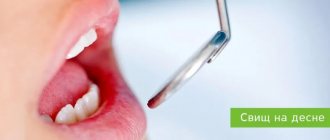
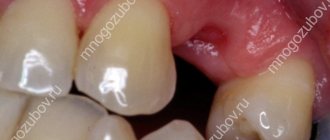
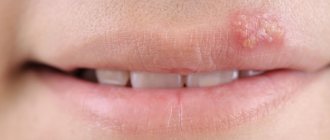
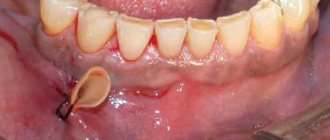
In this article, we will analyze the main factors for the formation of pus in the gums, and what treatment of the pathology is recommended by the dentists of the Dentika clinic.
The accumulation of exudate in the gingival membranes is a dangerous symptom indicating the development of an inflammatory process. This phenomenon should not be ignored. If an inflamed infiltrate appears in the mouth, you should immediately seek professional help. No less serious organic diseases can be hidden under the guise of dental pathologies. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose the disease and select the optimal treatment.
Why does pus come out of the gums?
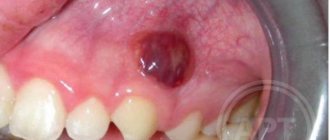
The pathological process is of infectious origin and develops when food particles enter the gum pocket and decay begins. Dead microbes and dead immune cells (exudate) gradually accumulate inside. An abscess indicates infection of deep tissues. The human body strives to protect itself and cleanse the affected area from the pathogen. When pathogens spread, blood circulation increases. As a result, immune cells are rapidly transported to the source of infection to detect and neutralize bacteria.
Then pus accumulates on the upper or lower gum and a purulent sac is formed. Gradually, the flux expands, reaches the periosteum, causing swelling, swelling of the gum tissue and the inside of the cheeks. The mucous membrane of the jaw becomes red and a fistula forms on it. A fistula is a kind of channel through which there is a copious flow of exudate from the source of infection to the outside.
Signs indicating a problem
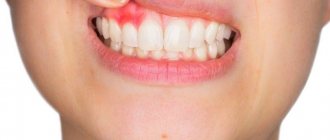
The first signs of infection of the oral mucosa are pain and discomfort during meals. A fistula in the jaw is not at all a harmless phenomenon. Clinical symptoms of the pathology:
- Taste of bitterness.
- Unpleasant sensations when eating cold and hot foods.
- Burning throbbing pain.
- Facial asymmetry.
- Discomfort during palpation.
- The gums are swollen, inflamed, when pressure is applied there is pus, blood, and an unpleasant odor from the fistula.
- Cheek swelling.
- Edema.
- Changing the natural shade of teeth.
The formation of a fistula in the jaw indicates a hidden course of the pathological process in the body. The diseased unit near which the abscess is located is most often covered with plaque or affected by caries. If you ignore the symptoms, the condition will worsen. Possible increased body temperature, weakness, migraine, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes. If any of the listed symptoms appear, you should seek qualified medical help.
The condition when pus has formed in the gum is called an abscess. The progression of pathology leads to disruption of the dentogingival apparatus, increased mobility of units and their loss. With inflammation of the periosteum of the upper jaw, swelling of the lip and facial area under the eye increases. When the lower rows are affected, swelling of the chin and cheek area is observed. Swelling may remain for two to five days after treatment.
Types of dental abscess
Pyogenic bacteria enter healthy gum tissue through the bloodstream or due to mechanical damage. An abscess appears in the area of the affected element. When the abscess matures, the mucous membrane acquires a bluish tint, and a whitish spot or characteristic bubble appears. With its rupture, a fistula is formed in the periodontium, through which the contents flow out. This phenomenon does not lead to the disappearance of the problem, the inflammation remains. The pathology is indicated by the flow of pus from the gums when pressing on the affected area. There are several types of abscess:
- Desnevoy. The lesion is on the surface of the soft membrane and interdental papillae. The cause of infiltration is associated with the ingress of food debris and mechanical injuries. If detected early, it responds well to treatment.
