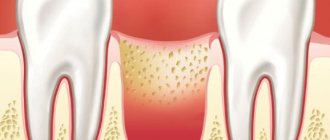
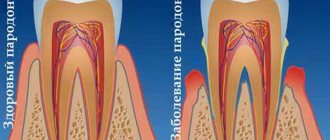
Periodontitis: what is this disease?
Before moving on to considering treatment methods for periodontitis, it is worth finding out what kind of dental disease it is and why it appears. In dentistry, periodontal tissue is the tissue that tightly surrounds the roots of the teeth and holds the tooth itself in its socket. When an infection penetrates into the periodontium, an inflammatory process begins in the tissue, which leads to the occurrence of periodontitis. Treatment of periodontitis should be started immediately, however, the disease cannot always be recognized in a timely manner and independently, since it can develop completely asymptomatically. It is for this reason that it is recommended to undergo regular examinations by a dentist: a specialist will determine the signs of periodontitis and treatment of the disease will be as effective as possible.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
The main cause of periodontitis is pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate into the deep layers of the periodontium, however, there are factors that contribute to the appearance of the disease and accelerate the process of its development. These factors include:
- Untreated or advanced gingivitis;
- Autoimmune diseases (diabetes mellitus, HIV);
- Bite defects;
- Increased tone of the jaw muscles;
- Injuries to soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Poorly performed dental procedures: prosthetics, fillings;
- Stressful and depressive conditions, the presence of bad habits;
- Poor or irregular oral and dental hygiene;
- Some gastrointestinal pathologies.
The listed factors will complicate the treatment of periodontitis, and therefore it is recommended to eliminate them before starting a course of therapy, which means that for effective treatment of periodontitis you will need to visit not only the dentist, but also specialists in other areas of medicine.
Treatment methods
Treatment includes a complex of local and general measures, prescribed individually, based on the results of the examination, according to the severity of the disease, the characteristics of its course, and general health. Effective comprehensive treatment of periodontitis is aimed at eliminating periodontal pockets, strengthening teeth and gums, and preventing the destruction of soft and hard tissues.
Hygienic cleaning
Regardless of the stage of the disease, the first stage of treatment is the removal of all dental plaque. For this purpose, special ultrasonic equipment is used, which allows you to carefully remove plaque and stone even in the most inaccessible places. After curettage (scraping) or ultrasonic cleaning performed using manual instruments, the gums are treated with an antiseptic, and medicinal dressings with an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent are applied.
Drug therapy
For mild cases of the disease, local medications for periodontitis are prescribed (gels, ointments, rinses) that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and healing effects. In difficult cases, systemic antibiotic therapy, hormonal and antihistamine medications, and vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed. Conservative treatment is effective at an early stage of the disease.
Preparations for the treatment of gum periodontitis have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antiseptic effects. The therapeutic effect is provided by using the drug as rinsing solutions, applications to the gums, tablets for oral administration, injections into the gums (vitamins, FiBS, aloe preparations, etc.). Course of treatment – from 2 to 4 weeks
at intervals of several days.
Physiotherapy
For the speedy elimination of the infectious focus and active tissue regeneration, additional physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed - ultraphonophoresis, darsonvalization, ozone therapy, electrophoresis, gum massage, laser therapy. Localized periodontitis can be completely cured at an early stage without resorting to drastic measures. That’s why it’s so important to see a dentist at the first warning signs of illness.
Orthopedic treatment
During the treatment, orthopedic structures are corrected, parts of the fillings are removed from the interdental spaces, and crowns that have sunk deeply under the gum or are installed incorrectly are replaced. Splinting for periodontitis is indicated for degree II tooth mobility. Temporary splinting is carried out before curettage or immediately after it, permanent splinting is carried out a month after treatment.
Surgical methods
In severe cases of periodontitis, with deep periodontal pockets and defects of the gingival margin, in addition to conservative treatment, surgical treatment is required. Radical intervention involves cleaning the periodontal pockets with and without dissection of the gums, gingivectomy is an operation to remove inflamed, overgrown areas of the gums. The intervention involves reducing the volume of gum pockets and forming an aesthetic gingival margin. After the procedure, the natural process of tissue regeneration begins. When the alveolar septa are completely reabsorbed, excessively mobile, non-viable teeth are removed.
