Dental implantation is one of the best methods for restoring lost teeth and allows you to completely restore the anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the dentofacial apparatus. Despite the fact that dental implantation today is performed at a high quality level and is devoid of any disadvantages, sometimes patients still encounter some problems.
One of them is a change in the color of the gums near the dental implant. The Apex dental clinic uses dental implants from the world's leading manufacturers. They boast of their characteristics and allow you to achieve all your treatment goals.
The clinic’s experienced doctors do not make mistakes in their work, which guarantees impeccable quality of dental services with no negative consequences after the installation of dental implants.
And since doctors at the Apex dental clinic are often asked the question of why the gums near the dental implant turn black, today we will talk about exactly this, paying attention to ways to prevent the development of such a complication. Let's start, perhaps, by identifying the possible causes of darkening of the gums after installation of the implant.
Gingivitis: my gums hurt
The process, which is characterized by gum inflammation, swelling, redness and bleeding, is called gingivitis and is one of the most common periodontal diseases in both children and adults. Only 3% of people can boast of absolutely healthy gums. How to get into such a small percentage of lucky ones? The answer is simple - follow the necessary measures to prevent gum inflammation, regularly visit the doctor and not let even seemingly harmless signs of an incipient disease take their course.
Gingivitis is the last of all diseases in periodontology in which the inflammatory process can still be stopped. Next comes periodontitis, a disease in which inflammation spreads to other periodontal tissues. From this point on, treatment is based only on bringing the disease into remission and attempts to relieve symptoms as much as possible at the time of relapses, as well as in the future when it is necessary to resort to tooth extraction. Therefore, gingivitis in children and adults requires increased attention in order to avoid serious periodontal problems.
Questions for the doctor
Teething
Tell me, my son has erupted one upper incisor, and in place of the second, the gums have slightly swollen and a dark spot has appeared. Do I need to take any measures or just wait until the tooth erupts?
The appearance of an eruption cyst at the site of a future tooth is a common occurrence. And usually such a cyst goes away on its own, without outside intervention. But to monitor the condition of the child’s teeth and gums, it is necessary to show him to a pediatric dentist.
Hematoma on the gum
My daughter has a small black dot under one of her lower incisors. We can see a doctor only in a week. What could this be and does it need to be treated somehow?
If, apart from the black dot on the child’s gum, nothing bothers him, there is no swelling or redness, then most likely this is the result of mechanical damage to the gums from a fall or impact. Such a hematoma usually resolves on its own within a few days, so no additional therapeutic measures are required.
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis differs in the nature of its course:
- Acute gingivitis is a disease whose symptoms appear suddenly and progress quite quickly.
- Chronic gingivitis is a sluggish process, the symptoms of which increase gradually.
- Aggravated gingivitis (recurrent stage of a chronic process) is an increase in the symptoms of a chronic disease.
- Gingivitis in remission is the moment of complete relief of all symptoms.
The form is:
- catarrhal gingivitis, which is manifested by swelling and redness;
- ulcerative (ulcerative-necrotic) gingivitis, with necrotic (dead) areas of the gums;
- hypertrophic gingivitis, in which there is a significant increase in the volume of gum tissue and its bleeding;
- atrophic gingivitis, on the contrary, is characterized by a decrease in the volume of gingival tissue;
- desquamative (geographic) gingivitis, which is manifested by intense redness and abundant desquamation of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
According to its distribution in the oral cavity, gingivitis can also be local (affects some areas of the teeth) and generalized (the process affects the gums of the entire jaw or both jaws). And according to severity - mild, moderate and severe gingivitis.
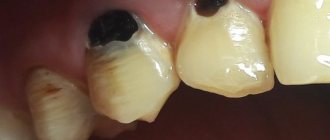
What is black caries?
There is no such term as black caries in dentistry. But among ordinary people this is the name given to the stage of the carious process at which the teeth darken. How does this happen?
“Black caries” may be at the initial stage. In this case, first white and then black dots form on the surface of the enamel - areas of demineralization. In these places, the enamel is thinned and vulnerable to the damaging effects of acid. If you do not pay attention to the blackheads in time and do not treat them, then the caries will go deeper and spread to the dentin.