- Periapical. A common type of pathology that develops as a result of untreated carious lesions or periodontitis. Infection of the dental root system leads to the accumulation of exudate in the upper part of the root. When immunity decreases, the periosteum of the unit and the mucous membrane are affected, a fistula is formed, purulent sacs appear above the gum, and pus is released.
- Periodontal. The infiltrate develops inside the gum tissue. Infected contents accumulate in the mucous membrane, forming a protrusion in the periodontal pocket. Due to the lack of a channel for fluid to flow out, damage occurs to the bone and soft tissue surrounding the diseased element. There is a high probability of developing periodontitis.
- Pericoronal. The pathological process is characteristic of erupting units. Bacteria and food debris fall under the “hood” of the mucous membrane. As a result, pus accumulates above the tooth, the gums swell and cause pain. The disease is dangerous due to complications: swelling of the neck, angina pectoris.
- Periodontal-endodontic. Infectious damage to the pulp and periodontal tissues occurs. There is a risk of periodontitis.
Flux is characterized by several stages of development, which have characteristic manifestations:
- Serous. Lightning current. The inside of the cheek and mucous membranes swell within a couple of days.
- Purulent. Continuous, debilitating, throbbing pain in the unit. Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. Hyperthermia.
- Diffuse. Swelling and soreness of the entire surface of the oral cavity, affecting the nose, lips, and outer cheeks.
- Chronic. Gradual progression over months or years. Long-term remissions are followed by relapses. As the swelling decreases, the inflamed areas remain firm.
What diseases are there?
Staphylococcal and streptococcal infections include:
- boils,
- carbuncles,
- hidradenitis,
- abscesses,
- purulent wounds with damage to the integrity of the skin.
The most common ways of charging are your own skin, skin folds, subungual area, nasopharyngeal mucosa, as well as contact with an infected person. Reduced immunity is a predisposing factor in the occurrence and development of purulent infections.
Boils
A furuncle is an inflammatory process of the hair follicle of the skin. Staphylococcus aureus is the cause of the disease. Clinically, a boil looks like this: the appearance of a pustule in the form of tension and soreness of the skin in the hair area, with redness of the affected area. The affected area has a clear rounded outline and over time takes on a dark purple color with a purulent grain in the middle. The size of boils reaches from 0.5 cm to 1.5 cm. Favorite localization: neck, face and back. But it can develop on any part of the body.
Carbuncles
A carbuncle is the same boil that involves several hair follicles and sebaceous glands in the process. It has many heads with purulent contents. The cause of development is: staphylococci and streptococci. In terms of the size of the skin lesion, the carbuncle is larger (up to 2.5 cm) and clinically develops more clearly. When developing, a multi-headed carbuncle causes fever and general malaise. The favorite localization of the carbuncle is the skin of the back, shoulders and neck.
Carbuncles often give complications in the form of lymphadenitis, thrombophlebitis, meningitis and the development of sepsis.
Hidradenitis
Hidradenitis (otherwise called “bitch udder”) is a purulent inflammation of the axillary sweat glands, as well as the apocrine glands of the perineal region. The routes of transmission of infection are through lymphatic vessels or damaged skin. The clinical picture begins with the development of a dense nodule accompanied by a painful symptom; a pustule does not form at the site of inflammation and there are no necrotic masses. With myomalacia of the affected area, pus comes out in the form of a fistula. If several glands are involved in the process, they merge. Intoxication increases with increasing temperature, malaise, etc.
Abscesses
An abscess is an infectious and inflammatory process involving the skin layers and subcutaneous tissue, with the formation of a purulent “sac”. The causes of abscesses are very different: superficial and deep injuries, hematomas involving secondary infection, post-injection complications, furunculosis, carbuncles, etc. Accompanied by pain in the developmental area, as well as increased temperature and fever.
Purulent wounds
A purulent wound is damage to the integrity of the skin (deep or superficial) with the addition of staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. Wounds of this kind do not have a specific localization due to the spontaneity of the occurrence of injuries of various etiologies (mechanical, chemical or somatic origin).
Causes
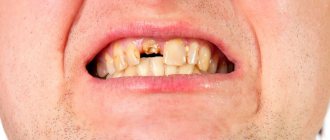
In the vast majority of cases, the reason for the development of dental diseases is improper oral care and negligent attitude towards health. As practice shows, infiltration is formed due to cuts, injuries, and the use of dental prosthetic structures of the wrong size or shape. Constant damage to the mucous membrane leads to suppuration.
