7061
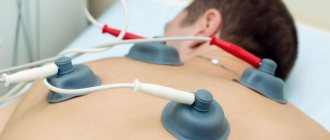
Electrophoresis is a physiotherapeutic treatment method that involves introducing medications into tissues using a low-voltage direct electric current.
This method of delivering drugs to the affected areas has a number of advantages over others (enteral, parenteral, local in the form of regular rubbing, etc.).
In addition, electric current of certain parameters itself has a healing effect on the tissues of the human body.
General information
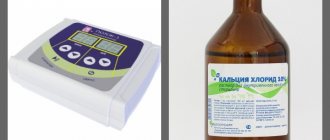
Electrophoresis is performed using special devices - direct current sources with special characteristics. Electrophoresis devices may differ from each other in design and parameters. In 80-85% of cases in dentistry, galvanic type devices are used.
In particular, the Potok-1 device has the following parameters:
- The current value varies in the range of 0-50 mA.
- The output voltage depends on the conductivity of the patient’s skin and ranges from 40-80 V.
- A sound timer with an interval of 1-99 minutes indicates the end of the procedure.
The device has smooth current regulation, stable output voltage and protection against network breaks.
drugs are in the form of solutions in which the therapeutic substances are in the form of negative and positive ions. It is their charge that ensures movement along the electrical circuit and penetration into the affected tissue.
In a simplified form, electrophoresis technology looks like this: pads or tampons, moistened with a medicinal solution, are applied to the oral mucosa (gums) or inserted into the canal (carious cavity) of the tooth.
An electrode called active is connected to them through a hydrophilic gasket. Its second end is connected to the terminal of the device that has the same charge as the drug ions. Another electrode (passive), necessary to complete the circuit, is attached to the skin through a hydrophilic pad.
When voltage is applied to the electrodes, negative ions of the drug solution begin to move towards the anode, and positive ions towards the cathode. In this case, the drugs penetrate into the tissues, accumulate there and actively act on the pathogenic focus.
The duration of one electrophoresis session is 10 - 30 minutes. For a full course of treatment, 10-20 sessions are usually required, carried out every day or every other day.
What is gum, why should it be protected?
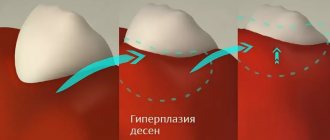
The gum is a mucous surface that covers the alveolar parts of both jaws and covers the incisors in the neck area. The main cause of diseases of the gum area is non-compliance with oral hygiene measures. The destructive effects of periodontal disease begin with the formation of the dental shell from the accumulation of soft deposits and bacteria on the incisors. If all harmful microorganisms are not removed, tartar will form, which subsequently leads to the development of a periodontal pocket and loss of incisors.
The mucous membranes must be protected and gums treated in a timely manner, because in addition to inconvenience and discomfort, this can result in serious diseases.
Indications
Oral diseases for which electrophoresis is indicated include:
- pulpitis (infection in the tooth canal);
- alveolitis (inflammation of the socket in which the tooth is located);
- cysts and granulomas formed in various dental pathologies;
- post-filling pain that sometimes occurs after dental treatment;
- stomatitis (inflammation of the oral mucosa of various etiologies);
- arthritis and arthrosis of the mandibular joints;
- periodontal diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, periodontolysis, periodontoma, apical chronic periodontitis);
- scars on the mucous membranes and skin of the jaws;
- inflamed salivary glands (sialoadenitis);
- injuries, including surgical ones;
- glossalgia (pain and discomfort in the tongue);
- pathologies of peripheral nerves (neuralgia, neuritis).
The need and possibility of electrophoresis is determined by the doctor in each specific case, taking into account the nature of the disease and the patient’s condition.
Modern types of local anesthesia in dentistry and drugs popular among dentists.
Come here if you are interested in methods of treating dental enamel hypoplasia in children.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/zubyi/karies/tsementa-naskolko-opasna.html all the most important things about the treatment of tooth root caries.
