Drainage in the gums: what is it, what to do in case of accidental loss
Untimely treatment of many dental diseases can provoke complications in which pus accumulates in the tissues.
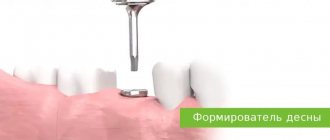
Popularly, this pathology is called gumboil. To eliminate it, endodontic treatment is performed. But, unfortunately, it does not always give a positive result. In this case, the help of a surgeon is required. After the manipulations, the doctor installs drainage in the gum. If many processes do not raise questions among patients, then it is not always clear why the last stage is being carried out. How is drainage installed, for what purpose is it used, what are the features of its application? Let's figure it out together.
Methods of drainage of the biliary tract
Oncologists prefer to perform external internal or, if technically feasible, external drainage of the bile ducts in patients with obstructive jaundice of tumor origin. Both methods are quite effective in preoperative preparation for radical surgery or as a final treatment method. Their advantage is:
- constant monitoring of bile flow;
- the possibility of active removal of blood, pus, and clots from the bile ducts;
- washing the ducts with aseptic solutions;
- dynamic x-ray monitoring of the location of the drainage tube.
Unlike external-internal drainage, bile completely flows out through the external drainage of the gallbladder. The disadvantage of external drainage of the bile ducts compared to external internal drainage is the complete flow of bile through the drainage to the outside. To compensate for the vital substances contained in bile, patients are forced to drink their own bile or medical personnel administer it through a nasogastric drainage. With external internal drainage, the distal end of the tube is located further than the narrowing site and most of the bile flows directly into the intestine. It remains possible to control the patency and flush the drainage and replace it with an internal transpapillary endoprosthesis.
Internal endoprosthetics of the bile ducts is performed after the elimination of jaundice. This is the final stage of treatment for inoperable patients. To successfully perform external or external internal cholangiostomy, oncologists use a set of special instruments: wire guides, special puncture needles, bougies and catheters.
Under local anesthesia using a Shiba needle, the surgeon tightly fills the bile ducts with a contrast agent. A long needle with a diameter of 1.5-1.7 mm performs a puncture of one of the segmental ducts. A conductor wire is then passed through it. The end of the conductor is passed beyond the narrowing, the narrowed area is widened with bougies, and a drainage tube is installed. It is fixed to the skin and the bile ducts are washed with sterile solutions.
This drainage method has disadvantages: there is a risk of bile and blood leaking into the abdominal cavity when the needle is removed, when passing a guidewire or bougienage the canal. Additionally, this complication may be encountered if the outer diameter of the needle is larger than the outer diameter of the guidewire. In order to reduce the number of complications associated with liver puncture, oncologists use the technique of installing a cholangiostomy using a stylet catheter.
Why is medical drainage used in dentistry?
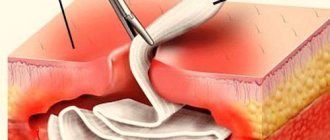
Elimination of purulent diseases of the oral cavity often requires the installation of drainage. This product is a thin tube or strip. It can be rubber or latex. The material is moisture resistant, so it retains its qualities when in contact with saliva. Main functions of drainage:
- removal of purulent exudate from the source of inflammation;
- preventing wound healing until it is completely clean;
- providing access to the incision when it is necessary to introduce drugs into the infected tissue.
When the drainage is installed correctly, the patient almost does not feel it in the mouth. If you feel discomfort or even pain, you need to contact a specialist again.
Almost any disease of the oral cavity, during the development of which an infection is added, requires treatment with the installation of drainage. Most often these are dental diseases:
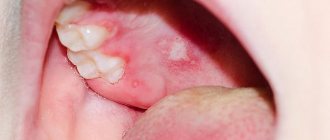
- pericoronitis – inflammation due to difficulty in teething (in adults this is an incorrectly positioned “figure eight”);
- alveolitis - the development of a pathological process in the socket after tooth extraction;
- periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum;
- periodontitis – involvement of the tissues that hold the tooth in the disease process;
- cyst or abscess, periodontitis
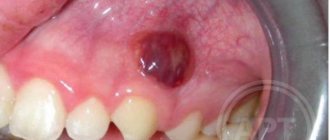
Suppuration may appear as a result of an injury (during complex tooth extraction, damage to the jaw, etc.). For the pathologies described above, drug treatment alone will not help. It is imperative to create an outflow of pus.
Drainage is a complex procedure
It is widely known that in the treatment of a patient, not only the choice of a medical institution and the timeliness of seeking help, but also the qualifications of the doctor treating him are of great importance. The knowledge, experience and skill of a specialist are embodied not only during the operation, but also directly during the patient’s rehabilitation period. In general, the postoperative period is a very difficult period of time, during which all human vital functions are restored. At this time, he is still under the supervision of a doctor who monitors the patient’s condition and carries out all necessary medical procedures to care for the patient. The main problem that can await a patient during this period of his rehabilitation is considered to be inflammation of postoperative sutures. This phenomenon can increase the patient's time in a medical facility, as well as interfere with the healing and recovery process. One of the techniques that prevents the onset of inflammation is the wound drainage method.