Sometimes “black caries” is a carious lesion in which a hole has already formed in the tooth. Bacteria produce organic acids and gases, which not only destroy the structure of tissues, but also stain them. With caries, black spots can even show through tooth enamel.
Causes of gingivitis
Most often, gingivitis develops as an independent disease, but sometimes the causes of its occurrence are acute and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, hematopoietic organs, infectious diseases, and changes in hormonal levels. In this case, gingivitis is one of the symptoms of the underlying pathology. The causes of gingivitis can be internal or external.
Internal reasons include:
- tooth growth that injures the gums - the eruption of wisdom teeth;
- vitamin deficiency, hypovitaminosis (most often lack of vitamin C and zinc);
- weakened immune system;
- metabolic disease;
- allergic diseases;
- diabetes;
- stress, mental illness;
- anomalies and various deformations of the gums;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
External reasons are a number of factors:
- physical (injuries, burns);
- chemical (the influence of aggressive substances);
- medical (incorrectly applied fillings, incorrectly installed veneers, traumatic wearing of braces);
- bad habits (smoking, mouth breathing);
- biological (infectious process);
- hygienic (insufficiently thorough hygienic procedures).
Toxins from microorganisms that enter the oral cavity with food and water, as well as those that live there permanently, form dental plaque (plaques) due to insufficient hygiene measures. They are the most common cause of the inflammatory process.
Inflammation can develop differently depending on the cause. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis occurs most often due to unsatisfactory hygiene measures or as a result of gum injury or burns. Hypertrophic gingivitis is caused by crowded teeth, incorrectly installed fillings or dental crowns, as well as changes in hormonal levels, for example, during pregnancy (pregnant gingivitis) or puberty (adolescent or juvenile gingivitis). Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (Vincent gingivitis) is usually caused by an infectious process. It occurs due to the activation of two microorganisms (Vincent spirochete and spindle bacillus) against a background of weakened immunity, hypothermia, stress or malnutrition.
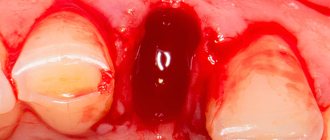
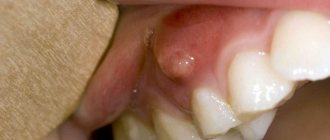
Causes of gum darkening after implant installation
Successful implantation of dental implants is achieved at the Apex dental clinic in more than 90% of cases. Our patients almost never encounter the problem of subsequent darkening of the gums at the site of the installed dental implant, however, for many first-time visitors, this particular problem becomes the reason for seeking help.
Darkening of the gums after dental implant placement can have several causes. First of all, the quality of the selected implant is not high enough. In such situations, despite rapid healing, unpleasant symptoms (including darkening of the gums) may still occur.
Errors during dental implantation can also lead to the development of peri-implantitis. It is often caused by improper oral care after a successful operation.
Some chronic diseases, as well as bad habits, also increase the risk of developing peri-implantitis. Doctors at the Apex dental clinic always carefully analyze the condition of the patient’s teeth in order to issue correct recommendations for caring for a dental implant and inform about the possibility of unwanted symptoms.
Forms of gingivitis and symptoms
Signs of gingivitis directly depend on the nature of the disease and its form. Let's look at each form of gingivitis separately. So, complaints and visual inspection.
Catarrhal gingivitis
This form of the disease usually occurs without obvious pain. Its immediate symptom is bleeding gums when brushing teeth, eating solid foods and other mechanical effects on the dental system.
Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis
This is one of the most unpleasant forms of gingivitis, which is characterized by a feeling of itching of the gingival papillae, severe pain, copious flow of saliva, fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes and the formation of necrotic areas of the gums.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
Patients suffering from this form of gingivitis complain of severe pain, constant bleeding of the gums and a significant increase in the volume of the gums, which can partially cover the crowns of the teeth from the outside (not from the tongue). At the same time, the patient’s gum remains quite hard and under it, on the teeth, tartar forms, which creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms. With hypertrophic gingivitis, teeth may move slightly.