When asked what to do if a tooth hurts, a purulent sac on the gum bursts and pus starts to flow, a qualified dentist should answer. In such a situation, urgent sanitation of the abscess is required. In a person who ignores the symptoms of infiltration, the infection can invade the periosteum tissue. The onset of complications is indicated by hyperthermia and unbearable toothache. The pathology does not disappear on its own. A person needs quick and qualified medical care.
Inflammation with discharge of pus during periodontitis
If a bubble with putrefactive contents is located near the top of the root, the flux can spread to nearby elements. The affected area becomes swollen, touching it provokes severe pain.
Periodontitis is accompanied by the appearance of periodontal pockets between the mucous membranes and the surface of the tooth root. Deposits accumulate in the cavity, causing inflammation. There is swelling, bleeding, and pus is squeezed out of the gums during hygiene procedures.
Violation of the outflow of fluid from the pocket leads to the formation of periodontal suppuration.
Presence of injury
The development of an abscess can be triggered by mechanical damage:
- careless use of toothpicks or dental floss;
- cleaning with a stiff brush;
- incorrect installation of the crown;
- the presence of destroyed units with sharp edges.
Injuries accompanied by damage to the periosteum can lead to periostitis with the leakage of putrefactive contents through the fistulous tracts.
Timely seeking medical help will make it possible to understand that pus has accumulated between the tooth and gum and prevent the development of phlegmon. Diffuse inflammation appears due to rupture of the cyst and spread of infection to surrounding tissues. This is caused by the patient’s negligent attitude towards medical prescriptions and refusal of antibiotic therapy.
Emergency actions in case of suppuration
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the source of infection. Don't delay visiting the dentist. Self-medication is dangerous to health.
Before seeking medical help, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- The use of warm compresses is prohibited. Heat can cause the disease to worsen.
- It is allowed to apply a piece of ice to the problem area. This will reduce pain.
- If an abscess is detected in the mouth, then qualified dental care is required.
Only a doctor can correctly diagnose the pathogenesis of infiltration and determine how and how to treat a purulent pimple and gum inflammation.
It is necessary to contact the dentist on time to prevent complete destruction of the pulp and the onset of putrefactive processes in the periosteum. To relieve inflammatory pathology, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications are taken under the supervision of a specialist.
Purulent diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue
Purulent diseases of the skin and subcutaneous fat are the most common purulent diseases (about 30% of diseases in this group). At an outpatient clinic appointment with a surgeon, they account for almost 70%. The most common causative agent of these diseases is staphylococcal flora (70-90%).
The main conditions for the development of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the skin and subcutaneous fat are:
- reduction of local tissue resistance;
- reduction of general resistance and immune defense of the body;
- the presence of microflora in sufficient quantity for the development of the disease.
Furuncle
Furuncle is a purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding tissues.
As the process develops, inflammation spreads to the sebaceous gland and surrounding tissues. The causative agent is most often Staphylococcus aureus. Their occurrence is facilitated by: dirt, cracks, skin abrasions, non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements, diabetes mellitus, vitamin deficiencies, hypothermia, etc. Boils do not develop on hairless skin (palms, palmar surfaces of fingers, soles).
Clinic. A pustule with a small inflammatory infiltrate in the form of a nodule forms around the hair root. The skin over the infiltrate is hyperemic and painful on palpation. Boils in the vestibule of the nose, in the external auditory canal are accompanied by significant pain. Necrosis forms at the top of the infiltrate. For 3-7 days. the infiltrate melts, and the necrotic tissues, along with the remnants of hair, are excreted with pus. Boils on the face and scrotum are accompanied by severe swelling, which is explained by the looseness of the subcutaneous tissue. The resulting wound is cleaned, granulated, and a white scar is formed.
With boils in the area of the upper lip, nasolabial fold, nose, suborbital region, a serious condition is possible with the development of progressive thrombophlebitis and transition to the venous sinuses, dura mater, and the development of basal meningitis and sepsis (fever above 40°C, facial swelling, stiff neck).
