Content:
- What is a tooth abscess
- Classification of abscess in dentistry
- Causes of the disease
- Signs of illness
- Breakthrough of purulent masses with an abscess
- Treatment of the disease
- How to prevent a tooth abscess from occurring
A tooth abscess is an unpleasant and dangerous dental disease. It can occur in anyone. It is impossible not to notice its presence, since acute pain appears in the affected area and accumulations of pus form. Let's take a closer look at what this disease is, how to recognize it and treat it.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a tooth abscess is pain. It is localized in one place and intensifies when pressed or chewed. The tooth becomes sensitive to cold, hot or sour foods. If the tumor appears in the upper jaw, pain spreads along the trigeminal nerve.
The following manifestations of pathology are also common:
- malaise, weakness, headache;
- temperature increase;
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- the appearance of greenish discharge;
- the face becomes asymmetrical;
- if there is pus in the mouth, an unpleasant odor and bitter taste appear.
What is a tooth abscess
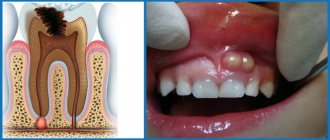
This is an infectious process caused by the accumulation of purulent masses in the outer or inner part of the alveolar process of the upper/lower jaw. Pathology develops due to the abnormal activity of pathogenic microorganisms that accumulate in the soft pulpal (often dead) part of the tooth.
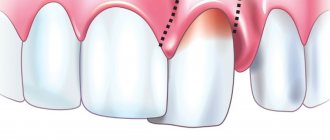
A small bulge appears on the gum. It is painful to the touch and causes discomfort in a person. Gradually, pus begins to accumulate in the “bump.” The difficulty is that you cannot open it yourself, or even more so, squeeze it out - under the influence of external pressure, the necrotic masses will not only come out, but will also penetrate into the deeper layers of the gum. Then they can get into the blood and lymph - the infection will spread throughout the body.
Types and forms of abscess
Depending on where the pus accumulates, there are three types of pathology:
- gum abscess or gumboil affects only the gums;
- periodontal develops in the periodontal pocket;
- periapical appears with severe destruction of the pulp and other dental tissues.
This pathology often occurs in an acute form and requires immediate dental treatment. But sometimes the fistula opens on its own. The pus comes out and the patient feels relief. If complex therapy is not carried out, the pathology can become chronic.
Classification of abscess in dentistry
Doctors say there are three types of tooth abscess:
- Desnev. Only the soft tissues of the mouth are damaged. But, if the disease is started, the periodontal ligaments and periosteum will be drawn into the inflammatory process. Then flux develops.
- Periapical. The pulp is affected. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, you will have to perform depulpation or, even worse, tear out the affected unit. More often, this type of disease is diagnosed in children with primary occlusion, which is why dentists have to remove a preschooler’s incisors, canines and molars without waiting for their natural replacement by molars.
- Periodontal. The abscess has a destructive effect on the root, so the tooth becomes loose and falls out prematurely.
The main danger of a purulent tooth abscess is that the pus that has accumulated inside the tumor can penetrate into the blood. Then a general intoxication of the human body will occur. Internal organs, bones, and brain come under attack. A person who ignores the presence of an abscess may develop meningitis, sepsis, and even die.
Why is an abscess dangerous?
The tissues of the oral cavity are rich in blood vessels, so it is easy for infectious pathological processes to spread from one area to another. A limited abscess without treatment can lead to the following local complications:
- abscess of the adjacent area;
- phlegmon - diffuse tissue damage by infection;
- periostitis – transition of inflammation under the periosteum;
- inflammation of the bone - osteitis.
In particularly severe clinical cases, if the symptoms of an abscess are ignored for a long time, osteomyelitis can develop - melting of part of the jaw bone tissue as a result of purulent inflammation. Pathology leads to the formation of voids in the bone, jaw fractures, and tooth loss.
An abscess in the area of the retromolar fossa (near the last chewing teeth) is especially dangerous, since the infectious-inflammatory process without adequate treatment can spread to the tissues of the pharynx, and from there to the mediastinum, which leads to serious complications from vital internal organs. Another possible way for the infection to spread is into the membranes of the brain, which leads to the development of meningitis. An abscess on the gum without treatment can also be complicated by sepsis when a large number of bacteria enter the bloodstream, which is life-threatening for the patient. You should not postpone a visit to the dentist if there are signs of inflammation of any location, since self-treatment of an abscess with purulent contents leads to a worsening of the condition and serious consequences.