In case of significant destruction of the jawbone, when it cannot firmly hold the tooth in place, osteoplastic surgery is performed - directed bone regeneration. To do this, the area between the tooth and the bone is filled with a biocompatible osteoplastic material, which serves as a platform for the formation of new osteoblasts and restoration of bone volume.
Modern methods of treating periodontitis, such as laser and vector therapy, show impressive results. In just one procedure, gum pockets are reduced, swelling, pain, and bleeding disappear. Non-contact methods have a biostimulating effect and significantly accelerate tissue healing. Regardless of the severity of periodontitis, the correct occlusion is determined for all patients, and selective grinding of the teeth is carried out according to indications.
Main symptoms of the disease
It is necessary to know the symptoms of the disease in order to identify the disease in time and begin treatment of periodontitis. Symptoms of periodontal inflammation largely depend on the area of occurrence of the inflammatory process, the phase of its development and form. But the main signs of periodontitis include:
- The appearance of bad breath.
- Yellow plaque on tooth enamel and bleeding gums.
- Inflamed red gums in the area where periodontitis develops.
- Formation of periodontal pockets and gaps between the gums and teeth.
- Pus in periodontal pockets.
6. The appearance of increased sensitivity of teeth, pain when chewing food, the formation of noticeable interdental spaces.
7. Exposure of the roots of the teeth and the appearance of mobility of units, which can lead to their loss.
The symptoms of periodontitis are quite bright and pronounced, but they usually appear in later phases of the development of the disease. The best way to promptly identify periodontitis and begin its treatment in a timely manner is regular visits to the dentist and a preventive examination.
Classification of periodontitis
The most effective treatment for periodontitis can be chosen when its form is accurately diagnosed. Classification of types of disease is carried out according to the severity of its symptoms, the presence of complications and consequences of the development of periodontitis.
Based on the form of the disease, the following types of disease are distinguished:
1. An acute form of periodontitis, in which the process of inflammation in the periodontium develops at a rapid pace and can cause the appearance of abscesses and fistulas.
2. Chronic periodontitis is asymptomatic and its development is slow. The disease may not show itself in any way, but tissue destruction will still occur, and therefore it is so important to diagnose the disease in a timely manner and begin treatment of chronic periodontitis.
According to the area of manifestation, periodontitis is graded into the following types:
1. Localized periodontitis. This type of disease arises mainly from gum trauma and responds well to treatment.
2. Generalized periodontitis. Treatment of generalized periodontitis is a complex and lengthy process, since the disease spreads to a significant part of the periodontium.
Periodontitis is also classified according to the stages of its development and the appearance of various complications that arise due to improper or late treatment of the disease. It is important to understand that only a qualified doctor can correctly diagnose the type of periodontitis and choose a method of treatment. In our clinic in Moscow, Vanstom, innovative methods and means are used to diagnose and treat periodontitis. Come to us for your dental health! Address of our clinic: Moscow, Baumanskaya metro station, st. Bakuninskaya, 17/28.
Causes of periodontitis
A decisive role in the development of the disease is played by pathogenic microorganisms in dental plaque, which contribute to gum inflammation. The accumulating bacterial plaque hardens. Tartar builds up and penetrates deep into the gums, causing the mucous membrane to begin to peel off from the tooth, creating a free space that is gradually filled with pathogenic bacteria. Gingivitis develops, which without proper treatment quickly transforms into acute periodontitis.
Factors that provoke the development of periodontitis also include:
- regular injury to the gums due to incorrectly installed dentures and orthodontic systems;
- incorrect occlusion;
- accumulation of food particles and plaque under prosthetic and orthodontic structures;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- decreased immunity;
- physical trauma to teeth (impact);
- bruxism.
The development of chronic periodontitis can be influenced by problems with the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders, insufficient chewing load (the predominance of soft foods in the diet), autoimmune pathologies, and allergies to certain medications.
Scheme of complex treatment of periodontitis
Treatment of periodontitis is a whole complex of measures and it always begins with a visit to a periodontist, examination and diagnosis. If the disease has reached a moderate and severe stage of development, in addition to consulting a periodontist, it will be necessary to undergo examination and treatment from other specialists - a therapist, prosthetist, and non-dental doctors.
