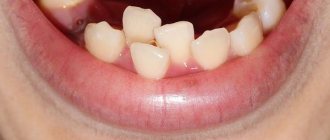
The health of your teeth and the beauty of your smile largely depend on the condition of your gums. Soft tissues are the first to respond to the negative influence of external and internal factors. Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane are the first signs of inflammation. This is the body’s protective reaction to the actions of pathogenic agents and mechanical damage.
Are you worried about pain in your mouth? Do unpleasant sensations interfere with eating, talking and smiling? Let's look at why the gums between the teeth hurt, how to eliminate the discomfort, and in what cases it is necessary to consult a specialist.
Causes of pain in the gums
Unpleasant sensations in soft tissues can be temporary or permanent. Most often pain occurs:
- due to damage to the gums by hard food, bone, toothpick,
- using a toothbrush with stiff bristles,
- untimely removal of soft plaque,
- consuming hot foods and drinks,
- allergies to mouthwash components,
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body.
When the mucous membrane is injured, the pain goes away within 2-4 days. Also, sometimes it is enough to change the brush to a softer one, buy another toothpaste and rinse to get rid of discomfort in the oral cavity.
Food gets stuck between teeth - what to do?
Food getting stuck between teeth is one of the symptoms that you should pay attention to, because this may be a signal of the presence of pathology.
What could be the reason?
Firstly , the carious process on the contact surfaces of the teeth. Over time, when the defect in hard tissues increases, a cavity forms on the contact wall, or a piece of enamel may break off, so food can get stuck in this area.
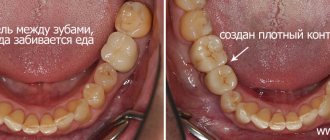
Secondly , poorly manufactured orthopedic structures, when there is a loose fit or an overhanging edge of the crowns, as well as overhanging edges of fillings, a non-physiologically restored contact point or its absence.
Thirdly , problems of a periodontal nature, when there are so-called pathological pockets where bone loss occurs, which also leads to food getting stuck and accumulated.
Fourthly , wisdom teeth. Very often they do not have enough space and are not located in the dental arch, at an angle. This makes it difficult to carry out thorough hygiene and leads to the formation of a pocket where food debris constantly accumulates.
Let's look at a few clinical cases.
Clinical case 1.
Ekaterina went to the clinic for comprehensive treatment.
At the time of contact there were complaints:
- for partial loss of teeth and the inability to chew food well
- for food getting stuck between teeth
- for bleeding gums
- for bad breath
We conducted an examination and x-ray examination.
There are several areas on the upper jaw where food debris constantly accumulates.
Let's take a closer look at each tooth.
On the CT scan, on the distal surface of the 17th tooth (which is in contact with the wisdom tooth), we see a deep hidden carious cavity, which is almost invisible upon visual inspection. Food gets stuck in this area, which is also facilitated by the presence of a pocket between the 17th and 18th teeth.
The coronal part of tooth 26 is almost completely destroyed as a result of the carious process. There is a cavity and overhanging edges, which is also an area for food accumulation.
On tooth 24 there is an old filling with a defect in the marginal fit and signs of secondary caries.
On a computed tomogram we see a deep subgingival carious defect.
After the consultation, we drew up a treatment plan, but the patient did not start treatment immediately, and after 6 months she went to the clinic with a complaint about a filling falling out of the 24th tooth. This is what it looked like visually:
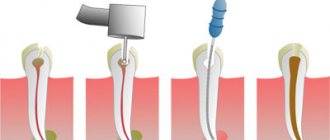
The carious process had already affected the nerve, there was also significant destruction under the gum, but we managed to save the tooth. We removed all the caries, restored the wall, and treated the root canals. To preserve this tooth, it must be covered with a crown in the near future, since in this case the filling cannot guarantee a hermetically sealed restoration for a long time, there is a risk of re-infection of the root canals and chipping of the tooth.
This could have been avoided with timely replacement of this filling and good interdental hygiene!
Clinical case 2.
Dmitry went to the clinic for a routine examination.
Complaints:
- for missing tooth 17
- for food getting stuck between teeth
- for plaque
- for bleeding gums
- for bad breath
Initial situation.