Phonophoresis in dentistry
With phonophoresis, the medicine is applied to the surface of the affected organs and injected into the deep layers of tissue using ultrasound.
Indications for phonophoresis
- Ultrasound enhances the effect of antispasmodics and analgesics, so phonophoresis is used to relieve pain after treatment of caries, pulpitis, and tooth extraction;
- Treatment of lymphadenitis;
- Postoperative rehabilitation and scar treatment.
Phonophoresis gives effect after 1-2 procedures. To treat scars and recover after surgery, a course of 5-10 procedures is required.
Contraindications for phonoresis
- Metabolic diseases;
- Acute inflammatory diseases;
- Benign tumors and oncological diseases;
- Facial nerve paralysis.
All methods of physiotherapy are contraindicated in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy.
Sources:
- Personal experience as a dentist;
- Therapeutic dentistry / M.: Geotar-Media, 2012;
- Therapeutic dentistry: textbook: in 3 parts. Part 3. Diseases of the oral mucosa, ed. prof. G. M. Barera. — Moscow: GEOTAR-Media. – 2010;
- Prevention of dental diseases. / Kuzmina E.M. Textbook, publishing house "Poly Media Press" 2001;
- Techniques and methods of physiotherapeutic procedures, ed. Prof. V.M. Bogolyubova. Moscow, 2003;
- Bogolyubov V.M., Ponomarenko G.N. - General physiotherapy. - M., St.-Pb. - 2007;
- Bogolyubov V.M. - Technique and methodology for conducting physiotherapeutic procedures. - M. - 2002;
- Efanov O. I.; Sukhanova Yu. S. - Therapeutic electrophoresis in dentistry. - St. Petersburg. - 2002;
- Muravyannikova Zh. G. - Fundamentals of dental physiotherapy. - Rostov-on-Don. - 2002;
- Ebisu, S. Oral Biofilms and bone resorption / S. Ebisu, Y. Noiri // Clin. Calcium. - 2007;
- Myers, T.D. Lasers in dentistry. Their application in clinical practice / TDMyers // J. Amer. Dent. Ass. — 1991.
Contraindications
Due to the peculiarities of the action of electric current, electrophoresis is not indicated for all patients; there are a number of restrictions on its use:
- Cardiovascular diseases in the stage of decompensation.
- Sclerosis of cerebral vessels.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Oncological diseases (in particular, neoplasms on the oral mucosa).
- Allergy to medications used for electrophoresis.
- Purulent-inflammatory processes accompanied by an increase in temperature above 38 °C.
- Systemic blood diseases.
- Bleeding or susceptibility to it.
- Epilepsy with frequent seizures.
- Presence of a pacemaker.
- Hypertension.
- Active phase of tuberculosis.
- Toxicoses.
- Cachexia.
- Psychosis and hysteria, accompanied by psychomotor agitation.
- Individual intolerance to electric current.
Advantages and disadvantages
Compared to other methods of dental treatment, electrophoresis has a whole set of advantages that allow it to still be widely used in dentistry.
- Complexity of effects (pain relief, bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect, increased trophism and microcirculation in tissues).
- Efficiency and speed of action of the drug thanks to its directional input.
A high concentration of drugs is created in the affected area, which allows you to quickly relieve inflammatory processes in the internal and external tissues of the tooth and gum.At the same time, other areas and the body as a whole are not exposed to the unwanted effects of medications.
- The ability to inject medicine into places that are inaccessible to other methods (tooth enamel, difficult-to-penetrate canals and cavities).
- Insignificant side effects from the medications used . Thanks to their strict dosing and precise administration, the systemic effect is minimized.
- The procedure is painless (only a slight burning and tingling sensation may be noted in the tissues to which the electrodes are connected).
- Low risk of allergic reactions.
- Prolonged action (up to several weeks) of drugs that accumulate (deposit) in the tissues adjacent to the affected area and gradually enter the pathogenic zone.
In contrast to the advantages, the disadvantages of electrophoresis are few. The main one is a significant number of contraindications.
