
To avoid serious problems with the jaws, preventive measures should be taken in advance:
- correct abnormal bite;
- treat caries in the early stages of occurrence;
- install fillings and prostheses taking into account anatomical features;
- chew food on both sides;
- promptly treat inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx;
- avoid stressful situations.
If your jaw starts to click when chewing, you can’t do anything on your own - you should immediately contact a doctor. Dental pathologies cannot be treated independently at home.
Preventive measures
The main preventive measure against the development of TMJ diseases is careful attention to the condition of the body as a whole.
Regarding the prevention of clicking in the jaw, experts recommend the following:
- treat dental diseases at the initial stages of their development;
- removed or damaged teeth should be immediately replaced with artificial analogues;
- After receiving an injury, immediately consult a doctor;
- treat ear, nose and throat diseases in a timely manner;
- Do not eat too hard and hard foods.
These simple tips will help you maintain healthy jaw joints for life.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Possible complications
If the jaw joint clicks and there is no other discomfort, then this cannot be ignored by a specialist. The dentist must examine and examine the patient, after which the patient receives instructions on therapy and prevention.
The appearance of a crunch may herald the development of serious inflammatory processes that will affect the ear, trigeminal nerve and other organs.
This threatens:
- joint diseases and dysfunction;
- hearing loss;
- severe neuralgia, in which the pain is so severe that the facial expression of the suffering person is called suicidal;
- spasms of the chewing muscles, which can spread to the neck muscles and even complicate the work of the spine.
You will find more details about the disease and possible complications in the video in this article.