Causes of the disease
Most often, abscesses are encountered by people who pay insufficient attention to oral health. Thus, untimely treatment of caries, pulpitis, gingivitis, granuloma, stomatitis, cysts can lead to the described disease. It has also been noted that the risk group for the development of pathology includes people with weakened immune systems, diabetics, cancer patients, people with HIV, obesity, and hormonal disorders.
An injury often leads to the accumulation of pus in the jaw. A less common reason is mistakes made by the dentist when treating tooth canals.
A gingival abscess is usually the result of traumatic injuries to the oral mucosa. It often appears a few days after a person burns himself while drinking a hot drink or scratches his gums with hard food.
Signs of illness
It is almost impossible not to notice the presence of pathology - the symptoms are always very clear. Anyone, even those far from the medical field, can understand that something is wrong with their gums.
- First there is an acute toothache. It becomes more pronounced if you press on the unit, touch it, or knock on it. It intensifies if the patient drinks or eats something hot or cold.
- Soon the gums swell. Even the cheek may swell. This indicates that the inflammation is spreading quickly.
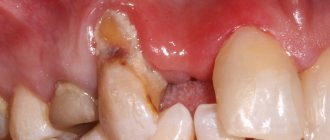
- A bulge forms on the gum. At first it is red or with a bluish tint. But it also happens that it is not there, and pus simply begins to ooze from the gums.
Due to the purulent masses, the patient has an unpleasant taste and a foul odor appears from the mouth. It is not possible to remove it using standard hygiene products - a toothbrush and toothpaste, since pus continues to actively form after brushing your teeth.
An advanced abscess contributes to an increase in body temperature, decreased appetite, and decreased performance. In many patients, the cervical lymph nodes become enlarged.
Gum abscess - symptoms
A limited focus of infection in the gum most often forms during an exacerbation of existing periodontal pathologies, so signs of an abscess appear suddenly and grow rapidly. Quite pronounced local symptoms are characteristic, and due to intoxication with waste products of bacteria, the general condition also worsens.
An abscess is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the gums;
- limited tissue swelling (“flux”);
- temperature increase;
- redness and swelling of the mucous membrane;
- sometimes – tooth mobility;
- headache, weakness.
In the absence of timely treatment, a fistula can form - a canal in the gum with a hole through which pus spontaneously discharges from the lesion to the outside. After the fistula appears, the pain is relieved, but an abscess remains on the gum, treatment of which is necessary to completely relieve the infection.
Breakthrough of purulent masses with an abscess
Often the “bump” grows, swells, and then bursts. Then the pus inside it flows out. After this, the pain goes away and the patient’s well-being improves significantly. But this does not mean that the problem is a thing of the past. It should be remembered that with an abscess, fistula tracts often form. They serve as a protective reaction of the body - they ensure the unhindered outflow of pus and prevent the inflammatory process from further progressing.
The disease may recur. Purulent exudate is able to penetrate into the tissue surrounding the tooth. Therefore, even if the “bump” has burst, you still need to make an appointment with the dentist so that the doctor can conduct an examination and tell you what to do to prevent the disease from returning.
Diagnostics
To diagnose a tooth abscess, the dentist must conduct an examination of the oral cavity and take an x-ray of the tooth. An X-ray image reveals signs of an inflammatory process (widening of the periodontal fissure, thinning of the spongy substance of the alveolar process).
A visual examination reveals swollen, bright red areas of the gum mucosa and increased tooth mobility. With periodontal abscess, periodontal pockets up to 6 mm deep and higher, filled with purulent discharge and granulation tissue, are noticeable.
The purpose of diagnostic measures for a tooth abscess is to differentiate the pathology from an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, cysts, periostitis, osteomyelitis.
Treatment of the disease
You should not try to cure a purulent “bump” on your own. Therapy should be carried out by an experienced dentist. First, the specialist carries out an examination and carries out the necessary diagnostic measures. Then he proceeds to opening the purulent formation. To do this, he uses a scalpel or laser beams. Since the drainage procedure is performed under local anesthesia, the patient does not feel pain.
The next step is to wash the wound and treat it with antiseptics, and apply antibacterial compounds. It also happens that drainage is installed in the affected area for several days to avoid re-accumulation of pus.
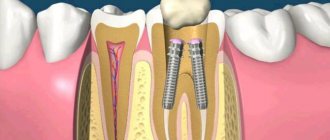
Afterwards, the tooth is treated or pulled out. In the first case, the nerve is removed. To do this, medicine is put into the unit and after a few days the dead nerve is removed. Afterwards, the canals are cleaned and sealed. Filling material or an individually made inlay is placed on top.
A tooth is pulled out only in advanced cases, when the roots have become unusable and cannot be treated. To prevent this, you need to see a doctor in a timely manner, and not hope that the disease will go away on its own.