A furuncle can be single, but sometimes many foci of inflammation appear simultaneously or sequentially one after another in different areas of the skin - furunculosis. The appearance of many boils on a limited area of the body is called local furunculosis, on a large surface of the skin - general furunculosis. Sometimes the appearance of boils in the form of multiple rashes continues with small remissions for several years. This process is called chronic, recurrent furunculosis.
Treatment. Treatment of boils is carried out according to the general principles of treatment of surgical infection. When the boil is localized above the nasolabial fold, antibacterial, detoxification, anti-inflammatory, restorative therapy, bed rest, prohibition of talking and chewing (liquid food) are required. “Squeezing a boil on the face is like death!”
For patients with chronic recurrent furunculosis, in addition to general and local treatment, it is advisable to prescribe nonspecific stimulating therapy in the form of autohemotherapy. Transfusion of small doses of preserved blood, subcutaneous administration of staphylococcal vaccine or autovaccine, immunization with staphylococcal toxoid, γ-globulin are also used. After analyzing the immunogram, immunostimulating therapy aimed at correcting immunodeficiency is indicated. Recently, ultraviolet irradiation and laser irradiation of autologous blood have been widely used.
Carbuncle
Carbuncle is a confluent purulent-necrotic inflammation of several hair follicles and sebaceous glands with the formation of general extensive necrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
The disease is caused by staphylococcus, sometimes by streptococcus. Extensive necrosis forms, around which suppuration develops. The course of the disease is accompanied by symptoms of intoxication. Complications – lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, thrombophlebitis, meningitis, sepsis.
When differentially diagnosing a carbuncle, it is necessary to remember about anthrax carbuncle, which is characterized by a dense black painless necrotic scab in the center, the phenomenon of regional lymphadenitis and severe general intoxication.
Treatment Treatment of carbuncle is carried out in a hospital setting, bed rest is prescribed. Surgical treatment of the purulent-necrotic lesion (with excision of necrosis) is performed under general anesthesia. Antibacterial, detoxification, anti-inflammatory, and restorative therapy are mandatory. If the process is localized on the face - prohibition of talking, liquid nutrition.
Hidradenitis
Hidradenitis is a purulent inflammation of the apocrine sweat glands, which are located in the armpits, perineum, and nipple area (in women).
The infection enters through the ducts of the glands through the lymphatic vessels or through damaged skin. A dense, painful nodule appears in the thickness of the skin. When the latter melts, a symptom of fluctuation is determined, spontaneous opening of the abscess occurs with the formation of a fistula. Merging infiltrates form a conglomerate with multiple fistulas.
Differential diagnosis. Unlike a boil, hidradenitis does not form a pustule or necrosis. Hidradenitis also needs to be differentiated from lymphadenitis, tuberculosis of the lymph nodes, lymphogranulomatosis, and lymphosarcoma. The main difference is that hidradenitis develops in the thickness of the skin, and all types of lymph node lesions develop in the subcutaneous tissue.
Treatment. The main method of treatment is radical surgery to excise conglomerates of inflamed sweat glands. The second component of treatment choice is anti-inflammatory radiation therapy. For recurrent forms, specific immunotherapy and restoratives are indicated.
Abscess
An abscess (ulcer) is a limited accumulation of pus in tissues and various organs.
The cause of an abscess may be the penetration of infection through damaged skin, as a complication of other local infections (furuncle, lymphadenitis, hidradenitis, etc.), as well as metastatic abscesses during sepsis. A feature of the abscess is the presence of a pyogenic membrane, the inner wall of which is lined with granulations.
Clinic. The course of an abscess can be acute or chronic. With this purulent disease, all the typical signs of inflammation are revealed - color, dolor, tumor, rubor, functio lese. An abscess is characterized by a symptom of fluctuation (“fluctuating”). General symptoms depend on the location of the abscess.
Differential diagnosis. Chronic abscess must be differentiated from tuberculous leaks, aneurysm, and vascular tumors.
Treatment of abscesses is carried out according to the general principles of treatment of surgical infection, including surgery and drug therapy.
Phlegmon
Phlegmon is a diffuse inflammation of tissue (subcutaneous, intermuscular, retroperitoneal, etc.).