Atrophic gingivitis
The last and most advanced stage of gingivitis, often leading to periodontitis, is atrophic gingivitis. With it, the gum tissue becomes thinner, decreases in size, the necks of the teeth, and sometimes their roots, are exposed. Teeth become more sensitive to temperature changes (cold or hot drinks, frosty air), to sour or sweet foods, to the mechanical impact of a toothbrush.
Desquamative (geographic) gingivitis
The symptoms of this form of gingivitis differ from others by pronounced red spots on the gums, desquamation of the upper layer of the epithelium, the appearance of blisters on the gums and the formation of mouth ulcers and erosions.
Prevention of subgingival caries
The development of the disease is provoked by many external and internal factors. And even if caries has never bothered you, preventive measures will help prevent its occurrence and development. Here are some simple rules doctors recommend following:
- Brush your teeth with toothpastes high in minerals.
- After each meal, use a mouthwash and dental floss - it will help effectively remove pieces of food stuck between your teeth. Oral irrigators can also be used.
- Half an hour after eating, brush your teeth if possible. This should be done twice a day for a couple of minutes.
- Include in your mandatory daily diet foods rich in fluoride, calcium and other beneficial microelements to strengthen enamel, eat more solid vegetables and fruits.
- Avoid excessive consumption of sweets, flour and sour foods.
- Periodically massage the gums: it improves blood circulation in the gum tissues, protects against the formation of deep periodontal pockets and the accumulation of deposits in them, which reduces the risk of caries formation at the neck of the tooth.
If the enamel is thin and susceptible to the rapid formation of tartar on it, regular remotherapy helps a lot - this is the name for applying fluoridating compounds to the teeth. The procedure reduces the risk of enamel destruction and improves the condition of hard tissues. To further strengthen the enamel, you can periodically take special vitamin complexes containing useful minerals. In addition, it is necessary to visit the dentist’s office at least once every six months for a dental examination. The doctor will make sure that everything is fine with them, or will prescribe additional diagnostics using x-rays. Once every 6-9 months, it is recommended to carry out professional enamel cleaning using ultrasound or other methods. During the procedure, plaque and tartar are removed from the surface of the teeth. It polishes and becomes smoother, and less deposits accumulate on the enamel. During cleaning, the doctor can also clean periodontal pockets if plaque and deposits accumulate under the edge of the gums.
People who are at risk for endocrine diseases need to be especially attentive to pain in their teeth. With them, teeth are often affected by cervical caries. Treatment must be comprehensive and systemic to prevent caries from damaging the tooth root. Gingival caries is a dangerous pathological process if it is started, but it can be successfully treated in the early stages.
Modern dentistry eliminates caries of various types, but it also happens that if the stage of the disease is too deep, some teeth cannot be saved. We have to remove them and resort to various methods of restoring the dentition. You just need to be attentive to your oral health, taking simple preventive measures, so as not to have to deal with expensive treatment later. With regular dental examinations, you will be able to detect the problem in time and solve it.
Diagnostic tests
- Schiller-Pisarev test
This test is based on determining the level of glycogen in the gum. Its amount increases significantly during inflammation, while healthy gums do not contain glycogen. Lubricating the inflamed gums with Schiller-Pisarev solution gives a color change reaction from light brown to brown. This research method is used to make diagnoses of both periodontitis and gingivitis.
- Assessment of oral hygiene level
A solution (2 g of potassium iodide, 1 g of crystalline iodine, 40 ml of distilled water) is applied to the outer surface of the six lower front teeth.
The assessment is carried out using a five-point system and each tooth is assessed separately:
- 5 points – complete staining of the entire tooth surface;
- 4 points – staining of ¾ of the tooth surface;
- 3 points – staining of half the tooth surface;
- 2 points - staining of a quarter of the tooth surface;
- 1 point - absence of any staining of the tooth surface.
Then the scores of all examined teeth are summed up and divided by their number (usually the test is carried out on six teeth). This is how the hygiene index is obtained.
As a result, the quality of hygiene is assessed:
- 1.1-1.5 points – good hygiene index;
- 1.6—2.0—satisfactory hygiene index;
- 2.1—2.5—unsatisfactory hygiene index;
- 2.6—3.4—poor hygiene index;
- 3.5-5.0 - very poor hygiene index.