If the patient complains of acute and pronounced pain, he is prescribed a painkiller. Most often these are tablets, but it is also possible to use a special anesthetic gel.
In order to achieve a guaranteed victory over inflammation and prevent recurrence of the abscess, the patient is also prescribed an antibiotic. The average course for the described diagnosis is from five to seven days. It is unacceptable to interrupt it in the middle because the condition has improved - the disease may return.
Local treatment, carried out at home after the dental surgeon has opened the abscess, consists of applying compresses with antibacterial compounds and performing therapeutic rinses. These procedures stimulate regeneration and accelerate tissue renewal.
Basic methods of treating abscess
After carrying out all diagnostic measures, the dentist determines the treatment tactics necessary in a particular clinical case. Abscess therapy is complex, including eliminating the cause of the pathology, alleviating symptoms and accelerating tissue regeneration. If the patient turned to dentistry in the early stages of the development of the disease, a conservative method can alleviate the condition. During this procedure, tissues affected by caries are removed and the canals of the tooth that are causing the abscess are cleaned. The source of inflammation is washed with antiseptic solutions, a course of antibiotics, painkillers, anti-inflammatory and hyposensitizing agents is prescribed.
With a more pronounced inflammatory process and the development of signs of suppuration, it is necessary to use a surgical method of treatment. After opening the abscess, conditions are created for the unhindered exit of exudate from the lesion and the gradual subsidence of symptoms. Rinses and mouth baths with an antiseptic effect speed up healing. Another method of surgical treatment of an abscess is tooth extraction. After extraction, the purulent contents of the abscess are released through the hole, which is cleaned and treated with antimicrobial agents.
At the Dentistry Academy Dent, located in the south-west of Moscow, abscess treatment is carried out using modern methods of high efficiency. The clinic is equipped with advanced dental equipment and materials, the quality of which is recognized throughout the world. A specialist with many years of experience in the successful treatment of inflammatory and destructive gum diseases, after a thorough diagnosis, will create an individual treatment package and give professional recommendations.
How to prevent a tooth abscess from occurring
To reduce the likelihood of developing a disease, you need to constantly follow these simple rules:
- brush your teeth two to three times a day;
- After each meal, rinse the mouth with warm water;
- use only high-quality hygiene products, carefully choose toothpaste, brushes, dental floss, irrigators, dental lotions and rinses;
- eat a balanced diet, eat as many fresh fruits and vegetables as possible, make sure that your diet includes solid foods that require thorough chewing;
- visit the dentist twice a year;
- undergo professional oral hygiene procedures annually;
- promptly treat all emerging diseases of the teeth and gums, prevent the progression of caries, pulpitis, and gingivitis.
It is also important to pay special attention to gum health. If they often become inflamed and bleed, perhaps the body lacks vitamins, minerals, or the tartar has become too large and is putting pressure on the delicate gum tissue. It is necessary to establish the cause of the problem and be sure to eliminate it.
People who take good care of the health of their teeth are much less likely to encounter an abscess and the complications caused by it. Therefore, do not forget the importance of maintaining oral hygiene.
Opening a gum abscess
The mainstay of treatment for most cases of gum abscess is surgery. An abscess is a source of infection, most often developing due to prolonged lack of treatment for carious complications of the corresponding tooth. A swelling that forms on one side of the gum may contain pus, exudate, dead lymphocytes and a large number of pathogenic microorganisms. Over time, the abscess becomes larger and the risk of the contents spreading into surrounding tissue increases. Therefore, for effective treatment, removal of pathological contents from it remains a prerequisite.
An abscess is opened as follows:
- the doctor examines the extent of the lesion and determines the causative tooth;
- the oral cavity is thoroughly treated with an antiseptic solution;
- an anesthetic is administered for pain relief;
- Using a scalpel, a small incision is made on the gum, which should pass through the most protruding area of the abscess;
- the cavity of the lesion is washed with drugs with antimicrobial activity, the pathological contents are removed;
- A therapeutic and protective bandage is applied, and recommendations on its contents are given.
After the operation, the acute period of the disease subsides, pain and swelling decrease. Further treatment consists of taking medications prescribed by the dentist; it is recommended to do rinses and mouth baths. In some clinical cases, an abscess can be treated only after extraction (removal) of the tooth that caused the development of the disease. After complete recovery, suitable prosthetic methods are considered. If during the diagnosis it turns out that it is possible to avoid removal and save the causative tooth, after stopping the acute processes in the area of the abscess on the gum, therapeutic treatment is carried out (preparation, cleaning of the canals).