Cellulitis is caused by both aerobic and anaerobic (usually non-clostridial) microorganisms. According to the nature of the exudate, phlegmons are divided into serous, purulent and putrefactive. The difference between phlegmon and an abscess is the absence of a pyogenic membrane, which ensures a fairly rapid and extensive spread of the purulent process. Clinically, phlegmon is determined by all signs of inflammation.
In case of serous form of phlegmon, conservative treatment is allowed; other forms are treated according to the general principles of treatment of surgical infection.
To avoid purulent skin diseases or to receive professional treatment, you need to make an appointment with a surgeon.
How are gums treated?
Periodontitis therapy begins with the removal of plaque and tartar. The use of local remedies relieves the problem only for a short period of time. The latent course of the inflammatory process continues, leading to an increase in the depth of periodontal pockets and increased destruction of the bone tissue adjacent to the element.
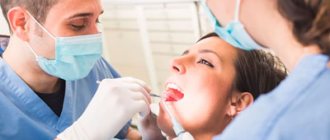
An abscess in the mouth is a source of infection. The surgeon must open it up and remove the pus from under the tooth in the gum without pain. Infiltration anesthesia is used. The resulting wound is treated with antiseptic solutions. Drainage is used to prevent premature overgrowing and ensure the flow of contents.
Therapy in dentistry
Depending on the severity of the condition, drug or surgical treatment is chosen.
Conservative technique is a long and labor-intensive process consisting of several stages:
- Survey. The dentist studies the patient’s medical history and finds out when and under what circumstances a purulent formation appeared on the gum. It is important to know how quickly the pathology progressed.
- Clinical examination. The location, shape and color of the abscess are studied. If necessary, X-ray diagnostics of the diseased part of the jaw is performed. An image is required for an objective assessment of the state of the structure of internal tissues. The further method is chosen depending on the severity of the case.
- Disinfection of the oral cavity. Thorough removal of food debris, plaque and tartar. Antiseptics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
- Treatment of purulent gums by creating an outflow of contents from the abscess. The medical procedure is performed at the Dentika clinic under local anesthesia. The surgeon carefully dissects the affected area and installs a drain into the created incision to cleanse the cavity of infected fluid.
Long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs is required. To prevent re-formation of the infiltration site, antibiotics and local antiseptic rinses are prescribed.
Some patients are bothered by excruciating toothache and complaints that pus is released when pressing on the gums while chewing. At the same time, there is no lump on the jaw. In this situation, the scheme described above will be ineffective. Surgery is required. If there is a filling, the surgeon carefully removes it and cleans the canals, washing out purulent accumulations. A small area of inflammation allows for filling.
If a granuloma or cyst is present, a temporary filling is placed for 3 months. At the end of the specified period, an x-ray is taken. If positive dynamics are observed, filling and crown installation are performed.
Additional procedures
A qualified dentist will tell you how to treat your gums if a purulent sac bursts and pus appears, and will give recommendations for further care of your teeth and oral cavity. To increase the effectiveness of conservative therapy, most doctors prescribe a course of physiotherapeutic procedures: electrophoresis, ultrasound and laser techniques. After passing, positive dynamics are noticeable. If all medical recommendations are followed, there is a decrease in discomfort and swelling, and a general improvement in well-being.
Recovery
Many patients are wary of going to the dentist and wonder whether treatment for purulent gums can be painless. Dental invasive interventions are performed under anesthesia without discomfort for the patient. Despite this, opening and draining an abscess is additional stress for the body. To speed up healing, you should follow the recommendations:
- Follow medical instructions.
- Take prescribed medications.
- Protect yourself from stress.
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet.
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Perform daily hygiene procedures.
- Use irrigator, floss and dental rinse.
Compliance with the recommendations contributes to accelerated recovery and prevention of relapses.
Purulent wound - symptoms and treatment
An infected wound should be treated immediately. It requires an integrated approach, i.e. it must affect both the wound and the body as a whole.
To combat the causative agent of wound infection, use:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antiseptics (miramistin, chlorhexidine, prontosan, betadine);
- immunological preparations (pentaglobin, gabryoglobin, imbioglobulin).
On the first day, empirical antibacterial therapy (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, ciprofloxacin) is most often prescribed. Therapy is then adjusted depending on the results of bacterial cultures, taking into account the sensitivity of the identified infection to antibiotics. In addition to antibacterial drugs, patients are prescribed bacteriophages (viruses that selectively kill bacterial cells).