Further treatment of dental periodontitis will be divided into the following stages:
1. Cleaning the supragingival and subgingival space from plaque and tartar. The main cause of periodontitis is poor oral hygiene, and therefore the basis of its treatment will be thorough sanitation of the oral cavity and removal of all types of plaque. The procedure is carried out using ultrasound, which can efficiently remove pigment and tartar from dental surfaces.
The Vector device can also be used to sanitize the oral cavity during periodontitis. This device for the treatment of periodontitis has recently become used in dentistry and its use allows you to efficiently clean the teeth and the space above and below the gums from all types of deposits. The Vector apparatus for the treatment of periodontitis also uses ultrasonic waves, but their action is as gentle as possible and more targeted. Another advantage of using Vector in the treatment of periodontitis is that during the procedure, teeth and gums are treated with a special solution that relieves inflammation, swelling, and promotes rapid healing and tissue regeneration.
2. Treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs. Its goal is to eliminate such unpleasant symptoms of the disease as pain impulses, pus in periodontal pockets, swelling and bleeding of the gums. Anti-inflammatory therapy for periodontitis will be divided into several separate stages:
Local therapy.
Local treatment of gums for periodontitis consists of rinsing and washing the oral cavity with antibacterial solutions; the doctor may also advise treating the areas of manifestation of the disease with antiseptic gels. For the treatment of gums with periodontitis, drugs are prescribed exclusively by a specialist, and they must be used regularly throughout the course of therapy, which usually lasts 10 days.
In some cases, local therapy for periodontitis can be supplemented with physiotherapy or laser manipulation. Treatment of periodontitis with a laser is a service that is advertised by many clinics, but you should know that it is possible to completely cure the disease only by using an integrated approach to its treatment.
Treatment of periodontitis with antibiotics.
The type of antibiotics is selected based on the phase of development of the disease and its form. The drugs can be prescribed to the patient, both in tablets and in the form of injections. In reviews of the treatment of periodontitis from specialists, it is the second option that is recommended, since antibiotic injections give faster positive results in the fight against eliminating the inflammatory process.
In parallel with the treatment of periodontitis, medications are used to eliminate caries and, if necessary, preparation for prosthetics is carried out, which consists of depulping teeth. The depulpation procedure for periodontitis is needed when significant atrophy of bone tissue is observed and the depth of the formed periodontal canals has reached 2/3 of the total length of the tooth root. If the disease has not reached the acute or deep phase of development, then orthopedic treatment of periodontitis will be the final stage of the process. But if there are complications and consequences, therapy for periodontal inflammation can be continued with splinting or the use of surgical techniques.
Symptoms of chronic periodontitis:
But in almost all cases, patients turn to the periodontist precisely with chronic generalized inflammation of the gums, and the medical history is always the same. First, insufficient oral hygiene leads to the accumulation of microbial plaque on the teeth, pathogenic bacteria in which produce “toxins” that trigger inflammation in the gums. At first, the inflammation is only superficial in nature, and is manifested by bleeding and pain when brushing teeth, as well as swelling, redness or cyanosis of the gingival margin.
At this stage, there is still no destruction of the periodontal attachment, destruction of bone tissue or destruction of periodontal fibers, due to which the tooth is attached to the bone tissue. This inflammation of the gums is called catarrhal gingivitis. If it is treated incorrectly or untreated, gingivitis sooner or later transforms into the next form of gum inflammation, i.e. in periodontitis. The starting point for the development of periodontitis is the destruction of the dentogingival attachment (i.e., the attachment of soft gum tissue to the neck of the teeth).
The dentogingival (enamel) attachment is an anatomical barrier that prevents the penetration of pathogenic bacteria below the gum level. As soon as this barrier is destroyed, inflammation affects not only the soft gum tissue, but also bone tissue, as well as periodontal fibers, due to which the tooth root is attached to the bone tissue. This leads to their gradual destruction. Symptoms and treatment of periodontitis will depend on its severity (i.e., the degree of destruction of the tissue around the teeth). There are mild, moderate and severe forms of this disease.