In addition, electrophoresis is not an independent method of treatment. It is used only in combination with other methods of therapeutic or surgical intervention.
Uses of calcium
To restore the enamel and return it to its original characteristics, physiotherapy with calcium gluconate is prescribed.
The session is carried out on an outpatient basis, and in combination with the main treatment. The procedure compacts the tooth surface and fills it with important elements.
Calcium is introduced using electrodes and special solutions. Electrodes are inserted behind the gum, and flat terminals are brought out to connect wires from the device to them. To complete the circuit, another electrode is attached to the hand.
Afterwards, a tampon moistened with a calcium solution is placed behind the lip. After such preparation, the device parameters are set to the required values. Session duration – 20 minutes .
Feelings, achieved effect
Electrophoresis does not cause pain or any significant discomfort. The patient feels only minor sensations in the form of:
- slight tingling in the tissues through which electric current is passed;
- irritation in the hand that holds the electrode (it is recommended to change hands during sessions).
There may be redness of the skin in the area where the hydrophilic pad is applied.
The positive effect of treatment occurs gradually as the number of sessions increases. It is caused not only by the effects of medications.
Electric current itself intensifies metabolism in the area of its action (increases metabolism at the cellular level), improves microcirculation of blood and lymph, and increases tissue trophism.
Who needs electrophoresis and why?
Physiotherapy is used both in medicine and in cosmetology. But in what cases do you choose one method or another? Electrophoresis will help solve such problems in cosmetology as:
- acne, increased sebum production;
- puffiness of the face, bags under the eyes;
- wrinkles and nasolabial folds;
- acne, scars;
- enlarged pores, general skin depletion.
In medicine, electrophoresis is used much more widely, as evidenced by the following indications for use:
- diseases of the respiratory system: pneumonia, tracheitis, bronchitis, etc.
- diseases of the ENT (ear, throat, nose) organs: otitis media, pharyngitis, etc.
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, colitis, etc.
- diseases of the cardiovascular system: atherosclerosis, angina, etc.
- diseases of the genitourinary and nervous systems;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal and endocrine systems;
- skin diseases;
- postoperative rehabilitation: wounds, scars;
- dental and eye diseases.
Before starting electrophoresis procedures, in any case, you should consult your doctor. He will prescribe the required session time (usually from 10 to 20 minutes), the required concentration of the solution and select the medicine. Also, if you are taking any medications or doing other physical therapy procedures, it is worth warning about this. It is very important not to overload the body, especially for children. Electrophoresis for children should last no more than 10-15 minutes a day, for adults - no more than 25 minutes.
Technique
The electrophoresis technique involves placing hydrophilic and medicinal pads (tampons) on the affected teeth and gums, connecting electrodes to them, setting the desired operating mode of the device and supplying current. The steps are performed in the following order:
- A pad or tampon soaked in a medicinal solution is placed on the treatment area (skin, oral mucosa, gums, tooth cavity).
- A hydrophilic pad of the same size, soaked in tap water, is placed on top of the medicinal tampon. It is needed to evenly distribute the current over the entire surface of the treatment pad and ensure the penetration of the medicine into the tissue.
- The second hydrophilic pad is placed on the skin at the place where the passive electrode is connected (most often on the wrist).
- Electrodes are connected to hydrophilic pads: active from the side of the treatment pad or inside the channel with a tampon, passive - to the hydrophilic pad placed on the skin.
- If necessary, the entire structure is secured with bandages.
- The electrodes are attached to the corresponding terminals of the device, the desired mode is selected, and the voltage is turned on.
The current strength, duration and number of sessions are determined by the type of electrophoresis. For example, with transcanal, used to introduce drugs into the tooth cavity, a current strength of 3 mA is used, the session duration is about 20 minutes.
The number of sessions is also determined by the type of pathology. For fibrous periodontitis, for example, 1-2 sessions are performed, for granulomatous or granulating periodontitis - 3-4 sessions (for lesions up to 2 mm) or 5-6 (for lesions up to 5 mm).