Also, in the case of a purulent wound, a comprehensive detoxification of the body :
- hemodilution - dosed dilution of blood with plasma-substituting fluids;
- accelerated neutralization, destruction and elimination of toxins, metabolites and biologically active substances using forced diuresis (increased urine volume), intravenous administration of solutions and blood purification methods - plasmapheresis, hemofiltration and hemodialysis.
Symptomatic therapy includes pain relief and correction of damaged organs and systems.
In addition to surgical treatment, wound drainage . It allows you to improve the outflow of pus. To do this, various tubes, half-tubes and glove drains are installed in the damaged area.
Hypertonic solutions, hydrogels, proteolytic enzymes in the form of powders or solutions, UHF therapy, various methods of cavitation (ultrasonic exposure), plasma and laser treatment of the wound can be used locally to cleanse the wound. In particular, proteolytic enzymes, acting as a “biological scalpel,” help remove dead tissue from the wound [14].
Treatment of a purulent wound should only be carried out under the supervision of a physician, since the drugs used can cause an allergic reaction [6].
To stimulate regeneration, zinc-containing ointments, vitamins, ultraviolet irradiation, sea buckthorn and rose hip oil are used. The method of applying secondary sutures is also widely used . They are applied only after the wound has been cleansed of pus. To speed up healing and prevent the formation of a hypertrophic scar, it is possible to use a laser, a pulsating magnetic field and electrophoresis with lidase (a special enzyme).
Modern treatment methods include systemic ozone therapy . It improves the utilization of oxygen in the body, has a detoxifying and immunostimulating effect [16].
There are several methods of ozone therapy. The most commonly used in the treatment of purulent wounds include:
- external use of a gaseous ozone-oxygen mixture (direct exposure to a device that supplies ozone to the wound);
- the use of special caps with normal or reduced gas pressure (for example, “ozone boots” - the limbs are placed in a hermetically sealed plastic bag, into which an ozone-oxygen mixture is then supplied at a certain pressure for 15-30 minutes).
Hyperbaric oxygenation (HBO) has also shown good results in the treatment of purulent wounds . It is carried out in special medical pressure chambers: the patient is placed for a certain period of time in a pressure chamber containing oxygen under high pressure. In addition to eliminating tissue hypoxia (lack of oxygen), HBOT suppresses the proliferation of anaerobic bacteria and destroys aerobic bacteria. This method also reduces the formation of toxins and increases the body's immunity.
Dermoplastic surgeries are used:
- with extensive defects against the background of a satisfactory general condition of the patient;
- after cleansing the wound;
- in the absence of inflammation and circulatory disorders in the tissues surrounding the wound;
- when bright granulations appear (young connective tissue with an abundance of blood vessels);
- in the presence of a small amount of serous discharge from the wound;
- when self-healing is impossible.
There is full-thickness skin grafting, which allows you to completely restore the skin, providing good cosmetic and functional results. It is divided into plasty using local tissues and a displaced skin flap (Indian plasty, Italian plasty on a feeding pedicle, as well as microvascular plasty techniques). These methods of surgical wound closure are not always feasible (for example, with extensive soft tissue defects, localization of wounds in sedentary areas of the skin). Therefore, in some cases, plastic surgery with a free split skin flap is used [12]. After this operation, the wound heals through a scar - the skin is not completely restored.
The choice of skin grafting method is carried out taking into account the type and location of the wound, the individual characteristics of the patient, the condition of the surrounding skin and the nature of the tissue.
The modern and most effective method of treating purulent wounds is the VAC (vacuum therapy) method [18]. Due to the effect of negative pressure on the bottom and edges of the wound, it accelerates the formation of granulation tissue, improves local blood supply and reduces swelling. All this promotes rapid wound healing and enhances the effect of drug treatment [20].
Vacuum therapy is carried out as follows:
- to begin with, dead and damaged tissue is completely removed from the wound;
- the cleaned wound cavity is filled with special foam (polyurethane sponge);
- a drainage tube is attached to the surface of the sponge to remove air and exudate;
- to fix the bandage and maintain the vacuum, the resulting structure, together with the edges of healthy skin, is covered with an adhesive transparent film;
- the drainage tube is connected to an aspirator (VAC device), which creates the required level of pressure and draws fluid from the wound [19].