Objectively: a significant amount of soft and pigmented plaque, supragingival and subgingival tartar.
Hygiene is unsatisfactory. The patient does not use interdental hygiene products.
On the X-ray:
We see signs of chronic periodontitis (generalized loss of bone tissue), which leads to the formation of pathological pockets.
But let’s pay special attention to 2 zones: the 15th tooth and the interdental space of 46-47 teeth.
Between the 46th and 47th teeth there is a deep periodontal pocket, the loss of bone tissue is more significant in this place, which indicates constant food entrapment and the presence of a chronic inflammatory process.
In the oral cavity:
After we removed part of the old filling, we discovered caries on the contact surfaces in the gum area.
On the 15th tooth there is a filling of considerable size with an overhanging edge.
Visually, everything in the oral cavity does not look so scary.
But we take a targeted intraoral photograph, which will allow us to assess the true condition of the periodontal tissues in the area of interdental contacts.
A filling with a huge overhanging edge, which not only contributes to the accumulation of food, but is also a chronic traumatic factor for the gums.
This patient underwent professional oral hygiene in 2 visits, interdental hygiene products (dental floss, brushes, irrigator) were selected and training in the correct technique for their use. After all, home hygiene plays a significant role in the success of our treatment, especially in patients with periodontal tissue diseases.
We then replaced all the old defective fillings and cured tooth decay.
The patient was referred for consultation to a periodontist and orthopedist.
Clinical case 3
Elena came to the clinic for professional oral hygiene.
At the time of treatment, there were complaints about the presence of plaque and constant food getting stuck between the 25th and 26th teeth, rupture of the thread and periodic bleeding.
Objectively: on tooth 26 there is a filling with a defect in the marginal fit, a copious amount of plaque between teeth 25-26. When you try to clean the interdental space with floss, bleeding and an unpleasant odor appear.
On the targeted radiograph: a filling with a defect in the marginal fit and signs of secondary caries on the 26th tooth. Carious cavity on the distal and mesial surfaces of the 25th tooth.
In this case, caries treatment was carried out on the 25th tooth.
The patient was referred to have the 26th tooth restored with a crown by an orthopedic dentist, since the tooth had been treated endodontically and had a significant area of destruction.
Clinical case 4
Evgenia went to the clinic for planned sanitation.
I was concerned about the reaction of some teeth to sweets, food getting stuck in some places, especially in the contact area of 37 and 38 teeth.
Objectively: tooth 38 is dystopic (there is a violation of position - the tooth is tilted towards tooth 37), there is a carious cavity of a significant size on it.
Tooth 37 has a defective filling and a deep carious cavity on the distal surface (in contact with tooth 38), which was formed as a result of prolonged food stuck and the inability to thoroughly clean this area.
In this case, tooth 38 needs to be removed, tooth 37 needs treatment.
Clinical case 5
Victoria went to the clinic to sanitize her oral cavity.
I haven’t been to the dentist for a long time, at the time of contacting I was worried about the following complaints:
- for food getting stuck
- to change the color of fillings
- for increased tooth sensitivity
- reaction of some teeth to sweets
On examination: a significant number of defective fillings with signs of secondary caries.
There are also metal-ceramic crowns in the oral cavity, which were installed about 5 years ago. I would like to draw attention to them to show why low-quality orthopedic structures can cause problems.
In the panoramic image we see that the marginal fit of the crowns is not ideal; food gets clogged in these areas.
But I especially want to pay attention to teeth 45 and 46.
On tooth 45 we see a “gap” between the edge of the crown and the root. On the 46th tooth there is an overhanging edge of the crown and there is a possibility of a carious process at the root. In this case, we may suspect root caries, but the orthopedic surgeon will be able to say for sure after removing the old crowns.
What to do?
If you regularly get food debris between your teeth, you need to make an appointment with your dentist to understand and eliminate the cause. If the problem is left unsolved, it can lead to serious complications:
- Caries
- Root caries, which can lead to tooth loss
- Chronic inflammation of the gums - gingivitis, or the development of localized periodontitis, as a result of traumatization by sharp, overhanging edges of fillings or crowns.