- Vacuum test according to Kulazhenko
Using a Kulazhenko vacuum apparatus, it is possible to determine the time of hematoma formation when a vacuum is applied to the gum area. Typically, the test is carried out in the incisor area by placing a tube of the device on the gum. The formation of a hematoma in 60 seconds indicates the normal condition of the gums, while the appearance of a hematoma in 29-30 seconds signals an inflammatory process.
- Oxygen tension in gum tissue
The sensor of the device is applied to the gum, and the device records the level of tissue hypoxia. Reduced oxygen tension indicates a prolonged inflammatory process.
After implantation, the gums turned blue: other symptoms and diagnosis of peri-implantitis
Regardless of the reasons that caused peri-implantitis, this disease can be characterized not only by changes in the color of the gums, but also by other symptoms. These include bleeding gums in the area of the dental implant, deformation of the gums in this area, mobility of the crown, as well as painful or uncomfortable sensations in this localization.
Only a dentist can diagnose peri-implantitis when conducting an objective examination of the patient’s oral cavity. As a rule, this complication is characterized by all signs of inflammation and may involve swelling and redness, a local increase in temperature in the soft tissues of the oral cavity, etc.
When contacting the Apex dental clinic, already at the initial appointment, the doctor will accurately determine the cause of darkening of the gums after installation of the implant,, if necessary, prescribe additional instrumental research methods (radiography), and also select an individual treatment regimen.
By choosing the Apex dental clinic, you are making a choice in favor of high-quality dentistry and a quick solution to all dental problems that arise!
Differential diagnosis of gingivitis
It is based on the complaints presented to the patient, a visual examination of the patient, the results of functional tests and laboratory tests. The goal of differential diagnosis is to distinguish gingivitis from other periodontal diseases, such as periodontitis and periodontal disease.
The main feature that distinguishes gingivitis from other periodontal diseases is that the inflammatory process affects only the gum tissue, the remaining structures (muscle ligaments that hold the tooth in the jaw and bone tissue) remain unchanged.
Along with this symptom, gingivitis is not characterized by periodontal pockets, exposure of the necks of teeth, or their mobility. And the x-ray shows no signs of bone resorption.
Identifying gingivitis in a timely manner, determining its form and prescribing the correct treatment is the task of a periodontist. But not to forget about prevention and regularly visit the dental clinic is the maximum program for the patient. This is the only way to avoid a more serious periodontal disease – periodontitis.
What to do if the gums near the implant have darkened
Answering this question, we immediately note that darkening of the gums near the implant and the occurrence of peri-implantitis are highly treatable and allow you to solve the problem in a short time.
Of course, as soon as you notice any changes in the area of the installed dental implant, you must immediately consult a doctor to determine the exact reasons for their development, make a diagnosis and carry out the necessary amount of treatment.
Already at the initial appointment, the doctor at the Apex dental clinic will conduct an objective examination and determine a further treatment plan. The specialist will tell you what you can do at home if the gums near the implant have darkened, and will also confirm whether the gums really turned blue after implantation - or in your case this is normal during the rehabilitation period.
A late visit to a specialist is fraught with the development of more serious complications, and therefore we strongly recommend not delaying your visit to the doctor.
Spots on teeth due to fluorosis
It is generally accepted that fluoride is a microelement beneficial for teeth, because it strengthens tooth enamel, increases its protective properties, and prevents the leaching of calcium. But with an excess of fluoride in the body, a disease such as fluorosis can develop. It causes destructive changes in the hard tissues of teeth. Fluorosis is typical for residents of regions where drinking water is fluoridated, as well as for those who constantly brush their teeth with fluoride paste and eat a lot of fluoridated foods. One of the most striking signs of the disease are spots on the enamel. At first they are light, but as the pathology develops they become yellow or dark brown.
Teeth with fluorosis lose strength, chewing surfaces quickly wear away, chips and areas of erosion may appear, and sometimes the disease leads to complete destruction of the dental crown. The choice of treatment method depends on the degree of tooth decay.