Unlike aseptic gauze dressings, which need to be changed every day, vacuum dressings can be left in the wound for 3-7 days. Due to their tightness, they reduce the risk of new infection [17]. In this case, the destruction and removal of pathogenic microorganisms occurs two times faster than with other methods of treating a purulent wound [20].
Contraindications to vacuum therapy:
- incomplete cleansing of the wound;
- osteomyelitis (inflammation of bone tissue);
- blood clotting disorder;
- malignant tumor in the wound;
- skin fistulas;
- allergic reaction to the components used [20].
Is it possible to cure an abscess at home?
Patients with acute conditions are admitted to dentistry without a queue. Therefore, if your health worsens, you should not postpone your visit.
The first question that a patient has is: why does pus appear in the gums and how to treat the pathology? The cause of infiltration is a weakened immune system and non-compliance with dental care measures. At the first symptoms of inflammation, you should immediately consult a dentist. Self-opening of a flux neoplasm threatens the addition of a secondary infection.
It is strictly forbidden to heat the inflamed area. Heat activates purulent-necrotic processes and accelerates the spread of infectious agents.
Timely sanitation of the inflammatory focus in a clinical setting prevents complications.
Symptoms and causes, what to look for
Furunculosis and carbunculosis are serious pathological phenomena. Symptoms include general malaise and fever. Over time, the patient's general condition may worsen. Inflammation takes on a wide scale. The necrotic process can involve nearby tissues, penetrating deeper into the subcutaneous tissue and muscles, and pus can spread throughout the fascia. This is fraught with purulent meningitis, peritonitis and sepsis. When pustules with purulent contents appear, surgical intervention is necessary.
Hidradenitis, abscess and purulent wounds do not require delay, but immediate surgical treatment. These infectious diseases quickly cause complications, especially in patients with reduced immunity (patients with diabetes mellitus, lymogranulomatosis, tuberculosis, anemia, etc.).
Folk remedies
The effectiveness of treatment depends on proper diagnosis and strict adherence to medical prescriptions. Dentists at the Dentika clinic are able to correctly diagnose the problem and correctly select therapy. It is worth remembering that any disease is easily eliminated at the initial stage.
If it is not possible to immediately visit a doctor for dental diseases, the use of traditional medicine methods is allowed.
Pus under a tooth or above the gum can be an independent disease or signal the development of periodontitis or gingivitis. These are serious pathologies that do not go away on their own.
The use of antiseptic rinses helps to temporarily relieve inflammation:
- You can dissolve a teaspoon of soda, table salt or two furatsilin tablets in 200 ml of water.
- 3% hydrogen peroxide solution and warm water in a 50/50 ratio.
- Chamomile decoction. Two tablespoons of the plant are poured with boiling water and allowed to brew.
- Miramistin or chlorhexidine biglucanate solution.
The key manifestation of the disease is pain. Taking analgesics will help ease the wait for a medical consultation.
For applications, use an aloe leaf cut in half.
Why you shouldn't delay visiting the dentist
At first glance, pus on the gums looks like a problem that you can deal with on your own. This is a misconception. A negligent attitude towards one's own health and ignoring the need for treatment increases the risk of complications.
Putrefactive forms of dental diseases occur with symptoms of general intoxication. In the absence of adequate medical intervention, the course of the disease can lead to pathological loosening and tooth loss, and provoke blood loss and sepsis. Acute periostitis is especially dangerous, which can lead to phlegmon of the jaw and other serious consequences, including death.
Prevention
- A healthy lifestyle and daily oral care using personal hygiene products will help prevent the development of gumboil. For cleaning, use a medium-hard brush.
- After each meal, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with a special mouthwash or use dental floss. Instead of a pharmaceutical composition, it is allowed to use an aqueous solution of food salt, sea salt or an alcoholic tincture of propolis.
- Do not use non-sterile objects as toothpicks. Such actions lead to mechanical injuries and infection.
- Periodic professional dental cleaning helps remove stone, which provokes the development of inflammation of the gums with pus.
- The daily diet must be supplemented with fresh vegetables and fruits. Apples, carrots and other solid plant foods cleanse plaque from enamel and strengthen teeth.