Important detail. The location of the positive or negative electrode depends on the form in which the drug is present in the solution - cations (+) or anions (-).
If anions, then a negative electrode (cathode) is connected to the hydrophilic pad placed on the medicinal pad. When current passes, negative ions of the drug will move from the cathode to the anode, penetrating into the skin or mucous membrane.
Intraoral electrode
The device is designed for connection to the oral mucosa. May have different shapes. One option is a round plate with a diameter of 10 mm made of lead, to which a wire in a waterproof sheath is soldered.
The plate is wrapped in a hydrophilic pad made of cotton wool 10 mm thick. The electrode is placed in a rubber cap, which has a hole opposite the plate. When applied to the gum, the hydrophilic pad is adjacent to the area of the mucous membrane that is planned to be exposed to current.
Gingival electrode
Gingival electrodes are designed to supply current to the pre-root area of the gum. They look like a rectangular plate 2-10 cm long with a soldered insulated wire. A bandage rolled into a strip of about 10 layers is used as a pad.
The current strength supplied to the gingival electrode depends on its size and should not exceed:
- 5 mA – for electrode up to 10 cm;
- 3 mA – up to 6 cm;
- 2 mA - up to 4 cm.
Let's consider together the causes of tooth enamel destruction in children and possible preventive measures.
In this publication, read about the importance of premedication in pediatric dentistry.
Here https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/zubyi/kakim-obrazom-deystvuyut-antibiotiki-pri.html we will tell you which antibiotics for toothache are the safest and most effective.
Root canal electrophoresis
Before the procedure, the canals of the teeth are cleaned - first mechanically, then medicinally (with alcohol, ether or a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide).
A cotton swab soaked in drugs is placed at the bottom of the dental cavity and the bare end of an insulated single-core wire (active electrode) is inserted into it.
To prevent saliva from entering the cavity, the exiting wire and tooth are covered with sticky wax (rosin mixed with beeswax in a ratio of 60% and 40%). The second end of the wire is connected to the corresponding terminal of the device. A passive electrode 5x10 cm is connected to the forearm of either hand.
On a note. If there is a gingival fistula, a passive electrode is installed on it to ensure the penetration of the medicine into the fistula.
The current strength during root canal treatment should not exceed 3 mA. The duration of one session is 20 minutes. After its completion, all components (wax, tampon, electrode) are removed from the tooth and a bandage is made of artificial dentin, under which a tampon soaked in eugenol mixed with 5% iodine tincture is left. Sessions are carried out every day or every day.
Uses of calcium
Demineralization is the loss of mineral elements from tooth enamel. Mainly hydroxyapatite (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2), the content of which in the surface of teeth reaches 96%. To restore the composition and properties of enamel, calcium remineralization - electrophoresis with calcium and fluorine.
A 5% (for children) or 10% (for adults) calcium gluconate solution is used as a medicinal solution. The current strength is set to 30 µA. The session lasts 10-20 minutes, after which sodium fluoride is additionally injected into the enamel for 2-3 minutes. The procedure is carried out daily for 1.5-2 weeks.
Calcium remineralization uses disposable gingival electrodes inserted between the gum and lip. A gauze pad is attached between the electrode and the lip.
A long electrode can be applied to the dentition to simultaneously restore several teeth at once. The passive electrode is attached through a damp cloth to the forearm.
Sequence of remineralization:
- Cleaning the surface of the teeth with a special stand, treating with 0.5–1% hydrogen peroxide, drying.
- Electrophoresis with calcium gluconate for 20 minutes. During the procedure, tampons with medication are changed every 5 minutes.
- Electrophoresis with 2–4% sodium fluoride solution.
After remineralization, it is recommended not to eat for 2 hours.