Mild periodontitis –
With a mild form of periodontitis, firstly, all the symptoms of catarrhal gingivitis will persist, i.e. the patient will continue to complain of occasional pain and bleeding when brushing teeth. In addition, swelling, bluishness or redness of the gingival margin will continue to be observed, as well as accumulations of microbial plaque or tartar in the area of the necks of the teeth (Fig. 4-5).
What periodontitis looks like: photo
The main diagnostic criterion that distinguishes the symptoms of the initial stage of periodontitis from the symptoms of catarrhal gingivitis is the formation of periodontal pockets (gingival pockets) - up to 3.5 mm deep. Such pockets are formed due to the destruction of the attachment of soft gum tissue to the necks of the teeth, which leads to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria below the gum level. As soon as this happens, inflammation and pathogenic bacteria lead to the destruction of periodontal tissue and bone tissue near the tooth root (Fig. 6).
On the surface of the tooth root (in the depths of the periodontal pocket) there are hard dental deposits, and the lumen of the pocket is filled with serous-purulent discharge. During a period of decreased immunity, the patient may notice that purulent discharge may be released from the periodontal pockets - this becomes especially noticeable when pressing on the gums in the projection of the periodontal pocket. In patients with this stage of periodontitis, a panoramic radiograph shows a decrease in the level of bone tissue (interdental septa) - up to 1/3 of the length of the roots of the teeth, and there may be 2 types of inflammatory bone resorption:
- Horizontal bone resorption is typical for elderly and relatively elderly people; the disease usually progresses slowly (with a uniform decrease in the height of bone tissue in the area of all teeth). Thus, in this group of patients, periodontal pockets with a depth of 3.0-3.5 mm may sometimes not be visible, but there is a uniform decrease in bone level in the area of all teeth.
- Vertical bone resorption is typical for young and relatively young people. The nature of the inflammation is usually aggressive (with rapid progression). Bone destruction occurs only in the area of periodontal pockets that form along the surfaces of the roots of the teeth. At the same time, as such, a decrease in the height of the interdental bone septa is not observed. This form is the most difficult to treat.
Important: with mild periodontitis, tooth mobility is not yet observed, as well as their displacement under the influence of chewing pressure (all this is typical for moderate and especially severe periodontitis).
Moderate periodontitis –
This stage of the inflammatory process is distinguished by the fact that the number of periodontal pockets increases significantly, and their depth can already reach 5.0 mm. An increase in the depth of the pockets creates excellent conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic pyogenic bacteria, and therefore the release of serous-purulent exudate from the pockets becomes rather the norm (which is especially visible when pressing on the gums in the projection of the periodontal pocket). In addition to pathogenic bacteria, periodontal pockets at this stage may also contain fungal flora, which is important in the choice of drugs for the treatment of periodontitis.
An increase in the depth of periodontal pockets to 5.0 mm means a decrease in bone level by approximately 1/3-1/2 of the length of the roots. Visually, this can be expressed in a decrease in the gingival margin relative to the necks of the teeth, i.e. Root exposure may already be occurring. In addition, with such a degree of bone destruction, 1) mobility of teeth of 1-2 degrees occurs, 2) tilting of some teeth may appear, 3) fan-shaped discrepancy of the front teeth may begin to appear. The latter is especially typical for patients with the absence of a large number of lateral chewing teeth.
Moderate periodontitis –
At this stage of inflammation, patients often complain of a deterioration in their general condition - increased fatigue, weakness, and a decrease in immunity + frequent colds. This is due to the fact that serous-purulent discharge is always present in periodontal pockets, from which toxins and pathogens are absorbed into the blood and spread throughout the body, affecting primarily the immune system.
Very important: once again we draw your attention to the fact that at this stage of periodontitis, “secondary deformations of the dentition” already occur, i.e. the teeth begin to “move apart” (changing their position depending on the direction of the usual chewing pressure). Therefore, the treatment of moderate periodontitis is already much more complex - in comparison with mild periodontitis, and will require you to spend quite a lot of money on splinting and prosthetic teeth. Therefore, it is important not to bring it to such a state, and not to self-medicate (24stoma.ru).
Severe periodontitis -
Severe periodontitis is characterized by further deterioration of all symptoms. The depth of periodontal pockets can already reach 6.0 or more. Accordingly, the decrease in the level of bone tissue in the area of the interdental septa reaches 2/3 or more of the root length. Mobility is observed in most teeth, and in some teeth it already reaches 3-4 degrees. With this severity of periodontitis, exacerbations of the inflammatory process often occur, which are accompanied by the formation of abscesses, sharp swelling of the gums, pain in them, and a sharp increase in tooth mobility.