It is also important to treat dental defects immediately and undergo regular clinical examinations at least twice a year. It is much easier to prevent dental disease than to treat its negative consequences. You should be attentive to your health and not ignore the warning signals that your body gives.
Let's sum it up
A timely visit to a qualified dentist will help eliminate purulent inflammation of the gums and restore good health.
People who pay little attention to daily hygiene are susceptible to the development of pathology. Bacteria and microbes easily penetrate through damage to the surface of the tooth, causing an outbreak in the pulp. Since there are nerve endings in this area, the inflammatory process is painful and painful. The disease has a rapid course and develops within a day. In the absence of proper treatment, an abscess threatens to damage the jaw bone, tooth loss and generalization of infection in the body.
Most often, flux is detected in adults. Due to bad habits and poor hygiene. People overloaded with work and everyday problems put off visiting the hospital until later. They are interested in what to do if the gums are inflamed, painful, swollen and pus comes out at home. Without professional treatment, advanced diseases provoke inflammation of the root dental tissues.
In young children, the disease manifests itself with mild symptoms. This is due to reduced immune activity in children who are not able to adequately resist infection. The child needs treatment for the initial manifestations of flux, otherwise the weakened body will have to face dangerous complications.
The Dentika clinic has modern equipment and high-class dentists with a rich medical practice. Specialists will quickly determine where the pockets of pus are located in the gums and how to remove them.
Local treatment of purulent wounds
Local treatment is one of the most ancient methods of treating purulent wounds. Currently, the main method of treating purulent wounds, incl. purulent wounds in diabetes mellitus, is radical surgical treatment followed by plastic closure of the wound defect. However, in some cases, surgical intervention does not always manage to adequately remove all non-viable tissue. In this situation, to prepare a suppurating wound for skin grafting or its spontaneous healing, local therapy plays an important role.
The main principle in the conservative treatment of purulent wounds is the targeted use of dressings with a differentiated effect on the wound process, taking into account its phase and characteristics of the course.
The course of the first phase of the wound process is heterogeneous and can manifest itself as limited dry necrosis, scab, or a profusely exuding wound. The objectives of treatment in the first phase are: suppression of infection in the wound, activation of the processes of rejection of necrotic masses, sorption and evacuation of wound discharge.
In the first phase of the wound process, drugs from the group of antiseptics (iodophors, prontosan, lavasept) and hydrophilic ointments (levomekol, dioxykol) are most often used as local treatment for purulent wounds. In the treatment of highly exuding purulent wounds, it is advisable to use biologically active dressings from the group of draining sorbents (diotevin, anilodiothevin). In case of weak wound exudation with the formation of dry necrosis, it is possible to combine drainage sorbents with hydrogel dressings (Hydrosorb, Suprasorb G, APOLLO-PAK) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Treatment of a patient with a burn wound of the leg using hydrogel dressings
If there are areas of wet necrosis in the wound, calcium alginates (Sorbalgon, Suprasorb A, Algisayt) are used as local therapy to quickly reject dead tissue (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 Local treatment of a purulent wound in a patient with diabetic foot
carried out with a sorbalgon bandage
After cleansing the wound of necrosis, the appearance of granulations, eliminating perifocal inflammation and tissue infiltration, it is necessary to solve the following problems: suppressing infection in a purulent wound, creating optimal conditions for the growth of granulation tissue and epithelization, stimulating reparative processes, preparing for plastic closure of the wound defect.
Rice. 3 Structure of modern wound coverings
In the second and third phases of the wound process, treatment of purulent wounds continues with ointments on a water-soluble and hydrophilic emulsion basis (Vinilin, Actovegin, Solcoseryl, sea buckthorn oil), stimulating wound coverings (Collahit) (Fig. 4), hydrogels (Hydrosorb, APPOLO PAK, Suprasorb G) and hydrocalloids (Hydrocoll, Suprasorb N). It is carried out until complete epithelization of the wound or skin grafting.
Fig.4. Collachite wound covering
Thus, local treatment of purulent wounds with differentiated use of modern dressings, taking into account the phase and nature of the wound process, allows you to quickly prepare the wound for skin grafting, and if it is impossible to perform it in the shortest possible time, achieve complete epithelization of the wound defect.
dr-anikin.ru