Conclusion
The most pronounced antimicrobial effect is provided by procedures in which an electrode placed in the tooth cavity is connected to the plus of a current source - transchannel anode galvanization and apex phoresis. During the procedure, the active part of the electrode undergoes anodic dissolution, and metal ions, which have a bactericidal effect, enter the surrounding tissues. With transchannel anode galvanization, these are copper ions, and with apex phoresis, they are a combination of silver ions with copper ions. Both methods showed high antibacterial activity against all representatives of anaerobic microflora obtained from the root canals of teeth. in vitro experimental study
confirmed using a bacteriological method and a molecular genetic method for identifying difficult-to-cultivate virulent anaerobic bacteria using a diagnostic kit for PCR MultiDent-5. The data obtained allow us to conclude that transcanal anode galvanization and apex phoresis are an effective means of disinfecting the contents of the root canal in the treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis in teeth with partially obliterated root canals.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Information about authors
Dikopova Natalya Zhorzhevna - Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of the Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education "First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia (Sechenov University); e-mail: [email protected] ; tel.: +7(903)504-9038
Features of use for pregnant women and children
Electrophoresis has no contraindications associated with pregnancy; it is allowed in any phase of pregnancy, as well as immediately after childbirth. The safety of this procedure for pregnant women is explained by the local administration of drugs. The administered drug accumulates only in the tissues of the affected area and does not have a systemic effect on the body.
Important. There are several clinical cases when electrophoresis is contraindicated for pregnant women. This is severe gestosis in the phase of both preeclampsia and eclampsia (a serious complication of pregnancy in the form of high blood pressure, edema, protein leakage in the urine, convulsions), as well as severe toxicosis.
For children, local electrophoresis can be prescribed at the age of 4-6 weeks, and in some cases - from the first days. This requires compliance with some special rules.
- Electrodes with soldered conductors are used, ensuring their reliable fixation to the tissues with bandages.
- A reduced current intensity and fewer sessions are used compared to adults. The current density for preschool children should not exceed 0.03 mA/cm², for school children - 0.05 mA/cm². In some cases, an increase to 0.08 mA/cm² is allowed.
- The procedure begins with small vines and gradually increases after 3-4 minutes to the specified values.
- The duration of the session should not exceed 10 minutes.
- The time between courses should be at least a month.
Important. During the entire course, active monitoring of the child’s response to treatment is necessary - in relation to behavior, sleep, appetite, body weight.
Price
The cost of electrophoresis in private and public clinics depends on the type of equipment, medications used, and payment terms for doctors used in the clinic.
In the price list of organizations, the name “electrophoresis” may mean a different set of procedures and services, so the stated prices may vary greatly.
Electrophoresis itself, excluding medications, is usually inexpensive - from 100 to several hundred rubles per session.
If inexpensive medications are used, in particular, calcium gluconate, the purchase of which for the entire course will require from 100 to 200 rubles, then the price of the entire remineralization course will cost a little more than 1000 rubles.
In the price lists of various dental companies you can see the following prices for one session of various types of electrophoresis.
- Transchannel – 1000 rub.
- Depophoresis of one root canal – from 250 to 500 rubles.
- Electrophoresis of dentin and gums – 400-500 rubles.
Advice. The given data can only serve as a guide; prices in specific conditions may differ significantly from them. When deciding on electrophoresis, you must definitely clarify for how many sessions the price is indicated, and whether the cost of medications is included in it.
How much does the electrophoresis procedure cost?
The pricing policy for the electrophoresis procedure depends on the use of medications, equipment, and forms of ownership of the medical institution. Private clinics offer patients high-quality services and, accordingly, prices differ slightly from the services of municipal medicine.
Electrophoresis in dentistry is used as an effective tool for treating patients.
The therapeutic effect is achieved through the combined effects of electric current and local administration of medications. The body's defense processes are activated.
Reviews
Reviews from patients about a particular treatment procedure are often superior in their benefits to official information.
People are interested in knowing the personal impressions and feelings experienced by a person in their position.
If you have already used electrophoresis for dental treatment, share your impressions with those who have yet to do so. Leave your review at the bottom of the page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags toothache electrophoresis for teeth
Did you like the article? stay tuned