Severe periodontitis: photo
It should be noted that in severe cases, patients begin to suffer not only from local symptoms in the oral cavity, but also complain of weakness, malaise, poor sleep, and appetite. Severe chronic inflammation of the gums can also affect the frequency of exacerbations of chronic diseases of the internal organs. The condition of patients with diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular, hormonal, and rheumatoid diseases is especially deteriorating.
Exacerbation of periodontitis – there is also such a thing as “course of the disease”. As a rule, periodontitis is characterized by a sluggish chronic course, i.e. when the symptoms are smoothed out (there are no acute phenomena of inflammation), but exacerbations of the inflammatory process may periodically occur. During exacerbations, the symptoms become much more pronounced - tooth mobility and bleeding gums increase, swelling of the gums and the formation of purulent abscesses may occur, and purulent discharge from periodontal pockets may also appear. The development of exacerbation may be associated both with the depletion of local protective mechanisms of the oral cavity and with a decrease in the body's immunity. Next, we will talk about how to treat periodontitis.
Splinting procedure for periodontitis
The need for splinting in the treatment of periodontitis arises when there is mobility of more than 2-3 dental units in a row. Splinting helps strengthen teeth and also helps to quickly eliminate inflammatory processes in soft tissues.
Splinting can be carried out in different ways. A specialist can use fiberglass tapes in manipulations, install welded dental crowns or a clasp denture. The method of splinting is selected based on the clinical picture of a particular case.
Surgical treatment of periodontitis
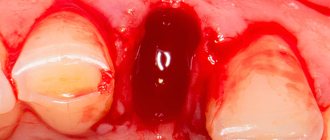
Surgical treatment of periodontitis is the most radical method of combating this disease; it is used when other means are not able to stop the development of inflammatory processes in the periodontium. The essence of the surgical intervention is the high-quality removal of the affected tissue and the replanting of synthetic bone material in the area of manipulation.
It should be noted that this type of operation is complex, requiring certain skills and knowledge from the doctor, and therefore, to perform surgical intervention for periodontitis, it is so important to choose the right clinic and specialist. You can see how the process of surgical treatment of periodontitis takes place in the photos below.
Causes of the disease
Periodontitis is considered a polyetiological disease - it is formed in most cases by a combination of several predisposing factors. Activation of the inflammatory process is provoked by external and internal factors, systemic and local disorders of the body. The causes of periodontitis are divided into two large groups: endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous causes of periodontitis:
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- some types of vitamin deficiencies, especially lack of ascorbic acid;
- endocrinopathies - diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis;
- vascular diseases;
- bruxism.
Some researchers describe a hereditary predisposition to periodontitis, but it has not yet been fully proven.
Exogenous causes of periodontitis:
- plaque and tartar - found in approximately 90% of patients with periodontitis;
- pathogenic microorganisms;
- chronic dental injuries associated with malocclusion;
- Iatrogenesis - consequences of improper dental treatment, for example, non-compliance with prosthetic technology;
- basal caries;
- gum recession;
- the absence of several teeth - the formation of periodontitis in this case is associated with a violation of the distribution of chewing load.
The causes of periodontitis in most cases act in combination: a combination of several factors leads to disruption of microcirculation in the area of the periodontal junction. Then an infection occurs, which intensifies the inflammatory process. The impact of waste products of microorganisms on bone tissue is accompanied by its resorption (resorption), which leads to a weakening of the fixation of teeth in the jaw. If left untreated, the symptoms of periodontitis continue to worsen and ultimately lead to edentulism.
Prosthetics for periodontitis
Prosthetics for periodontitis are necessary in cases where a person has no dental units in his rows. Carrying out prosthetics allows you to prevent the displacement of teeth in rows and completely restore the correct chewing load in the oral cavity. Prosthetics is the final stage in the conservative treatment of periodontitis and must be carried out before surgery (if the operation is planned in the general treatment plan).
For prosthetics in the treatment of periodontitis, it is extremely important to choose the right prosthesis. It must be of high quality and modern, otherwise it will not be possible to stop the process of bone atrophy.