All this is accompanied by such unpleasant symptoms as:
- bleeding gums
- painful sensations
- constant discomfort, bursting sensations
- bad breath
At the appointment, the dentist will conduct an examination and the necessary additional diagnostic measures, which will help find the cause and carry out appropriate treatment:
- cause of caries ➝ treatment of caries and functional restoration of the tooth
- defective seals ➝ replacement of seals
- defective orthopedic structures ➝ consultation with an orthopedic dentist, removal of old dentures and replacement with new ones
- the presence of wisdom teeth that make it difficult to carry out hygiene measures ➝ referral to a dental surgeon for removal
- old fillings of significant size on teeth in which root canals were treated ➝ restoration with crowns, because it is the crown that provides good sealing and will help preserve the function of the tooth for many years, prevent the risk of chips and fractures, which often leads to tooth loss
- if there are periodontal pockets ➝ consultation with a periodontist, professional hygiene, selection of products and training in home hygiene is required, you may need medication or Vector therapy.
To summarize, if food is constantly stuck between your teeth, you should immediately contact your dentist. After all, solving a problem at the initial stage is much easier and cheaper than waiting for complications to develop.
Possible diseases
Constant pain in the gums is one of the main symptoms of the following oral diseases.
- Gingivitis. Acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane. Develops due to the accumulation of plaque. Soft deposits mineralize and turn into tartar, which cannot be removed with a regular brush. Pain occurs in the gums between the teeth.
- Periodontitis. Periodontal inflammation, in which the dentogingival joints are destroyed. Develops due to advanced gingivitis. The risk group includes patients with a hereditary predisposition to the disease.
- Stomatitis. An inflammatory process accompanied by the formation of blisters or ulcers. They cause burning and pain in the mouth when eating and brushing teeth. Stomatitis can be triggered by injuries, burns, as well as pathogens - herpes simplex virus, Candida fungi.
How to fix the problem?
Only a specialized dentist can accurately determine the cause of food retention and eliminate it!
I think it’s time to start living a comfortable life, enjoying food and not thinking about how and where it will get stuck next time. Don’t waste time, sign up for a consultation and start living in peace. The main treatment is to form the correct contact point (the point of contact between the lateral teeth). Caries is cured using modern filling materials and matrix systems. It is very important that the filling has the correct shape and there is tight contact at the point of contact with the adjacent tooth (dental floss passes through interdental contact with resistance and a click).
If the problem of food getting stuck between the teeth is the overhanging edge of the filling or its irregular shape, then the filling is replaced with a new one. Dental prosthetics are required when there are unsatisfactory dentures and crowns, which also need to be replaced. Food does not get stuck only when there is a complete removable denture. But when partial removable dentures are used, the accuracy of the fit of the prosthesis to the adjacent teeth is important.
The presence of deep pockets or “black triangles” can be corrected using surgical treatments.
Diastema, trema and crowding of teeth are corrected with the help of orthodontic treatment or aesthetic restoration of teeth (veneers, fillings, crowns).
Supra- and subgingival tartar can be removed during professional teeth cleaning. Using a special tool, hard dental deposits are removed by polishing the roots.
Treatment of teeth and gums
A dentist can determine why the gums between the teeth hurt based on diagnostic results - a visual examination. The treatment regimen is developed individually for each patient. This may include:
- antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity,
- professional teeth cleaning,
- treatment of periodontal pockets,
- treatment of caries and other diseases.
To prevent the situation from worsening, patients need to follow a diet for several weeks after treatment, use hygiene products and rinses recommended by the doctor, and avoid physical activity and stress.
Recommendations
First of all, take good care of your mouth. When the first signs of food stuck appear, we recommend contacting your dentist for specialist advice. Don't forget to go to the prof 2 times a year. inspections. During a consultation with our specialists, you can find out which teeth should be treated and which fillings need to be replaced with new ones. You also need to come for professional teeth cleaning twice a year.
Secondly, we recommend contacting only trusted clinics with many years of history and experienced doctors. We would like to warn you against the temptation to use free dentistry under compulsory medical insurance; remember, good treatment and prosthetics cannot be free. Don't skimp on your health!
We hope that our article helped you and you found answers to your questions. If you have any further questions or would like to make an appointment, there is an appointment form below.