Postoperative wound drainage
This technique is aimed at preventing processes that cause irritation and inflammation of the skin. It is based on the use of special drainages, which promote wound healing after surgery and serve as an antibacterial means of protection against external damage and viruses. And this is an incredibly important point that occurs in most cases after complex surgical interventions. Drainage is installed if there is a risk of wound infection, if there is bleeding or discharge from other postoperative departments. Thanks to its use, the process of releasing blood clots or lymph outside the wound occurs. If the wound festers, but drainage allows you to remove clots of pus, which contribute to the proliferation of bacteria and microbes. In most cases, multilayer gauze dressings are used as drainage; latex or silicone dressings are also used, sometimes Teflon. The choice of drainage lies with the surgeon who performed the operation, depending on the degree of infection of the wound. All drainages are treated with special antiseptic substances (like the wound itself), which increases the chances of rapid healing of the suture.
How to make an appointment with a specialist? It's simple. You just need to call the number listed above and make an appointment with a doctor
Contraindications to gum drainage and possible complications
The procedure is not performed in the following cases:
- bleeding disorders;
- individual intolerance to anesthetic substances;
- unstable mental health.
What to do when drainage is impossible? In this case, alternative methods of disinfection and cleaning of the affected area are used. Even when the procedure is performed as indicated, complications are possible. This may include bleeding, ulcers, pain, or increased body temperature. To identify the cause of the complication and eliminate it, you need to visit a dentist.
Endoscopic method
Using an endoscope, doctors perform nasobiliary drainage of the biliary tract. Indications for endoscopic drainage of the biliary tract are:
- obstructive jaundice caused by malignant and benign neoplasms;
- acute purulent cholangitis;
- external biliary fistulas;
- damage to the walls of the extrahepatic ducts, retroduodenal perforations;
- acute cholecystitis.
There are no contraindications to endoscopic drainage, except in cases where the tube for drainage of the biliary tract cannot be passed through the area of tumor narrowing. The endoscopic kit for drainage of the biliary tract through the nose includes:
- conductor wire;
- drainages of various shapes;
- a connecting tube for collecting bile and flushing the drainage;
- nasal tube, clamp and spatula.
The operation of endoscopic drainage of the biliary tract includes the following steps:
- cholangiography to determine the level and location of drainage;
- introduction of drainage with a metal guide-conductor;
- removal of the guidewire and endoscope;
- control cholangiography;
- assessment of drainage position;
- transferring the drainage from the mouth to the nose and fixing it on the head.
After using the endoscopic method of drainage of the bile ducts, complications do not develop. They may occur due to the progression of the disease.
How and for how long drainage is installed
The drainage procedure involves performing the following actions:
- anesthesia of a specific area or the entire cavity;
- incision of the gum in the area of suppuration;
- artificial pressure build-up for cleaning purposes;
- cavity disinfection;
- drainage - installation of a strip or tube.
Only a doctor can tell you how many days drainage is installed. It all depends on the diagnosis and the complexity of the clinical picture. More often, the tube is removed three days after surgical procedures. But the timing may vary in one direction or another. So, if a wisdom tooth has been removed, the drainage can be removed after a day, although it is rarely installed during such an intervention. When a complex surgical procedure was performed, you will need to wear it for a week. If the abscess is not serious and the inflammation has not returned, there is no need to change the gum often. If necessary, the doctor will set a date for the next visit.
It is better to have a doctor remove the drainage. He must ensure that the procedure is completed successfully. Otherwise, a relapse may occur. When the swelling subsides, this indicates complete cleaning of the wound and the beginning of its healing. Independent extraction is possible with the permission of a doctor and after instructions. To do this, you need to thoroughly wash your hands, disinfect your mouth, and pull the free edge of the strip or tube in front of a mirror. The actions are simple, but unsafe, so it’s better not to take risks.
Types of drainage
Drainage has its own types:
- Active - installed for the outflow of liquids through a special tube or hole from the bottom up;
- Passive - on the contrary, is installed according to the top-down principle.
The use of any of the presented types of drainage depends on the patient’s well-being, the degree of complexity of the operation performed, and the presence or absence of signs of inflammation. It is worth noting that failure to use wound drainage greatly contributes to the deterioration of suture healing time and can lead to the entry of microorganisms and infections into the wound, which are especially dangerous for patients in the postoperative period.
You can ask all questions on the topic by phone: +7-(928)-900-32-69
How long does it take to recover after draining pus?
The healing time of the incision depends on the complexity of the clinical picture and the medications used, including antibiotics. To speed up recovery, you must follow the recommendations of specialists:
- do not sleep on the sore side;
- limit physical activity;
- eat soft diet foods;
- refuse hot drinks and food;
- Avoid putting foreign objects into your mouth. This will prevent re-infection;
- take all prescribed medications.
After successful removal of pus, you should not stop treatment. Experts recommend rinsing your mouth with one of the solutions for several days: “Chlorhexidine”, “Miramistin” or hydrogen peroxide (1 tablespoon per 200 ml of water).
If the drainage has been left in place for the allotted time, and after it is removed, the wound swells again and begins to hurt, you need to visit a specialist as soon as possible.