How to restore teeth with severe periodontitis
In severe cases of the disease, the risk of losing a tooth or an entire row of teeth is very high. Tooth extraction for periodontitis is indicated in cases of excessive mobility, when the unit is barely held in the bone and moves in all directions around its axis. If it is impossible to save the tooth, orthopedic treatment is carried out - prosthetics supported by natural teeth or implants.
For single defects or restoration of a tooth segment, two-stage implantation with delayed loading is used. Implants are implanted after a course of gum treatment and restoration of bone volume. Bone parameters are restored through osteoplastic surgery. After new bone tissue is formed (after 6 months), implants are implanted, the prosthetic system is fixed after they have fused with the jaw bone ( after 3-6 months
). Treatment may take about a year.
In case of complete edentia, one-stage implantation methods with immediate loading demonstrate high efficiency. The ability to install implants in deep bone layers that are not subject to inflammation allows you to avoid osteoplasty and sinus lifting. Treatment will take no more than a week.
Is it possible to treat periodontitis at home?
Many patients ask the question: can treating periodontitis with folk remedies be effective? Experts give a clear answer to this question: it is impossible to cure periodontitis at home, since even potent pharmaceutical drugs are sometimes ineffective against this disease. The inflammatory process develops in the deep layers of tissue and therefore neither decoctions nor herbal infusions can stop it.
Some folk recipes can make periodontitis therapy faster, but before using them, you should definitely consult with the specialist leading your treatment. Using folk recipes on your own is simply dangerous, since they may not only not help, but also aggravate the situation. For example, some traditional healers advise making hot compresses, but heating the area of inflammation means catalyzing the process of its development. Therefore, do not waste time treating periodontitis with folk remedies. The most effective treatment for this disease is complex therapy carried out by competent specialists and in a clinical setting.
Types of periodontitis
By place of development:
- localized - a small lesion affecting only one tooth; often results from mechanical damage to tissue;
- generalized - damage to several teeth also affecting the gingival and bone tissue.
According to the nature of the course:
- acute - characterized by sudden pain attacks and rapid development of symptoms;
- chronic periodontitis is the transition of untreated acute periodontitis to a chronic form, in which pain and other symptoms practically disappear, but the disease progresses and deforms the tissue.
A few words about the importance of periodontitis prevention
Treatment of periodontitis is a complex and lengthy process, sometimes it can last for several years. And naturally, carrying out the necessary procedures will require you not only time, but also significant financial expenses. Both time and money costs can be avoided if you prevent the development of periodontitis.
To effectively prevent the development of periodontitis, dentists advise following the following simple recommendations:
1. Regularly carry out high-quality dental and oral hygiene at home and from time to time - professional teeth cleaning in dentistry.
2. Contact the dental clinic at the first signs of not only periodontitis, but also caries, and undergo treatment on time.
3. Monitor your diet: it must be balanced and your menu must contain foods containing vitamins and minerals.
4. If you lose even one tooth, do not postpone the prosthetic procedure.
5. Regularly undergo preventive examinations at the dentist.
Also, for effective prevention of periodontitis, you should avoid stressful conditions, strengthen the body’s immune system, and protect your gums from injury. Follow these simple rules, and then you won’t have to waste time and money on periodontitis treatment.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Prices for periodontitis treatment
How much will it cost to treat periodontitis in a clinic? The price of the service will depend on a number of factors and, first of all, on what regimen and methods of therapy will be chosen. Therefore, you can find out the exact price for periodontitis treatment after visiting the dentist, conducting diagnostic tests and drawing up a treatment plan. Some clinics offer turnkey periodontitis therapy at an inexpensive price, but such an offer is a reason to be wary. Treatment of periodontitis requires a whole range of measures, the set of which is determined on the basis of diagnosis and therefore simply cannot cost a penny.
You can undergo treatment for periodontitis in Moscow by contacting our dentistry - Vanstom. We are located at: Moscow, metro station Baumanskaya, st. Bakuninskaya, 17/28. To effectively combat periodontitis, we offer our patients modern techniques and use innovative technologies and equipment, and therefore we can guarantee the high quality of all dental services we provide. To make an appointment with our specialists, you just need to dial our phone number!