Causes of food getting stuck between teeth
Below is a list of reasons why food gets stuck between teeth:
- Excessive contour of the prosthesis;
- Cement not removed by the dentist, squeezed out by a crown;
- Errors at the stage of manufacturing the intermediate part of the bridge, when the shape of the prosthesis does not match the anatomy of the patient’s oral cavity.
- The edges of poorly made crowns hang over the gums.
- Poor quality filling. If the edges of the filling overhang, the dentist has poorly formed the anatomical shape. The presence of pores in the filling material on the side surface of the tooth leads to the absence of a contact point.
- The gingival papilla is absent. Its purpose is to fill the space between the teeth so that food does not accumulate in this area.
- Caries. As soon as a carious cavity forms on the side of the tooth, food debris immediately collects in it. Cleaning them out is not at all easy.
- Tartars formed above and below the gums. They are called “subgingival” and “supragingival”. These are hard deposits that trap food.
- Gaps between teeth. In the dentist's dictionary, a distinction is made between diastemas and tremas. Solid food stuck in them is removed using cleansing threads. Soft food can be removed by regular rinsing.
- Inclined and uneven position of the teeth, their crowding.
Interdental caries is caries that forms on the interdental surfaces of teeth. Most often in people who do not know what dental floss is and do not have the habit of cleaning the interdental spaces from food debris.
Consequences of food stuck between teeth
The result of constant jamming is that the teeth lose their hardness.
Important! Food remains between the teeth for a long time, while their enamel is damaged and periodontal pockets are formed. They provide direct access to various infections, which leads to gum abscess.
And there is a negative progression in this problem. The food penetrates further into the pocket, deepening it, and the bone is affected. Tooth decay occurs when food gets stuck between adjacent teeth. It doesn't show up right away. And treatment is complicated by poor access to the lesion site. The damage caused by stuck food is irreversible. Not only the tooth suffers, but also the tissues supporting it. If left untreated, its destruction and removal cannot be avoided. When stuck food sits in your mouth for a long time, it can ferment and cause an unpleasant odor.
A periodontal pocket is a space formed due to the destruction of the dentogingival junction and circular ligament of the tooth, as well as resorption of bone tissue and alveolar walls.
Open curettage of periodontal pockets: features of the procedure
The intervention involves the following stages:
- Cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar.
- Use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
- If necessary, splinting of mobile teeth.
- A gingival incision near the neck of the teeth, helping to peel off the mucous membrane from the bone tissue.
- Removal of granulations with a curette and stones with ultrasound.
- Antiseptic treatment of dental roots.
- Inserting synthetic tissue into cleaned pockets to encourage natural bone growth.
- Apply sutures and cover the wound with a gum bandage.
1.5 weeks after surgery, the sutures are removed. After a few months, complete restoration of the damaged tissue occurs, and the gingival papillae again close the gaps between the teeth. Sometimes the operation leads to exposure of the roots, but the degree of gum recession directly depends on how much bone tissue has been destroyed.
Curettage of periodontal pockets is often the only way to get rid of loose teeth and purulent discharge from the gums. Therefore, if the disease has already progressed, and the operation seems too expensive, there is no need to save. Further dental implantation will cost a much larger amount.
How to solve the problem without a doctor?
The first thing that comes to mind for a person experiencing discomfort from food stuck between their teeth is the use of toothpicks. Dentists strongly recommend excluding their use in everyday practice. Such “helpers” can seriously injure the gums and accelerate the loosening produced by stuck food.
Attention! The best way to remove food debris in such cases is dental floss. If you happen to see a wide thread with wax on sale, it is better to purchase it. She will help out well at a party.
At home, an irrigator will help more effectively. It perfectly washes away food debris in the mouth. When a person already has periodontal pockets, the irrigator will become a lifelong assistant. It is rightly said that you do not need to care only for those teeth that the surgeon has removed. Floss and regular brushing are effective in making you feel better. But they don't solve the problem completely. Repeated food getting stuck between the teeth tells the patient that he needs to see a dentist who not only does fillings, but also knows how to work with dentures.
Dental floss, also known as floss, is an additional oral hygiene product that is used to clean interdental spaces and prevent the occurrence of caries and periodontitis.